Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (11): 1780-1787.doi: 10.12307/2022.366
Previous Articles Next Articles
Activation of Nrf2/ARE signal pathway reduces radiotherapy-induced tissue injury
Lin Peiqi1, Long Yuanzhu1, Zhang Nini2, Huang Guilin2
- 1Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Maxillofacial Surgery, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2021-06-15Revised:2021-06-16Accepted:2021-07-10Online:2022-04-18Published:2021-12-13 -
Contact:Huang Guilin, MD, Professor, Department of Maxillofacial Surgery, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Lin Peiqi, Master candidate, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81960204 (to HGL) and 81860198 (to ZNN)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lin Peiqi, Long Yuanzhu, Zhang Nini, Huang Guilin. Activation of Nrf2/ARE signal pathway reduces radiotherapy-induced tissue injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1780-1787.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
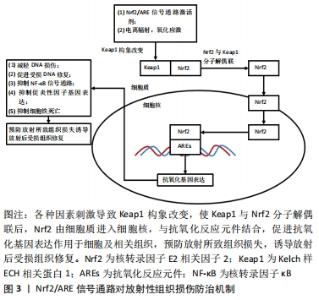
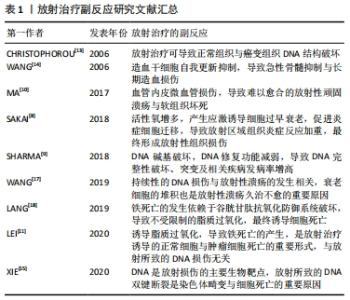
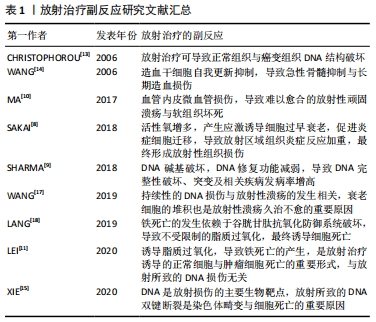
放射性损伤的来源可分为直接损伤以及间接损伤:直接损伤为电离辐射直接破坏包括核酸、蛋白质、脂质在内的关键生物分子,使其分子内键均裂,产生自由基与活性氧;间接损伤是由于H2O辐射分解,产生具有组织毒性的羟基自由基(?OH)。在放射性损伤中,间接损伤导致的正常组织破坏占到了60%-70%[12]。 CHRISTOPHOROU团队[13]研究表明,电离辐射在体外和体内都能产生较高水平的DNA损伤,常常导致肿瘤细胞与正常组织细胞衰老和细胞凋亡。WANG等[14]发现,放射治疗可导致造血干细胞自我更新抑制,导致急性骨髓抑制与长期造血损伤。DNA是放射损伤的主要生物靶点,同时放射所致的DNA双链断裂最具危害性,是染色体畸变与细胞死亡的重要原因[15]。目前,电离辐射对DNA的损害效应由直接和间接2种机制引起,直接机制为电离辐射作用于细胞中的DNA分子,使得分子内键均裂;间接机制则是通过电离辐射与细胞中的水分子相互作用,通过高反应性自由基与活性氧的产物破坏DNA共价键[16]。持续性的DNA损伤与放射性溃疡的发生相关,同时放射性溃疡可导致衰老细胞在组织中广泛堆积,从而对DNA损伤灶持续存在的细胞产生持久影响[17]。 LEI等[11]进一步研究发现,电离辐射除了诱导DNA损伤外,还可导致铁死亡的产生,并指出铁死亡是电离辐射诱导的正常细胞与肿瘤细胞死亡的重要形式,与放射所致的DNA损伤无关,其主要机制为电离辐射不仅导致了活性氧的增加,同时还诱导了长链脂酰辅酶A合成酶4的表达,从而导致脂质过氧化以及铁死亡的产生。LANG等[18]的研究也表明铁死亡作为一种独特的铁依赖的细胞死亡形式,其特征是铁依赖性的脂质过氧化物堆积,在形态和机制上与其他形式的细胞死亡不同,它的启动依赖于谷胱甘肽抗氧化防御系统破坏,导致不受限制的脂质过氧化,最终诱导细胞死亡,是恶性肿瘤放射治疗、化学药物治疗以及免疫疗法协同治疗的潜在交叉点。 2.2 放射性损伤防治现状 为了减轻放射治疗所致的组织损失,在过去的50年间,学者们对放射性损伤防治药物进行了广泛研究,但尚未找到一个理想的放射性损伤防治策略[19]。目前,临床上针对放射性组织损伤患者的防治方案多为对症处理,如药物治疗及基因疗法等。氨磷汀是美国食品和药物管理局(FDA)批准的广谱细胞保护剂,也是已知有效的辐射防护药物,该药物通过与细胞膜碱性磷酸酯酶脱磷酸结合,生成含自由巯基的活性代谢物 WR-1065,可清除细胞内自由基;尽管在防治消化系统放射性组织损伤中取得了实验及临床的证据支持[20-21],但由于其存在如严重且频繁的消化道反应、低血压等毒副反应,目前氨磷汀仅限于减轻晚期卵巢癌患者顺铂治疗引起的肾毒性,以及改善头颈部恶性肿瘤患者放疗性唾液腺损伤症状[22]。 此外,一些药物也对放射性组织损伤有一定对症缓解作用,如人角化细胞生长因子(帕利夫明)、血管紧张素转换酶抑制剂(卡托普利和雷米普利)、环氧化酶2抑制剂(塞来昔布和布洛芬)等[20]。针对放射治疗后口干症的基因疗法亦有临床试验的报道,该疗法是通过注射的方法,在腮腺内注入带外源性水通道基因重组腺病毒,用于改善人体内基因缺陷与基因不足,以此修复腮腺,缓解各种原因引起的口干症症状[23]。 除了上述方法外,近年来以Nrf2/ARE信号通路为基础的治疗方案显示出了独特的效果。作为机体对氧化应激重要的内源性防御机制,基于Nrf2/ARE信号通路的放射性损伤防治方案与药物研究,为降低放射性组织损伤发生率、缓解症状、提高患者生存质量提供新的思路。 2.3 Nrf2/ARE信号通路与放射性损伤 Nrf2由NFE2L2基因编码,是碱性亮氨酸拉链结构核转录因子CnC(cap’n’-collar)家族成员,1994年首次从慢性髓系白血病细胞K562中发现并分离。CnC家族成员包括SKn-1、Nrf1、Nrf2、Nrf2、Nrf3、CNCC、Bach1及Bach2,作为抗氧化反应介体发挥作用[24]。Nrf2被认为是抗氧化反应的主要调节者,其下游靶基因控制细胞抗氧化反应、细胞保护和解毒基因的表达,参与预防与纠正细胞中的氧化还原失衡[25]。 Nrf2/ARE信号通路是有效的机体内源性抗氧化防御机制,可以抵御各种物理或化学来源的氧化应激。Kelch样ECH相关蛋白1(kelch-like ECH-association protein 1,Keap1)是一种与Nrf2结合位于细胞质的抑制蛋白,可以促进Nrf2 泛素化及对蛋白质酶体的降解,在非应激条件下维持细胞质内较低水平的Nrf2[26]。在氧化应激条件下,随着Nrf2和Keap1的分子解偶联,Nrf2进入人体的细胞核,与抗氧化反应元件中的GCTGAGTCA位点结合,从而激活包括谷胱甘肽S-转移酶、γ-谷氨酰半胱氨酸合成酶、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶、血红素加氧酶1、过氧化氢酶、醌氧化还原酶1等抗氧化反应元件的表达,增强细胞抗氧化应激的能力[27-29],减轻羟基自由基介导的DNA损伤,促进受损DNA的修复[5]。