Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (13): 2081-2086.doi: 10.12307/2022.337
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine regulating mesenchymal stem cell-derived exocrine for ischemic stroke
Chen Na, Fan Feiyan, Li Shuangli, Zhang Yunke
- Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2020-11-09Revised:2020-11-13Accepted:2020-12-25Online:2022-05-08Published:2021-12-20 -
Contact:Zhang Yunke, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Post-doctoral cooperative supervisor, Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China -
About author:Chen Na, Doctoral candidate, Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81974564 (to ZYK)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Na, Fan Feiyan, Li Shuangli, Zhang Yunke. Effect and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine regulating mesenchymal stem cell-derived exocrine for ischemic stroke[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(13): 2081-2086.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
间充质干细胞源性外泌体因其独特的生物特点,可应用于肿瘤、宫腔粘连、肺损伤、骨关节炎及缺血性脑卒中等临床各种疾病。XING等[26]研究结果显示间充质干细胞源性外泌体通过作用于GARP抑制细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭,发挥靶向GARP在小鼠结肠癌细胞MC38中的治疗作用。TAN等[27]研究表明骨髓间充质干细胞源性外泌体在体外能促进细胞增殖和迁移,并能修复宫腔粘连模型小鼠的子宫内膜,骨髓间充质干细胞源性外泌体可能通过过表达miR-29a在子宫内膜修复过程中起到抵抗纤维化的作用。MIZUTA等[28]应用间充质干细胞源性外泌体治疗急性肺损伤小鼠模型,结果显示间充质干细胞源性外泌体中miR-126表达增加,明显提高了小鼠的存活率,抑制了肺出血和水肿,并减小血管通透性,进一步发现间充质干细胞源性外泌体可能通过激活PI3K/Akt通路对内皮细胞发挥保护作用。在缺血性卒中实验研究中发现间充质干细胞源性外泌体具有改善血流恢复、减少梗死体积及药物传递的作用[24-25],有很好的临床应用价值。 2.2.1 间充质干细胞源性外泌体与血脑屏障 缺血性脑卒中后发生的病理改变主要在神经血管单元。神经血管单元主要有周细胞、脑血管内皮细胞、脑实质细胞及血脑屏障相关紧密连接蛋白构成[29]。缺血性脑卒中后血脑屏障被破坏,周细胞和大脑内皮细胞相互作用,促进血管新生,修复血脑屏障[10]。研究表明,过表达miR-21-3p通过调节MAT2B功能,促进细胞凋亡和炎症,加重血脑屏障损伤[30]。LI等[31]研究显示间充质干细胞能够增加大脑中动脉闭塞大鼠模型中的紧密连接蛋白ZO-1和Claudin-5的分布,改善血脑屏障状态,减轻脑水肿,进一步表明间充质干细胞通过抑制miR-21-3p水平和上调MAT2B水平,抑制细胞凋亡、炎症反应起到缺血性脑损伤的保护作用。大脑中动脉闭塞模型侧脑室注射miR-132,结果显示外源性miR-132可以降低血脑屏障紧密连接的降解,减少梗死体积,减轻脑水肿,改善神经功能[32]。通过调节血脑屏障通透性对于卒中后康复具有重要的意义。 2.2.2 间充质干细胞源性外泌体与血管新生 脑缺血后血管阻塞会破坏血管本身的结构,改变血管通透性,能够正常供血供氧的血管减少。间充质干细胞源性外泌体通过调节神经血管单元细胞间的信息交流,促进血管生成,改善大脑微环境,从而恢复脑组织氧和能量供应,改善血管功能,促进卒中后患者的康复[33-34]。XIN等[11]构建大脑中动脉闭塞大鼠模型24 h后尾静脉注射间充质干细胞源性外泌体,结果显示血管内皮细胞数量显著增加,表明间充质干细胞源性外泌体可以改善卒中后血管新生。间充质干细胞源性外泌体实验组大鼠Ki67+DCN+细胞增加,外泌体分泌miR-210、miR-184、miR-137表达上调,可能与血管新生、神经发生有关[35]。由于外泌体的功能一部分与来源干细胞有关,神经元及血管内皮细胞来源外泌体对卒中后血管修复有着重要的作用[36]。 2.2.3 间充质干细胞源性外泌体与神经分化 神经系统中的神经干细胞具有分化为神经元、星形胶质细胞和少突胶质细胞的潜能,从而产生具有自我更新能力的脑组织细胞。实验研究表明,脑卒中后静脉注射间充质干细胞源性外泌体可以改善卒中后神经新生与血管重建[36]。大脑中动脉闭塞模型大鼠尾静脉注射骨髓间充质干细胞源性外泌体,可促进脑卒中后的功能恢复,增强神经突起重塑、神经发生和血管生成,是治疗脑卒中的一种新方法[11]。静脉输注富含外泌体的骨髓间充质干细胞可显著改善大脑中动脉闭塞模型大鼠缺血皮质的轴突重塑[37],间充质干细胞源性外泌体已经被证实可促进神经分化,进而改善神经功能。 2.2.4 间充质干细胞源性外泌体与神经修复 由于卒中后缺血缺氧会损伤神经功能,加速神经细胞的凋亡。缺血性卒中模型大鼠静脉给予含miR-17-92的外泌体,可以增加脑卒中后神经可塑性和功能恢复,其机制可能是通过靶向PTEN激活下游PI3K/Akt/mTOR/GSK-3β信号通路[38]。