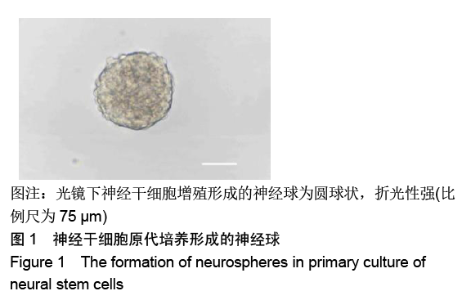
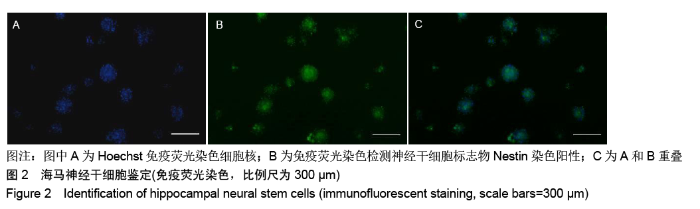
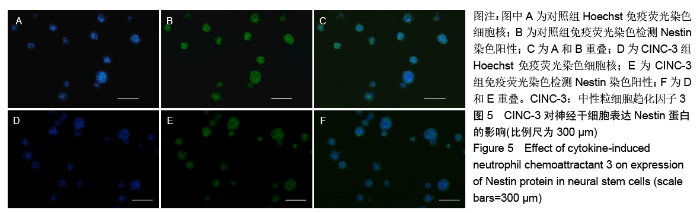
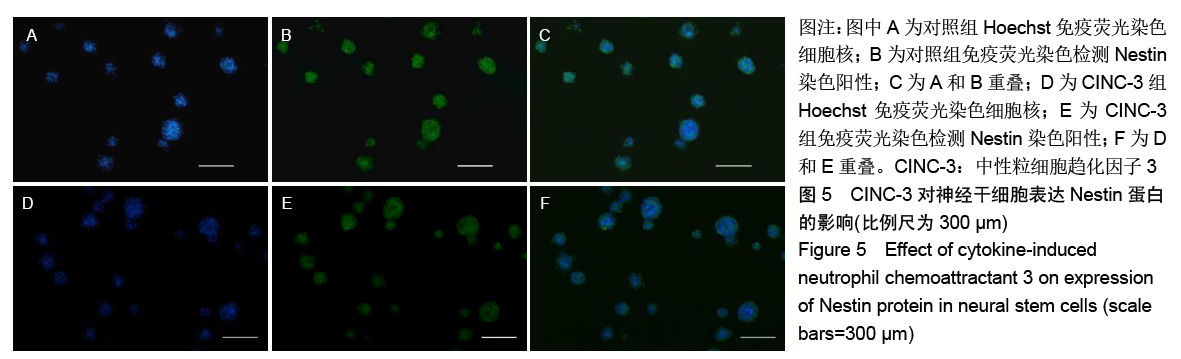
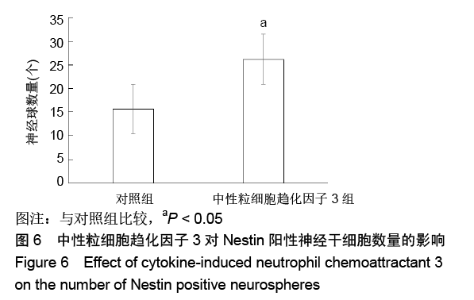
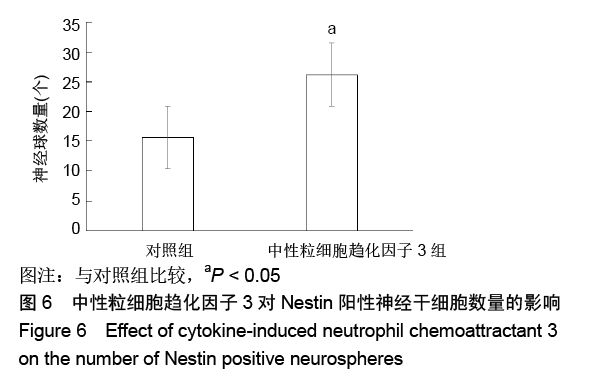
[1] HARRIS L, ZALUCKI O, CLÉMENT O, et al. Neurogenic differentiation by hippocampal neural stem and progenitor cells is biased by NFIX expression. Development. 2018;145(3): dev155689.
[2] NARUSE M, SHIBASAKI K, ISHIZAKI Y. Temporal Changes in Transcription Factor Expression Associated with the Differentiation State of Cerebellar Neural Stem/Progenitor Cells During Development. Neurochem Res. 2018;43(1):205-211.
[3] AUGESTAD IL, NYMAN AKG, COSTA AI, et al. Effects of Neural Stem Cell and Olfactory Ensheathing Cell Co-transplants on Tissue Remodelling After Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia in the Adult Rat. Neurochem Res. 2017;42(6):1599-1609.
[4] STEWART AN, KENDZIORSKI G, DEAK ZM, et al. Co-transplantation of mesenchymal and neural stem cells and overexpressing stromal-derived factor-1 for treating spinal cord injury. Brain Res. 2017;1672:91-105.
[5] WANG C, LU CF, PENG J, et al. Roles of neural stem cells in the repair of peripheral nerve injury. Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(12):2106-2112.
[6] 刘宗秀,高维娟.神经干细胞移植治疗缺血性脑损伤的研究进展[J].承德医学院学报,2019,36(1):69-72.
[7] WANG Y, PAN J, WANG D, et al. The Use of Stem Cells in Neural Regeneration: A Review of Current Opinion. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;13(7):608-617.
[8] 王珊,李萍萍,王晓良,等.神经干细胞微环境在神经再生中的作用[J].药学学报,2018,53(5):684-690.
[9] RUDDY RM, MORSHEAD CM. Home sweet home: the neural stem cell niche throughout development and after injury. Cell Tissue Res. 2018; 371(1):125-141.
[10] ZUO FX, BAO XJ, SUN XC, et al. Transplantation of Human Neural Stem Cells in a Parkinsonian Model Exerts Neuroprotection via Regulation of the Host Microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(11): 26473-26492.
[11] 刘珍,武衡,谢明.神经干细胞及其应用研究新进展[J].社区医学杂志, 2011,9(2):41-42.
[12] CONNELL BJ, GORDON JR, SALEH TM. ELR-CXC chemokine antagonism is neuroprotective in a rat model of ischemic stroke. Neurosci Lett. 2015;606:117-122.
[13] OEI GT, ASLAMI H, KERINDONGO RP, et al. Prolonged helium postconditioning protocols during early reperfusion do not induce cardioprotection in the rat heart in vivo: role of inflammatory cytokines. J Immunol Res. 2015;2015:216798.
[14] DING YP, ZHANG JY, FENG DX, et al. Advances in molecular mechanism of cardioprotection induced by helium. Med Gas Res. 2017;7(2): 124-132.
[15] LI Y, DU XL, HE BP. Lipopolysaccharide Upregulates the Expression of CINC-3 and LIX in Primary NG2 Cells. Neurochem Res. 2016;41(6): 1448-1457.
[16] GU P, QIU FC, HAN R, et al. Efficient differentiation of neural stem cells induced by the rat bone marrow stromal cells. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015; 8(5):6713-6724.
[17] VISHWAKARMA SK, BARDIA A, TIWARI SK, et al. Current concept in neural regeneration research: NSCs isolation, characterization and transplantation in various neurodegenerative diseases and stroke: A review .J Adv Res. 2014;5(3):277-294.
[18] MICCI MA, BOONE DR, PARSLEY MA, et al. Development of a novel imaging system for cell therapy in the brain. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015; 6:131.
[19] FUENTEALBA LC, OBERNIER K, ALVAREZ-BUYLLA A. Adult neural stem cells bridge their niche. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;10(6):698-708.
[20] VAN PRAAG H, SCHINDER AF, CHRISTIE BR, et al. Functional neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Nature. 2002;415(6875): 1030-1034.
