Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (13): 2116-2123.doi: 10.12307/2023.232
Previous Articles Next Articles
Methods, technologies and future of Chinese medicine modulation of cellular autophagy in the treatment of spinal cord injury
Wang Yaxin, Lin Yican, Guo Yinuo, Zhang Bo, Ma Yuying, He Xiaoping
- Hebei Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine Research on Cardio-cerebrovascular Disease, Hebei University of Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang 050091, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2022-01-10Accepted:2022-03-10Online:2023-05-08Published:2022-08-12 -
Contact:He Xiaoping, Master, Hebei Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine Research on Cardio-cerebrovascular Disease, Hebei University of Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang 050091, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Wang Yaxin, Hebei Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine Research on Cardio-cerebrovascular Disease, Hebei University of Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang 050091, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:a grant from Hebei Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. 2022105 (to HXP); a grant from Hebei Provincial Health Commission, No. 20221046 (to HXP); Yanzhao Medical Research Project, No. YZYX2021006 (to HXP)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Yaxin, Lin Yican, Guo Yinuo, Zhang Bo, Ma Yuying, He Xiaoping. Methods, technologies and future of Chinese medicine modulation of cellular autophagy in the treatment of spinal cord injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(13): 2116-2123.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
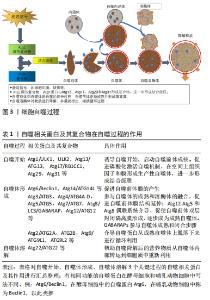
2.1 细胞自噬概述 2.1.1 细胞自噬形式 现已知道的细胞自噬有3种形式,分别为微自噬、分子伴侣介导的自噬和巨自噬[5]。按照其发生频率,微自噬过程发生最少,巨自噬过程发生最普遍,分子伴侣介导的自噬相对于前两种方式比较特殊。 2.1.2 细胞自噬过程 在细胞自噬相关蛋白和细胞器周围,自噬相关基因(Autophagy-related gene,Atg)聚集并组装形成自噬前体,接着自噬前体膨胀并最终形成隔离膜和自噬体,自噬体与溶酶体的融合成为自噬溶酶体[6],物质在自噬溶酶体中被分解并随着自噬体的溶解释放出来,以此循环[7]。 自噬过程的发生需要许多自噬相关蛋白及其复合物的参与[8-9],每一个过程对应的相关蛋白都发挥着重大作用[10-11],见图3,表1。 "
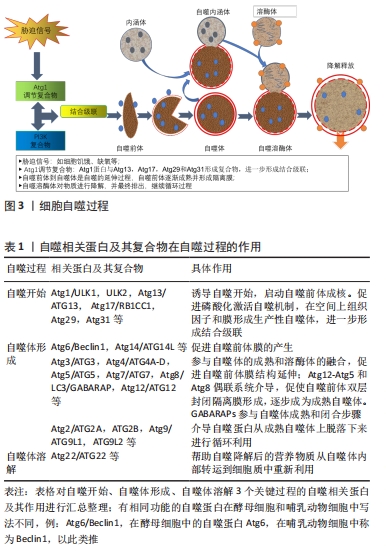

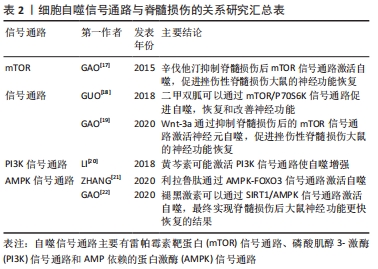
2.2 细胞自噬与脊髓损伤的关系 2.2.1 细胞自噬对脊髓损伤的影响 已有大量研究证实,神经元细胞死亡是脊髓损伤患者神经功能缺损的重要原因,而正常的自噬通量是维持神经元稳态不可或缺的条件。脊髓损伤后相关神经元死亡常不是由于直接的机械损伤引起的,而是损伤后继发的生化变化导致细胞的延迟死亡[12],其中脊髓损伤后表现最明显的特征之一是大量与炎症相关的基因表达,此时损伤局部进一步促进炎症细胞释放炎症因子产生炎症反应,致使损伤局部内环境发生紊乱,促进神经元细胞死亡和轴突变性的发生[13]。而增强细胞自噬活性能够减少细胞炎症反应,促进脊髓轴突内源性生长[14],起到保护脊髓损伤后受损神经元的作用。在脊髓损伤后修复方面,ZHANG等[15]近期研究表明,外周巨噬细胞能有效改善损伤局部抗炎微环境,其衍生的外泌体通过增强自噬促进小胶质细胞尤其是抗炎型小胶质细胞的极化有利于脊髓损伤局部抗炎,极大提高了脊髓损伤后神经元的存活率,有利于脊髓损伤后的修复。因此,适量激活细胞自噬有助于脊髓损伤的治疗,从而为临床对脊髓损伤受损部位的修复、保护提供一种新思路。 2.2.2 介导细胞自噬信号通路与脊髓损伤的治疗 自噬信号通路主要有雷帕霉素靶蛋白(Mammalian target of rapamycin,mTOR)信号通路、磷酸肌醇3-激酶(Phosphoinositol 3-kinase,PI3K)信号通路和AMP依赖的蛋白激酶(Adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase,AMPK)信号通路[16]。近年来研究证实多种治疗方法通过细胞自噬信号通路影响脊髓损伤的治疗,因而着眼于多个信号通路进行探究具有重要意义,目前研究最广泛的有AMPK/mTOR和PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路[17-22],见表2。"