此外,Nrf2除了能诱导下游抗氧化因子的基因表达,同时还能抑制核转录因子κB信号通路以及促炎性细胞因子基因表达[30-31]。 自由基与活性氧的增加,导致脂质过氧化,谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4、胱氨酸/谷氨酸转运蛋白系统在内的抗氧化体系表达量的降低,诱导铁死亡的发生。其中谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶 4与胱氨酸/谷氨酸转运蛋白系统均为Nrf2下游产物[6],Nrf2/ARE信号通路激活后,前者利用谷胱甘肽减少氧化脂质种类,抑制铁死亡[32],后者作为胱氨酸/谷氨酸逆转运体的关键成分,通过输入胱氨酸并促进谷胱甘肽生物合成阻止铁死亡发生[33-34]。Nrf2/ARE信号通路对铁死亡的抑制可分为铁代谢、中间代谢和谷胱甘肽合成/代谢3类[6]。 Nrf2/ARE信号通路在铁/血红素代谢中起关键作用[35],影响着与铁储存、运输和新陈代谢相关的蛋白质编码基因的表达。铁作为氧运输、氧化磷酸化和代谢物氧化反应的辅助因子,过量时会导致氧自由基的产生,Nrf2通过激活编码铁蛋白重链(Fth1)和铁蛋白轻链(Ftl)表达,从而提高铁蛋白水平,促进铁储存,降低细胞内氧化还原活性的游离铁原子的水平[36]。除了铁/血红素代谢外,Nrf2还调节许多参与中间代谢的产物,介导反应中间体的分解与解毒,对氧化底物还原所需的关键电子供给体还原型辅酶Ⅱ(NADPH)再生有重要意义。许多药物的代谢酶和其他抗氧化反应系统都需要还原型辅酶Ⅱ作为其主辅因子,包括醛酮还原酶和醌氧化还原酶1等;NADPH生成酶6-磷酸葡萄糖脱氢酶和6-磷酸葡萄糖酸脱氢酶等受Nrf2控制调节[37-38]。谷胱甘肽合成和代谢相关酶受Nrf2调控,如前文所提到的谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4是利用谷胱甘肽抑制铁死亡的过氧化脂质还原剂[39]。XIE等[15]的研究表明,Nrf2/ARE信号通路可以抑制电离辐射导致的细胞死亡与铁死亡,同时Nrf2抑制剂可阻断该信号通路对细胞铁死亡的保护作用,见图3。"
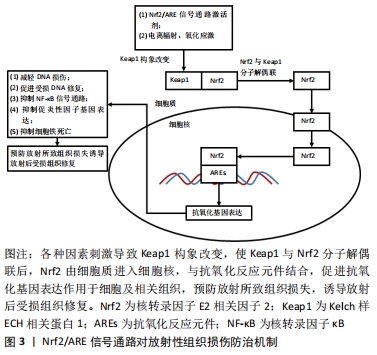
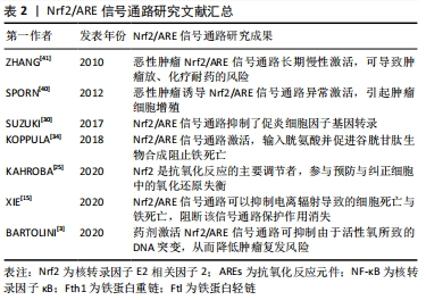
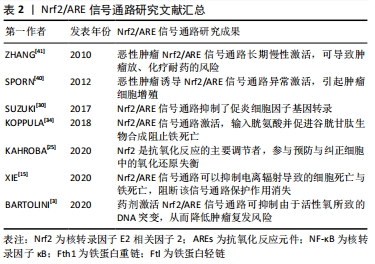
既往研究表明,使用药剂激活Nrf2/ARE信号通路可抑制由于活性氧所致的DNA突变,从而降低肿瘤复发风险[3]。也有学者指出,由于Nrf2/ARE信号通路的激活,促进压力状态下的细胞存活,在癌细胞中的长期处于过表达状态将影响放、化疗的治疗效果。部分恶性肿瘤,包括皮肤癌、乳腺癌、前列腺癌、肺癌、头颈部癌和子宫内膜癌的肿瘤细胞中发现Nrf2的Neh2结构域或 Keap1的Kelch结构域中产生突变,这些突变能够诱导Nrf2/ARE信号通路异常激活,并导致Keap1与其他调节增殖和凋亡的蛋白质结合功能障碍,引起肿瘤细胞增殖,产生更广泛的致癌作用[40-41]。即Nrf2/ARE信号通路的激活对恶性肿瘤放射治疗并发症防治方案可能存在有两面性,如何在保护正常组织损失的同时,减小肿瘤对放射治疗耐药性,避免肿瘤复发,也是未来针对围放射治疗期基于Nrf2/ARE信号通路治疗方案研究的挑战。 电离辐射诱导的症状与放射治疗期间活性氧和炎症因子的增加,导致生物损伤以及细胞通路的改变,这严重损害了患者的生活质量[42-43]。近年来众多研究表明,Nrf2的靶基因如血红素加氧酶1、γ-谷氨酰半胱氨酸合成酶、谷胱甘肽S-转移酶等氧化反应元件的表达水平,随着放射治疗的剂量增加而增加,反映了抗氧化应激状态,不仅可作为评估电离辐射损伤的潜在生物标志参考[27,42],同时也为寻找、研发基于Nrf2/ARE信号通路,围放射治疗期间及放射治疗后,邻近正常组织不良反应的防治药物与防治方案选择提供了重要思路[15-17,44-45],近年来Nrf2/ARE信号通路的研究内容,见表2。"
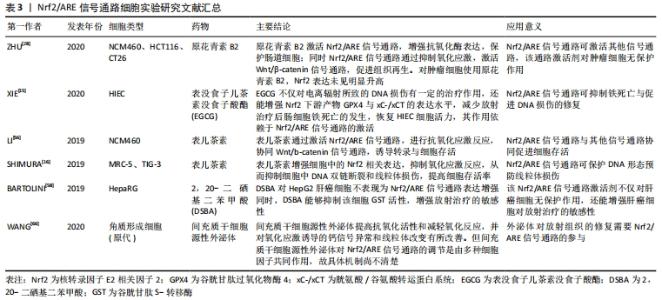
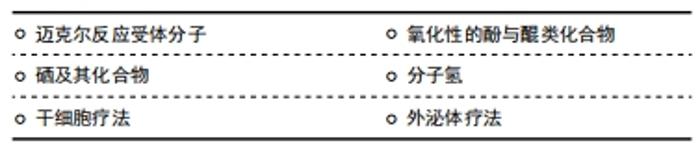
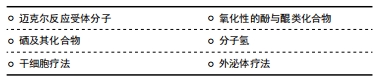
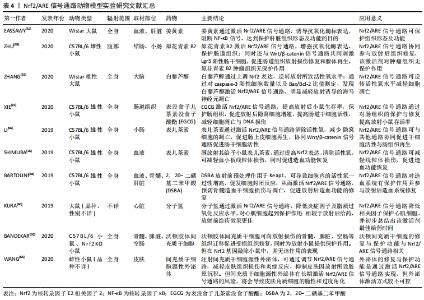
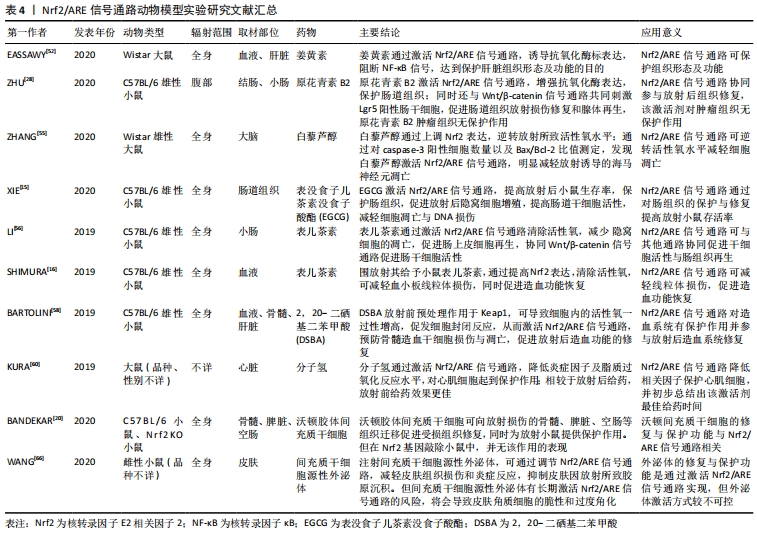
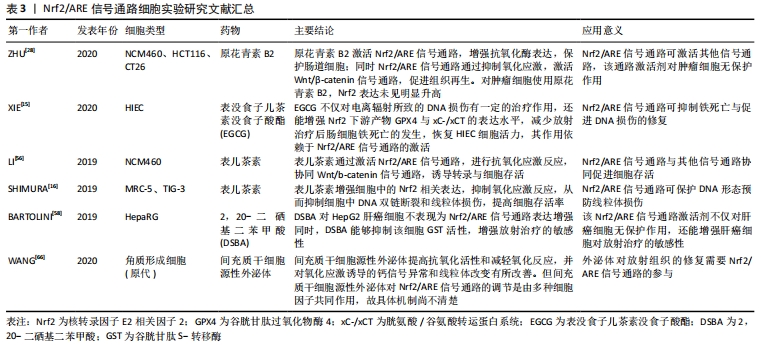
Nrf2/ARE信号通路的激活,对放射性组织损伤有一定的预防与治疗作用,目前激活Nrf2/ARE信号通路的药物多为Keap1与Nrf2相互作用的抑制剂,且具有亲电性[46]。当细胞处于亲电或氧化应激状态时,Nrf2逃脱Keap1介导的降解反应,进入细胞核,并在细胞核中将抗氧化和细胞保护基因激活[47]。激活剂通过氧化或烷基化与Keap1半胱氨酸上的巯基共价结合,改变Keap1构象,从而达到抑制Nrf2泛素化的目的[48]。此类通过直接抑制 Keap1与Nrf2结合,从而激活Nrf2/ARE信号通路的药物称作蛋白-蛋白相互作用抑制剂[49],如迈克尔反应受体分子、氧化性的酚与醌类化合物;此外,还有硒及其化合物、分子氢等具有亲电性的物质,也起到了Nrf2/ARE信号通路的激活作用。近年来,由于再生医学的兴起,通过干细胞疗法或借由外泌体,诱导Nrf2/ARE信号通路表达,达到对电离辐射的防护以及促进放射性组织损伤修复的目的,见表3,4。"

2.4.1 迈克尔反应受体分子 迈克尔受体分子含有α,β-不饱和羰基,能够同Keap1中的半胱氨酸残基共价结合,使得Keap1的构象改变,抑制因Keap1介导的Nrf2泛素化反应,是一类效果较好的Nrf2激活剂[50]。目前,放射性组织损伤防治潜在的迈克尔反应受体分子主要有姜黄素与原花青素B2。 姜黄素是一种潜在的Nrf2激活剂,不仅是因为它能够通过氧化反应(供氢反应)清除活性氧,同时姜黄素还是典型的迈克尔反应受体分子,能够参与迈克尔加成反应。但在临床实际运用中,姜黄素存在吸收能力差、肝脏排出迅速、半衰期短等缺陷,故生物利用率极低,目前为提高姜黄素的生物利用率,基于生物学和药用性质对姜黄素衍生物和类似物的研究受到了广泛关注[51]。 EASSAWY等[52]研究发现,姜黄素可以改善由于放射治疗或对乙酰氨基酚所致的肝脏损伤。通过姜黄素预处理,不仅保持肝细胞膜结构与肝脏组织的完整性,还可提高实验大鼠的肝酶、抗氧化酶活性,降低脂质过氧化反应终产物丙二醛、炎症标记物、核转录因子 κB和钙离子水平。同时,进一步研究表明,姜黄素能够提高Nrf2及其下游基因血红素加氧酶1、醌氧化还原酶1的表达,以及上调血红素加氧酶1、醌氧化还原酶1相对蛋白表达率发挥保护作用。姜黄素通过抑制肝组织中的脂质过氧化作用激活Nrf2/ARE信号通路,保护细胞和组织免受炎性损伤,其机制可能与抗氧化酶的激活以及核转录因子κB信号的阻断有关。 原花青素B2是另一种天然黄酮类迈克尔反应受体分子,作为抗氧化剂,相较于姜黄素,具有更好的化学稳定性以及更强的生物利用率。ZHU等[28]在关于原花青素 B2 对放射后肠道损伤修复影响的研究中发现,原花青素 B2不仅可以通过调节Nrf2/ARE信号通路活性,增加抗氧化酶的表达,防御氧化应激,对肠组织及其腺体起到放射保护作用;还通过Nrf2/ARE信号通路抑制氧化应激反应,进而激活 Wnt/β-Catenin信号通路,共同刺激Lgr5阳性肠干细胞,驱动肠道干细胞增殖,促进放射后组织再生。