中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (16): 4154-4165.doi: 10.12307/2026.658
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
不同骨骼疾病动物模型中H型血管的生成及作用
彭 皓1,蒋 阳1,宋艳萍2,吴 泉3,姚 娜2,陈奇刚2,申 震2
- 1云南师范大学体育学院,云南省昆明市 650500;云南中医药大学第三附属医院,2康复科,3老年病科,云南省昆明市 650011
-
收稿日期:2025-04-27接受日期:2025-08-05出版日期:2026-06-08发布日期:2025-11-28 -
通讯作者:陈奇刚,主任医师,教授,硕士生导师,云南中医药大学第三附属医院康复科,云南省昆明市 650011 通讯作者:申震,博士,主治医师,云南中医药大学第三附属医院康复科,云南省昆明市 650011 -
作者简介:彭皓,男,1998年生,在读博士研究生,主要从事运动健康促进、运动康复研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(82360943),项目负责人:申震;云南省科技厅研究计划项目(20221AU070120,202101AZ070001-123),项目负责人:申震;云南省“兴滇英才”支持计划青年人才专项项目(XDYC-QNRC-2022-0609),
项目负责人:申震
H-type angiogenesis and its role in various skeletal disease animal models
Peng Hao1, Jiang Yang1, Song Yanping2, Wu Quan3, Yao Na2, Chen Qigang2, Shen Zhen2
- 1School of Physical Education, Yunnan Normal University, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China; 2Department of Rehabilitation, 3Department of Geriatrics, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Yunnan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650011, Yunnan Province, China
-
Received:2025-04-27Accepted:2025-08-05Online:2026-06-08Published:2025-11-28 -
Contact:Chen Qigang, Chief physician, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Rehabilitation, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Yunnan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650011, Yunnan Province, China Co-corresponding author: Shen Zhen, PhD, Attending physician, Department of Rehabilitation, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Yunnan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650011, Yunnan Province, China -
About author:Peng Hao, PhD candidate, School of Physical Education, Normal University, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82360943 (to SZ); Research Program of Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Department, Nos. 20221AU070120 and 202101AZ070001-123 (both to SZ); Young Talent Special Project of Yunnan Province “Xingdian Yingcai” Support Program, No. XDYC-QNRC-2022-0609 (to SZ)
摘要:
文题释义:
H型血管:是一种对CD31和内皮黏蛋白EMCN同时高表达的特异性毛细血管亚型,具有特殊的形态、功能和分子特性。这些H型血管可参与骨内血管的生长,维持血管周围骨祖细胞的数量,并促进血管生成与骨生成。
动物模型:指在医学和生物学研究中,使用特定动物代替人类进行疾病机制研究、药物开发和治疗方案探索的实验对象。
背景:H型血管因其独特的功能为深入理解血管介导的骨代谢调控机制提供了新的视角和切入点。
目的:探讨H型血管在不同骨骼疾病动物模型中的生成机制及对骨代谢的影响。
方法:系统检索CNKI、维普、万方、PubMed、Scopus和Web of Science数据库中2014年1月至2025年2月收录的H型血管相关中英文文献。剔除重复及不符合纳入标准的文献,对141篇涉及不同骨骼疾病动物模型中H型血管生成的文献进行系统分析。
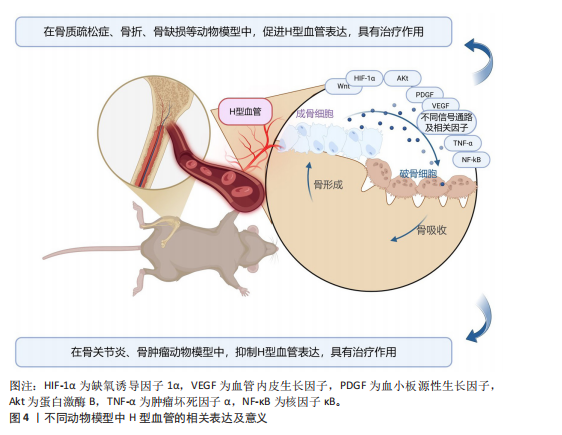
结果与结论:研究表明,H型血管在不同的骨骼疾病模型中表现出特定的生成机制和生物学功能。H型血管不仅在骨内血管生成中发挥重要作用,还与骨代谢密切相关,能够作为评估骨量水平的早期标志物。不同骨骼疾病动物模型中H型血管生成及作用不尽相同。在骨质疏松症、骨折、骨坏死等骨骼疾病中,通过促进H型血管表达,可显著改善血管重塑与骨再生能力;而在骨关节炎、骨肿瘤等恶性骨骼疾病中,选择性抑制H型血管表达则成为潜在的治疗干预策略。研究还揭示了多条关键信号通路在H型血管生成中的重要作用,如缺氧诱导因子1α/血管内皮生长因子、血小板源性生长因子BB、Wnt/β-catenin等,为理解血管介导的骨代谢调控机制提供了新的科学视角,同时为H型血管作为潜在治疗靶点的临床应用价值提供了重要理论基础。通过分析不同骨骼疾病动物模型中H型血管生成的作用,将为进一步深入探究人类骨关节疾病机制及治疗靶点提供重要依据。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
彭 皓, 蒋 阳, 宋艳萍, 吴 泉, 姚 娜, 陈奇刚, 申 震. 不同骨骼疾病动物模型中H型血管的生成及作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(16): 4154-4165.
Peng Hao, Jiang Yang, Song Yanping, Wu Quan, Yao Na, Chen Qigang, Shen Zhen. H-type angiogenesis and its role in various skeletal disease animal models[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(16): 4154-4165.
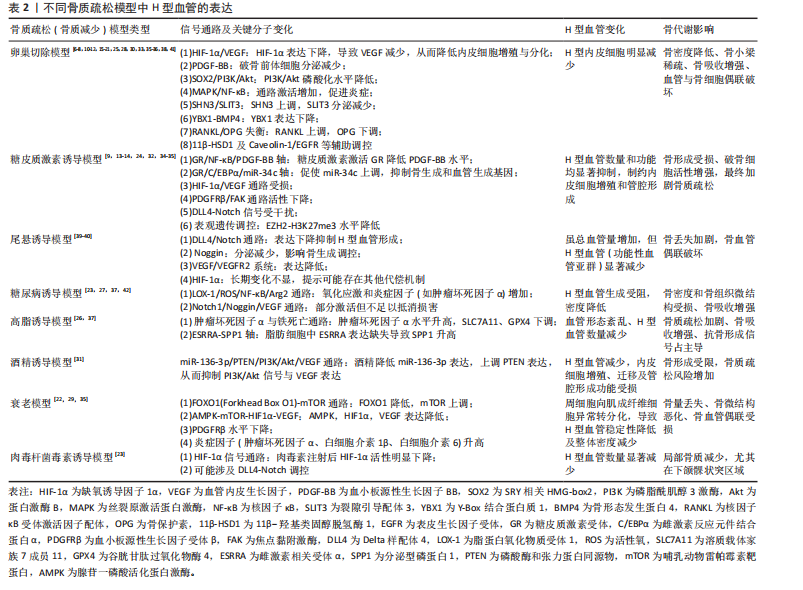
2.2 骨质疏松模型中H型血管的生成及作用 骨质疏松症是一种以骨量减少、骨微结构破坏为特征的全身性骨代谢性疾病,严重影响患者的生活质量。H型血管作为连接血管网络与骨组织的特殊血管亚型,在骨代谢中扮演着核心角色。在此次纳入的37篇有关骨质疏松(骨质减少)动物模型研究中[6-42],涵括了卵巢切除模型[6-8,10-12,15-21,25,28,30,33,35-36,38,41]、糖皮质激素诱导模型[9,13-14,24,32,34-35]、尾悬诱导模型[39-40]、糖尿病诱导模型[23,27,37,42]、高脂诱导模型[26,37]、酒精诱导模型[31]、衰老模型[22,29,35]、肉毒杆菌毒素诱导模型[23],见表2。研究表明,H型血管数量减少往往先于骨密度下降出现,是骨质疏松早期的重要标志,揭示了其作为早期干预潜在靶点的价值。虽然不同病理模型中的触发机制存在差异,但多个模型却显示出一些共性机制的异常,如缺氧诱导因子1α/血管内皮生长因子通路在卵巢切除、糖皮质激素、肉毒素和衰老模型中均受到抑制;血小板源性生长因子BB相关信号在卵巢切除和糖皮质激素模型中显著减少;磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路在卵巢切除和酒精诱导模型中活性降低;氧化应激和炎症反应在糖尿病和高脂饮食模型中表现突出;Notch信号通路虽在多个模型中均有参与,但在骨组织中呈现出与其他器官不同的特性,主要为正向调节作用等。
在骨质疏松的病理状态下,H型血管数量的减少与骨生成能力下降呈现正相关关系。这一过程受到多种因素的影响,如雌激素缺乏、糖皮质激素长期使用、年龄增长、慢性炎症和代谢紊乱等。值得注意的是,现有研究显示在多病共存状态下,多种病理因素的叠加可能对H型血管产生更严重的损害[22,27,37]。如糖尿病合并高脂饮食可能通过白细胞氧化物结合蛋白1/活性氧/核因子κB通路和肿瘤坏死因子α介导的铁死亡通路协同作用,加剧氧化应激和炎症反应,进一步抑制H型血管生成[27,31,37]。
衰老合并糖皮质激素治疗导致的叉头框蛋白O1-哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白通路和腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶-哺乳动物目标雷帕霉素-缺氧诱导因子1α-血管内皮生长因子通路异常,叠加糖皮质激素对缺氧诱导因子1α/血管内皮生长因子通路的抑制,可能对H型血管形成产生更严重的阻碍[9,13-14,22,24,29,32,34-35]。
此外,衰老合并糖皮质激素对周细胞功能的共同影响可能进一步削弱血管稳定性。绝经后骨质疏松合并糖尿病时,雌激素缺乏导致的缺氧诱导因子1α/血管内皮生长因子和磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B通路活性降低,结合糖尿病状态下的白细胞氧化物结合蛋白1/活性氧通路激活,可能加速H型血管损伤,并通过多重机制促进骨吸收,加剧骨质疏松进
程[23,27,37,42]。当多种病理因素同时存在时,可能导致多个信号通路的同时紊乱,使恢复H型血管功能的难度显著增加,需要综合考虑多靶点干预策略。在未来研究中,深入阐明多病共存状态下H型血管的协同损伤机制,研发针对多靶点的综合干预策略,将有助于为复杂病理环境下的骨质疏松症提供更有效的治疗方案。
