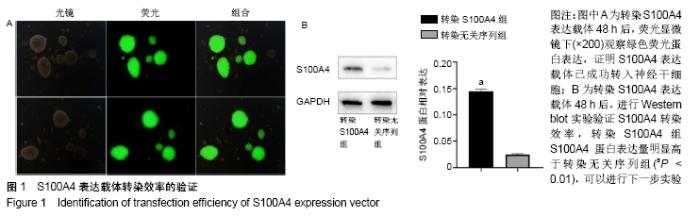
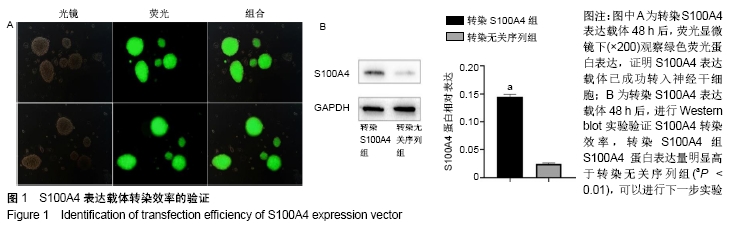
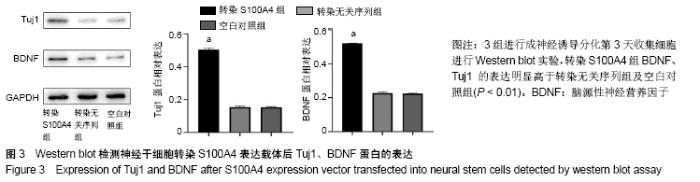
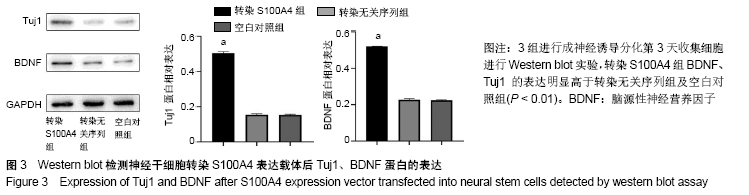
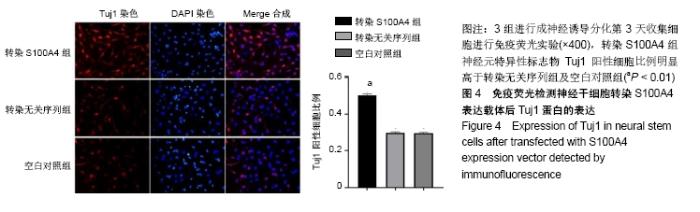
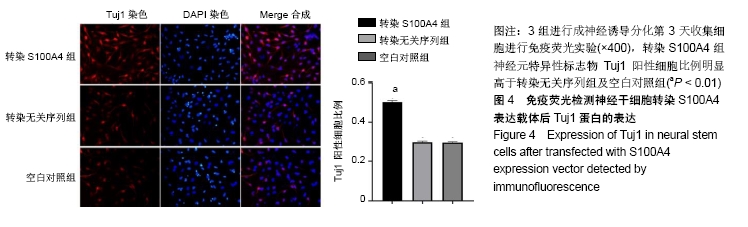
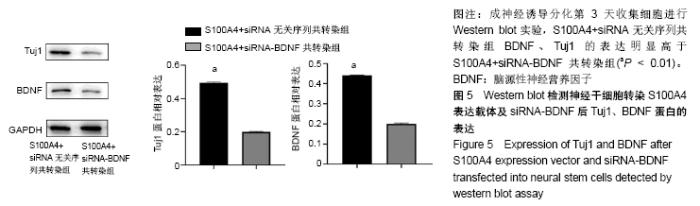
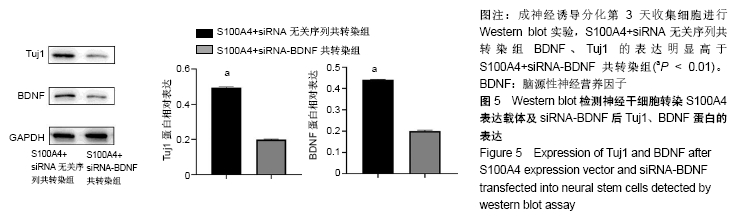
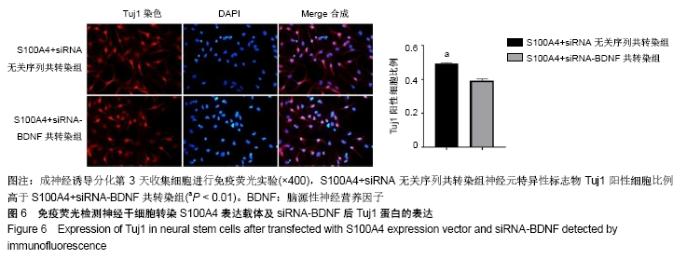
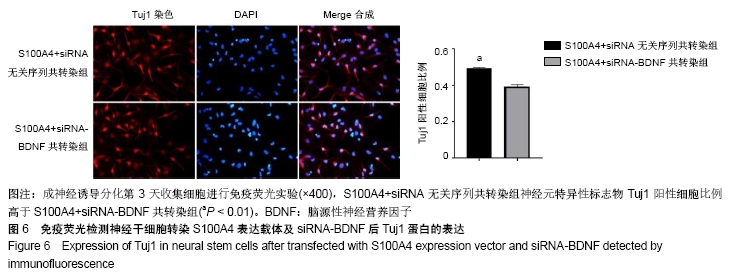
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (19): 3029-3034.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2076
Previous Articles Next Articles
S100A4 promotes differentiation of neural stem cells through up-regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor
Du Xiaowen1, Lin Dapeng2, Tu Guanjun1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110001, Liaoning Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou 121001, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2019-09-16Revised:2019-09-18Accepted:2019-10-19Online:2020-07-08Published:2020-04-08 -
Contact:Tu Guanjun, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110001, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Du Xiaowen, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110001, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the Guidance Program of the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province, No. 201602857
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Du Xiaowen, Lin Dapeng, Tu Guanjun. S100A4 promotes differentiation of neural stem cells through up-regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(19): 3029-3034.
share this article
| [1] ZHENG W, ZHUGE Q, ZHONG M, et al. Neurogenesis in adult human brain after traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 2013;30(22): 1872-1880. [2] BOYE K, MAELANDSMO GM. S100A4 and metastasis: a small actor playing many roles. Am J Pathol. 2010;176(2):528-535. [3] LEI L, TANG L. Schwann cells genetically modified to express S100A4 increases GAP43 expression in spiral ganglion neurons in vitro. Bioengineered. 2017;8(4):404-410. [4] CHENG G, HE T, XING Y. Silencing of S100A4, a metastasis- associated protein, inhibits retinal neovascularization via the downregulation of BDNF in oxygen-induced ischaemic retinopathy. Eye (Lond). 2016;30(6):877-887. [5] CHMIELNICKI E, BENRAISS A, ECONOMIDES AN, et al. Adenovirally expressed noggin and brain-derived neurotrophic factor cooperate to induce new medium spiny neurons from resident progenitor cells in the adult striatal ventricular zone. J Neurosci. 2004;24(9):2133-2142. [6] COULL JA, BEGGS S, BOUDREAU D, et al. BDNF from microglia causes the shift in neuronal anion gradient underlying neuropathic pain. Nature. 2005;438(7070):1017-1021. [7] 方康权,曾宪辉.脊髓损伤的生物化学研究概况[J].医学理论与实践, 2018, 31(18):2723-2724,2727. [8] 黄辉.继发性脊髓损伤发病机制的研究进展[J].医学综述, 2013, 19(7): 1162-1165. [9] 张盼,赵红卫,卢斌,等.继发性脊髓损伤微环境的研究进展[J].海南医学, 2018, 29(19): 2774-2777. [10] ECKERT MJ, MARTIN MJ. Trauma: Spinal Cord Injury. Surg Clin North Am. 2017;97(5):1031-1045. [11] BADHIWALA JH, WILSON JR, FEHLINGS MG. Global burden of traumatic brain and spinal cord injury. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18(1): 24-25. [12] SABAPATHY V, THARION G, KUMAR S. Cell Therapy Augments Functional Recovery Subsequent to Spinal Cord Injury under Experimental Conditions. Stem Cells Int. 2015;2015:132172. [13] WITIW CD, FEHLINGS MG. Acute Spinal Cord Injury. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2015;28(6):202-210. [14] DOOLEY D, VIDAL P, HENDRIX S. Immunopharmacological intervention for successful neural stem cell therapy: New perspectives in CNS neurogenesis and repair. Pharmacol Ther. 2014;141(1):21-31. [15] TUSZYNSKI MH, WANG Y, GRAHAM L, et al. Neural stem cell dissemination after grafting to CNS injury sites. Cell. 2014;156(3): 388-389. [16] LUDWIG PE, THANKAM FG, PATIL AA, et al. Brain injury and neural stem cells. Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(1):7-18. [17] ORMOND DR, SHANNON C, OPPENHEIM J, et al. Stem cell therapy and curcumin synergistically enhance recovery from spinal cord injury. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e88916. [18] MARIANO ED, BATISTA CM, BARBOSA BJ, et al. Current perspectives in stem cell therapy for spinal cord repair in humans: a review of work from the past 10 years. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2014;72(6): 451-456. [19] HORKY LL, GALIMI F, GAGE FH, et al. Fate of endogenous stem/progenitor cells following spinal cord injury. J Comp Neurol. 2006;498(4):525-538. [20] CAWSEY T, DUFLOU J, WEICKERT CS, et al. Nestin-Positive Ependymal Cells Are Increased in the Human Spinal Cord after Traumatic Central Nervous System Injury. J Neurotrauma. 2015;32(18):1393-1402. [21] KADOYA K, LU P, NGUYEN K, et al. Spinal cord reconstitution with homologous neural grafts enables robust corticospinal regeneration. Nat Med. 2016;22(5):479-487. [22] GARBOSSA D, BOIDO M, FONTANELLA M, et al. Recent therapeutic strategies for spinal cord injury treatment: possible role of stem cells. Neurosurg Rev. 2012;35(3):293-311. [23] VAWDA R, WILCOX J, FEHLINGS M. Current stem cell treatments for spinal cord injury. Indian J Orthop. 2012;46(1):10-18. [24] ZHANG SQ, WU MF, PENG CG, et al. Improvements in neuroelectrophysiological and rear limb functions in rats with spinal cord injury after Schwann cell transplantation in combination with a C5a receptor antagonist. Genet Mol Res. 2015;14(4):15158-15168. [25] WANG D, ZHANG J. Effects of hypothermia combined with neural stem cell transplantation on recovery of neurological function in rats with spinal cord injury. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11(3):1759-1767. [26] DU XJ, CHEN YX, ZHENG ZC, et al. Neural stem cell transplantation inhibits glial cell proliferation and P2X receptor-mediated neuropathic pain in spinal cord injury rats. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(5):876-885. [27] LEONG C, ZHAI D, KIM B, et al. Neural stem cell isolation from the whole mouse brain using the novel FABP7-binding fluorescent dye, CDr3. Stem Cell Res. 2013;11(3):1314-1322. [28] 陈刚,秦尚振,马廉亭,等.人胚脑与脊髓神经干细胞体外生物学特性的差异[J].脑与神经疾病杂志, 2006,14(3):183-186. [29] HUANG H, ZHENG HY, LIU ZL, et al. Prognostic significance of relaxin-2 and S100A4 expression in osteosarcoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014;18(19):2828-2834. [30] LI HJ, CHEN YX, WANG Q, et al. S100A4 mRNA as a prognostic marker and therapeutic target in Wilms tumor (WT). Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014;18(6):817-827. [31] TARABYKINA S, GRIFFITHS TR, TULCHINSKY E, et al. Metastasis-associated protein S100A4: spotlight on its role in cell migration. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2007;7(3):217-228. [32] XU X, SU B, XIE C, et al. Sonic hedgehog-Gli1 signaling pathway regulates the epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) by mediating a new target gene, S100A4, in pancreatic cancer cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e96441. [33] KHAN MI, YUAN T, CHOU RH, et al. S100A4 inhibits cell proliferation by interfering with the S100A1-RAGE V domain. PLoS One. 2019;14(2):e0212299. [34] LINK T, KUHLMANN JD, KOBELT D, et al. Clinical relevance of circulating MACC1 and S100A4 transcripts for ovarian cancer. Mol Oncol. 2019;13(5):1268-1279. [35] ABERG F, KOZLOVA EN. Metastasis-associated mts1 (S100A4) protein in the developing and adult central nervous system. J Comp Neurol. 2000;424(2):269-282. [36] KOBORI N, CLIFTON GL, DASH P. Altered expression of novel genes in the cerebral cortex following experimental brain injury. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2002;104(2):148-158. [37] KOZLOVA EN, LUKANIDIN E. Mts1 protein expression in the central nervous system after injury. Glia. 2002;37(4):337-348. [38] NOVITSKAYA V, GRIGORIAN M, KRIAJEVSKA M, et al. Oligomeric forms of the metastasis-related Mts1 (S100A4) protein stimulate neuronal differentiation in cultures of rat hippocampal neurons. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(52):41278-41286. [39] EYILETEN C, KAPLON-CIESLICKA A, MIROWSKA-GUZEL D, et al. Antidiabetic Effect of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Its Association with Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J Diabetes Res. 2017;2017:2823671. [40] WURZELMANN M, ROMEIKA J, SUN D. Therapeutic potential of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and a small molecular mimics of BDNF for traumatic brain injury. Neural Regen Res. 2017; 12(1):7-12. [41] 李小华,冷锦红.脑源性神经营养因子对糖尿病能量代谢及神经病变的影响[J].中国糖尿病杂志, 2019, 27(8): 629-631. [42] MAROSI K, MATTSON MP. BDNF mediates adaptive brain and body responses to energetic challenges. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2014; 25(2):89-98. |
| [1] | Min Youjiang, Yao Haihua, Sun Jie, Zhou Xuan, Yu Hang, Sun Qianpu, Hong Ensi. Effect of “three-tong acupuncture” on brain function of patients with spinal cord injury based on magnetic resonance technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-8. |
| [2] | Jiang Hongying, Zhu Liang, Yu Xi, Huang Jing, Xiang Xiaona, Lan Zhengyan, He Hongchen. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on pressure ulcers after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1149-1153. |
| [3] | Wan Ran, Shi Xu, Liu Jingsong, Wang Yansong. Research progress in the treatment of spinal cord injury with mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| [4] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [5] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [6] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| [7] | Li Cai, Zhao Ting, Tan Ge, Zheng Yulin, Zhang Ruonan, Wu Yan, Tang Junming. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB promotes proliferation, differentiation and migration of skeletal muscle myoblast [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1050-1055. |
| [8] | Wang Feng, Zhou Liyu, Saijilafu, Qi Shibin, Ma Yanxia, Wei Shanwen. CaMKII-Smad1 promotes axonal regeneration of peripheral nerves [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1064-1068. |
| [9] | Ma Binxiang, He Wanqing, Zhou Guangchao, Guan Yonglin. Triptolide improves motor dysfunction in rats following spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 701-706. |
| [10] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [11] | Xu Weilong, Zuo Yuan, Xin Daqi, He Chenyang, Zhao Peng, Shi Ming, Zhou Boyuan, Liu Yating, Zhao Yan. Selection of modeling methods for acute compressive spinal cord injury: a network Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3767-3772. |
| [12] | Zhou Wu, Wang Binping, Wang Yawen, Cheng Yanan, Huang Xieshan. Transforming growth factor beta combined with bone morphogenetic protein-2 induces the proliferation and differentiation of mouse MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3630-3635. |
| [13] | Yan Peng, Ma Yufei, Cui Jingfu, Hao Shaofei, Liu Jinhui, Guan Chunlei, Wang Xiaoran, Yang Xiaoyu. Mechanism of anodic block electrical stimulation of sacral nerve root to reconstruct bladder function [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3684-3689. |
| [14] | Lu Yi, Deng Wenchong. Regulation and difference of different exercise styles on brain structure and cognitive function [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3252-3258. |
| [15] | Su Mingzhu, Ma Yuewen. Radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy regulates the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells in the hippocampus via Notch1/Hes1 pathway after cerebral ischemia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3009-3015. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||