Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (1): 84-89.doi: 10.12307/2022.014
Previous Articles Next Articles
Expression and significance of DNA topoisomerase II in neural stem cells of ICR mice
Sun Mengjun1, Guo Jianmei2, Zhou Gengsu3, Dong Zefei4, Zheng Chungui3, Cao Cuili5
- 1Public Teaching Department, 2Department of Basic Medicine, 3Department of Nursing, 4Department of Stomatology, Xingtai Medical College, Xingtai 054000, Hebei Province, China; 5Department of Neurobiology, Basic Medical College, Heibei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050017, Hebei Province, China
-
Received:2020-07-07Revised:2020-07-13Accepted:2020-10-16Online:2022-01-08Published:2021-10-25 -
Contact:Cao Cuili, MD, Professor, Department of Neurobiology, Basic Medical College, Heibei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050017, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Sun Mengjun, Master, Lecturer, Public Teaching Department, Xingtai Medical College, Xingtai 054000, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:the Key Science and Technology Research Plan of Hebei Health Commission, No. 20200168 (to SMJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Sun Mengjun, Guo Jianmei, Zhou Gengsu, Dong Zefei, Zheng Chungui, Cao Cuili. Expression and significance of DNA topoisomerase II in neural stem cells of ICR mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(1): 84-89.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
2.1 ICR小鼠神经干细胞体外培养与鉴定结果[12] 接种后细胞从单细胞形式向细胞团转化,并且体积增大,形成神经球。神经球内大部分细胞呈nestin阳性,阳性反应产物主要聚集在细胞浆内。经诱导分化后,先爬出的细胞为GFAP阳性细胞,胞体较小,突起较多,染色深浅不一,向多个方向伸展;后爬出的细胞为NSE阳性细胞,随着诱导时间增加,突起逐渐延伸增长,体积较大,突起明显的细胞NSE染色较深,体积较小,突起少的细胞NSE染色较浅。 2.2 ICR小鼠神经干细胞诱导分化结果[12] 将神经球消化成单细胞后,接种在Matrigel基质胶铺底的培养皿中,用条件培养液诱导分化。诱导后1 d,可以观察到两种形态的细胞:突起较细小,胞体呈三角形或圆锥形的具备神经元形态的细胞和另一种突起较粗大且较长的具备星形胶质细胞特征的细胞;诱导后2 d,具备神经元形态特征的细胞突起继续生长,相互交织;另一种具备胶质细胞特征的细胞突起变化不明显,细胞数量下降;诱导后3 d,具备神经元形态特征的细胞突起继续生长,具有胶质细胞特征的细胞死亡较多。 免疫荧光染色结果显示:nestin阳性细胞在神经球中数量较多且分布均匀;随着诱导分化时间的延长,nestin阳性细胞逐渐减少。MAP-2阳性细胞仅在神经球中央少量存在;随着诱导分化时间的延长,MAP-2阳性细胞逐渐增多。GFAP阳性细胞在神经球中较多;随着诱导分化时间的延长,GFAP阳性细胞逐渐减少,见表2。"
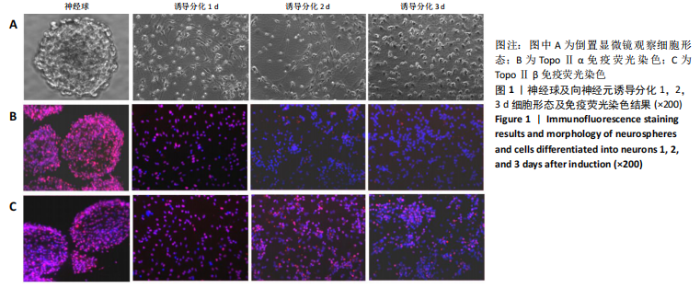
2.3 神经干细胞分化过程中TopoⅡ的表达 2.3.1 免疫细胞化学染色 TopoⅡα阳性细胞在神经球内数量较多,且均匀分布,阳性细胞率为(83.0±6.5)%;TopoⅡα阳性细胞在向神经元诱导分化1 d后数量有所减少,阳性细胞率为(76.0±4.9)%;诱导分化2 d后明显减少,阳性细胞率为(24.0±1.7)%;诱导分化3 d后继续减少,阳性细胞率为(16.0±2.2)%,见图1。统计学结果表明,TopoⅡα阳性细胞率在各组之间差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),进一步两两组间比较,神经球组和向神经元诱导分化1 d组之间,向神经元诱导分化2 d组与3 d组之间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),其他各组之间差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表2。"

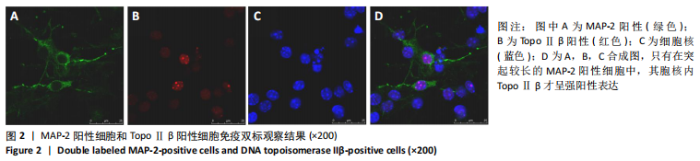
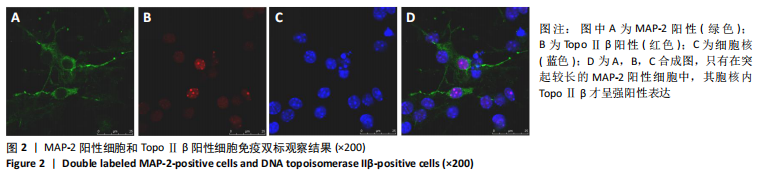