2.3 骨折模型中H型血管生成及作用 骨折模型是研究骨折愈合机制和评估治疗策略的重要工具。自20世纪初以来,各种动物骨折模型已被广泛应用于骨折研究领域,然而对于骨折愈合的分子机制和细胞交互作用的认识仍有待深入。近年来,通过调控骨折愈合过程中的血管生成来促进骨修复已成为国内外学者研究的热点方向之一,其中H型血管在骨折愈合中的关键作用尤其受到广泛关注[43-64]。多种骨折模型研究显示,H型血管在正常骨折愈合早期(1-7 d)比例持续升高,于第7天达到峰值后逐渐下降,而骨质疏松状态下则呈现显著延迟表达模 式[43,50-54]。这种时间依赖性变化为理解骨折愈合的关键时间窗口提供了重要依据,同时也揭示了H型血管与成骨过程之间存在的动态耦合关系。
H型血管的生成受多条信号通路精密调控(表3),其中前破骨细胞分泌的血小板源性生长因子BB被认为是促进H型血管形成的核心因子。研究显示,Omentin-1可通过抑制炎症因子(特别是肿瘤坏死因子α)影响破骨细胞分化,促进前破骨细胞积累,增加血小板源性生长因子BB的产生,进而增强H型血管形成,最终促进骨修复[45]。相反, G蛋白偶联受体激酶相互作用蛋白1基因敲除则会降低H型血管相关的破骨前体细胞中血小板源性生长因子BB的分泌,从而损害骨修复过程[49]。
在骨生成过程中,血小板源性生长因子BB主要由血小板脱颗粒化释放,发挥着多重生物学功能。它通过上调血管内皮生长因子表达促进血管生成,同时向成骨细胞传递趋化性和促有丝分裂信号以增强骨形成[147]。XIE等[148]研究进一步揭示,骨膜区域的破骨前体细胞是血小板源性生长因子BB的另一重要来源。血小板源性生长因子BB在骨血管偶联中起到双重作用:一方面刺激内皮祖细胞和间充质干细胞迁移,促进血管网络形成;另一方面作为关键调控因子,动员间充质来源细胞,维持新生血管稳定性,并协同调节成骨细胞分化过程。
除血小板源性生长因子BB外,多种信号通路协同参与H型血管调控。缺氧诱导因子1α/血管内皮生长
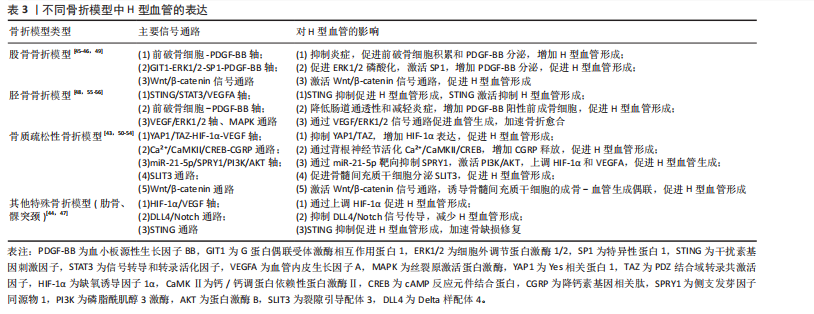
因子通路在骨折后低氧微环境中被迅速激活,强化局部血管网络建立,并通过调控相关转录因子介导血管内皮细胞的存活和分化。Wnt/β-catenin及YAP1/PDZ结合基转录共激活因子信号通路为骨组织微环境中成骨细胞和血管内皮细胞之间的信息交流提供了重要平台,两者的交互作用不仅促进血管生成,还通过诱导成骨细胞的定位和活化推动新骨形成[43,50-54]。近期研究还发现STING信号和Delta样配体4/Notch通路等在调控H型血管生成中发挥着辅助作用,展现出复杂的网络调节特性[44,47]。由此可见,不同骨折模型中揭示的上述多条信号通路不仅阐明了H型血管在血管生成与骨形成偶联中的生物学功能,更为临床上利用药物重定位策略或生物工程手段改善骨折愈合,尤其是骨质疏松性骨折的治疗效果提供了前沿启示。对于未来的临床应用而言,进一步精准调控这些信号通路,构建高效促进H型血管增生的策略,将可能显著改善骨折修复的质量和愈合速度。
2.4 骨缺损模型中H型血管生成及作用 骨缺损修复是临床上亟待攻克的难题,而促进骨再生和血管生成是实现成功修复的关键。研究表明,H型血管在骨缺损修复过程中扮演着至关重要的角色[65-104]。无论是在扁平骨还是长骨骨缺损中,H型血管不仅为骨再生提供必要的营养和氧气支持,还通过结合多种生长因子和细胞因子,直接参与骨细胞的募集、分化及成骨微环境的构建。为探究不同类型骨缺损的修复过程及机制,研究者建立了多种动物模型,如大鼠颅骨临界尺寸缺损模型、大鼠胫骨钻孔缺损模型、小鼠股骨及下颌骨缺损模型以及兔颅骨增高模型等[65-104]。相较于骨折模型,这些骨缺损模型的研究主要聚焦于生物材料的修复、植入等方面。
在骨缺损修复早期,局部组织缺氧环境激活缺氧诱导因子1α信号通路,是H型血管形成的关键调控机制[149]。多项研究证实,在股骨缺损模型中,通过去铁胺等缺氧诱导因子1α稳定剂处理后,可显著增加缺损区H型血管密度[150]。具体而言,去铁胺通过抑制脯氨酰羟化酶活性,防止缺氧诱导因子1α降解,进而上调血管内皮生长因子及其受体表达,促进H型血管生成[86]。而在大鼠牙槽骨缺损模型中,研究者观察到Notch信号相关分子高度活跃于H型血管内皮细胞。通过γ-分泌酶抑制剂DAPT抑制Notch信号,导致H型血管标志物Emcn表达显著降低,而过度激活Notch则增加H型血管数量及覆盖面积[81]。值得注意的是,Notch信号的激活还增强了H型血管内皮细胞与Osterix+/Runx2+骨祖细胞的空间共定位,提示Notch信号参与调控血管-骨偶联过程。进一步研究发现,在小鼠股骨和颅骨缺损模型中,SLIT3可通过其受体ROBO1作用于内皮细胞,激活YAP1转录调控因子,进而促进H型血管形成[103],特别是在力学刺激条件下,这一通路被进一步增强,形成“SLIT3/ROBO1/YAP1/缺氧诱导因子1α”复合调控网络。例如,靶向蛋白降解技术处理使间充质干细胞中SLIT3表达上调,通过ROBO1激活内皮细胞中的YAP1,进而稳定缺氧诱导因子1α,增强H型血管生成及其促骨再生功能[103]。机械负荷对H型血管生成同样发挥着重要作用。研究发现,在机械刺激下,鞘氨醇-1-磷酸受体1在H型血管中的表达显著增强。作为一种机械敏感性受体,鞘氨醇-1-磷酸受体1激活后通过Rho/ROCK(rho相关蛋白激酶)通路促使YAP转移至细胞核,调控血管生成相关基因表达。若抑制鞘氨醇-1-磷酸受体1或阻断YAP核转位,都会显著影响机械负荷诱导的H型血管形成[63]。
在骨缺损修复过程中,H型血管呈现明显的时空动态变化特征[65-104]。早期(数小时至3 d)阶段,局部创面形成缺氧环境迅速激活缺氧诱导因子1α通路,在缺损边缘及肉芽组织中开始出现H型血管;中期(7 d至2周)阶段,H型血管数量达到高峰,并在新生骨小梁的生长前沿区域呈稳定的空间分布,周围聚集大量的Osterix+和Runx2+骨祖细胞,实现“血管-骨偶联”;晚期(4周及以后)阶段,虽然整体H型血管数量逐步减少,但功能性和成熟性增强,形成与新生骨组织紧密整合的血管网络。
对H型血管在骨再生中作用机制的深入研究为开发新型骨修复策略提供了理论依据,如基于支架材料的功能化设计、针对关键通路的药物干预以及机械刺激与材料协同疗法等。未来,随着对H型血管动态变化和空间分布机制的进一步认识,有望实现精准调控局部微环境,加速骨愈合并提高骨愈合质量,为复杂骨损伤和骨质疏松性骨折等难治性疾病带来新的转化医学契机。
2.5 牵引成骨模型中H型血管生成及作用 牵引成骨技术又称Ilizarov技术,是Ilizarov GA医生于20世纪60年代提出的一种骨再生技术[151],通过将截断的骨段按一定速度和频率牵开,机械牵拉刺激诱导骨段间隙中新骨形成,继而达到修复骨缺损的目的。血管生成和成骨分化是骨修复重建中的关键环节,二者之间在空间和时间上存在的密切关系被称为“成血管-成骨偶联作用”。 牵引成骨技术中新骨生成耦合血管新生,成血管-成骨偶联作用贯穿整个牵引成骨过程,而H型血管亦可耦合骨生成,可增强局部成血管-成骨偶联作用,在牵引成骨调控骨修复过程中扮演重要角色[105-110]。赵芝鹤等[152]在SD大鼠颅骨骨缝牵引成骨动物模型中鉴定出了H型血管形成,证实了H型血管在颅骨骨缝牵引成骨模型中对早期骨生成发挥着重要作用。课题组通过前期研究在SD大鼠胫骨牵引成骨模型中同样鉴定出了H型血管的形成,证实了牵张应力对H型血管生成具有促进作用,且牵引成骨模型中H型血管生成与牵引成骨过程中血管生成和骨生成效果强弱表现协同一致性,即H型血管高增殖,增强了牵引成骨过程中成血管-成骨偶联作用,继而进一步促进了骨生成[105,153]。与此同时,进一步的研究成果也证实了口服骨碎补总黄酮可促进牵引成骨技术修复SD大鼠胫骨骨缺损,且潜在机制与血小板源性生长因子BB信号调控H型血管生成有关[109-110],这表明了H型血管在牵引成骨技术中扮演的重要角色,为深入探究牵引成骨技术修复骨缺损机制和药物作用靶点提供了新的思路。