ZHU等[28]研究团队还发现,原花青素 B2 的放射防护作用仅针对正常细胞,而对于需要放射治疗的恶性肿瘤细胞并没有类似防护效果,研究人员考虑这可能与恶性肿瘤细胞已经异常激活Nrf2/ARE信号通路有关。 2.4.2 氧化性的酚与醌类化合物 部分多羟基酚类化合物,如儿茶酚、对苯二酚,可通过氧化反应形成醌。这些化合物具有亲电子活性,可与Keap1半胱氨酸的巯基反应,使Nrf2与Keap1解偶联,在细胞核中激活ARE。然而还有部分多羟基酚类化合物,如间苯二酚无法诱导ARE活性,这是由于间二苯酚既无法参与氧化还原反应,也无法产生醌。对于多羟基酚类化合物而言,氧化还原不稳定性是激活Nrf2/ARE信号通路的关键[53]。研究发现,内皮细胞摄取多羟基酚类化合物在一定程度上依赖于小窝蛋白1(caveolin-1),当多羟基酚类化合物取代小窝蛋白1或利用小干扰 RNA(siRNA)诱导小窝蛋白1沉默后,Nrf2激活,血红素加氧酶1、醌氧化还原酶1等AREs下游产物表达上调[54]。 治疗神经退行性疾病(如阿尔茨海默病)的白藜芦醇,也可用于放射治疗所致脑损伤的防治。ZHANG等[55]的研究发现,大鼠的大脑受到放射性损伤后,海马区存在高水平的活性氧,同时核转录因子κB被激活,这导致大鼠的神经元丢失和认知功能损害;通过对Caspase-3阳性细胞数量以及Bax/Bcl-2比值测定,发现白藜芦醇激活Nrf2/ARE信号通路,促使其进入细胞核中,触发细胞内对氧化应激的防御反应,明显减轻放射诱导的海马神经元凋亡,达到神经保护的目的。 绿茶衍生物表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯,占绿茶中的儿茶素含量50%以上,是茶多酚的主要有效成分。XIE等[15]研究发现表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯介导的放射性肠损伤防护作用依赖于Nrf2/ARE信号通路,同时,它的抗氧化活性是白藜芦醇的2倍,不仅对电离辐射所致的DNA损伤有一定的治疗作用,还能增强谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4与胱氨酸/谷氨酸转运蛋白系统的表达水平,减少放射治疗后肠细胞铁死亡的发生,从而提高放射后小鼠生存率,保护肠组织,促进放射后隐窝细胞增殖,提高肠道干细胞活性。LI等[56]在表儿茶素的研究中也发现,表儿茶素对放射性肠损伤的保护以及促进放射后肠再生作用依赖于Nrf2/ARE信号通路;通过Nrf2/ARE信号通路清除活性氧,可进一步提高肠干细胞的活性。表儿茶素通过Nrf2/ARE信号通路,可对全身多个系统进行电离辐射的防护,包括胃肠道、口腔黏膜和造血系统等,并减轻由于活性氧所导致的线粒体损伤,促进造血功能恢复[16]。 2.4.3 硒及其化合物 硒(Se)是人体重要的微量元素,是硒半胱氨酸(SeC)的组成部分,也是包括硒依赖的谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶和硫氧还蛋白还原酶1在内的硒蛋白辅助因子,具有清除自由基和细胞保护作用[57]。硒在放射治疗中的使用可分为无机硒与有机硒,虽然二者均有防治电离辐射损伤的功能,但有机硒较无机硒具有更低的毒性,故近年来有关硒及化合物在放射性损伤的研究以有机硒化合物为主[3]。 BARTOLINI等[58]研究中发现,硒激动剂,如2,20-二硒基二苯甲酸,对细胞进行放射前预处理,作用于Keap1,可导致细胞内的活性氧一过性增高,促发细胞封闭反应,从而激活Nrf2/ARE信号通路,上调Nrf2蛋白并增加Nrf2依赖基因的表达,预防骨髓造血干细胞损伤与凋亡,促进放射后造血功能的修复。SCHILLING等[59]在有关恶性肿瘤细胞放射治疗与硒的相关性研究中发现,在放射前预防性补硒,在保护正常细胞的同时,不仅不影响甚至还能够增加肿瘤细胞对放射的敏感性。 2.4.4 分子氢 分子氢(H2)是一种高效、无毒分子,拥有多种生物学效应,包括抗氧化、抗炎、抗凋亡和抗休克等[31];具有治疗包括放射性损伤在内,因活性氧引起的相关疾病的潜力。分子氢在放射性组织损伤的治疗中最大优势为具备广泛给药的可能性。在动物实验中,分子氢已被证明可通过激活Nrf2通路,减少大鼠由于电离辐射导致的心脏脂质过氧化反应[60]。LEBARON研究团队[12]总结出分子氢在氧化应激中的作用机制包括如下几点:①对羟自由基与过氧亚硝基阴离子的特定清除活性;②能够减轻炎症反应;③调节信号传导;④改变基因表达。研究表明,在放射治疗前预处理给予分子氢的效果,要优于放射治疗后的效果[12]。分子氢已经被证明可以模仿温和的生理应激的影响,通过瞬间增加超氧化物的产生、轻微增加氧化应激产物、一过性激活核转录因子κB及诱导热休克蛋白等方式,达到抑制Keap1与Nrf2结合,激活Nrf2/ARE信号通路的目的。 2.4.5 干细胞疗法 由于电离辐射会造成包括干细胞在内的增殖细胞广泛损害,故干细胞疗法为放射治疗后的损伤组织修复提供了一种可行的治疗选择。ABDEL-MAGEED等[61]的研究已经证明,通过静脉注射细胞外超氧化物歧化酶基因修饰的骨髓间充质干细胞,可提高放射后小鼠存活率。另一项研究表明,通过骨髓基质细胞(包括间充质细胞、内皮细胞和巨噬细胞)的移植,能够减轻小鼠放射后的肠道反应,并提高肠道生长因子水平,诱导放射损伤的肠组织再生[62]。但骨髓来源的干细胞存在有人类白细胞抗原配型、提取过程痛苦、分离效率低下等问题,而干细胞本身也存在成瘤风险。BANDEKAR等[20]从人脐带中分离出沃顿胶体间充质干细胞,异体移植入放射后小鼠体内,并通过激活Nrf2/ARE信号通路起到辐射防护作用,促进沃顿胶体间充质干细胞向放射损伤的骨髓、脾脏、空肠等组织迁移,辅助受损组织形态及功能修复,但无法对Nrf2基因敲除小鼠放射性损伤组织进行预防与修复,其机制推测可能与沃顿胶体间充质干细胞分泌的造血细胞因子有关。 2.4.6 外泌体疗法 近年来研究表明,干细胞疗法对于组织再生的治疗效果很大部分来自于相关细胞的旁分泌效应产物,即外泌体的作用[63]。与单纯的抗氧化剂不同,治疗效果为外泌体内多种细胞因子组合的共同作用,相较于干细胞疗法没有成瘤风险[64]。目前研究已证实,外泌体-Nrf2介导产物具有诱导靶器官组织修复与再生的能力,并对糖尿病足、动脉粥样硬化、慢性心力衰竭、生殖细胞衰竭和神经退行性疾病等有一定治疗意义[25],故外泌体在组织抗炎和损伤修复方面表现出相当大的前景。CHEN等[65]关于小鼠溃疡愈合的研究中发现,人类胚胎干细胞源性外泌体(HESC-Exos)通过 miR200a介导Keap1下调,激活Nrf2/ARE信号通路诱导血管生成,从而提高溃疡愈合的效率。WANG等[66]研究证明了间充质干细胞源性外泌体的抗氧化能力受Nrf2防御系统的调节,减少包括羟基自由基在内的活性氧产生、DNA损伤、钙信号的异常以及线粒体的变化,改善因放射氧化应激诱导的皮肤损伤,减轻皮肤组织炎症反应,抑制皮肤胶原沉积;然而外泌体长期慢性地激活Nrf2/ARE信号通路,可造成皮肤角质细胞脆性增加和过度角化。就放射性损伤的组织而言,外泌体疗法是把双刃剑,既促进活性氧的产生与炎性因子的表达,又能够利用蛋白质和 miRNA诱导抗氧化信号通路的激活[67],一方面参与电离辐射的组织损伤,另一方促进放射性组织损伤的修复再生,同时在对放射后受损组织修复的过程中,也展现出不可控的一面。虽然外泌体疗法能够避免部分细胞疗法的潜在风险,但其修复与保护机制尚待进一步阐明,便于研究者对Nrf2/ARE信号通路进行调控,达到理想的防治效果。"

| [1] WEN S, DOONER M, PAPA E, et al. Biodistribution of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in a radiation injury bone marrow murine model. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(21):1-15. [2] ZHOU R, LONG H, ZHANG B, et al. Salvianolic acid B, an antioxidant derived from Salvia militarize, protects mice against gammaradiationinduced damage through Nrf2/Bach1. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(2):1309-1317. [3] BARTOLINI D, TEW KD, MARINELLI R, et al.Nrf2-modulation by seleno-hormetic agents and its potential for radiation protection. Biofactors. 2020;46(2):239-245. [4] ANURANJANI, BALA M. Concerted action of Nrf2-ARE pathway, MRN complex, HMGB1 and inflammatory cytokines-implication in modification of radiation damage. Redox Biol. 2014;2:832-846. [5] ZHANG T, SHI L, LI Y, et al. Polysaccharides extracted from Rheum tanguticum ameliorate radiation-induced enteritis via activation of Nrf2/HO-1. J Radiat Res. 2021;62(1):46-57. [6] DODSON M, CASTRO-PORTUGUEZ R, ZHANG DD. Nrf2 plays a critical role in mitigating lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 2019; 23:101107. [7] HYBERTSON B M, GAO B, BOSE SK, et al. Oxidative stress in health and disease: the therapeutic potential of Nrf2activation. Mol Aspects Med. 2011;32(4-6):234-246. [8] SAKAI Y, YAMAMORI T, YOSHIKAWA Y, et al. NADPH oxidase 4 mediates ROS production in radiation-induced senescent cells and promotes migration of inflammatory cells. Free Radic Res. 2018;52(1):92-102. [9] SHARMA N, CHAKRAVARTHY S, LONGLEY MJ, et al. The C-terminal tail of the NEIL1 DNA glycosylase interacts with the human mitochondrial single-strandedDNAbinding protein.DNARepair (Amst). 2018;65:11-19. [10] MA X, JIN Z, LI G, et al. Classification of chronic radiation-induced ulcers in the chest wall after surgery in breast cancers. Radiat Oncol. 2017;12(1):135. [11] LEI G, ZHANG Y, KOPPULA P, et al. The role of ferroptosis in ionizing radiation-induced cell death and tumor suppression. Cell Res. 2020; 30(2):146-162. [12] LEBARON TW, KURA B, KALOCAYOVA B, et al. A New approach for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disorders. molecular hydrogen significantly reduces the effects of oxidative stress. Molecules. 2019;24(11):2076. [13] CHRISTOPHOROU MA, RINGSHAUSEN I, FINCH AJ, et al. The pathological response toDNAdamage does not contribute to p53-mediated tumour suppression. Nature. 2006;443(7108):214-217. [14] WANG Y, SCHULTE BA, LARUE AC, et al. Total body irradiation selectively induces murine hematopoietic stem cell senescence. Blood. 2006;107(1):358-366. [15] XIE LW, CAI S, ZHAO TS, et al. Green tea derivative (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) confers protection against ionizing radiation-induced intestinal epithelial cell death both in vitro and in vivo. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;161:175-186. [16] SHIMURA T, KOYAMA M, AONO D, et al. Epicatechin as a promising agent to countermeasure radiation exposure by mitigating mitochondrial damage in human fibroblasts and mouse hematopoietic cells. FASEB J. 2019;33(6):6867-6876. [17] WANG Z, CHEN Z, JIANG Z, et al. Cordycepin prevents radiation ulcer by inhibiting cell senescence viaNrf2and AMPK in rodents. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):2538. [18] LANG X, GREEN MD, WANG W, et al. Radiotherapy and immunotherapy promote tumoral lipid oxidation and ferroptosis via synergistic repression of SLC7A11. Cancer Discov. 2019;9(12):1673-1685. [19] MISHRA K, ALSBEIH G. Appraisal of biochemical classes of radioprotectors: evidence, current status and guidelines for future development. 3 Biotech. 2017;7(5):292. [20] BANDEKAR M, MAURYA DK, SHARMA D, et al. Xenogeneic transplantation of human WJ‐MSCs rescues mice from acute radiation syndrome via Nrf-2-dependent regeneration of damaged tissues. Am J Transplant. 2020;20(8):2044-2057. [21] KOUKOURAKIS MI. Radiation damage and radioprotectants: new concepts in the era of molecular medicine. Br J Radiol. 2012;85(1012):313-330. [22] OBRADOR E, SALVADOR R, VILLAESCUSA JI, et al. Radioprotection and radiomitigation: from the bench to clinical practice. Biomedicines. 2020;8(11):461. [23] SINGH VK, SEED TM. Pharmacological management of ionizing radiation injuries: current and prospective agents and targeted organ systems. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020;21(3):317-337. [24] SYKIOTIS GP, BOHMANN D. Stress-activated cap’n’collar transcription factors in aging and human disease. Sci Signal. 2010;3(112):re3. [25] KAHROBA H, DAVATGARAN-TAGHIPOUR Y. Exosomal Nrf2: from anti-oxidant and anti-inflammation response to wound healing and tissue regeneration in aged-related diseases. Biochimie. 2020;171-172:103-109. [26] LOBODA A, DAMULEWICZ M, PYZA E, et al. Role of Nrf2/HO-1 system in development, oxidative stress response and diseases: an evolutionarily conserved mechanism. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73(17):3221-3247. [27] HAMADA N, SHIMURA T, NAKASHIRO C, et al. Induction of oxidative stress biomarkers following whole-body irradiation in mice. Plos One. 2020;15(10):e0240108. [28] ZHU X, TIAN X, YANG M, et al. Procyanidin B2 promotes intestinal injury repair and attenuates colitis-associated tumorigenesis via suppression of oxidative stress in mice. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2020;35(2):75-92. [29] YUAN L, DUAN X, ZHANG R, et al. Aloe polysaccharide protects skin cells from UVB irradiation through Keap1/Nrf2/ARE signal pathway. J Dermatol Treat. 2019;31(3):300-308. [30] SUZUKI T, YAMAMOTO M. Stress-sensing mechanisms and the physiological roles of the Keap1-Nrf2 system during cellular stress. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(41):16817-16824. [31] SLEZAK J, KURA B, LEBARON TW, et al. Oxidative stress and pathways of molecular hydrogen effects in medicine. Curr Pharm Des. 2020; 27(5):610-625. [32] URSINI F, MAIORINO M. Lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis: the role of GSH and GPx4. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;152:175-185. [33] ARENSMAN MD, YANG XS, LEAHY DM, et al. Cystine-glutamate antiporter xCT deficiency suppresses tumor growth while preserving antitumor immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(19):9533-9542. [34] KOPPULA P, ZHANG Y, ZHUANG L, et al. Amino acid transporter SLC7A11/xCT at the crossroads of regulating redox homeostasis and nutrient dependency of cancer. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2018;38(1):12. [35] KERINS MJ, OOI A. The roles of Nrf2 in modulating cellular iron homeostasis. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018;29(17):1756-1773. [36] SAHA S, BUTTARI B, PANIERI E, et al. An overview of Nrf2signaling pathway and its role in inflammation. Molecules. 2020;25(22):5474. [37] PANIERI E, TELKOPARAN-AKILLILAR P, SUZEN S, et al. The Nrf2/KEAP1 axis in the regulation of tumor metabolism: mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives. Biomolecules. 2020;10(5):791. [38] HAYES JD, DINKOVA-KOSTOVA AT. The Nrf2 regulatory network provides an interface between redox and intermediary metabolism. Trends Biochem Sci. 2014;39(4):199-218. [39] JIANG GP, LIAO YJ, HUANG LL, et al. Effects and molecular mechanism of pachymic acid on ferroptosis in renal ischemia reperfusion injury. Mol Med Rep. 2021;23(1):63. [40] SPORN MB, LIBY KT. Nrf2and cancer: the good, the bad and the importance of context. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12(8):564-571. [41] ZHANG DD. TheNrf2-Keap1-ARE signaling pathway: the regulation and dual function of Nrf2in cancer. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2010;13(11): 1623-1626. [42] MIURA S, YAMAGUCHI M, YOSHINO H, et al. Dose-dependent increase of Nrf2target gene expression in mice exposed to ionizing radiation. Radiat Res. 2019;191(2):176-188. [43] KIRSCH DG, SANTIAGO PM, DI TOMASO E, et al. p53 controls radiation-induced gastrointestinal syndrome in mice independent of apoptosis. Science. 2010;327(5965):593-596. [44] ABDEL-MAGIED N, SHEDID SM. The effect of naringenin on the role of nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like2 (Nrf2) and haem oxygenase 1 (HO-1) in reducing the risk of oxidative stress-related radiotoxicity in the spleen of rats. Environ Toxicol. 2019;34(7):788-795. [45] BAILLY C. Potential use of edaravone to reduce specific side effects of chemo-, radio- and immuno-therapy of cancers. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;77:105967. [46] O’BRIEN J, WENDELL SG. Electrophile modulation of inflammation: a two-hit approach. Metabolites. 2020;10(11):453. [47] ZHANG DD. Mechanistic studies of theNrf2-Keap1 signaling pathway. Drug Metab Rev. 2006;38(4):769-789. [48] LU H, ZHOU Q, HE J, et al. Recent advances in the development of protein-protein interactions modulators: mechanisms and clinical trials. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5(1):213. [49] JIANG ZY, LU MC, YOU QD. Discovery and Development of Kelch-like ECH-Associated Protein 1. Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 (KEAP1:NRF2) Protein-Protein Interaction Inhibitors: achievements, Challenges, and Future Directions. J Med Chem. 2016;59(24):10837-10858. [50] MENG X, WADDINGTON JC, TAILOR A, et al. CDDO-imidazolide targets multiple amino acid residues on the Nrf2 adaptor, Keap1. J Med Chem. 2020;63(17):9965-9976. [51] NOUREDDIN SA, EL-SHISHTAWY RM, AL-FOOTY KO. Curcumin analogues and their hybrid molecules as multifunctional drugs. Eur J Med Chem. 2019;182:111631. [52] EASSAWY MMT, SALEM AA, ISMAIL AFM. Biochemical study on the protective effect of curcumin on acetaminophen and gamma-irradiation induced hepatic toxicity in rats. Environ Toxicol. 