[21] STUCHLIK A. Dynamic learning and memory, synaptic plasticity and neurogenesis: an update. Front Behav Neurosci. 2014;8:106.
[22] SONG CG, ZHANG YZ, WU HN, et al. Stem cells: a promising candidate to treat neurological disorders. Neural Regen Res. 2018; 13(7):1294-1304.
[23] NAPOLI E, LIPPERT T, BORLONGAN CV. Stem Cell Therapy: Repurposing Cell-Based Regenerative Medicine Beyond Cell Replacement. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1079:87-91.
[24] ZHANG R, ZHANG Z, CHOPP M. Function of neural stem cells in ischemic brain repair processes. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2016; 36(12): 2034-2043.
[25] SPALDING KL, BERGMANN O, ALKASS K, et al. Dynamics of hippocampal neurogenesis in adult humans. Cell. 2013;153(6): 1219-1227.
[26] MOSHER KI, SCHAFFER DV. Influence of hippocampal niche signals on neural stem cell functions during aging. Cell Tissue Res. 2018; 371(1):115-124.
[27] 高学虎,罗玉萍.神经干细胞激活的研究进展[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2018, 40(5):836-843.
[28] PUTTONEN KA, RUPONEN M, KAUPPINEN R, et al. Improved method of producing human neural progenitor cells of high purity and in large quantities from pluripotent stem cells for transplantation studies. Cell Transplant. 2013;22(10):1753-1766.
[29] LU P, CETO S, WANG Y, et al. Prolonged human neural stem cell maturation supports recovery in injured rodent CNS. J Clin Invest. 2017;127(9):3287-3299.
[30] LÓPEZ-SERRANO C, TORRES-ESPÍN A, HERNÁNDEZ J, et al. Effects of the Post-Spinal Cord Injury Microenvironment on the Differentiation Capacity of Human Neural Stem Cells Derived from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Cell Transplant. 2016;25(10):1833-1852.
[31] BJORNSSON CS, APOSTOLOPOULOU M, TIAN Y, et al. It takes a village: constructing the neurogenic niche. Dev Cell. 2015;32(4):435-446.
[32] 肖霁函,王珊珊,周琳.一些细胞因子对哺乳动物神经干细胞增殖分化的影响[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2016,38(7):886-896.
[33] GONZALEZ A, MOYA-ALVARADO G, GONZALEZ-BILLAUT C, et al. Cellular and molecular mechanisms regulating neuronal growth by brain- derived neurotrophic factor. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2016; 73(10):612-628.
[34] ANNAMALAI P, THANGAM EB. Local and Systemic Profiles of Inflammatory Cytokines in Carrageenan-induced Paw Inflammation in Rats. Immunol Invest. 2017;46(3):274-283.
[35] BOLAND C, COLLET V, LATERRE E, et al. Electrical vagus nerve stimulation and nicotine effects in peritonitis-induced acute lung injury in rats. Inflammation. 2011;34(1):29-35.
[36] SZMYDYNGER-CHODOBSKA J, STRAZIELLE N, ZINK BJ, et al. The role of the choroid plexus in neutrophil invasion after traumatic brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2009;29(9):1503-1516.
[37] MEIRELES M, MARQUES C, NORBERTO S, et al. The impact of chronic blackberry intake on the neuroinflammatory status of rats fed a standard or high-fat diet. J Nutr Biochem. 2015;26(11):1166-1173.
[38] HIRBE AC, MORGAN EA, WEILBAECHER KN. The CXCR4/SDF-1 chemokine axis: a potential therapeutic target for bone metastases. Curr Pharm Des. 2010;16(11):1284-1290.
[39] WANG Y, LUO W, REISER G. Activation of protease-activated receptors in astrocytes evokes a novel neuroprotective pathway through release of chemokines of the growth-regulated oncogene/cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant family.Eur J Neurosci.2007;26(11):3159-3168.
[40] 顾平,马芹颖,王彦永,等.骨髓基质细胞条件培养液调节神经干细胞分化有效成分的蛋白质微阵列分析[J].解剖学报, 2008,39(6):845-849.
|