2.6 诱导膜模型中H型血管生成及作用 诱导膜技术即Masquelet技术,是法国医师Masquelet于1986年首次提出的一种骨缺损治疗技术[154]。经过数十年的发展,诱导膜技术被广泛应用于肢体形态与功能重建领域,已成为临床中处理各类型骨缺损的有效手段[155]。然而,当前对于诱导膜技术促进骨缺损修复的认识尚不够全面。课题组团队在2020年指出,当前诱导膜技术仍需要深入研究,以进一步明确诱导膜的生物特性[156]。近年来,通过调控诱导膜血管生成来增强诱导膜技术的骨修复效果已成为国内外学者该领域研究的方向之一,而H型血管在诱导膜技术中所发挥的作用又成为关注的重点。课题组团队在SD大鼠胫骨大段骨缺损模型上的最新研究成果也进一步发现了骨诱导膜中H型血管呈动态表达并在骨水泥植入后6周达高峰,这表明了H型血管在诱导膜模型中对促进骨缺损修复具有积极作用和重要意义[112]。
2.7 骨坏死模型中H型血管生成及作用 骨坏死是一种病因复杂、涉及多个病理过程的严重骨骼疾病。近年来,调控骨血管生成以改善骨坏死已成为国内外学者研究的重要方向之一。H型血管在骨坏死模型中的作用逐渐引起关注[113-121]。研究表明,在骨坏死的早期阶段,缺氧诱导因子1α和血管内皮生长因子的表达降低,伴随骨血管生成的减少[157]。于海洋等[115]在大鼠股骨头坏死模型中发现,糖皮质激素可通过下调缺氧诱导因子1α/血管内皮生长因子信号通路,进而抑制H型血管的形成,导致骨组织缺血缺氧,最终引发骨坏死,免疫荧光染色结果显示,与正常对照组相比,骨坏死模型组大鼠股骨头中H型血管数量明显减少。这一发现提示了H型血管损害可能是糖皮质激素性骨坏死的关键致病环节之一。在实验动物模型中,可以观察到H型血管标志物(如CD31和内皮黏蛋白EMCN)的表达数量在不同修复阶段的显著变化。实验结果表明,骨坏死早期H型血管的数量普遍较低,但随着治疗(如使用血小板源性生长因子BB或天然药物如银杏叶提取物)的实施,H型血管的数量逐渐增加,这与骨质新生反应呈正相关[113-121]。在一些实验组中,特别是在促进血管生成治疗后,标志物浓度的显著提升不仅验证了H型血管生成的促进作用,也显示了其在骨坏死修复过程中的监测和评估价值。H型血管由于其独特的功能,为深入理解血管介导的骨骼代谢调控机制提供了新的视角和切入点。这一研究进展也促使骨科学研究从传统的“骨本位”范式向“骨-血管整合”方向的重要转变。
2.8 骨关节炎模型中H型血管生成及作用 骨关节炎是一种复杂的慢性关节退行性疾病,其发展过程中H型血管扮演着至关重要的角色。这类特殊血管不仅仅是被动的结构单元,更是疾病进展的关键调控因子,通过复杂的信号通路网络参与骨代谢重塑、炎症调控和软骨退变过程。在骨关节炎的发病机制中,H型血管的生成与功能表现出显著的病理特征,其异常扩张往往与疾病的加重密切相关。多种研究模型,包括前交叉韧带切断小鼠模型、高脂饮食诱导的小鼠模型和腰椎关节炎小鼠模型等,揭示了H型血管生成的核心机制[122-143]。以C57BL/6J小鼠和前交叉韧带切断小鼠模型为例,骨桥蛋白通过促使H型血管在软骨下骨中的形成,影响骨转化及重塑,同时磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路的活化又进一步促进这一过程[133];而在腰椎关节炎模型中,低氧处理脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体通过抑制血小板源性生长因子BB,显著减少了H型血管的生成,显示出治疗骨关节炎的潜力[132];在高脂饮食诱导的小鼠模型中,巨噬细胞活性增加和前列腺素分泌的变化促进了H型血管的形成,反映出炎症在骨代谢调控中的重要性等[137]。
在骨关节炎的不同发展阶段,H型血管数量往往呈现动态变化:早期阶段,血管数量显著增加,促进骨生成和软骨重塑;中期阶段,血管密度持续增长,参与炎症和代谢调节;晚期阶段,过度血管生成可能加剧关节退变。其中,软骨下骨的异常重塑在骨关节炎的发生发展中起关键作用,H型血管形成增加被认为是促进疾病进展的重要因素。研究者在内侧半月板不稳定诱导的骨关节炎小鼠模型中发现哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白复合体1激活可刺激关节软骨细胞中血管内皮生长因子A的产生和软骨下骨中H型血管的形成[143]。值得注意的是,血小板源性生长因子受体β通过调节血小板源性生长因子受体β/Talin1/FAK复合物促进血管生成,被认为是骨关节炎中H型血管异常的关键环节[130]。而内皮细胞特异性血小板源性生长因子受体β缺失可显著减少H型血管形成,改善软骨下骨退化并缓解上覆软骨变性。除血小板源性生长因子受体β外,研究者还发现多种药物和生物制剂可通过调节H型血管的生成发挥骨关节炎防治作用。如邻苯二甲酸二丁酯[129]、丹参酮IIA等化合物具有抑制骨关节炎进展的潜力[140]。这些化合物可以通过下调血管内皮生长因子A和血管生成素1等因子的表达,影响H型血管的异常增殖,从而抑制了成骨和血管形成的病理偶联机制,延缓疾病进展。这些发现不仅拓展了对骨关节炎发病机制的认识,也为开发为新型治疗策略提供了重要的理论基础和潜在靶点。
2.9 骨肿瘤模型中H型血管生成及作用 骨髓是多种实体瘤的首选转移部位,研究表明癌细胞在骨髓内的特定生态位中定植,以支持其长期繁殖,然而,目前尚不清楚介导这些生态位相互作用的确切位置和机制[145]。近年来,随着骨髓微环境研究的深入,H型血管在其中的关键作用逐渐被揭示。H型血管在骨髓微环境中扮演着核心角色,不仅支持正常造血功能,还与肿瘤转移和进展密切相关[144-146]。
SINGH等[144]研究表明,H型血管通过提供小动脉壁龛来支持造血干细胞和间充质干细胞的增殖。这种微环境具有维持细胞静止的特性,不仅适用于造血干细胞,也适用于播散性肿瘤细胞。随着年龄增长,小动脉壁龛数量逐渐减少,可能影响骨髓微环境的稳态。在骨转移性肿瘤中,特别是乳腺癌,H型血管为肿瘤细胞的骨髓浸润提供了有利环境[145]。随着肿瘤进展,癌细胞能够重塑局部血管网络,导致血管形态异常、内皮细胞表型改变和血管密度降低。值得注意的是,尽管重塑后的血管表达高水平的EMCN和CD31,但它们缺乏正常H型血管的特征性周细胞和骨前体细胞覆盖,形成了一种独特的肿瘤相关血管亚型,这种肿瘤诱导的血管重塑进一步促进了肿瘤生长和骨质破坏。深入理解H型血管在骨转移中的双重作用,既为播散性肿瘤细胞提供休眠微环境,又为肿瘤生长提供有利条件,有望为开发针对肿瘤-血管相互作用的新型治疗策略提供重要依据,特别是在靶向早期转移和预防肿瘤复发方面具有潜在的临床应用价值。
不同动物模型中H型血管的相关表达及意义,见图4。
| [1] 彭荟桢,蔡明详,刘湘宁.骨修复过程中的血管生成调控:新思路与新方法[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(15):2400-2405. [2] KUSUMBE AP, RAMASAMY SK, ADAMS RH. Coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by a specific vessel subtype in bone. Nature. 2014;507(7492):323-328. [3] RAMASAMY SK, KUSUMBE AP, WANG L, et al. Endothelial Notch activity promotes angiogenesis and osteogenesis in bone. Nature. 2014;507(7492):376-380. [4] PENG Y, WU S, LI Y, et al. Type H blood vessels in bone modeling and remodeling. Theranostics. 