2020. doi: 10.1002/tox.23077. [53] DINKOVA-KOSTOVA AT, WANG XJ. Induction of the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE pathway by oxidizable diphenols. Chem Biol Interact. 2011;192(1-2): 101-106. [54] ZHENG Y, MORRIS A, SUNKARA M, et al. Epigallocatechin-gallate stimulates NF-E2-related factor and heme oxygenase-1 via caveolin-1 displacement. J Nutr Biochem. 2012;23(2):163-168. [55] ZHANG Y, ZHU XB, ZHAO JC, et al. Neuroprotective effect of resveratrol against radiation after surgically induced brain injury by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis throughNrf2/HO-1/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2020;34(12):e22600. [56] LI Y, MA S, ZHANG Y, et al. (-)-Epicatechin mitigates radiation-induced intestinal injury and promotes intestinal regeneration via suppressing oxidative stress. Free Radic Res. 2019;53(8):851-864. [57] TINDELL R, WALL SB, LI Q, et al. Selenium supplementation of lung epithelial cells enhances nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) activation following thioredoxin reductase inhibition. Redox Biol. 2018;19:331-338. [58] BARTOLINI D, WANG Y, ZHANG J, et al. A seleno-hormetine protects bone marrow hematopoietic cells against ionizing radiation-induced toxicities. PLoS One. 2019;14(4):e0205626. [59] SCHILLING D, HEROLD B, COMBS SE, et al. Selenium does not affect radiosensitivity of breast cancer cell lines. Radiat Environ Biophys. 2019;58(3):433-438. [60] KURA B, BAGCHI AK, SINGAL PK, et al. Molecular hydrogen: potential in mitigating oxidative-stress-induced radiation injury. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2019;97(4):287-292. [61] ABDEL-MAGEED AS, SENAGORE AJ, PIETRYGA DW, et al. Intravenous administration of mesenchymal stem cells genetically modified with extracellular superoxide dismutase improves survival in irradiated mice. Blood. 2009;113(5):1201-1203. [62] SAHA S, BHANJA P, KABARRITI R, et al. Bone marrow stromal cell transplantation mitigates radiation-induced gastrointestinal syndrome in mice. PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24072. [63] 刘涛,张霓霓,黄桂林.细胞外囊泡与放射性组织损伤的关系[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(13):2121-2126. [64] FAIS S, O’DRISCOLL L, BORRAS FE, et al. Evidence-based clinical use of nanoscale extracellular vesicles in nanomedicine. ACS Nano. 2016; 10(4):3886-3899. [65] CHEN B, SUN Y, ZHANG J, et al. Human embryonic stem cell-derived exosomes promote pressure ulcer healing in aged mice by rejuvenating senescent endothelial cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):142. [66] WANG T, JIAN Z, BASKYS A, et al. MSC-derived exosomes protect against oxidative stress-induced skin injury via adaptive regulation of theNrf2defense system. Biomaterials. 2020;257:120264. [67] BODEGA G, ALIQUE M, PUEBLA L, et al. Microvesicles: ROS scavengers and ROS producers. J Extracell Vesicles. 2019;8(1):1626654. |
| [1] | Li Qin, Mao Shuangfa, Li Min, Cheng Jiyan. Protective effect and mechanism of dendrobium on fibroblasts damaged by ultraviolet B [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1228-1233. |
