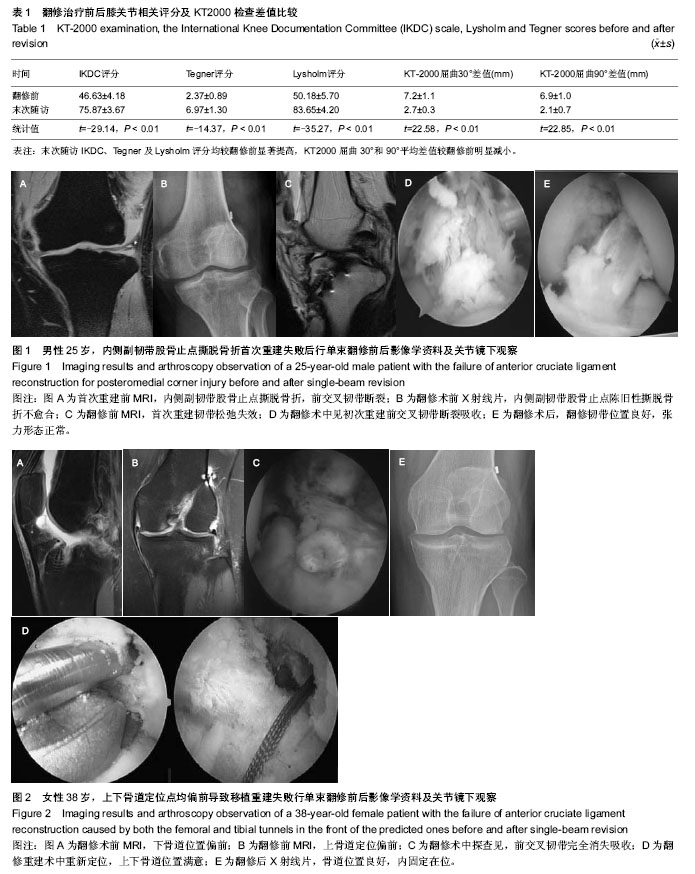
| [1] Sherman OH, Banfy MB. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: Which graft is best. Arthroscopy.2004;20(9): 974-980.
[2] 黄迅悟,常青,白一冰,等.关节镜下应用深低温冷冻异体跟腱重建后交叉韧带[J].骨与关节损伤杂志,2003,18(2):91-93.
[3] 张春礼,樊宏斌,吕荣,等.自体和异体肌腱移植重建前十字韧带后止点转归的组织学研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2004,24(3):146-149.
[4] Persson A, Fjeldsgaard K, Gjertsen JE, et al. Increased Risk of Revision With Hamstring Tendon Grafts Compared With Patellar Tendon Grafts After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Study of 12,643 Patients From the Norwegian Cruciate Ligament Registry, 2004-2012. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(2):285-291.
[5] Mariscalco MW, Flanigan DC, Mitchell J, et al. The influence of hamstring autograft size on patient-reported outcomes and risk of revision after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a Multicenter Orthopaedic Outcomes Network (MOON) Cohort Study. Arthroscopy.2013;29(12):1948-1953.
[6] Maletis GB, Inacio MC, Desmond JL, et al. Reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament: association of graft choice with increased risk of early revision. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(5): 623-628.
[7] Ventura A, Legnani C, Terzaghi C, et al. Revision surgery after failed ACL reconstruction with artificial ligaments: clinical, histologic and radiographic evaluation. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014;24(1):93-98.
[8] 马勇,敖英芳,崔国庆,等.前交叉韧带重建后翻修的临床研究[J].中华外科杂志,2008,46(9:650-653.
[9] 敖英芳,马勇,崔国庆,等.前交叉韧带重建失败的原因分析[J].中华外科杂志,2007,45(2):86-89.
[10] Song EK,Oh LS,Gill TJ,et al. Prospective comparative study of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using the double-bundle and single-bun- dle techniques. Am J Sports Med.2009;37(9):1705-1711.
[11] Lee S, Kim H, JalIg J, et al. Comparison of anterior and rotatory Laxity using navigation between single- and double-bundle ACL reconstruction:prospective randomized trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2012;20(4): 752-761.
[12] 张辉,冯华,洪雷,等.导航辅助下前十字韧带单束与双束重建的比较研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2012,32(6):557-564.
[13] Song EK, Seon JK, Yim JH, et al.Progression of osteoarthritis after double- and single-bundle anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(10):2340-2346.
[14] Taketomi S,Inui H, Nakamura K, et al. Three-dimensional fluoroscopic navigation guidance for femoral tunnel creation in revision anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Arthrosc Tech.2012;1(1):e95-99.
[15] Hofbauer M, Muller B, Murawski CD, et al. Strategies for revision surgery after primary double-bundle anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(9):2072-2080.
[16] 陈百成.合理选择单束和双束移植物重建前交叉韧带[J].中华关节外科杂志:电子版, 2009, 3(2): 137-140.
[17] Chen JL, Allen CR, Stephens TE, et al. Differences in mechanisms of failure, intraoperative findings, and surgical characteristics between single- and multiple-revision ACL reconstructions: a MARS cohort study.Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(7):1571-1578.
[18] Behrens SB, Lee BJ, Paller D, et al. Mechanical Properties of Revision ACL Reconstruction.J Knee Surg. 2014;27(2): 119-124.
[19] Ra HJ,Ha JK,Kim JG.One-stage revision anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with impacted bone graft after failed primary reconstruction. Orthopedics. 2013;36(11):860-863.
[20] Buda R, Ruffilli A, Di Caprio F, et al. Allograft salvage procedure in multiple-revision anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction.Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(2):402-410.
[21] Kievit AJ, Jonkers FJ, Barentsz JH, et al. A cross-sectional study comparing the rates of osteoarthritis, laxity, and quality of life in primary and revision anterior cruciate ligament reconstructions. Arthroscopy.2013;29(5):898-905.
[22] Griffith TB, Allen BJ, Levy BA, et al. Outcomes of repeat revision anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Am J Sports Med.2013;41(6):1296-1301. |