给予大鼠注射沉默miR-133b的间充质干细胞源性外泌体可以增加缺血性脑组织中CTGF和RhoA水平,导致神经功能衰减,而miR-133b水平升高具有相反的作用,因此间充质干细胞源性外泌体可以抑制靶点RhoA,促进神经突触的增加[39-40]。大脑中动脉闭塞模型大鼠静脉注射脂肪间充质干细胞源性外泌体,可以降低大鼠脑梗死面积,促进神经功能修复[41-42]。 2.2.5 间充质干细胞源性外泌体与免疫炎症及氧化应激 脑卒中后发生的免疫炎症和氧化应激反应可以促进脑卒中的进展,多种炎症因子、淋巴细胞、氧化分子作用可导致梗死面积扩大,加重病情,因此调节免疫反应、抗炎、抗氧化对于缺血性卒中具有重要临床意义[43-44]。CECI等[45]通过研究比较斑马鱼和哺乳动物神经元再生情况以及哺乳动物神经元再生失败的机制,认为炎症作用是神经元再生的主要抑制剂。间充质干细胞源性外泌体在器官炎症损伤中起着重要的作用,有研究表明间充质干细胞源性外泌体通过逆转CysLT2R-ERK1/2介导的小胶质细胞M1极化减弱了脑损伤并抑制了小胶质细胞炎症反应[41]。脑卒中后神经元和小胶质细胞相互作用调节免疫炎症反应,骨髓间充质干细胞源性外泌体miR-138-5p通过靶向作用抑铁素2,促进缺血性卒中后星形胶质细胞增殖,抑制炎症反应,从而减轻神经功能损伤,可能为缺血性卒中治疗提供新的靶点。研究表明,局灶缺血性脑卒中大鼠谷氨酰胺酶1表达水平上调,通过谷氨酰胺酶抑制剂CB839抑制谷氨酰胺酶1活性降低梗死体积,减轻炎症反应[21]。外泌体治疗可以降低炎症因子肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6的表达,升高抗炎因子白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10的表达,减轻脑损伤[46]。间充质干细胞源性外泌体可以增强CD4和CD8淋巴细胞的激活以及树突状细胞的减少,调节脑卒中引起的外周免疫抑制[47],外泌体可以通过血脑屏障,将抗原传递到免疫系统[48]。 综上所述,间充质干细胞源性外泌体可以调节脑卒中后血脑屏障通透性、促进血管新生、改善神经功能、促进神经修复,有望成为缺血性脑卒中一种新的治疗方法。 2.3 间充质干细胞源性外泌体作为中药载体治疗缺血性脑卒中的作用 "
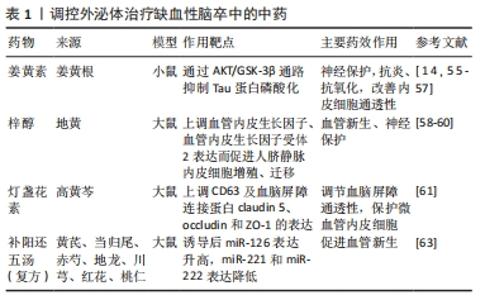
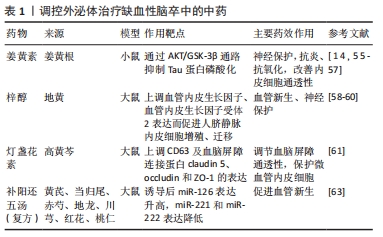
现代研究表明,外泌体作为一种可靠载体靶向传递信息物质,传统中药可通过多靶点对机体进行调控,外泌体作为内源性药物传递纳米系统具有很大的治疗潜力,因此研究将中药有效成分通过外泌体精准运输至靶细胞,发挥药效,成为近年来研究的热点[49]。外泌体可作为药物载体的机制特点如下:①外泌体表面存在特殊的蛋白及磷脂双分子层结构,不仅对外泌体所负载药物有保护作用,而且可以避免被体内系统捕获,长时间发挥作用;②外泌体的天然结构特点,使其更容易与受体细胞融合,其所负载药物更容易被细胞接受[50];③外泌体由于其体积微小(< 100 nm),可有效避免单核巨噬细胞的吞噬,能够较自由地穿过血管壁及细胞外基质发挥作用[51];④外泌体具有独特的特性,包括低免疫原性、固有稳定性、高传递效率和能穿过血脑屏障,作为治疗脑缺血的内源性药物递送纳米系统前景广阔。外泌体负载药物可以用多种方式,目前可通过以下方式进行:①直接转染法,将药物与分离出的外泌体混合培养,通过顺浓度梯度直接进入外泌体内;②间接转染法,将药物与分泌外泌体的细胞一起培养,然后分离出含有药物的外泌体;③穿孔,通过电穿孔法使药物通过小孔进入外泌体内[52]。外泌体目前所负载的药物主要包括基因类、抗癌症药物、抗炎症药物、调节免疫的抗原、蛋白类和中药类药物[50]。将中药有效成分通过外泌体运输到体内可更好地发挥中药作用,进行靶向治疗疾病。目前用于治疗肿瘤性疾病较为广泛,近年来也相继应用于骨性疾病、肝脏疾病及脑血管疾病等。缺血性卒中目前需要探索更有效的治疗方法,研究显示间充质干细胞源性外泌体可以通过负载中药姜黄素、梓醇、灯盏花素等药物起到神经保护、血管新生的作用。 2.3.1 间充质干细胞源性外泌体作为中药载体与神经保护作用 间充质干细胞源性外泌体作为姜黄素的载体,治疗缺血性脑卒中可以起到神经保护作用。姜黄素是一种发现于姜黄根块茎的黄色化合物。姜黄具有行气活血、通经止痛的作用,用于治疗气滞血瘀、经络不畅证。姜黄素在结构上是一种二酮类化合物,在水中以酮形式存在,在有机溶剂中以酚形式存在[14]。姜黄素含有有效成分多酚,具有抗血脂、抗炎、抗氧化、抗癌及神经保护作用[53]。姜黄素作用广泛,但是在临床运用中存在一定缺陷,虽然其神经保护作用使该化合物进入了Ⅰ期临床试验,但其溶解度不高、稳定性差、吸收率低、代谢快、半衰期短等缺点,导致其利用度低,限制了在治疗疾病中的应用[54]。研究发现,通过不同大小载体运输会影响其溶解度和治疗效果,用姜黄素调控外泌体可以提高其溶解度、利用率和稳定性[21]。一些外泌体能够避开免疫系统,在血液中表现出低免疫反应和高稳定性,延长药物在体内的循环从而更好发挥药效[55]。KALANI等[14,56]证明负载姜黄素的外泌体不仅具有抗血脂、抗氧化和抗炎的作用,还可以改善内皮细胞通透性,减少氧化应激,减轻连接蛋白的结构损伤,从而起到保护神经的作用。研究显示负载姜黄素的外泌体通过AKT/GSK-3β通路抑制Tau蛋白磷酸化,保护神经[57]。综上所述,姜黄素是一种具有临床研究价值的神经保护性药物。 2.3.2 间充质干细胞源性外泌体作为中药载体与血管新生 间充质干细胞源性外泌体作为梓醇中药的载体,治疗缺血性脑卒中可以有助于血管新生。梓醇是地黄的主要有效成分,地黄为玄参科地黄属植物,具有养阴补血、填精益髓的功效,用于治疗血虚证、肝肾阴虚证。梓醇通过上调血管内皮生长因子、血管内皮生长因子受体2表达而促进细胞增殖、迁移,进而发挥促进血管新生的作用。梓醇在神经方面的治疗机制包括促进缺血后神经功能恢复、保护神经血管单元、促进局灶脑缺血大鼠神经元新生、轴突形成新的突触连接、上调神经营养因子表达,但其本身入脑效果较差,与冰片配伍后可促进梓醇透过血脑屏障[58-59]。此外,研究还发现通过构建转铁蛋白、脑啡肽和间充质干细胞源性外泌体组成特异性小泡,特异性靶向跨越血脑屏障后的神经元,在体内外发挥抑制神经细胞凋亡和促进神经细胞再生的作用[60]。 2.3.3 间充质干细胞源性外泌体作为中药载体与血脑屏障 间充质干细胞源性外泌体作为灯盏花素的载体,治疗缺血性脑卒中可以有助于调节血脑屏障通透性。灯盏花素是来源于植物高黄芩的叶,高黄芩为有唇科植物。黄芩具有清热燥湿、止血的作用,可泄实火、除湿热、止血。