Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (19): 2970-2977.doi: 10.12307/2022.373
Previous Articles Next Articles
Ciliary neurotrophic factor combined with forskolin and 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine induced muscle derived stem cells to differentiate into Schwann cells phenotype through cyclic adenosine monophosphate signaling pathway
Gong Chao1, Zhi Xiaodong1, 2, 3, Zhang Yuqiang1, 2, 3, Wang Chenliang1, Wang Kang1, Wang Wei1, 2, 3
- 1Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital, Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou 121000, Liaoning Province, China; 2Institute of Extra-orbital Sciences, Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou 121000, Liaoning Province, China; 3Liaoning Provincial Key Laboratory of Medical Tissue Engineering, Jinzhou 121000, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2021-01-08Revised:2021-02-05Accepted:2021-07-19Online:2022-07-08Published:2021-12-28 -
Contact:Wang Wei, MD, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital, Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou 121000, Liaoning Province, China; Institute of Extra-orbital Sciences, Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou 121000, Liaoning Province, China; Liaoning Provincial Key Laboratory of Medical Tissue Engineering, Jinzhou 121000, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Gong Chao, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital, Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou 121000, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the School-Enterprise Cooperation Fund Project of Jinzhou Medical University, No. 2020002 (to WW); Science and Technology Foundation of Liaoning Provincial Department of Science and Technology, No. 20180551216 (to ZXD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gong Chao, Zhi Xiaodong, Zhang Yuqiang, Wang Chenliang, Wang Kang, Wang Wei. Ciliary neurotrophic factor combined with forskolin and 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine induced muscle derived stem cells to differentiate into Schwann cells phenotype through cyclic adenosine monophosphate signaling pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 2970-2977.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
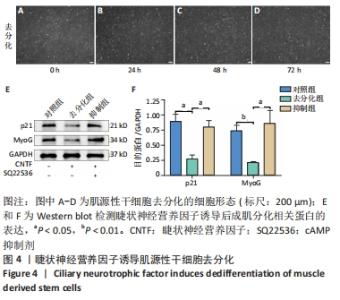
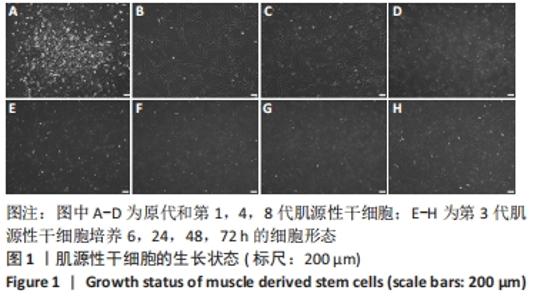
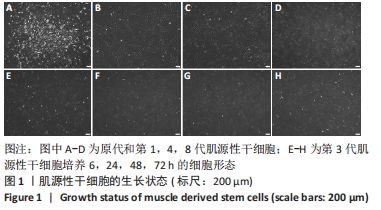
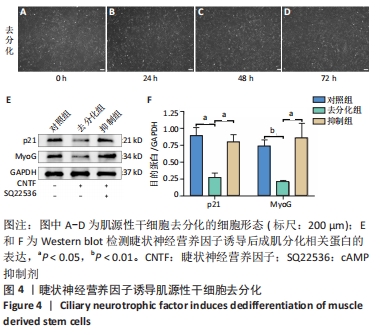
2.4 睫状神经营养因子诱导肌源性干细胞去分化 睫状神经营养因子诱导肌源性干细胞去分化过程中,细胞形态无明显改变,折光性无明显增强,细胞密度随着去分化的进程有所增加,虽有增殖现象,但低于正常生长扩增状态下的肌源性干细胞,见图4A-D。 睫状神经营养因子诱导肌源性干细胞72 h后,Western blot结果显示,与对照组相比,去分化组细胞成肌分化相关蛋白p21和MyoG的表达明显降低(P < 0.05),而抑制组p21和MyoG的表达较对照组无明显变化,与去分化组相比有所增加(P < 0.05),见图4E和4F,结果表明,睫状神经营养因子可以诱导肌源性干细胞去分化,而睫状神经营养因子的这种去分化作用可以被cAMP抑制剂SQ22536抑制。"
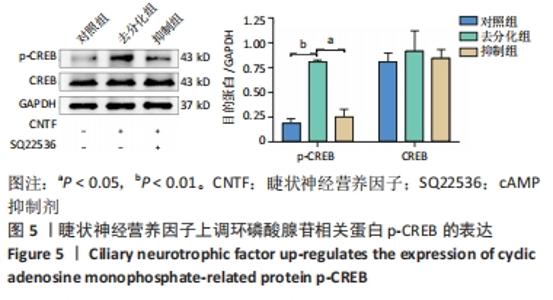
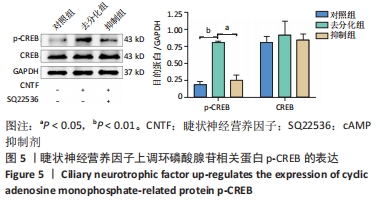