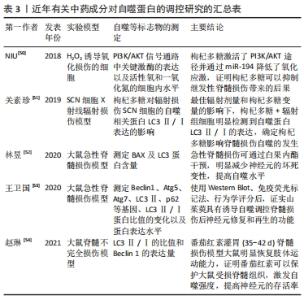
BAI等[23]通过Western blot检测脊髓损伤后3 d的大鼠自噬相关蛋白的表达,与假手术组对比发现脊髓损伤组脊髓组织中呈现明显的AMPK磷酸化增多,并说明由此抑制mTOR磷酸化。研究发现这一结果在Netrin-1处更为明显,表明脊髓损伤后Netrin-1使AMPK/mTOR信号通路进一步激活,并最终显现脊髓损伤后运动神经元及组织损失减少的效果。ZHOU等[24]同样着眼于AMPK/mTOR信号通路的研究,表明东莨菪碱也通过此信号通路使脊髓损伤大鼠细胞自噬增强,发挥神经保护作用。对于PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路的研究,BORGES等[25]说明抑制PI3K/Akt/mTOR通路可上调Beclin1的表达,从而激发神经元自噬。CHEN等[26]研究报道依折麦布有减少脊髓损伤大鼠脊髓组织的神经元损伤以及促进脊髓损伤后组织恢复等作用,并通过实验证实Eze可抑制PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路激发自噬和减少细胞凋亡。WANG等[27]说明4-PBA通过此通路增强内质网应激介导的自噬,最终达到改善脊髓损伤后运动的效果。总而言之,介导细胞自噬信号通路治疗脊髓损伤已经有理论和实验依据支撑,也为进一步探究脊髓损伤相关机制提供方向。 2.3 中医药调控细胞自噬治疗脊髓损伤 2.3.1 脊髓损伤中医发病机制及治疗 中医学者多将脊髓损伤归为“痿证”范畴。继发性脊髓损伤属中医的外伤性病证,由于受到直接或间接暴力损伤,导致血脉破损,血溢于脉外,血不循经而淤血滞留,产生机体内气机运行不畅的后果。从中医理论理解为“气为血之帅,血为气之母,气能载血,血能载气”,二者互为因果,瘀血内停则导致气机紊乱。从中国现代医学中医病理医学动机病因学理论和现代病理医学动机病因论的两个角度看,脊髓损伤在疾病发生早期主要发病原因是损伤到督脉,督脉为“阳脉之海”,督脉受损会损及阳气,则气血失畅,淤血阻滞经脉,枢机不利则使患者全身肢体不能受气血温煦,从而产生一系列病变[28]。 活血化瘀以治疗脊髓损伤:中药治疗脊髓损伤作为近年的研究重点,大量实验数据表明部分中药及其提取物可以有效改善人体血液中的微循环、消除炎性不良反应、提高受损细胞自噬强度。《灵枢?邪气藏腑病形》述:“有所堕坠,恶血留内。”是指中药治疗气血型脊髓损伤多以调用活血化瘀、疏通气血督脉之药为主。近年不断有实验研究证实了活血中药提取物注射液有抗氧抗炎、抑制神经元凋亡、降低脊髓损伤模型大鼠的评分的效果,例如:丹参酮ⅡA、姜黄素、人参皂苷及川芎嗪等有效成分[29]。合理应用活血化瘀药可以调经理气止痛、补益肝肾、疏通督脉,同时依据中医整体观辅佐以补气活络药的效果更佳。补气药以被称为“补气之长”的黄芪为例,其出自《神农本草经》上经,是上中下内外三焦之药,具有黄芪甲苷、黄芪多糖等多项生物活性成分,ZHANG等[30]实验发现黄芪甲苷可以诱发自噬水平负相关蛋白p62表达降低,保护中枢神经系统细胞,也在一定程度上改善了人体内部脊髓的各种异常病理变化状态。 督脉论治机制:《奇经八脉考》明确指出:“督脉为阳脉之总督,故曰阳脉之海。”督脉总管一身阴阳之气,具有有效调节人体阴阳、十四经气血的作用。中医分析脊髓损伤主要由坠堕打仆等外因和筋脉失养等内因造成,人体督脉气血滞留导致脏腑脉络功能失常结瘀,气血津液不能濡养调达于四肢筋骨。久而出现肢体麻木、颈枕疼痛、小肠运行失调等各种邪气瘀阻的病理征象,与继发性脊髓损伤导致的全身系统器质性损伤、神经反射缓慢类同[31]。督脉作为脏腑气血循行的重要载体,与人的脊髓相互依承,相互为辅,总结出“病证结合,从督论治”和“椎管减压,疏通督脉”的脊髓损伤思路[32]。早在《黄帝内经?素问?骨空论篇第六十》就有“督脉者……与太阳起于目内眦,上额交巅,上入络脑”的理论,结合现代医疗科技,临床上从督脉论治常进行电针或针灸取穴,以对体内相关基因进行调控,如AFSHARI等[33]认为电针或针灸作为瘫痪脊髓损伤患者康复治疗的有效手段,可以通过调控相关基因的表达来调节大鼠(后肢)的神经系统与运动功能。在督脉进行电针治疗以调控细胞自噬是督脉论治的另一个机制,邹恩苗等[34]研究督脉电针治疗对脊髓损伤大鼠神经细胞自噬的影响,说明电针可以调控细胞自噬的激活以及抑制细胞凋亡来影响脊髓修复,对临床治疗具有指导意义。 2.3.2 脊髓损伤中自噬的中医病机理论研究 基于脊髓损伤发病机制,中医依据“整体观念,辨证论治”的原则进行治疗探索,目前主要认为自噬与中医阴阳平衡、气血互存理论有关。而针对不同病位的疾病进行脏腑辨证,自噬相关的中医理论有相应的丰富。 自噬与阴阳平衡:基于自噬机制的复杂性,其促进与抑制双重作用及维持动态平衡的过程是中医阴阳对立制约、互根互用的体现。《素问?生气通天论》云:“阴平阳秘,精神乃治”。自噬之间动态平衡调节生理系统也就如同阴阳自和一样,它可以通过相互联合进行制约、转化、作用等方式来直接维持体内各个细胞微环境的阴阳动态平衡。王志丹等[35]学者认为人体内微环境动态平衡的维持离不开细胞自噬的调节作用。胡朋言 等[36]也认为细胞自噬的调节通过互相制约、转化以及互根互用维持体内环境的平衡,与中医阴阳自和、阴阳平衡理论异曲同工。方俊锋等[37]把自噬动态过程中的代谢产物转化成新能量看作中医理论“体”“用”的转变,从而达到阴阳平衡的诉求。从另一方面说,阴阳平衡也对自噬产生影响。如侯媛等[38]认为阴阳平衡是维持细胞自噬稳态的原动力。常兴等[39]以“气分阴阳”理论为基,认为阴气的抑制性和阳气的激发性是人体内环境的稳定及自噬水平的维持的重要部分,并表示存在双向调整机制,如自噬信号通路的表达被抑制同时有自噬相关蛋白的表达升高,而这种机制与阴阳平衡互相辅助,这提示自噬与阴阳平衡理论之间存在较大的相似性与相关性,因此对自噬与阴阳平衡进行探讨具有重要意义。笔者认为,在脊髓损伤研究治疗中,自噬应在阴阳平衡的指导下人为干预采取一定的治疗手段加以调节,达到维持一定水平满足机体某一阶段需求的标准,进而最终满足阴阳相合。 自噬与气血互存:自噬作为维持细胞稳态的重要过程,是对机体正虚邪实的一种自我调节方式。从中医角度来看,脊髓损伤后人体内正气不足,激活了自噬的进程。而当正气亏虚达到一定程度或邪气内盛时,自噬的调节能力将逐步下降,导致气虚。“气为血之帅,血为气之母”,自噬的调节功能降低造成细胞功能活动受到影响,体现在微观层面上,气血运行无力,导致瘀证,即也是中医气虚血瘀证的病理机制[40-41]。黄海等[42]以气血思想为基础,探究针灸对自噬的调节作用,根据中医辨证配穴治疗,电针足三里等穴位调理脾胃生养气血,针灸督脉上穴位以温阳益气化浊,使气血行以祛瘀,针刺腧穴则激发经气调控自噬信号通路的传导,进而调节自噬水平。同时,也符合中医“扶正祛邪”的指导思想。