灯盏花素具有扩张血管、改善微循环、抗血小板聚集的作用,广泛用于缺血性脑血管疾病。灯盏花素干预的外泌体可以保护同型半胱氨酸诱导的大鼠微血管内皮细胞损伤,主要通过上调CD63及血脑屏障紧密连接蛋白claudin 5、occludin和ZO-1的表达发挥作用[61]。刘梦琳等[62]临床验证得出灯盏花素注射液联合常规治疗可以改善神经功能,改善血流变指标。由此说明灯盏花素通过外泌体作用治疗缺血性卒中具有一定前景。 课题组前期研究表明间充质干细胞源性外泌体经补阳还五汤诱导后miRNA-126表达升高,miR-221和miR-222表达降低,与卒中后脑血管新生有关[63]。复方补阳还五汤是治疗缺血性卒中的经典方剂,主要有黄芪、当归尾、赤芍、地龙、川芎、红花、桃仁组成。该方重用黄芪,补益元气,使气旺血行,为君药;当归尾活血通络不伤血,为臣药;地龙活血通络,周行全身,为佐药;赤芍、川芎、桃仁、红花协同当归尾以活血祛瘀。该方补气药与活血药配伍,补气不壅滞,活血不伤正,用于治疗中风病之气虚血瘀证。通过中药调控外泌体既可以更好地发挥中药的作用,又体现精准医疗的理念,提高临床治疗效果。 汇总调控外泌体治疗缺血性脑卒中的中药,见表1。 "
| [1] RAHMANI A, SALEKI K, JAVANMEHR N, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicle-based therapies protect against coupled degeneration of the central nervous and vascular systems in stroke. Ageing Res Rev. 2020;62:101106. [2] HOCUM STONE LL, XIAO F, ROTSCHAFER J, et al. Amelioration of Ischemic Brain Injury in Rats With Human Umbilical Cord Blood Stem Cells: Mechanisms of Action. Cell Transplant. 2016;25(8):1473-1488. [3] CHEN X, ARUMUGAM TV, CHENG YL, et al. Combination Therapy with Low-Dose IVIG and a C1-esterase Inhibitor Ameliorates Brain Damage and Functional Deficits in Experimental Ischemic Stroke. Neuromolecular Med. 2018;20(1):63-72. [4] BARTHELS D, DAS H. Current advances in ischemic stroke research and therapies. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020;1866(4):165260. [5] ZIVIN JA. Acute stroke therapy with tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) since it was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Ann Neurol. 2009;66(1):6-10. [6] THÉRY C, WITWER KW, AIKAWA E, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018;7(1):1535750. [7] LI Y, CHENG Q, HU G, et al. Extracellular vesicles in mesenchymal stromal cells: A novel therapeutic strategy for stroke. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(5):4067-4079. [8] DOEPPNER TR, HERMANN DM. Editorial: Stem cells and progenitor cells in ischemic stroke-fashion or future? Front Cell Neurosci. 2015;9:334. [9] XIONG Y, MAHMOOD A, CHOPP M. Emerging potential of exosomes for treatment of traumatic brain injury. Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(1):19-22. [10] LIU W, BAI X, ZHANG A, et al. Role of Exosomes in Central Nervous System Diseases. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019;12:240. [11] XIN H, LI Y, CUI Y, et al. Systemic administration of exosomes released from mesenchymal stromal cells promote functional recovery and neurovascular plasticity after stroke in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2013;33(11):1711-1715. [12] WEI M, WANG D, KANG D, et al. Overview of Cochrane reviews on Chinese herbal medicine for stroke. Integr Med Res. 2020;9(1):5-9. [13] LIU R, YU X, ZHANG L, et al. Computed tomography (CT) imaging evaluation of integrated traditional Chinese medicine cooperative therapy in treating acute cerebral infarction: A randomized controlled trial. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(18):e19998. [14] KALANI A, CHATURVEDI P. Curcumin-primed and curcumin-loaded exosomes: potential neural therapy. Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(2): 205-206. [15] OTERO-ORTEGA L, GUTIÉRREZ-FERNÁNDEZ M, RAMOS-CEJUDO J, et al. White matter injury restoration after stem cell administration in subcortical ischemic stroke. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6(1):121. [16] ZHANG HT, LIU ZL, YAO XQ, et al. Neural differentiation ability of mesenchymal stromal cells from bone marrow and adipose tissue: a comparative study. Cytotherapy. 2012;14(10):1203-1214. [17] LALU MM, MONTROY J, DOWLATSHAHI D, et al. From the Lab to Patients: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Stroke. Transl Stroke Res. 2020;11(3):345-364. [18] 钱楠楠,张潜,杨睿,等.间充质干细胞治疗脊髓损伤:细胞治疗及联合新药和生物材料[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(13):2114-2120. [19] KAWABORI M, SHICHINOHE H, KURODA S, et al. Clinical Trials of Stem Cell Therapy for Cerebral Ischemic Stroke. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(19): 7380. [20] BIANCONE L, BRUNO S, DEREGIBUS MC, et al. Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012;27(8):3037-3042. [21] DENG Y, CHEN D, GAO F, et al. Exosomes derived from microRNA-138-5p-overexpressing bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells confer neuroprotection to astrocytes following ischemic stroke via inhibition of LCN2. J Biol Eng. 2019;13:71. [22] PASHOUTAN SARVAR D, SHAMSASENJAN K, AKBARZADEHLALEH P. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: New Opportunity in Cell-Free Therapy. Adv Pharm Bull. 2016;6(3):293-299. [23] GUDURIC-FUCHS J, O’CONNOR A, CAMP B, et al. Selective extracellular vesicle-mediated export of an overlapping set of microRNAs from multiple cell types. BMC Genomics. 2012;13:357. [24] RAPOSO G, STOORVOGEL W. Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol. 2013;200(4):373-383. [25] DEHGHANI L, HASHEMI SM, SAADATNIA M, et al. Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes as Treatment for Stroke: a Systematic Review. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021;17(2):428-438. [26] XING H, LIANG C, XU X, et al. Mesenchymal stroma/stem-like cells of GARP knockdown inhibits cell proliferation and invasion of mouse colon cancer cells (MC38) through exosomes. J Cell Mol Med. 2020; 24(23):13984-13990. [27] TAN Q, XIA D, YING X. miR-29a in Exosomes from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Inhibit Fibrosis during Endometrial Repair of Intrauterine Adhesion. Int J Stem Cells. 