TopoⅡβ阳性细胞在神经球内数量较少,阳性细胞率为(55.0±2.4)%,主要分布在神经球中央;TopoⅡβ阳性细胞在向神经元诱导分化1 d后开始逐渐增多,阳性细胞率为(68.0±3.7)%,同时强表达的细胞也开始增多;TopoⅡβ阳性细胞在诱导分化2 d后显著增多,阳性细胞率为(77.0±3.3)%,且以强表达细胞为主;诱导分化3 d后仍然很多,与2 d组比较呈减少趋势,阳性细胞率为(64.0±2.2)%,见图1。统计学结果表明,TopoⅡβ阳性细胞率在各组之间差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),进一步两两组间比较,向神经元诱导分化1 d 组与3 d组之间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),其他各组之间差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见表2。 共聚焦显微镜免疫荧光双标显示:只有在突起较长的MAP-2阳性细胞中,其胞核内TopoⅡβ呈强阳性表达,说明二者在同一细胞中出现共表达,见图2。"
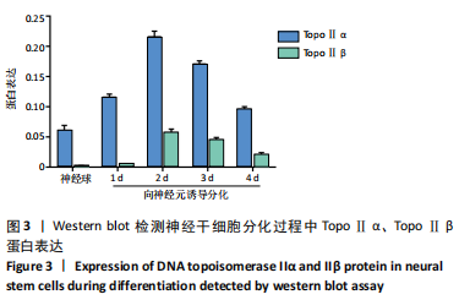
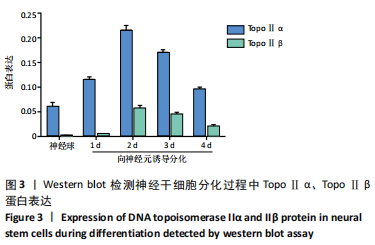
2.3.2 Western blot检测结果 TopoⅡα分子质量为170 kD, TopoⅡβ分子质量为180 kD。在神经球中TopoⅡα蛋白表达较高,在向神经元诱导分化1,2 d细胞中TopoⅡα蛋白表达仍然较高,达到高峰,在诱导分化3,4 d细胞中TopoⅡα蛋白表达逐渐降低。由此推测,TopoⅡα可能参与细胞的分裂增殖,而在分化细胞中出现下调。在神经球中TopoⅡβ蛋白表达很低,在向神经元诱导分化1 d细胞中TopoⅡβ蛋白表达稍高,在诱导分化2 d细胞中TopoⅡβ蛋白表达显著增高达到高峰,在诱导分化3,4 d缓慢下降。由此推测,TopoⅡβ在增殖细胞中的表达较低,但在向神经元分化过程中表达升高,见图3。"
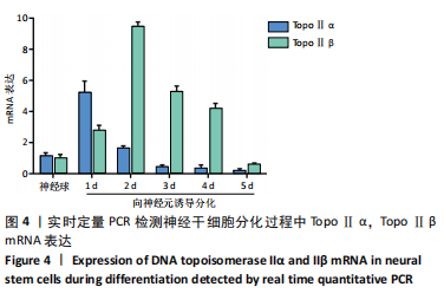
2.3.3 实时定量PCR检测结果 在神经球中TopoⅡα mRNA的表达较高,在向神经元诱导分化1 d细胞中TopoⅡα mRNA表达开始升高,2 d时表达明显下降,3-5 d仍逐渐降低,维持在较低水平。在神经球中TopoⅡβ mRNA表达较低,在向神经元诱导分化1 d细胞中TopoⅡβ mRNA表达缓慢增高,2 d时达到高峰,3-5 d又缓慢降低,见图4。 2.4 生物相容性 神经干细胞增殖性实验显示[12]:细胞在传代后4 d内以增殖为主。以5×108 L-1进行传代,CCK-8法测得吸光度值为0.117,细胞倍增时间为2 d;4 d时吸光度值达0.331,此时细胞密度最高,是传代细胞数的2.83倍;5 d后细胞增殖减慢,吸光度值逐渐下降。因此传代时间选择在神经球培养三四天进行。"

| [1] THAN-TRONG E, ORTICA-GATTI S, MELLA S, et al. Neural stem cell quiescence and stemness are molecularly distinct outputs of the Notch3 signalling cascade in the vertebrate adult brain. Development. 2018;145(10):dev161034. [2] MOORE L, SKOP NB, ROTHBARD DE, et al. Tethered growth factors on biocompatible scaffolds improve stemness of cultured rat and human neural stem cells and growth of oligodendrocyte progenitors. Methods. 2018;133:54-64. [3] FISCHER U, BACKES C, RASLAN A, et al. Gene amplification during differentiation of mammalian neural stem cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget. 2015;6(9):7023-7039. [4] COSACAK MI, BHATTARAI P, KIZIL C. Alzheimer’s disease, neural stem cells and neurogenesis: cellular phase at single-cell level. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(5):824-827. [5] DRAKE FH, ZIMMERMAN JP, MCCABE FL, et al. Purification of topoisomerase II from amsacrine-resistant P388 leukemia cells. Evidence for two forms of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1987;262(34): 16739-16747. [6] TSAI-PFLUGFELDER M, LIU LF, LIU AA, et al. Cloning and sequencing of cDNA encoding human DNA topoisomerase II and localization of the gene to chromosome region 17q21-22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988;85(19):7177-7181. [7] JENKINS JR, AYTON P, JONES T, et al. Isolation of cDNA clones encoding the beta isozyme of human DNA topoisomerase II and localisation of the gene to chromosome 3p24. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992;20(21): 5587-5592. [8] SOCZEK KM, GRANT T, ROSENTHAL PB, et al. CryoEM structures of open dimers of gyrase A in complex with DNA illuminate mechanism of strand passage. Elife. 2018;7:e41215. [9] YANG X, LI W, PRESCOTT ED, et al. DNA topoisomerase IIbeta and neural development. Science. 2000;287(5450):131-134. [10] TSUTSUI K, TSUTSUI K, SANO K, et al. Involvement of DNA topoisomerase IIbeta in neuronal differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276(8):5769-5778. [11] LYU YL, WANG JC. Aberrant lamination in the cerebral cortex of mouse embryos lacking DNA topoisomerase IIbeta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(12):7123-7128. [12] 孙孟军,郭建美,周更苏,等. ICR小鼠神经干细胞的体外培养与鉴定[J].河北医科大学学报, 2019, 40(3):258-263. [13] 孙孟军,郭建美,周更苏,等. ICR小鼠神经干细胞的诱导分化及鉴定[J].医学动物防制, 2021, 37(5):467-470. [14] BAKSHI RP, GALANDE S, MUNIYAPPA K. Functional and regulatory characteristics of eukaryotic type II DNA topoisomerase. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2001;36(1):1-37. [15] LEE JH, BERGER JM. Cell Cycle-Dependent Control and Roles of DNA Topoisomerase II. Genes (Basel). 2019;10(11):859. [16] TORRES-GUZMÁN R, CALSINA B, HERMOSO A, et al. Preclinical characterization of abemaciclib in hormone receptor positive breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(41):69493-69507. [17] MOROTOMI-YANO K, SAITO S, ADACHI N, et al. Dynamic behavior of DNA topoisomerase IIβ in response to DNA double-strand breaks. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):10344. [18] MILLS WE, SPENCE JM, FUKAGAWA T, et al. Site-Specific Cleavage by Topoisomerase 2: A Mark of the Core Centromere. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(2):534. [19] JOSHI RS, NIKOLAOU C, ROCA J. Structure and Chromosomal Organization of Yeast Genes Regulated by Topoisomerase II. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(1):134. [20] GOTHE HJ, BOUWMAN BAM, GUSMAO EG, et al. Spatial Chromosome Folding and Active Transcription Drive DNA Fragility and Formation of Oncogenic MLL Translocations. Mol Cell. 2019;75(2):267-283.e12. [21] MADABHUSHI R. The Roles of DNA Topoisomerase IIbeta in Transcription. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(7):1917. [22] BALDYS-WALIGORSKA A, WIERZBICKA I, SOKOLOWSKI G, et al. Markers of proliferation and invasiveness in somatotropinomas. Endokrynol Pol. 2018;69(2):182-189. [23] TERZIOGLU-USAK S, NEGIS Y, KARABULUT DS, et al. Cellular Model of Alzheimer’s Disease: Aβ1-42 Peptide Induces Amyloid Deposition and a Decrease in Topo Isomerase IIβ and Nurr1 Expression. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2017;14(6):636-644. [24] TSUTSUI K, TSUTSUI KM, MIYAJI M, et al. Regulation of neuronal gene expression by DNA topoisomerase IIbeta. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2009;54(11):1333-1343. [25] TSUTSUI K, TSUTSUI K, SAKURAI H, et al. Levels of topoisomerase II and DNA polymerase alpha are regulated independently in developing neuronal nuclei. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986;138(3):1116-1122. [26] TSUTSUI K, TSUTSUI K, HOSOYA O, et al. Immunohistochemical analyses of DNA topoisomerase II isoforms in developing rat cerebellum. J Comp Neurol. 2001;431(2):228-239. [27] WATANABE M, TSUTSUI K, TSUTSUI K, et al. Differential expressions of the topoisomerase II alpha and II beta mRNAs in developing rat brain. Neurosci Res. 1994;19(1):51-57. [28] TSUTSUI KM, SANO K, HOSOYA O, et al. Expression dynamics and functional implications of DNA topoisomerase II beta in the brain. Anat Sci Int. 2006;81(3):156-163. [29] KONDAPI AK, MULPURI N, MANDRAJU RK, et al. Analysis of age dependent changes of Topoisomerase II alpha and beta in rat brain. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2004;22(1):19-30. [30] BHANOTHU V, KONDAPI AK. Status of topoisomerase-2β protein in all-trans retinoic acid-treated human neuroblastoma (SK-N-SH) cells. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(4):5169-5182. [31] ZAIM M, ISIK S. DNA topoisomerase IIβ stimulates neurite outgrowth in neural differentiated human mesenchymal stem cells through regulation of Rho-GTPases (RhoA/Rock2 pathway) and Nurr1 expression. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):114. [32] NUR-E-KAMAL A, MEINERS S, AHMED I, et al. Role of DNA topoisomerase IIbeta in neurite outgrowth. Brain Res. 2007;1154: 50-60. [33] MAEDA Y, TSUTSUI K, TOKUNAGA A. Regional differences in the expression of DNA topoisomerase IIbeta in the pyramidal neurons of the rat hippocampus. Neurosci Res. 2000;36(4):291-296. |
| [1] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1191-1197. |
| [2] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| [3] | Li Jie, Ma Yuewen, Kang Nan, Zhang Jing, Zhang Yu. Radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy promotes the proliferation of neural stem cells in hippocampus of cerebral infarction rats and inhibits miR-124 expression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(31): 4981-4987. |
| [4] | Su Mingzhu, Ma Yuewen. Radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy regulates the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells in the hippocampus via Notch1/Hes1 pathway after cerebral ischemia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3009-3015. |
| [5] | Dai Yaling, Chen Lewen, He Xiaojun, Lin Huawei, Jia Weiwei, Chen Lidian, Tao Jing, Liu Weilin. Construction of miR-146b overexpression lentiviral vector and the effect on the proliferation of hippocampal neural stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3024-3030. |
| [6] | Zang Jing, Luan Zuo, Wang Qian, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wu Youjia, Guo Aisong. Two kinds of stem cell nasal transplantation for treating white matter injury in premature rat infants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 101-107. |
| [7] | Zhang Peigen, Heng Xiaolai, Xie Di, Wang Jin, Ma Jinglin, Kang Xuewen. Electrical stimulation combined with neurotrophin 3 promotes proliferation and differentiation of endogenous neural stem cells after spinal cord injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1076-1082. |
| [8] | Du Xiaowen, Lin Dapeng, Tu Guanjun. S100A4 promotes differentiation of neural stem cells through up-regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(19): 3029-3034. |
| [9] | Zhao Fei, Ding Dong, Gong Fan, Huang Yonglu, Yao Zhanchuan, Li Xiaoliang, Luo Xiaojun, Yue Jianming. Lycium barbarum polysaccharide intervenes with CD151 and matrix metalloproteinase 3 in the articular cartilage in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(17): 2648-2653. |
| [10] | Sun Nai, Wang Dali, Zhang Jun, Cao Jinming, Qiu Fucheng, Liu Huimiao, Li Dong, Gu Ping. Effects of cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant 3 on the survival and proliferation of neural stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(1): 118-123. |
| [11] | Hu Yuting, Liu Fei, Liu Jing, Tao Xinrong. Identification of proliferation and differentiation capability of hippocampal neural stem/progenitor cells by adherent culture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(9): 1330-1335. |
| [12] | Sun Wanying, Tang Ying, Chen Meijuan. Effect and mechanism of fasudil on proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(9): 1336-1341. |
| [13] | Cao Zongrui, Zheng Bo, Zhong Lin, Hu Liangcong, Zhang Xiuli, Qu bo, Jiang Tao. Collagen/heparin sulfate scaffold combined with neural stem cells promote motor function recovery after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(34): 5454-5461. |
| [14] | Xu Gexin, Zhang Yunxia, Zhang Haiying. Stem cell therapy for Alzheimer’s disease: research status and developmental trend [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(33): 5378-5384. |
| [15] | Zhang Bo1, Zhang Kaiwei2, Ma Wenjuan3, Shen Fengjun2, Chen Haixia1. Effect of Bushen Huoxue Decoction on the expression level of nuclear factor-KBp65 protein in chondrocytes of rabbit models of osteoporosis and osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(27): 4375-4380. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||