| [2] | Liu Wei, Li Fei, Li Lubing, Wang Xue, Wang Chengwei. Reliability and accuracy of digital software in measuring osseous markers related to stiff clubfoot [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 886-891. |
| [3] | Wu Saixuan, Zhang Mi, Dong Ming, Lu Ying, Niu Weidong. Regulatory role of Keap1/Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway in bone homeostasis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 271-275. |
| [4] | Gu Yueguang, Shen Jianhuan, Ni Jieli, Guo Shuyu, Yan Zhongyi, Zhang Yang. Effect of osteogenesis in patients with alveolar cleft after bone grafting investigated by volume analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1501-1504. |
| [5] | Xie Xingqi, Hu Wei, Tu Guanjun. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes combined with chondroitinase ABC for treating spinal cord injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 20-26. |
| [6] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [7] | Tang Qiang, Zhong Dejun, Wang Qing, Liao Yehui, Tang Chao, Ma Fei. Relationship between area ratio of interbody autograft and intervertebral fusion rate [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(36): 5821-5826. |
| [8] | Tan Rongbang, Wei Bo, Li Guangsheng. Nrf2-ARE regulated neurovascular interaction is involved in neural repair after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(35): 5694-5701. |
| [9] | Qin Qian, Yang Yang, Chen Jingfeng, Wang Shoujun, Ding Suying. Cut-off point of visceral fat area: predicting low bone mass in women [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(35): 5577-5581. |
| [10] | Gao Yi, Ma Yue, Zhao Zeyu, Wang Biao. Correlation of human barefoot morphological characteristics contact area with body height and mass: a statistical analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(32): 5103-5108. |
| [11] | Zhu Yin, Sheng Xiaolei, Sha Weiping, Zhang Xingxiang, Wang Jin, Zhu Xianwei, Wang Liming, Yan Fei. Comparison of the efficacy and biocompatibility of two anterior acetabular approaches with low-profile reconstruction plate fixation in the treatment of acetabular fractures involving quadrilateral area [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(27): 4348-4353. |
| [12] | Tian Yang, Tang Chao, Liao Yehui, Tang Qiang, Ma Fei, Zhong Dejun. Consistency and repeatability of CT and MRI in measurement of spinal canal area in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3882-3887. |
| [13] | Fan Jin, Zeng Luyao, Zhong Dongling, Li Yuxi, Tian Yanping, Huang Yijie, Jin Rongjiang. Development of functional near-infrared spectroscopy in recent 10 years: a visual analysis using CiteSpace [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3711-3717. |
| [14] | Zuo Zhenkui, Han Jiarui, Ji Shuling, He Lulu. Pretreatment with ginkgo biloba extract 50 alleviates radiation-induced acute intestinal injury in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3666-3671. |
| [15] | Lin Dongxin, Huang Xuecheng, Qin Qingguang, Yang Yang, Deng Yuping, Tan Jinchuan, Wang Mian, Su Weiwei, Huang Tao, Huang Wenhua. Comparison of motion range of cervical spine after two cervical manipulations based on motion capture technique [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3281-3285. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||