2020;13(3):414-423. [28] MIZUTA Y, AKAHOSHI T, GUO J, et al. Exosomes from adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate histone-induced acute lung injury by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway in endothelial cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):508. [29] NETTO JP, ILIFF J, STANIMIROVIC D, et al. Neurovascular Unit: Basic and Clinical Imaging with Emphasis on Advantages of Ferumoxytol. Neurosurgery. 2018;82(6):770-780. [30] GE X, LI W, HUANG S, et al. Increased miR-21-3p in Injured Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells after Traumatic Brain Injury Aggravates Blood-Brain Barrier Damage by Promoting Cellular Apoptosis and Inflammation through Targeting MAT2B. J Neurotrauma. 2019;36(8): 1291-1305. [31] LI C, FEI K, TIAN F, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuate ischemic brain injuries in rats by modulating miR-21-3p/MAT2B signaling transduction. Croat Med J. 2019;60(5):439-448. [32] ZUO X, LU J, MANAENKO A, et al. MicroRNA-132 attenuates cerebral injury by protecting blood-brain-barrier in MCAO mice. Exp Neurol. 2019;316:12-19. [33] BIAN X, MA K, ZHANG C, et al. Therapeutic angiogenesis using stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: an emerging approach for treatment of ischemic diseases. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):158. [34] ZAGREAN AM, HERMANN DM, OPRIS I, et al. Multicellular Crosstalk Between Exosomes and the Neurovascular Unit After Cerebral Ischemia. Therapeutic Implications. Front Neurosci. 2018;12:811. [35] MOON GJ, SUNG JH, KIM DH, et al. Application of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Stroke: Biodistribution and MicroRNA Study. Transl Stroke Res. 2019;10(5):509-521. [36] 胡琳,何圣佳,陈翠花,等.外泌体及其microRNA与缺血性脑卒中关系的研究进展[J].山东医药,2019,59(13):83-86. [37] XIN H, LI Y, LIU Z, et al. MiR-133b promotes neural plasticity and functional recovery after treatment of stroke with multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells in rats via transfer of exosome-enriched extracellular particles. Stem Cells. 2013;31(12):2737-2746. [38] XIN H, KATAKOWSKI M, WANG F, et al. MicroRNA cluster miR-17-92 Cluster in Exosomes Enhance Neuroplasticity and Functional Recovery After Stroke in Rats. Stroke. 2017;48(3):747-753. [39] CHOPP M, ZHANG ZG. Emerging potential of exosomes and noncoding microRNAs for the treatment of neurological injury/diseases. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2015;20(4):523-526. [40] ZHANG Y, UENO Y, LIU XS, et al. The MicroRNA-17-92 cluster enhances axonal outgrowth in embryonic cortical neurons. J Neurosci. 2013; 33(16):6885-6894. [41] CHEN KH, CHEN CH, WALLACE CG, et al. Intravenous administration of xenogenic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADMSC) and ADMSC-derived exosomes markedly reduced brain infarct volume and preserved neurological function in rat after acute ischemic stroke. Oncotarget. 