因此,从中医“气血互存”理论角度把握自噬作用机制的宏观层面,有助于推动脊髓损伤的相关治疗。 自噬与脏腑辨证:藏象学说首见于《素问?六节藏象论》,由古窥今,现代医学发现细胞自噬与祖国医学藏象理论之间相互联系,中医藏象“思外揣内”“见微知著”的辨证观为细胞自噬研究丰富了内涵,具有重要的启示和指导意义。例如继发性脊髓损伤激发的大规模神经元自噬失常,就可能导致人体脏腑机能失调,从而间接引发人体脏器功能性疾病的发生。 当前研究集中于肝、脾、肾三脏,尤其关于先天之本肾的辩证施治,《素问?逆调论篇》中记载:“肾不生则髓不能满。”说明人体肾精、肾气的充盛与否对人体骨髓有直接影响,若人体肾精生化不足,容易产生骨髓营养枯萎或老化、疼痛、小便失常等症状。所以肾精不足则髓海空虚,使骨髓失养,骨骼痿弱,最终髓减骨枯进而病发。中医“肾藏精主骨生髓”的理论表明,肾精作为阴阳之本,为骨骼形体的发育以及功能是否灵活有力提供营养支持。在排尿方面,蒋雪飞[43]使用温阳化气方联合中医外治法——敷脐,训练肾阳虚型脊髓损伤患者尿失禁,提升肾气的固摄温煦之力来恢复膀胱容量,减少脊髓损伤患者的膀胱残尿量。吴静怡等[44]认为自噬发生的基本条件之一是肾气亏虚,提出合理应用益肾清利治法(包括补虚药和清利湿热药)是治愈脊髓损伤等痼疾引发的慢性肾病的关键,例如人参皂苷[45]、黄连素等中药有效提取物就可以针对AMPK通路或AMPK/mTOR/PI3K信号通路等[46],刺激衰老受损细胞产生自噬活力,并对比物质、能量的转化和代谢失常引起产物堆积两个方面,说明“肾虚湿热”与自噬过程具有相关性。 脾为“后天之本、气血生化之源”,为人体脏器气血精微的生化代谢活动提供源泉,肝才能疏理人体气机,直接调达全身脏腑经脉中的气机。肝与脾共同负责调控着机体最为基本的代谢运转,肝脾运化有方,气血生化有源,肾精得以充养,精髓填充,骨骼坚韧有力。而继发性脊髓损伤患者气血生化乏源,精髓失养,骨骼痿弱无力,不用则废。机体的衰老或受损会致使脾肝肾之间气机升降浮沉逐渐虚弱,气化作用明显下降,引起肾脏细胞自噬代谢功能发生缺陷;身体调节自由基代谢的功能明显不足,导致肾脏细胞内部堆积了大量的过氧多肽片段及亚细胞器[47]。因此大部分继发性脊髓损伤患者的康复应着重调养肝脾,以预防慢性疾病的发生。郝民琦等[48]的最新研究证实理中汤合四神丸可以通过温补脾阳、温肾散寒影响相关基因、LC3B mRNA等因子的表达,从而抑制JNK/Beclin1/Bcl-2信号通路,避免脾肾阳虚型复发性炎症性肠病大鼠模型的过度自噬,对脊髓损伤患者卧床较久形成的慢性消化系统有一定提示。另外对其他脏腑的研究,如安冬等[49]通过对比中医理论赋予肺的宣发肃降等功能正常与失常情况对细胞自噬的影响,认为二者有相通之处。 2.3.3 脊髓损伤自噬实验研究 调控自噬信号通路及蛋白表达:大多数学者研究表明中药成分可以作用于单个或多个细胞自噬信号通路,影响自噬蛋白表达以发挥作用,加快脊髓损伤后神经元的恢复。竹节参性温,有滋补强壮、散瘀止痛、止血祛痰的功效,见表3。 "
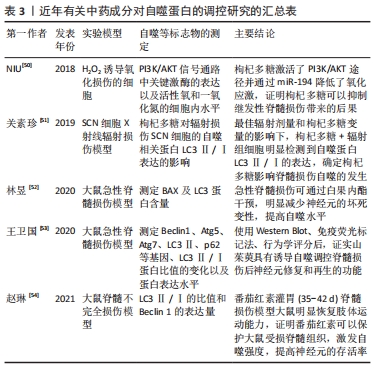

卜献忠等[55]研究观察到竹节参通过抑制单个mTOR信号通路激活细胞自噬,提高脊髓损伤模型大鼠改良Tarlov评分,进而改善脊髓损伤模型大鼠下肢运动功能。而有关研究显示一些中药有效提取物能同时启动多个信号通路。薯蓣皂苷糖苷是中药穿隆薯蓣根茎的提取成分。CHEN等[56]研究表明薯蓣皂苷糖苷能明显减弱p62表达并上调Rheb/mTOR信号传导途径,减少脊髓组织损伤和水肿,对脊髓神经功能起到显著的恢复作用。片仔癀味苦、微甘,可以清热解毒、凉血化瘀、消肿止痛,用于跌打损伤等症状。HUANG等[57]说明中成药片仔癀可以抑制NLRP3炎性体,减少促炎因子,并通过实验证实这与其调节AMPK/mTOR/ULK1信号通路使自噬增强有关。桦木酸的药理作用在近年来受到关注,WU等[58]评估桦木酸对自噬的作用,发现桦木酸激活了AMPK/mTOR/TFEB信号通路,增强了脊髓损伤后自噬作用,以此为基础诱导了线粒体自噬和减少了ROS积累,并有效减少了细胞焦亡,起到了改善脊髓损伤的效果。 还有一些研究表明在脊髓损伤初期增强自噬,后期减弱有助于脊髓神经元的恢复与保护,有研究对脊髓损伤大鼠分组观察,发现黄芪多糖组在前期有明显的LC3Ⅱ表达量增高,后期稍有下降,即自噬作用在前后期有增强和下降的表现,反映黄芪多糖对神经元的有利作用,另外通过RT-PCR定量检测到对自噬起正调节作用的Beclin蛋白在黄芪多糖组初期表达最高,在后期表达有所下降,也说明其对脊髓损伤后脊髓神经元的恢复有促进作用,且对于初期恢复更为显著[59]。值得一提的是,中医方剂应用于脊髓损伤治疗取得良好效果,郭晓辉等[60]将补阳还五汤应用于脊髓再灌注损伤大鼠,观察相关蛋白的表达,将缺血3,6 h后的模型组和假手术组相比,发现细菌自噬产生有关蛋白质Beclin1,LC3,P62均表现较升高,而观察组、3-MA组这3种蛋白表现则较降低,从而证明了补阳还五汤能够调控自噬蛋白的表达,促进细菌自噬机制产生,促进消化衰老细胞新陈代谢,并为神经细胞的再造、重组提供必要原材料,同时控制细菌自噬原来的过度产生,起到一定的神经元保护作用。总之,中医药通过调控自噬信号通路及相关蛋白的表达促进脊髓损伤后状态的改善毋庸置疑,而具体如何调控某一条信号通路以达到理想效果仍需要深入发掘。 调控自噬与抑制炎症:脊髓损伤后炎症因子的表达明显上调,从而诱发炎症。而中医药的使用有效调控自噬以抑制炎症反应。大量实验选取单味或多味中药提取物参与有关研究。黄连素是单味中药黄连中分离出来的一种季铵生物碱。WANG等[61]探究黄连素减轻脊髓损伤后模型大鼠神经元炎症的机制,通过蛋白质印迹表明黄连素触发了自噬相关蛋白如LC3B,ATG7和ATG16L等的表达,并经荧光染色观察到ATG5的表达增加以及存活神经元数量的相对增多,提示黄连素对脊髓损伤的影响可能与其提高细胞自噬水平有关。随后,李艳兵[62]证实黄连素可以抑制神经炎症,提出黄连素通过转化生长因子β介导的炎症通路促进脊髓损伤后大鼠神经元的恢复。四氢姜黄素是从姜科、天南星科中的一些植物的根茎中分离出的姜黄素氢化而来。研究发现,四氢姜黄素可以降低大鼠脊髓损伤模型中的炎症因子,有效降低基质金属蛋白酶3和13以及环氧化酶2的基因表达,促进Akt磷酸化,增强FOXO4蛋白表达,达到保护脊髓的效果[63]。 阿魏酸广泛存在于多种药用草本植物中,LIU等[64]证实其可通过增强自噬,抑制脊髓损伤后NLRP3炎性小体激活,从而减轻损伤脊髓神经元的炎症反应。由此可见,一些中医药有效成分通过控制自噬信号通路或自噬蛋白的表达来抑制炎症因子,进而减少炎症反应以保护脊髓。 针灸取穴调控自噬:针灸是针对神经系统疾病非常有效的传统疗法,且应用在脊髓损伤中效果显著。在各种神经系统疾病模型中,通过针灸或电针刺激周围神经能有效促进神经损伤后功能障碍的恢复。顾锡镇教授认为该病的病机关键在“肾督虚寒”,因此治疗脊髓损伤多以温通督脉法为主,同时重视疏通膀胱经气血,据此进行针灸取穴[65]。通过针灸取穴调控自噬治疗脊髓损伤是充满潜力的研究方向,中国已有多项相关研究正在进行。 夹脊穴位于督脉与膀胱经之间,受督脉阳气与膀胱经气血的联合温煦濡养作用,可采用夹脊电针作为治疗脊髓损伤的潜在策略。WEI等[66]研究夹脊电针对PTEN/mTOR/STAT3信号通路和自噬的调节机制,发现抑制自噬相关蛋白PTEN的异常表达后,自噬水平显示上调,因此指出夹脊电针可以有效干预脊髓损伤后自噬水平,并指出激活信号通路后电针与PTEN特异性抑制剂bpV可能具有协同上调细胞自噬的作用。另外电针通过调节自噬还可以达到间接调控机体内环境稳定的效果,如张雨墨等[67]研究表明夹脊电针可以抑制P2X7受体激活,从而避免NLRP3活化释放炎性因子以及大量免疫细胞因子对脊髓损伤模型鼠脊髓内环境造成的威胁,减少细胞凋亡。然而,不同学者对于电针调节自噬的治疗机制存在不同的看法,杨波等[68]认为电针通过调节作用降低不同时间段的LC3-Ⅱ和BNIP3表达以阻断自噬信号的传导,抑制细胞自噬,减缓脊髓损伤后的病理损害,进而对神经细胞保护起到重要作用;YIN等[69]则认为夹脊电针可以通过促进LC3-Ⅱ的表达和抑制P62的积累促使自噬流形成,有利于脊髓损伤的恢复;DAI等[70]也认为其作用机制是通过抑制小鼠脊髓损伤后的内质网应激以促进细胞自噬,进而加速了神经功能的恢复。因此,电针疗法在脊髓损伤中的应用不断延伸,其作用机制值得进一步探讨研究。 相关研究发现,不同频率电针刺激对脊髓损伤后神经细胞自噬也有不同的影响,对运动功能的恢复作用不尽相同。高频疏密波能够有效促进损伤后细胞自噬,对运动功能的恢复有较好作用[71]。而低频电针刺激T8-12节段夹脊穴和双侧昆仑穴和足三里穴,能提高急性自发痛模型大鼠痛阈,减轻脊髓损伤致痛超敏,并改善由自发痛引起的行为学变化[72]。因此,不同时期损伤区域自噬水平应使用恰当的电针参数治疗,以保证一定水平的自噬通量以保护神经元,促进损伤局部组织修复和神经功能的恢复,同样是该疗法的关注点和突破点之一。 "

| [1] ALIZADEH A, DYCK SM, KARIMI-ABDOLREZAEE S. Traumatic spinal cord injury: an overview of pathophysiology, models and acute injury mechanisms. Front Neurol. 2019;10:282. [2] LUO C, TAO L. The function and mechanisms of autophagy in spinal cord injury. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1207:649-654. [3] 熊静,王福民,曾芳,等.以自噬为切入点的中医药基础研究现状分析——基于近10年国家自然科学基金立项项目数据分析[J].世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2021,23(7):2427-2433. [4] XIONG Y, XIA Y, DENG J, et al. Direct Peritoneal Resuscitation with Pyruvate Protects the Spinal Cord and Induces Autophagy via Regulating PHD2 in a Rat Model of Spinal Cord Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:4909103. [5] GALLUZZI L, GREEN DR. Autophagy-Independent Functions of the Autophagy Machinery. Cell. 2019;177(7):1682-1699. [6] VARGOVA I, MACHOVA URDZIKOVA L, KAROVA K, et al. Involvement of mTOR pathways in recovery from spinal cord injury by modulation of autophagy and immune response. Biomedicines. 2021;9(6):593. [7] ZHAO YG, CODOGNO P, ZHANG H. Machinery, regulation and pathophysiological implications of autophagosome maturation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22(11):733-750. [8] LI X, HE S, MA B. Autophagy and autophagy-related proteins in cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):12. [9] TURCO E, FRACCHIOLLA D, MARTENS S. Recruitment and activation of the ULK1/Atg1 kinase complex in selective autophagy. J Mol Biol. 2020;432(1):123-134. [10] TAMARGO-GOMEZ I, MARTINEZ GARCIA GG, SUAREZ MF, et al. Correction to: ATG4D is the main ATG8 delipidating enzyme in mammalian cells and protects against cerebellar neurodegeneration. Cell Death Differ. 2021;28(11):3197. [11] WESCH N, KIRKIN V, ROGOV VV. Atg8-family proteins—structural features and molecular interactions in autophagy and beyond. Cells. 2020;9(9):2008. [12] LIU S, SARKAR C, DINIZO M, et al. Disrupted autophagy after spinal cord injury is associated with ER stress and neuronal cell death. Cell Death Dis. 2015;6(1):e1582. [13] GUO F, YUAN Y. Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha-Induced Proteins in Malignant Tumors: Progress and Prospects. Onco Targets Ther. 2020; 13:3303-3318. [14] HE M, DING Y, CHU C,et al. Autophagy induction stabilizes microtubules and promotes axon regeneration after spinal cord injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(40):11324-11329. [15] ZHANG B, LIN F, DONG J, et al. Peripheral Macrophage-derived Exosomes promote repair after Spinal Cord Injury by inducing Local Anti-inflammatory type Microglial Polarization via Increasing Autophagy. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17(5):1339-1352. [16] ZHAO H, CHEN S, GAO K, et al. Resveratrol protects against spinal cord injury by activating autophagy and inhibiting apoptosis mediated by the SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway. Neuroscience. 2017;348:241-251. [17] GAO K, WANG G, WANG Y, et al. Neuroprotective Effect of Simvastatin via Inducing the Autophagy on Spinal Cord Injury in the Rat Model. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:260161. [18] GUO Y, WANG F, LI H, et al. Metformin protects against spinal cord injury by regulating autophagy via the mTOR signaling pathway. Neurochem Res. 2018;43(5):1111-1117. [19] GAO K, NIU J, DANG X, et al. Wnt-3a improves functional recovery through autophagy activation via inhibiting the mTOR signaling pathway after spinal cord injury. Neurosci Lett. 2020;737:135305. [20] LI Y, LIN S, XU C, et al. Triggering of autophagy by baicalein in response to apoptosis after spinal cord injury: possible involvement of the PI3K activation. Biol Pharm Bull. 2018;41(4):478-486. [21] ZHANG D, YU D, MEI X, et al. Liraglutide provides neuroprotection by regulating autophagy through the AMPK-FOXO3 signaling pathway in a spinal contusion injury rat model. Neurosci Lett. 2020;720:134747. [22] GAO K, NIU J, DANG X. Neuroprotection of melatonin on spinal cord injury by activating autophagy and inhibiting apoptosis via SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway. Biotechnol Lett. 2020;42(10):2059-2069. [23] BAI L, MEI X, SHEN Z, et al. Netrin-1 improves functional recovery through autophagy regulation by activating the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway in rats with spinal cord injury. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):42288. [24] ZHOU R, KAN S, CAI S, et al. Scopoletin activates adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway and improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury in rats. Pharmacology. 2020;105(5-6):349-359. [25] BORGES JP, MEKHAIL K, FAIRN GD, et al. Modulation of pathological pain by epidermal growth factor receptor. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12: 642820. [26] CHEN G, LI J, WANG Z, et al. Ezetimibe protects against spinal cord injury by regulating autophagy and apoptosis through inactivation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(6):2685-2694. [27] WANG Z, ZHENG S, GU Y, et al. 4-PBA enhances autophagy by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress in recombinant human beta nerve growth factor–induced PC12 cells after mechanical injury via PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. World Neurosurg. 