2.5 睫状神经营养因子上调了cAMP相关蛋白p-CREB的表达 为了确定去分化过程中cAMP信号通路是否被激活,通过Western blot检测了CREB和p-CREB的表达。Western blot结果显示,与对照组相比,睫状神经营养因子诱导肌源性干细胞72 h后,p-CREB表达增加(P < 0.001),而CREB表达与对照组相比无明显差异(P > 0.05),见图5。但是,在SQ22536处理之后,与去分化组相比,p-CREB的表达水平降低(P < 0.01),CREB表达水平无明显变化(P > 0.05),这表明SQ22536可以减弱睫状神经营养因子对cAMP信号通路的影响,见图5。上述结果表明,睫状神经营养因子能够激活cAMP信号通路。"
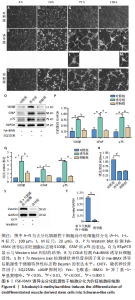
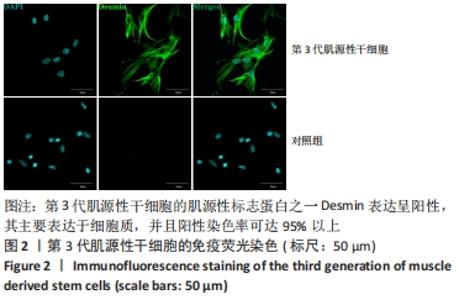
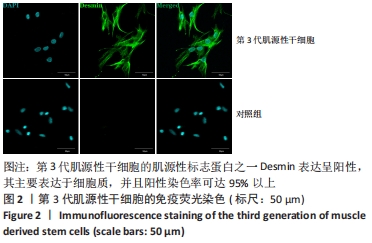
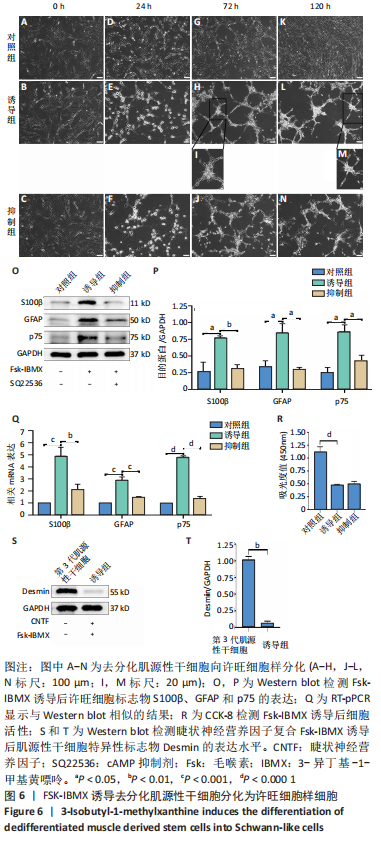
2.6 FSK-IBMX诱导去分化肌源性干细胞分化为许旺细胞样细胞 Fsk-IBMX诱导过程中可见诱导组和抑制组细胞随着培养时间的延长,细胞数量均逐渐减少,而对照组细胞则相反,细胞密度随着培养时间的延长明显增加,见图6A-N。Fsk-IBMX诱导后24 h,诱导组和抑制组细胞折光性增强,呈神经元样改变,细胞间有突触样结构形成,见图6E和6F,而对照组有少数细胞折光性增强,细胞形态无明显变化,见图6D;诱导后72 h,诱导组和抑制组细胞折光性明显增强,形态变化更为明显,细胞聚集成神经球,诱导组较抑制组更为聚集,突起明显增长并交织成网,见图6H-J,而对照组细胞折光性较24 h减弱,有轻微聚集现象,但无神经球形成,细胞生长有一定的方向性,见图6G;诱导后120 h,诱导组和抑制组神经球细胞折光性更强,更加聚集,交织成网的突起明显增粗,但抑制组均弱于诱导组,见图6L-N,而对照组细胞折光性较72 h无明显变化,部分细胞有轻微聚集现象,细胞变得细长,生长有明显的方向性,见图6K。 Fsk-IBMX诱导去分化肌源性干细胞120 h后,Western blot结果显示,与对照组相比,诱导组细胞S100β、GFAP和p75均明显增加(P < 0.05),而抑制组S100β、GFAP和p75的表达较对照组无明显变化,与诱导组相比均明显降低(P < 0.01,P < 0.05和P < 0.05),见图6O,P。RT-qPCR结果与Western blot结果一致,即诱导组细胞S100β、GFAP和p75 mRNA表达水平较对照组均明显增加(P < 0.001,P < 0.001和P < 0.000 1),而抑制组与诱导组相比mRNA表达水平均明显降低(P < 0.01,P < 0.001和P < 0.000 1),见图6Q。结果表明,Fsk-IBMX可以诱导去分化肌源性干细胞分化为许旺细胞样细胞,而SQ22536可以抑制这种诱导作用。 CCK-8法检测显示,与对照组相比,FSK-IBMX抑制了去分化肌源性干细胞的细胞活性(P < 0.000 1),而加入SQ22536后,这种抑制作用并未被明显减弱,见图6R。 为了证实睫状神经营养因子和Fsk-IBMX相继处理后,肌源性干细胞确实已发生了神经分化,对肌源性干细胞特异性标志物Desmin的表达水平进行了Western blot检测,结果显示,经睫状神经营养因子复合Fsk-IBMX诱导后,Desmin的表达水平显著降低(P < 0.01),见图6S和6T。"
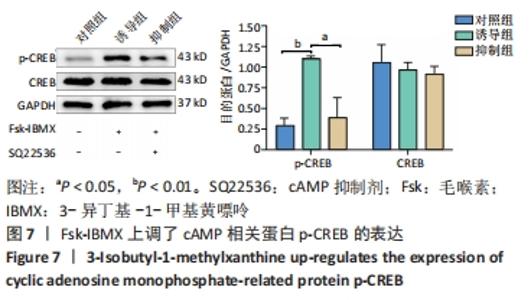
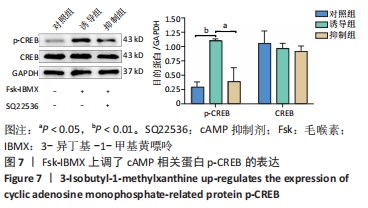
2.7 Fsk-IBMX上调了cAMP相关蛋白p-CREB的表达 为了确定Fsk-IBMX诱导去分化肌源性干细胞在向许旺细胞样细胞分化过程中cAMP信号通路是否被激活,通过Western blot检测了CREB和p-CREB的表达。Western blot结果显示,与对照组相比,Fsk-IBMX诱导肌源性干细胞120 h后,p-CREB表达增加(P < 0.01),而CREB表达与对照组相比无明显差异(P > 0.05),见图7。但是在加入SQ22536之后,p-CREB的表达水平与诱导组相比明显降低(P < 0.05),CREB的表达水平无明显变化(P > 0.05),这表明SQ22536可以抑制Fsk-IBMX对cAMP信号通路的影响,见图7。结果表明,Fsk-IBMX能够激活cAMP信号通路。"
| [1] YI S, ZHANG Y, GU X, et al. Application of stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration. Burns Trauma. 2020;8:tkaa002. [2] SULLIVAN R, DAILEY T, DUNCAN K, et al. Peripheral Nerve Injury: Stem Cell Therapy and Peripheral Nerve Transfer. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(12):2101. [3] LI R, LIU Z, PAN Y, et al. Peripheral nerve injuries treatment: a systematic review. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014;68(3):449-454. [4] JIANG L, JONES S, JIA X. Stem Cell Transplantation for Peripheral Nerve Regeneration: Current Options and Opportunities. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(1):94. [5] PANAGOPOULOS GN, MEGALOIKONOMOS PD, MAVROGENIS AF. The Present and Future for Peripheral Nerve Regeneration. Orthopedics. 2017;40(1):e141-e156. [6] MUSAVI L, BRANDACHER G, HOKE A, et al. Muscle-derived stem cells: important players in peripheral nerve repair. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018;22(12):1009-1016. [7] KUBIAK CA, GROCHMAL J, KUNG TA, et al. Stem-cell-based therapies to enhance peripheral nerve regeneration. Muscle Nerve. 2020;61(4):449-459. [8] LAVASANI M, THOMPSON SD, POLLETT JB, et al. Human muscle-derived stem/progenitor cells promote functional murine peripheral nerve regeneration. J Clin Invest. 2014;124(4):1745-1756. [9] ZHOU J, CUI H, LU H, et al. Muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration: reality or illusion? Regen Med. 2017;12(4):459-472. [10] SAYAD FATHI S, ZAMINY A. Stem cell therapy for nerve injury. World J Stem Cells. 2017;9(9):144-151. [11] TAMAKI T. Biomedical applications of muscle-derived stem cells: from bench to bedside. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2020;20(11):1361-1371. [12] CHEN ZX, LU HB, JIN XL, et al. Skeletal muscle-derived cells repair peripheral nerve defects in mice. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(1):152-161. [13] LV P, WANG W, CAO Z, et al. Fsk and IBMX inhibit proliferation and proapoptotic of glioma stem cells via activation of cAMP signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(1):321-331. [14] SHAHBAZI A, SAFA M, ALIKARAMI F, et al. Rapid Induction of Neural Differentiation in Human Umbilical Cord Matrix Mesenchymal Stem Cells by cAMP-elevating Agents. Int J Mol Cell Med. 2016;5(3):167-177. [15] ZHANG P, CHEN XP. The regulation of myoblast plasticity and its mechanism. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2012;28(6):524-531. [16] ZHANG L, SEITZ LC, ABRAMCZYK AM, et al. cAMP initiates early phase neuron-like morphology changes and late phase neural differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011;68(5):863-876. [17] THOMPSON R, CASALI C, CHAN C. Forskolin and IBMX Induce Neural Transdifferentiation of MSCs Through Downregulation of the NRSF. Sci Rep. 2019; 9(1):2969. [18] DE LA ROSA MB, KOZIK EM, SAKAGUCHI DS. Adult Stem Cell-Based Strategies for Peripheral Nerve Regeneration. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1119:41-71. [19] CHING RC, WIBERG M, KINGHAM PJ. Schwann cell-like differentiated adipose stem cells promote neurite outgrowth via secreted exosomes and RNA transfer. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):266. [20] ROTSHENKER S. Wallerian degeneration: the innate-immune response to traumatic nerve injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2011;8:109. [21] SEDDON HJ, MEDAWAR PB, SMITH H. Rate of regeneration of peripheral nerves in man. J Physiol. 1943;102(2):191-215. [22] WANG D, LIU XL, ZHU JK, et al. Bridging small-gap peripheral nerve defects using acellular nerve allograft implanted with autologous bone marrow stromal cells in primates. Brain Res. 2008;1188:44-53. [23] LU L, CHEN X, ZHANG CW, et al. Morphological and functional characterization of predifferentiation of myelinating glia-like cells from human bone marrow stromal cells through activation of F3/Notch signaling in mouse retina. Stem Cells. 2008;26(2):580-590. [24] MAURO A. Satellite cell of skeletal muscle fibers. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961; 9(2):493-495. [25] TAMAKI T. Therapeutic capacities of human and mouse skeletal muscle-derived stem cells for a long gap peripheral nerve injury. Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(11): 1811-1813. [26] TAMAKI T. Bridging long gap peripheral nerve injury using skeletal muscle-derived multipotent stem cells. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(14):1333-1336. [27] TAMAKI T, HIRATA M, NAKAJIMA N, et al. A Long-Gap Peripheral Nerve Injury Therapy Using Human Skeletal Muscle-Derived Stem Cells (Sk-SCs): An Achievement of Significant Morphological, Numerical and Functional Recovery. PLoS One. 2016;11(11):e0166639. [28] TAMAKI T, HIRATA M, SOEDA S, et al. Preferential and comprehensive reconstitution of severely damaged sciatic nerve using murine skeletal muscle-derived multipotent stem cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(3):e91257. [29] DEUMENS R, BOZKURT A, MEEK MF, et al. Repairing injured peripheral nerves: Bridging the gap. Prog Neurobiol. 2010;92(3):245-276. [30] XU Z, CHEN Z, FENG W, et al. Grafted muscle-derived stem cells promote the therapeutic efficiency of epimysium conduits in mice with peripheral nerve gap injury. Artif Organs. 2020;44(5):E214-E225. [31] DEASY BM, GHARAIBEH BM, POLLETT JB, et al. Long-term self-renewal of postnatal muscle-derived stem cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2005;16(7):3323-3333. [32] ARSIC N, MAMAEVA D, LAMB NJ, et al. Muscle-derived stem cells isolated as non-adherent population give rise to cardiac, skeletal muscle and neural lineages. Exp Cell Res. 2008;314(6):1266-1280. [33] ALESSANDRI G, PAGANO S, BEZ A, et al. Isolation and culture of human muscle-derived stem cells able to differentiate into myogenic and neurogenic cell lineages. Lancet. 2004;364(9448):1872-1883. [34] KWON JS, KIM GH, KIM DY, et al. Chitosan-based hydrogels to induce neuronal differentiation of rat muscle-derived stem cells. Int J Biol Macromol. 2012;51(5): 974-979. [35] KIM ES, KIM GH, KANG ML, et al. Potential induction of rat muscle-derived stem cells to neural-like cells by retinoic acid. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2011;5(5): 410-414. [36] TANG Y, HE H, CHENG N, et al. PDGF, NT-3 and IGF-2 in combination induced transdifferentiation of muscle-derived stem cells into Schwann cell-like cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e73402. [37] KINJO T, WATABE T, KOBACHI K, et al. Single-Cell Activation of the cAMP-Signaling Pathway in 3D Tissues with FRET-Assisted Two-Photon Activation of bPAC. ACS Chem Biol. 2020;15(11):2848-2853. [38] 江声伟,刘德武,孙宝丽,等.cAMP信号通路对卵泡发育调控机制的研究进展[J].