2016;7(46):74537-74556. [42] WANG Z, YUAN Y, ZHANG Z, et al. Inhibition of miRNA-27b enhances neurogenesis via AMPK activation in a mouse ischemic stroke model. FEBS Open Bio. 2019;9(5):859-869. [43] 安阳方,曹建华,汤永红.间充质干细胞来源外泌体在缺血性脑卒中的研究进展[J].中南医学科学杂志,2019,47(4):442-445. [44] KRISHNAN S, LAWRENCE CB. Old Dog New Tricks; Revisiting How Stroke Modulates the Systemic Immune Landscape. Front Neurol. 2019;10: 718. [45] CECI M, MARIANO V, ROMANO N. Zebrafish as a translational regeneration model to study the activation of neural stem cells and role of their environment. Rev Neurosci. 2018;30(1):45-66. [46] JIANG M, WANG H, JIN M, et al. Exosomes from MiR-30d-5p-ADSCs Reverse Acute Ischemic Stroke-Induced, Autophagy-Mediated Brain Injury by Promoting M2 Microglial/Macrophage Polarization. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;47(2):864-878. [47] DOEPPNER TR, HERZ J, GÖRGENS A, et al. Extracellular Vesicles Improve Post-Stroke Neuroregeneration and Prevent Postischemic Immunosuppression. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4(10):1131-1143. [48] ZHANG L, YU D. Exosomes in cancer development, metastasis, and immunity. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2019;1871(2):455-468. [49] 袁鹏,郭晓辰,张军平,等.外泌体对动脉粥样硬化的调控机制及中药干预作用[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2019,39(2):251-255. [50] 李思迪,侯信,亓洪昭,等.外泌体:为高效药物投递策略提供天然的内源性纳米载体[J].化学进展,2016,28(Z2):353-362. [51] 刘儒涛,王世伟,刘晶.细胞间信息交流的新载体——外泌体[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2013,40(8):719-727. [52] 解曼曼,张海涛,林文勇,等.外泌体作为药物载体的研究进展[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2019,17(22):3525-3528. [53] SUN D, ZHUANG X, XIANG X, et al. A novel nanoparticle drug delivery system: the anti-inflammatory activity of curcumin is enhanced when encapsulated in exosomes. Mol Ther. 2010;18(9):1606-1614. [54] KALANI A, TYAGI N. Exosomes in neurological disease, neuroprotection, repair and therapeutics: problems and perspectives. Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(10):1565-1567. [55] HOOD JL. Post isolation modification of exosomes for nanomedicine applications. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2016;11(13):1745-1756. [56] KALANI A, KAMAT PK, CHATURVEDI P, et al. Curcumin-primed exosomes mitigate endothelial cell dysfunction during hyperhomocysteinemia. Life Sci. 2014;107(1-2):1-7. [57] WANG H, SUI H, ZHENG Y, et al. Curcumin-primed exosomes potently ameliorate cognitive function in AD mice by inhibiting hyperphosphorylation of the Tau protein through the AKT/GSK-3β pathway. Nanoscale. 2019;11(15):7481-7496. [58] 周霞,张文倩,刘炬,等.从血管内皮生长因子及其受体调控角度探讨地黄梓醇促血管新生作用及分子机制研究[J].实用心脑肺血管病杂志,2020,28(2):64-68. [59] 罗辉,吴志方,沈玮,等.梓醇对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞体外增殖和成软骨分化能力的影响[J].