中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (46): 7528-7532.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.46.029
• 组织构建临床实践 clinical practice in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
膝骨关节炎关节液中丙二醛、超氧化物歧化酶在玻璃酸钠注射前后的变化
于清波,邓剑锋,高大新,宋 红,严佳亮,齐曦明,王东兴
- 秦皇岛市第一医院骨科,河北省秦皇岛市 066000
Effect of sodium hyaluronate on malondialdehyde and superoxide dismutase levels in the synovial fluid of patients with knee osteoarthritis
Yu Qing-bo, Deng Jian-feng, Gao Da-xin, Song Hong, Yan Jia-liang, Qi Xi-ming, Wang Dong-xing
- Department of Orthopedics, the First Municipal Hospital of Qinhuangdao, Qinhuangdao 066000, Shandong Province, China
摘要:
背景:玻璃酸钠关节腔注射是治疗膝骨关节炎的一种有效方法,疗效显著,不良反应少,但其作用机制尚不明确。
目的:通过检测玻璃酸钠注射前后膝骨关节炎关节液中丙二醛、超氧化物歧化酶水平,评价玻璃酸钠治疗膝骨关节炎的具体机制。
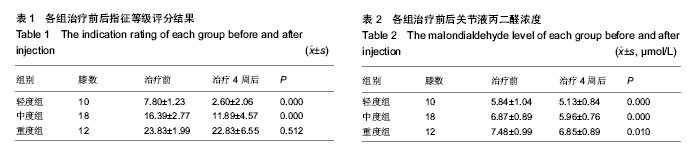
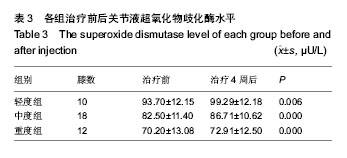
方法:纳入膝骨关节炎患者37例(40膝),根据日本膝骨关节炎指征等级分轻度组10例10膝、中度组17例18膝、重度组10例12膝,患膝关节注入玻璃酸钠25 mg,每周注射1次,连续5次为1个疗程。注射前及注射4周后检测关节液丙二醛、超氧化物歧化酶水平,以及按照日本膝骨关节炎指征等级对所有患者治疗前后行临床评分。
结果与结论:轻度组、中度组注射4周后临床评分较注射前显著降低(P < 0.05),重度组注射前后临床评分比较差异无显著性意义。3组注射4周后关节液丙二醛水平均较注射前显著下降(P < 0.05),关节液超氧化物歧化酶水平均较注射前显著升高(P < 0.05)。结果表明玻璃酸钠可通过降低关节液中丙二醛水平、升高超氧化物歧化酶水平治疗膝骨关节炎,并且更适用于轻、中度患者。
中图分类号: