Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (32): 5204-5209.doi: 10.12307/2021.225
Previous Articles Next Articles
Pyroptosis in the progression of osteoarthritis
Zhi Jiajia1, Du Chaozheng1, Wang Yuze2
- 1Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2020-09-03Revised:2020-09-05Accepted:2020-10-16Online:2021-11-18Published:2021-07-26 -
Contact:Wang Yuze, MD, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Zhi Jiajia, Master candidate, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:Shanxi Youth Science and Technology Research Fund, No. 201901D211505 (to WYZ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhi Jiajia, Du Chaozheng, Wang Yuze. Pyroptosis in the progression of osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(32): 5204-5209.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
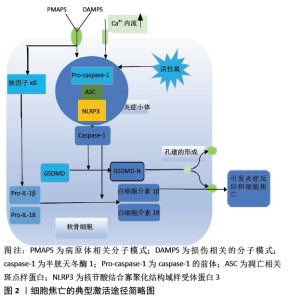
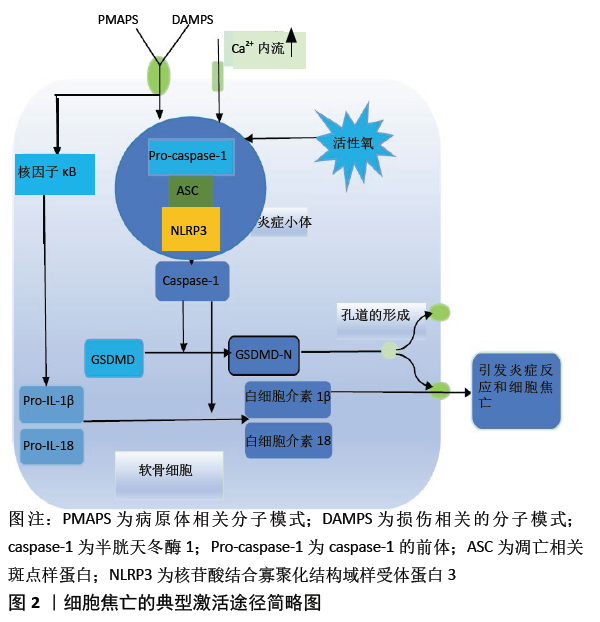
2.1 细胞焦亡的激活途径 细胞焦亡涉及两个途径:caspase-1介导的典型途径和caspase-4、caspase-5及caspase-11介导的非典型途径。在以caspase-1介导的细胞焦亡典型途径的启动阶段中,Toll样受体和核苷酸结合寡聚化域样受体(nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors,NLRs)识别出损伤相关分子模式或病原体相关分子模式[9],一方面直接促进炎症小体的组装,另一方面通过激活核因子κB促进与炎症小体相关分子的表达,如NLRP3、白细胞介素1β前体和白细胞介素18前体等[10]。接下来进入激活步骤,以组装炎症小体和活化caspase-1为主,查阅大量文献发现caspase-1可以被多种炎症小体活化,如由NLRs和黑色素瘤2样受体参与组成的炎症小体[11]。研究最广泛的是NLR家族,如核苷酸结合寡聚化结构域样受体蛋白(nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor pyrin domain containing,NLRP)1,NLRP3,NLRC4等,其中最常见的参与炎症小体组成的是NLRP3[12]。虽然这些蛋白分子参与焦亡途径的机制可能会略有不同,但所涉及的这些蛋白分子的结构决定了它们最终都会使caspase-1活化。NLRs包含C末端富含亮氨酸的重复序列结构域,中央核苷酸结合寡聚结构域(nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain,NOD),N末端半胱蛋白酶募集结构域或吡啶结构域等[13]。NLRP3通过NOD与凋亡相关斑点样蛋白结合,并通过凋亡相关斑点样蛋白的半胱天冬酶相关的募集域连接Pro-caspase-1,组装成NLRP3炎症小体。此后, pro-caspase-1被切割形成有活性的caspase-1,促进白细胞介素1 β和白细胞介素18的激活,而且还将GSDMD切割成2个片段[7,14],其中有活性的GSDMD-N移动到质膜上,快速导致细胞膜上形成直径为10-15 nm的质膜孔,这些膜孔的形成使细胞膜内外的离子梯度减小,从而使大量水分子涌入,增加了渗透压,导致细胞肿胀、质膜溶解和炎性因子的释放并使细胞焦亡[15]。细胞焦亡典型的激活途径见图2。 "

在非典型的途径中,涉及人的caspase-4、caspase-5和小鼠的caspase-11,且它们与caspase-1具有相似的功能。在脂多糖诱导的非典型的细胞焦亡途径中,Toll样受体4与细胞外的脂多糖结合,而caspases识别胞质脂多糖。caspase-4、caspase-5和caspase-11通过它们的氨酸蛋白酶募集结构域以高特异性和亲和力与脂质结合,进而被直接激活。Caspase-11也可以通过将脂多糖转染或电穿孔进入巨噬细胞而被激活[16]。在它们被激活后,可以直接裂解GSDMD,从而使细胞发生焦亡[17]。 另外,还有研究发现,GSDME能被caspase-3特异性切割以产生其N末端片段,并在质膜上穿孔以诱导细胞焦亡[18]。ZHOU等[19]发现铁激活的活性氧通过募集到线粒体的Bcl-2,进一步刺激Cyt c的释放以增强caspase-3活化,从而导致黑色素瘤细胞中GSDME的裂解,暴露N末端片段,继而发生细胞焦亡。 2.2 细胞焦亡与骨关节炎 骨关节炎发育过程中的软骨破坏可见于任何关节,但主要发生在膝、髋、手和脊椎等关节处。骨关节炎的病理特征主要包括关节软骨的降解、骨赘形成的增加、滑膜破坏、软骨下骨的硬化和在骨软骨交界处伴随血管的生成[20-21]。LIU等[22]研究发现低剂量吲哚美辛和Hedgehog信号抑制剂可协同减弱与细胞焦亡相关基因caspase-1、白细胞介素1 β和白细胞介素18的mRNA和蛋白质水平上的表达,同时减轻骨关节炎小鼠的软骨损伤。这表明骨关节炎的病理与细胞焦亡存在一定的因果关系。骨关节炎病理的研究大多集中在软骨变性和骨赘上,而忽略了有炎症和增厚的滑膜。滑膜纤维化是滑膜组织的另一种病理学变化,其特征是细胞外基质沉积过多,导致关节疼痛和触痛。有实验表明由成纤维样滑膜细胞产生的一系列促炎性因子和滑膜纤维化也是引起骨关节炎的原因之一,其中越来越多的证据表明成纤维样滑膜细胞和转化生长因子β在纤维化反应中起着关键的作用[23-24]。ZHANG等[24]研究证明,成纤维样滑膜细胞发生焦亡时加重了滑膜的纤维化,进而加速膝关节骨关节炎的病理发展。现从细胞焦亡激活途径中所涉及的NLRP3、核因子κB、caspase-1、GSDMD、白细胞介素1 β和白细胞介素18等分子在骨关节炎中的作用进行分析。 2.2.1 NLRP3与骨关节炎炎症 小体是由多种蛋白质组成的复合体,它们的形成促进pro-caspase-1的成熟,使促炎性细胞因子加工并裂解为活化形式,继而导致细胞发生焦亡。在细胞焦亡中,NLRP3是NLRs家族中被认识最透彻的,NLRP3炎症小体的NOD样受体正在成为许多退化性疾病的关键分子机制[25],如骨关节炎。NLRP3炎症小体可促进与多种关节炎疾病的发病机制相关的促炎性细胞因子和降解酶的表达,如白细胞介素18和基质金属蛋白酶可导致软骨退化和滑膜炎症[26-28]。在有关骨关节炎的实验中,脂多糖刺激关节软骨可模拟类似骨关节炎的炎症环境[29]。最近的一项研究显示在膝关节骨关节炎患者和体外脂多糖和ATP诱导的人成纤维样滑膜细胞中,NLRP3炎症小体参与了成纤维样滑膜细胞炎症和焦亡。当在脂多糖和ATP诱导的人成纤维样滑膜细胞中加入NLRP3 siRNA进行培养时,发现与未加入的细胞相比,在NLRP3 siRNA转染的培养基中凋亡相关斑点样蛋白、caspase-1、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素18和GSDMD等表达均减少和炎症减轻[30]。这提示NLRP3在骨关节炎中起着重要作用,可以调控细胞焦亡激活途径中炎症小体的组成和下游相关基因的表达。ZU等[31]在大鼠骨关节炎模型中,发现淫羊藿苷可以抑制NLRP3炎症小体的组成,从而抑制caspase-1参与的信号通路,抑制脂多糖诱导的细胞焦亡和胶原蛋白的形成;而NLRP3的过表达则逆转了由淫羊藿苷引起的上述变化;同时也发现抑制NLRP3可减轻脂多糖介导的软骨细胞损伤。这表明了抑制NLRP3可减少细胞焦亡,从而减轻软骨细胞的损伤和骨关节炎的发生。当前,已有几种模型来描述如何激活NLRP3炎症小体,包括K+外流、线粒体和内质网活性氧产生的增多[32]、溶酶体功能[33]、胞内Ca2+增加[34]、泛素化和微小RNA,特别是活性氧[25](图2),而活性氧诱导的氧化应激可能是骨关节炎发展中NLRP3炎性体激活和下游因子释放的主要因素[35]。虽然现在对NLRP3在细胞焦亡中的研究较多,但仍处于初级阶段,尤其在骨关节炎中的作用机制,因此需要更进一步去探究它们与骨关节炎的关系。 2.2.2 核因子κB与骨关节炎 核因子κB可以调控促炎性细胞因子的表达,是控制软骨正常发育和病理破坏的重要分子[36]。在细胞焦亡中,核因子κB不仅可以促进白细胞介素1β前体和白细胞介素18前体的分泌和活化[10,37],而且也是NLRP3炎症小体上游的重要激活剂,它通过诱导NLRP3的表达来触发相关炎症小体的合成[38]。有研究表明在骨关节炎中核因子κB的表达明显上调[39]。核因子κB信号通路通过上调胶原蛋白降解酶的表达和促进软骨细胞的肥大,从而参与骨关节炎病理发展[40]。HU等[41]发现马钱子苷通过抑制核因子κB的活化来减弱软骨的降解,抑制软骨细胞焦亡和减少异常血管的生成。因此,这些结果揭示了核因子κB参与软骨基质的分解代谢以及软骨细胞的焦亡。 2.2.3 caspase-1与骨关节炎 Caspases是先天免疫应答的关键调节因子,可以调节细胞的死亡和炎症反应。目前,研究所知参与细胞焦亡的caspases主要有caspase-1、caspase-4、caspase-5和caspase-11。无活性酶原的Pro-caspase-1存在于细胞质中,被炎症小体激活后形成由p20/p10二聚体组成的四聚体——caspase-1[42]。活化后的caspase-1对白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18的前体和GSDMD进行切割,形成有活性的白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素18和含有GSDMD-N氮端活性域的肽段,诱导细胞焦亡[6]。HU等[41]在骨关节炎小鼠的的模型中,发现软骨中的caspase-1表达增加。在膝关节骨关节炎细胞焦亡的实验中发现:①经 caspase-1抑制剂处理的大鼠滑膜细胞,与未经此处理的相比,其内膜排列更整齐,炎性细胞浸润更少;②用caspase-1 siRNA转染的巨噬细胞,发现焦亡的细胞和与焦亡相关的蛋白表达都减少,如转化生长因子β和金属蛋白酶组织抑制剂1等[43]。这些提示caspase-1参与骨关节炎中的炎症反应并促进了细胞发生焦亡。ZU等[31]研究表明,在脂多糖诱导的大鼠骨关节炎中,抑制caspase-1的信号传导,可以减少软骨细胞损伤和细胞焦亡,并减轻大鼠的骨关节炎。这些实验都表明了caspase-1参与骨关节炎的病理发展。 2.2.4 GSDMD与骨关节炎 gasdermin家族由几个成员组成,这些成员能够在质膜和细胞内的细胞器内层形成大的寡聚膜孔[44]。在细胞焦亡中,caspase-1或caspase-11可诱导GSDMD在细胞膜上成孔,导致细胞发生裂解[45-46]。在探讨膝关节骨关节炎滑膜组织中是否存在细胞焦亡的实验中,发现GSDMD-N的表达明显增加[47]。有研究发现在骨关节炎中,可以通过增加成纤维样滑膜细胞焦亡加重滑膜纤维化。当沉默GSDMD基因表达时可降低滑膜纤维化相关因子的基因表达和蛋白水平,如纤维化标志物转化因子β、前胶原赖氨酸和金属蛋白酶组织抑制剂等[24]。这些表明GSDMD参与的细胞焦亡与骨关节炎存在一定联系,但其中所涉及的相关机制尚未了解。 2.2.5 白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素18与骨关节炎 在细胞焦亡中,caspase-1通过切割白细胞介素1β前体和白细胞介素18的前体形成有活性的白细胞介素1 β和白细胞介素18。多年来,白细胞介素1一直被视为治疗骨关节炎的靶标,其中白细胞介素18和白细胞介素1 β都是白细胞介素1家族的成员。白细胞介素1是软骨降解的高效诱导剂,可诱导与疾病相关的蛋白酶mRNA的表达并控制它们的生物利用度,如ADAMTS5和基质金属蛋白酶13等。它们还可引起滑膜炎,并可诱导其他与疾病相关的基因表达,例如神经生长因子,这是骨关节炎中关键的疼痛敏感剂[48]。 在多数自身免疫、慢性炎症和退行性病变中,白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18的过量产生与疾病的严重程度有关[49],如骨关节炎。SUN等[50]研究显示当抑制白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18的表达时,发现基质金属蛋白酶的分泌减少,使软骨基质的降解受到了抑制以及骨关节炎的炎症反应减轻。这表明白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18直接或间接的参与了软骨基质的降解。大多数研究表明,它们在软骨、滑膜和软骨下骨中的表达水平与骨关节炎的发生和发展有关[51]。有证据表明白细胞介素1β可诱导白细胞介素6、诱导性一氧化碳合酶、环氧合酶2等炎性因子的分泌,并通过抑制Ⅱ型胶原蛋白等促进骨关节炎的病理发展,导致软骨细胞功能的障碍[52-53]。用白细胞介素1β刺激原代小鼠软骨细胞可增加细胞和线粒体活性氧的产生,从而模拟类似于骨关节炎中软骨的损伤的环境[54]。三结构域蛋白家族8已被证明可以调节炎症反应,发现敲低它可以使白细胞介素1β诱导的炎症反应减轻,以及软骨中的聚集蛋白多糖和胶原蛋白Ⅱ的表达增加以及基质降解酶的表达减少[55]。以上实验表明白细胞介素1β不仅参与骨关节炎的炎症反应,还与软骨的降解有关。 白细胞介素18通过促进Th1或Th2相关的反应,在大多数炎性疾病中发挥着致病作用[2]。白细胞介素18的受体是由2个亚基组成的异二聚体:白细胞介素18R α和白细胞介素18R β。当白细胞介素18与白细胞介素18R α亚基结合后,形成异二聚体复合物以传导细胞内信号,最终导致促炎性因子基因的转录[56]。BAO等[57]用不同浓度的白细胞介素18处理软骨细胞以评估Ⅱ型胶原,Sox9和聚蛋白多糖的mRNA表达和蛋白质水平,发现它们的蛋白水平呈现相同的趋势,即随着白细胞介素18浓度的增加,它们的表达下降。这些结果表明白细胞介素18可抑制软骨细胞特异性基因的表达,进而诱导软骨的降解。此外,他们还发现白细胞介素18可诱导软骨细胞衰老,进而促进骨关节炎的发展[57]。还有研究发现在骨关节炎患者的滑膜液中,过表达的白细胞介素18可以促进前列腺素E2的表达,参与软骨的降解[58]。ZHANG等[43]研究发现滑膜巨噬细胞的焦亡参与了膝关节骨关节炎的病理发展,抑制滑膜巨噬细胞焦亡可以减少白细胞介素 1β和白细胞介素18等因子的mRNA和蛋白表达,进而缓解膝骨关节炎中的滑膜炎症和纤维化。综上所述白细胞介素1 β和白细胞介素18不仅是炎症的重要促进剂,还是细胞焦亡的下游产物。 2.2.6 其他蛋白与骨关节炎 除以上所提到的一些蛋白和因子,还有许多也参与细胞焦亡激活的途径,如NLRP1[59]、caspase-4、caspase-5、caspase-11、caspase-3和GSDME等[18],但目前只发现NLRP1和caspase-3与骨关节炎有关系。NLRP1与NLRP3类似,也参与炎症小体的组成和控制促炎细胞因子的成熟和分泌。FAN等[60]研究发现,在人骨关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞中NLRP1的mRNA和蛋白质水平明显高于正常成纤维样滑膜细胞。当抑制NLRP1的表达时,发现白细胞介素1β减少。这表明NLRP1在骨关节炎中具有潜在作用。还有实验显示,caspase-3在骨关节炎中过表达[61]。 "

| [1] BOWDEN JL, HUNTER DJ, DEVEZA LA, et al. Core and adjunctive interventions for osteoarthritis: efficacy and models for implementation. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16(8):434-447. [2] PRIMORAC D, MOLNAR V, ROD E, et al. Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review of Pathogenesis and State-Of-The-Art Non-Operative Therapeutic Considerations. Genes (Basel). 2020;11(8):854. [3] 付长龙,叶锦霞,林洁,等.新型程序性细胞死亡对骨关节炎软骨基质稳态影响之初探[J].风湿病与关节炎,2020,9(5):55-57+80. [4] LIM Y, KUMAR S. A single cut to pyroptosis. Oncotarget. 2015;6(35): 36926-36927 [5] LU F, LAN Z, XIN Z, et al. Emerging insights into molecular mechanisms underlying pyroptosis and functions of inflammasomes in diseases. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(4):3207-3221. [6] XU YJ, ZHENG L, HU YW, et al. Pyroptosis and its relationship to atherosclerosis. Clin Chim Acta. 2018;476:28-37. [7] TSUCHIYA K. Inflammasome-associated cell death: Pyroptosis, apoptosis, and physiological implications. Microbiol Immunol. 2020; 64(4):252-269. [8] JIA C, CHEN H, ZHANG J, et al. Role of pyroptosis in cardiovascular diseases. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;67:311-318. [9] MENU P, VINCE JE. The NLRP3 inflammasome in health and disease: the good, the bad and the ugly. Clin Exp Immunol. 2011;166(1):1-15. [10] LI W, CAO T, LUO C, et al. Crosstalk between ER stress, NLRP3 inflammasome, and inflammation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020; 104(14):6129-6140. [11] HACHIM MY, KHALIL BA, ELEMAM NM, et al. Pyroptosis: The missing puzzle among innate and adaptive immunity crosstalk. J Leukoc Biol. 2020;108(1):323-338. [12] LIANG F, ZHANG F, ZHANG L, et al. The advances in pyroptosis initiated by inflammasome in inflammatory and immune diseases. Inflamm Res. 2020;69(2):159-166. [13] MEYERS AK, ZHU X. The NLRP3 Inflammasome: Metabolic Regulation and Contribution to Inflammaging. Cells. 2020;9(8):1808. [14] ZENG C, WANG R, TAN H. Role of Pyroptosis in Cardiovascular Diseases and its Therapeutic Implications. Int J Biol Sci. 2019;15(7):1345-1357. [15] ZHENG Z, LI G. Mechanisms and Therapeutic Regulation of Pyroptosis in Inflammatory Diseases and Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(4):1456. [16] MATHUR A, HAYWARD JA, MAN SM. Molecular mechanisms of inflammasome signaling. J Leukoc Biol. 2018;103(2):233-257. [17] SHI J, GAO W, SHAO F. Pyroptosis: Gasdermin-Mediated Programmed Necrotic Cell Death. Trends Biochem Sci. 2017;42(4):245-254. [18] ROGERS C, FERNANDES-ALNEMRI T, MAYES L, et al. Cleavage of DFNA5 by caspase-3 during apoptosis mediates progression to secondary necrotic/pyroptotic cell death. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14128. [19] ZHOU B, ZHANG JY, LIU XS, et al. Tom20 senses iron-activated ROS signaling to promote melanoma cell pyroptosis. Cell Res. 2018;28(12): 1171-1185. [20] SURI S, WALSH DA. Osteochondral alterations in osteoarthritis. Bone. 2012;51(2):204-211. [21] CHEN D, SHEN J, ZHAO W, et al. Osteoarthritis: toward a comprehensive understanding of pathological mechanism. Bone Res. 2017;5:16044. [22] LIU Q, WU Z, HU D, et al. Low dose of indomethacin and Hedgehog signaling inhibitor administration synergistically attenuates cartilage damage in osteoarthritis by controlling chondrocytes pyroptosis. Gene. 2019;712:143959. [23] HAN D, FANG Y, TAN X, et al. The emerging role of fibroblast-like synoviocytes-mediated synovitis in osteoarthritis: An update.J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(17):9518-9532. [24] ZHANG L, ZHANG L, HUANG Z, et al. Increased HIF-1α in Knee Osteoarthritis Aggravate Synovial Fibrosis via Fibroblast-Like Synoviocyte Pyroptosis.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:6326517. [25] ABAIS JM, XIA M, ZHANG Y, et al. Redox regulation of NLRP3 inflammasomes: ROS as trigger or effector? Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015;22(13):1111-1129. [26] ZHOU J, ZHAO Y, WU G, et al. Differential miRNAomics of the synovial membrane in knee osteoarthritis induced by bilateral anterior cruciate ligament transection in rats. Mol Med Rep. 2018;18(4):4051-4057. [27] MCALLISTER MJ, CHEMALY M, EAKIN AJ, et al. NLRP3 as a potentially novel biomarker for the management of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(5):612-619. [28] SCANZELLO CR, GOLDRING SR. The role of synovitis in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Bone. 2012;51(2):249-257. [29] MENDEZ ME, SEBASTIAN A, MURUGESH DK, et al. LPS-Induced Inflammation Prior to Injury Exacerbates the Development of Post-Traumatic Osteoarthritis in Mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2020;35(11): 2229-2241. [30] ZHAO LR, XING RL, WANG PM, et al. NLRP1 and NLRP3 inflammasomes mediate LPS/ATP‑induced pyroptosis in knee osteoarthritis. Mol Med Rep.2018;17(4):5463-5469. [31] ZU Y, MU Y, LI Q, et al. Icariin alleviates osteoarthritis by inhibiting NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):307. [32] WANG Y, LIU X, SHI H, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome, an immune-inflammatory target in pathogenesis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Clin Transl Med. 2020;10(1):91-106. [33] FORT BP, DUBYAK GR, GREENFIELD EM. Lysosomal disruption by orthopedic wear particles induces activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and macrophage cell death by distinct mechanisms. J Orthop Res. 2021;39(3):493-505. [34] LI JP, WEI W, LI XX, et al. Regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome by CD38 through cADPR-mediated Ca2+ release in vascular smooth muscle cells in diabetic mice. Life Sci. 2020;255:117758. [35] CHEN Z, ZHONG H, WEI J, et al. Inhibition of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling leads to increased activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21(1):300. [36] JIMI E, FEI H, NAKATOMI C. NF-κB Signaling Regulates Physiological and Pathological Chondrogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(24):6275. [37] SCHRODER K, TSCHOPP J. The inflammasomes. Cell. 2010;140(6):821-32. [38] GUO H, CALLAWAY JB, TING JP. Inflammasomes: mechanism of action, role in disease, and therapeutics. Nat Med. 2015;21(7):677-687. [39] RIGOGLOU S, PAPAVASSILIOU AG. The NF-κB signalling pathway in osteoarthritis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013;45(11):2580-2584 [40] CHOI MC, JO J, PARK J, et al. NF-κB Signaling Pathways in Osteoarthritic Cartilage Destruction. Cells. 2019;8(7):734. [41] HU J, ZHOU J, WU J, et al. Loganin ameliorates cartilage degeneration and osteoarthritis development in an osteoarthritis mouse model through inhibition of NF-κB activity and pyroptosis in chondrocytes.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;247:112261. [42] MIAO EA, RAJAN JV, ADEREM A. Caspase-1-induced pyroptotic cell death. Immunol Rev. 2011;243(1):206-214. [43] ZHANG L, XING R, HUANG Z, et al. Inhibition of Synovial Macrophage Pyroptosis Alleviates Synovitis and Fibrosis in Knee Osteoarthritis.Mediators Inflamm. 2019;2019:2165918. [44] MULVIHILL E, SBORGI L, MARI SA, et al. Mechanism of membrane pore formation by human gasdermin-D. EMBO J. 2018;37(14):e98321. [45] AGLIETTI RA, DUEBER EC. Recent Insights into the Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Pyroptosis and Gasdermin Family Functions. Trends Immunol. 2017;38(4):261-271. [46] DE VASCONCELOS NM, VAN OPDENBOSCH N, VAN GORP H, et al. Single-cell analysis of pyroptosis dynamics reveals conserved GSDMD-mediated subcellular events that precede plasma membrane rupture.Cell Death Differ. 2019;26(1):146-161. [47] 徐波. 滑膜巨噬细胞焦亡激活膝骨关节炎痛敏及“易层”贴敷的干预机制 [D]. 南京:南京中医药大学,2020. [48] VINCENT TL. IL-1 in osteoarthritis: time for a critical review of the literature. F1000Res. 2019;8:F1000 Faculty Rev-934. [49] MIGLIORINI P, ITALIANI P, PRATESI F, et al. The IL-1 family cytokines and receptors in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev. 2020;19(9):102617. [50] SUN Y, WANG C, GONG C. Repairing effects of glucosamine sulfate in combination with etoricoxib on articular cartilages of patients with knee osteoarthritis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):150. [51] KAPOOR M, MARTEL-PELLETIER J, LAJEUNESSE D, et al. Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(1):33-42. [52] YANG S, KIM J, RYU JH, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha is a catabolic regulator of osteoarthritic cartilage destruction. Nat Med. 2010;16(6):687-693. [53] CHAGANTI RK, PURDUE E, SCULCO TP, et al. Elevation of serum tumor necrosis factor α in patients with periprosthetic osteolysis: a case-control study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(2):584-589. [54] ANSARI MY, AHMAD N, HAQQI TM. Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: Role of polyphenols. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;129:110452. [55] LIU R, WU H, SONG H. Knockdown of TRIM8 Attenuates IL-1β-induced Inflammatory Response in Osteoarthritis Chondrocytes Through the Inactivation of NF-κB Pathway. Cell Transplant. 2020;29:963689720943604. [56] VECCHIÉ A, BONAVENTURA A, TOLDO S, et al. IL-18 and infections: Is there a role for targeted therapies. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(3): 1638-1657. [57] BAO J, CHEN Z, XU L, et al. Rapamycin protects chondrocytes against IL-18-induced apoptosis and ameliorates rat osteoarthritis. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(6):5152-5167. [58] PENG CZ, CAO JM, XIAO T, et al. Concentration of IL-18 and PGE2 in synovial fluid in patients with osteoarthritis and its significance. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2006;31(6):862-865. [59] JIAO Y, WANG L, LU L, et al.The Role of Caspase-4 and NLRP1 in MCF7 Cell Pyroptosis Induced by hUCMSC-Secreted Factors. Stem Cells Int. 2020;2020:8867115. [60] FAN C, ZHAO X, GUO X, et al. P2X4 promotes interleukin‑1β production in osteoarthritis via NLRP1. Mol Med Rep. 2014;9(1):340-344. [61] WU Y, WANG Z, LIN Z, et al. Salvianolic Acid A Has Anti-Osteoarthritis Effect In Vitro and In Vivo. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:682. |
| [1] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Tan Yetong, Zhu Guangyu, Wang Rongtian, Wang Jian, Xue Zhipeng, Ma Sheng, Hu Yuanyi, Huang Ye, Ding Tiansong. Changes of lower limb force line and knee function after high tibial osteotomy in osteoporotic medial ventricular knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1325-1329. |
| [2] | Huang Linke, Wei Linhua, Jiang Jie, Liu Qian, Chen Weiwei. Effects of estrogen combined with treadmill exercise on bone mass and articular cartilage in ovariectomized mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1166-1171. |
| [3] | Ke Weiqiang, Chen Xianghui, Chen Xiaoling, Meng Jie, Ma Yanlin. Rituximab combined with autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in the treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and the expression of related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 915-920. |
| [4] | Yan Le, Zhang Huiping, Dai Lintong. Mesenchymal stem cells for allergic rhinitis: a meta-analysis based on animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 977-984. |
| [5] | Yuan Changshen, Guan Yanbing, Li Zhe, Rong Weiming, Liao Shuning, Chen Lewei, Mei Qijie, Duan Kan. Screening and verification of key genes of necroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 695-700. |
| [6] | Chen Guodong, Zheng Meiyan, Zhang Peng, Wang Zhenchao, Jin Lixin. Changes in sensory neurons and astrocytes and the expression of interleukin 1beta and glial fibrillary acidic protein in the rat spinal cord after selective dorsal rhizotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 726-731. |
| [7] | Li Long, Li Guangdi, Shi Hao, Deng Keqi. Circular RNA as a competing endogenous RNA is involved in the regulation of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 751-757. |
| [8] | Wan Guoli, Shi Chenhui, Wang Weishan, Li Ang, Shi Xunda, Cai Yi. Retrospective analysis of the influencing factors of chronic pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 558-564. |
| [9] | Gu Mingxi, Wang Bo, Tian Fengde, An Ning, Hao Ruihu, Wang Changcheng, Guo Lin. Comparison of early efficacy and safety of simultaneous and staged bilateral total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 565-571. |
| [10] | Yu He, Zheng Jiafa, Song Xiufeng, Guan Shengyi. Tibiotalocalcaneal arthrodesis with blood supplied fibular flap combined with hollow screw in the treatment of end-stage ankle osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 588-593. |
| [11] | Guo Yingqi, Gong Xianxu, Zhang Yan, Xiao Han, Wang Ye, Gu Wenguang. Meniscus extrusion and patellofemoral joint cartilage injury and bone marrow lesions: MRI semi-quantitative score [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 600-605. |
| [12] | Yu Jiaan, Liu Xinwei, Lian Hongyu, Liu Kexin, Li Zitao. Medial open-wedge tibial osteotomy versus lateral closed-wedge tibial osteotomy for unicompartmental knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 632-639. |
| [13] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Tan Yetong, Xue Zhipeng, Ma Sheng, Hu Yuanyi, Huang Ye, Ding Tiansong. Effect of distal tibial tuberosity-high tibial osteotomy on patellofemoral joint degeneration and patellar height [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(27): 4367-4372. |
| [14] | Xia Yubo, Tang Xiaoxia, Luo Wen, Xu Yongsheng, Yuan Changfei, Wang Zhe, Zhou Xiaohan, Tian Miao, Wang Tao, Guo Ying. Biomechanical response of ankle traction arthroplasty for ankle osteoarthritis through finite element modeling [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(22): 3469-3475. |
| [15] | Hu Wei, Yan Xianke . Effect of posterior cruciate ligament preserving knee prosthesis on gait and lower extremity venous return in varus knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(22): 3503-3507. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||