2020;138:e659-e664. [28] 王璐璐,顾锡镇.顾锡镇教授从“肾督虚寒”理论治疗SCI的经验[J].中医药信息,2019,36(3):70-72. [29] LU Y, YANG J, WANG X, et al. Research progress in use of traditional Chinese medicine for treatment of spinal cord injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;127:110136. [30] ZHANG Y, ZHANG Y, JIN XF, et al. The role of astragaloside IV against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury: suppression of apoptosis via promotion of P62-LC3-autophagy. Molecules. 2019;24(9):1838. [31] TU WZ, JIANG SH, ZHANG L, et al. Electro-acupuncture at Governor Vessel improves neurological function in rats with spinal cord injury. Chin J Integr Med. 2017. doi: 10.1007/s11655-017-2968-9. [32] 王姣姣,周峻,王延雷,等.“椎管减压,疏通督脉”论治脊髓损伤的学术思想探析[J].中医正骨,2020,32(10):67-70. [33] AFSHARI K, MOMENI OUDSARI N, LASHGARI NA, et al. Antibiotics with therapeutic effects on spinal cord injury: a review. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2020;35(2):277-304. [34] 邹恩苗,高丽萍,胡洁,等.督脉电针治疗对脊髓损伤大鼠神经细胞自噬及凋亡的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2019,27(11):11-14. [35] 王志丹,贾连群,宋囡,等.从阴阳自和角度论肝脏脂质代谢与细胞自噬的关系[J].时珍国医国药,2017,28(4):924-925. [36] 胡朋言,王伟,梁雪,等.细胞自噬与相关中医辨证体系的研究进展[J].中华中医药学刊,2018,36(9):2217-2219. [37] 方俊锋,金政,吴伟.基于阴阳理论探究自噬在高血压中的作用[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2021,19(22):3998-4001. [38] 侯媛,杨生,韩烁,等.基于“气化理论”探讨细胞自噬在特发性肺纤维化中的作用[J].北京中医药大学学报,2021,44(11):1039-1043. [39] 常兴,姚舜宇,郭艳琼,等.基于“气分阴阳”理论探析人体之气与细胞自噬的联系性[J].辽宁中医杂志,2020,47(12):74-77. [40] 董平,宋敏,董万涛,等.基于气虚血瘀理论探讨血管内皮细胞自噬与椎动脉型颈椎病的关系[J].中华中医药杂志,2020,35(2):585-587. [41] 赵军,师建平,党赢.椎动脉型颈椎病的血管内皮细胞自噬与血瘀气虚关系探讨[J].中医学报,2021,36(6):1184-1186. [42] 黄海,陈丽,金劲松.基于“气血”思想浅谈针灸对自噬的影响[J].针灸临床杂志,2021,37(9):1-5. [43] 蒋雪飞.中药敷脐联合康复训练对肾阳虚型脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱的影响[J].上海针灸杂志,2020,39(9):1152-1156. [44] 吴静怡,蒋春波.基于“肾虚湿热”病机探讨自噬与慢性肾脏病的关系[J].中医学报, 2021,36(11):2346-2350. [45] MAO N, TAN RZ, WANG SQ, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 inhibits angiotensin II-induced podocyte autophagy via AMPK/mTOR/PI3K pathway. Cell Biol Int. 2016;40(8):917-925. [46] JIN Y, LIU S, MA Q, et al. Berberine enhances the AMPK activation and autophagy and mitigates high glucose-induced apoptosis of mouse podocytes. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017;794:106-114. [47] TANG C, LIVINGSTON MJ, LIU Z, et al. Autophagy in kidney homeostasis and disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020;16(9):489-508. [48] 郝民琦,罗蓉,王瑞琼,等.理中汤合四神丸对脾肾阳虚型溃疡性结肠炎大鼠JNK/Beclin 1/Bcl-2信号通路相关蛋白及基因表达的影响[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2022,29(1):65-72. [49] 安冬,李璐,毛慧芳,等.中医“肺”与细胞“自噬”的比较研究[J].西部中医药,2021,34(9):112-114. [50] NIU T, JIN L, NIU S, et al. Lycium barbarum polysaccharides alleviates oxidative damage induced by h2o2 through down-regulating MicroRNA-194 in PC-12 and SH-SY5Y cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;50(2):460-472. [51] 关素珍,德小明,庞克华,等.