黑龙江畜牧兽医,2020(23):44-47. [39] ROONEY GE, HOWARD L, O’BRIEN T, et al. Elevation of cAMP in mesenchymal stem cells transiently upregulates neural markers rather than inducing neural differentiation. Stem Cells Dev. 2009;18(3):387-398. [40] 张东云,靳伟东,刘宏亮,等.CREB信号通路在神经系统疾病中的调控作用及机制[J].中华全科医学,2019,17(4):644-648. [41] WANG H, XU J, LAZAROVICI P, et al. cAMP Response Element-Binding Protein (CREB): A Possible Signaling Molecule Link in the Pathophysiology of Schizophrenia. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018;11:255. [42] DEZAWA M, KANNO H, HOSHINO M, et al. Specific induction of neuronal cells from bone marrow stromal cells and application for autologous transplantation. J Clin Invest. 2004;113(12):1701-1710. [43] 徐如祥,戴宜武,姜晓丹,等.成年骨髓间质干细胞体外诱导分化成神经细胞研究[J].中华神经外科疾病研究杂志,2002,1(1):63-67. [44] HERMANN A, MAISEL M, STORCH A. Epigenetic conversion of human adult bone mesodermal stromal cells into neuroectodermal cell types for replacement therapy of neurodegenerative disorders. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2006;6(7):653-670. [45] EL-DEEB OS, GHANEM HB, EL-ESAWY RO, et al. The modulatory effects of luteolin on cyclic AMP/Ciliary neurotrophic factor signaling pathway in experimentally induced autoimmune encephalomyelitis. IUBMB Life. 2019;71(9):1401-1408. [46] HELLSTRÖM M, HARVEY AR. Cyclic AMP and the regeneration of retinal ganglion cell axons. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014;56:66-73. |
| [1] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [2] | Wang Baojuan, Zheng Shuguang, Zhang Qi, Li Tianyang. Miao medicine fumigation can delay extracellular matrix destruction in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1180-1186. |
| [3] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [4] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [5] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [6] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [7] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [8] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [9] | Gao Yujin, Peng Shuanglin, Ma Zhichao, Lu Shi, Cao Huayue, Wang Lang, Xiao Jingang. Osteogenic ability of adipose stem cells in diabetic osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 999-1004. |
| [10] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [11] | Zhou Ying, Zhang Huan, Liao Song, Hu Fanqi, Yi Jing, Liu Yubin, Jin Jide. Immunomodulatory effects of deferoxamine and interferon gamma on human dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1012-1019. |
| [12] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [13] | Wang Jifang, Bao Zhen, Qiao Yahong. miR-206 regulates EVI1 gene expression and cell biological behavior in stem cells of small cell lung cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1027-1031. |
| [14] | Liu Feng, Peng Yuhuan, Luo Liangping, Wu Benqing. Plant-derived basic fibroblast growth factor maintains the growth and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1032-1037. |
| [15] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||