中华中医药学刊,2020,38(2):149-153. [60] LIU Y, FU N, SU J, et al. Rapid Enkephalin Delivery Using Exosomes to Promote Neurons Recovery in Ischemic Stroke by Inhibiting Neuronal p53/Caspase-3. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:4273290. [61] ZHONG X, LUO C, DENG M, et al. Scutellarin-treated exosomes increase claudin 5, occludin and ZO1 expression in rat brain microvascular endothelial cells. Exp Ther Med. 2019;18(1):33-40. [62] 刘梦琳,樊根豪,安瑞丽,等.灯盏花素注射液辅助治疗急性脑梗死的Meta分析[J].中成药,2020,42(4):921-926. [63] YANG J, GAO F, ZHANG Y, et al. Buyang Huanwu Decoction (BYHWD) Enhances Angiogenic Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cell by Upregulating VEGF Expression After Focal Cerebral Ischemia. J Mol Neurosci. 2015; 56(4):898-906. [64] KIM MS, HANEY MJ, ZHAO Y, et al. Development of exosome-encapsulated paclitaxel to overcome MDR in cancer cells. Nanomedicine. 2016;12(3):655-664. [65] YU P, CHEN W. Advances in the diagnosis of exosomal miRNAs in ischemic stroke. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2019;15:2339-2343. [66] MA ZJ, YANG JJ, LU YB, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: Toward cell-free therapeutic strategies in regenerative medicine. World J Stem Cells. 2020;12(8):814-840. |
| [1] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhou Qian, Zhang Qiang, Chen Qiu. Human salivary components and osteoporosis/osteopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444. |
| [2] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [3] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [4] | Jing Jinpeng, Zhang Yue, Liu Xiaomin, Liu Yi. Traditional Chinese medicine injection for promoting blood circulation in prevention of deep vein thrombosis after orthopedic surgery: network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1467-1476. |
| [5] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [6] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [7] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhang Qiang, Liu Jing, Shao Ming. Acupuncture for Parkinson’s disease: an insight into the action mechanism in animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1272-1277. |
| [8] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [9] | Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun. Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [10] | Zhou Hongqin, Wu Dandan, Yang Kun, Liu Qi. Exosomes that deliver specific miRNAs can regulate osteogenesis and promote angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1107-1112. |
| [11] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [12] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [13] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [14] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [15] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||