枸杞多糖对脊髓神经细胞辐射损伤后的保护作用研究[J].癌变•畸变•突变,2019,31(1):45-48. [52] 林昱,王振宇,陈刚,等.白果内酯对急性脊髓损伤的神经保护作用[J].社区医学杂志,2020,18(11):787-791. [53] 王卫国.山茱萸提取物靶向自噬保护脊髓损伤神经的机制研究[J].中华灾害救援医学,2020,8(9):538-540. [54] 赵琳,许圣琳,贾鲲鹏,等.番茄红素对大鼠脊髓损伤后神经元自噬的影响[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2021,37(5):552-555. [55] 卜献忠,卜保献,郭晓辉,等.基于mTOR自噬信号通路探讨竹节参对脊髓损伤的保护作用[J].时珍国医国药,2021,32(11): 2565-2569. [56] CHEN X, WANG Z, YANG Q, et al. Diosgenin glucoside protects against spinal cord injury by regulating autophagy and alleviating apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(8):2274. [57] HUANG Z, ZHOU X, ZHANG X, et al. Pien-Tze-Huang, a Chinese patent formula, attenuates NLRP3 inflammasome-related neuroinflammation by enhancing autophagy via the AMPK/mTOR/ULK1 signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;141:111814. [58] WU C, CHEN H, ZHUANG R, et al. Betulinic acid inhibits pyroptosis in spinal cord injury by augmenting autophagy via the AMPK-mTOR-TFEB signaling pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17(4):1138-1152. [59] 茶晓锋,周琴.黄芪多糖对脊髓损伤大鼠脊髓运动神经元组织形态及自噬相关蛋白表达水平的影响[J].四川中医,2019,37(10):46-50. [60] 郭晓辉,卜保献,李艳侠,等.补阳还五汤对脊髓缺血再灌注损伤后细胞自噬相关蛋白影响的研究[J].新中医,2020,52(7):33-36. [61] WANG H, LIU C, MEI X, et al. Berberine attenuated pro-inflammatory factors and protect against neuronal damage via triggering oligodendrocyte autophagy in spinal cord injury. Oncotarget. 2017; 8(58):98312-98321. [62] 李艳兵.黄连素通过TGF-β介导的炎症通路对大鼠脊髓损伤后神经功能的影响[J/OL].中国现代医学杂志:1-17[2021-12-14]. [63] SUN J, CHEN F, BRAUN C, et al. Role of curcumin in the management of pathological pain. Phytomedicine. 2018;48:129-140. [64] LIU Y, SHI L, QIU W, et al. Ferulic acid exhibits anti-inflammatory effects by inducing autophagy and blocking NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Mol Cell Toxicol. 2022;10:1-11. [65] 李昀泽,姚阳婧,顾锡镇,等.基于顾锡镇教授学术思想创立扶元通督饮治疗视神经脊髓炎谱系疾病临床经验探析[J].河北中医, 2019,41(10):1445-1450. [66] WEI Z, ZHAO W, SCHACHNER M. Electroacupuncture restores locomotor functions after mouse spinal cord injury in correlation with reduction of PTEN and p53 expression. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018; 11:411. [67] 张雨墨,李晓宁,付豪,等.夹脊电针对脊髓损伤大鼠P2X7R/NLRP3信号通路相关蛋白的影响[J].针灸临床杂志,2021,37(2):73-78. [68] 杨波,隋汝波.电针对继发性脊髓损伤后大鼠神经元自噬及相关蛋白轻链3Ⅱ和bcl-2/腺病毒E1B19000相互作用蛋白3表达的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2015,35(9):2339-2341. [69] YIN HN, TIAN HZ, LI Q, et al. Jia-Ji electro-acupuncture improves locomotor function with spinal cord injury by regulation of autophagy flux and inhibition of necroptosis. Front Neurosci. 2021;14:616864. [70] DAI P, HUANG SQ, TANG CL, et al. Effects of electroacupuncture at “Jiaji”(EX-B2) on autophagy and endoplasmic reticulum stress in spinal cord injury mice. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021;46(1):45-51. [71] 罗慧颖,曾志威,于小波,等.不同频率电针刺激对大鼠脊髓损伤后早期功能恢复及脊髓细胞自噬和凋亡的影响[J].针刺研究,2019, 44(9):625-631. [72] 刘静,穆敬平,廖恒.低频电针对脊髓损伤致急性自发痛模型大鼠急性痛超敏的影响[J].神经损伤与功能重建,2021,16(10):606-608. |
| [1] | Nong Fuxiang, Jiang Zhixiong, Li Yinghao, Xu Wencong, Shi Zhilan, Luo Hui, Zhang Qinglang, Zhong Shuang, Tang Meiwen. Bone cement augmented proximal femoral nail antirotation for type A3.3 intertrochanteric femoral fracturalysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-10. |
| [2] | Pan Zhongjie, Qin Zhihong, Zheng Tiejun, Ding Xiaofei, Liao Shijie. Targeting of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of the osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [3] | Cai Zhihao, Xie Zhaoyong. Femoral neck anteversion measurement assessment: how to establish a unified method and standard [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1448-1454. |
| [4] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [5] | Yang Jiujie, Li Zhi, Wang Shujie, Tian Ye, Zhao Wei. Intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring of functional changes following durotomy with decompression for acute spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1232-1236. |
| [6] | Wang Ji, Zhang Min, Yang Zhongya, Zhang Long. A review of physical activity intervention in type 2 diabetes mellitus with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1272-1277. |
| [7] | Song Hehua, Wei Zairong. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: research and therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1278-1285. |
| [8] | Nie Chenchen, Su Kaiqi, Gao Jing, Fan Yongfu, Ruan Xiaodi, Yuan Jie, Duan Zhaoyuan, Feng Xiaodong. The regulatory role of circular RNAs in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1286-1291. |
| [9] | Gao Yu, Han Jiahui, Ge Xin. Immunoinflammatory microenvironment after spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1300-1305. |
| [10] | Zhao Lu, Zhao Yifei, Gao Da, Liu Yanfang, Fu Tingting, Xu Jiangyan. Expression of suppressor of Zeste 12 in kidney tissues of rats with diabetic nephropathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1179-1186. |
| [11] | Xu Xingxing, Wen Chaoju, Meng Maohua, Wang Qinying, Chen Jingqiao, Dong Qiang. Carbon nanomaterials in oral implant [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1062-1070. |
| [12] | Li Cheng, Zheng Guoshuang, Kuai Xiandong, Yu Weiting. Alginate scaffold in articular cartilage repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1080-1088. |
| [13] | Xu Cong, Zhao He, Sun Yan. Regeneration of facial nerve injury repaired by biomaterial nerve conduits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1089-1095. |
| [14] | Chen Shisong, Liu Xiaohong, Xu Zhiyun. Current status and prospects of bioprosthetic heart valves [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1096-1102. |
| [15] | Lu Di, Zhang Cheng, Duan Rongquan, Liu Zongxiang. Osteoinductive properties of calcium phosphate ceramic bone repair materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1103-1109. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||