2020;10(1):426-436. [5] 彭皓,陈奇刚,申震.H型血管在不同骨骼疾病中研究热点的可视化分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2026,30(3):760-769. [6] LI H, HU S, WU R, et al. 11β-Hydroxysteroid Dehydrogenase Type 1 Facilitates Osteoporosis by Turning on Osteoclastogenesis through Hippo Signaling. Int J Biol Sci. 2023;19(11):3628-3639. [7] 胡劲涛,阮立奇,钱剑胜,等.补肾活血方对去势骨质疏松小鼠骨-血管形成偶联调节作用的实验研究[J].中国中医药科技,2024,31(6):971-975. [8] WU F, SONG C, ZHEN G, et al. Exosomes derived from BMSCs in osteogenic differentiation promote type H blood vessel angiogenesis through miR-150-5p mediated metabolic reprogramming of endothelial cells. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024;81(1):344. [9] 李素丽,詹先琴,张艳君,等.高剂量糖皮质激素对成年雄性小鼠PDGF-BB分泌及H型血管生长的作用研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2021,27(12):1752-1756. [10] 王亮,盛茂,袁晔,等.骨内H型血管在去势骨质疏松症模型中的变化[J].中华骨科杂志,2020,40(13):873-879. [11] 田佳庆,韦雨柔,肖方骏,等.虎杖苷调控HIF-1α/VEGF信号通路对绝经后骨质疏松症大鼠H型血管生成的影响[J].中成药, 2024,46(5):1672-1676. [12] WANG X, LI X, LI J, et al. Mechanical loading stimulates bone angiogenesis through enhancing type H vessel formation and downregulating exosomal miR-214-3p from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. FASEB J. 2021;35(1):e21150. [13] WANG T, YANG L, LIANG Z, et al. Pulsed electromagnetic fields attenuate glucocorticoid-induced bone loss by targeting senescent LepR+ bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells. Biomater Adv. 2022;133:112635. [14] 申前进,吕珊,阳文新,等.糖皮质激素通过抑制内皮细胞形成骨血管导致骨质疏松的实验研究[J].颈腰痛杂志,2019, 40(6):727-731. [15] LI H, LIAO L, HU Y, et al. Identification of Type H Vessels in Mice Mandibular Condyle. J Dent Res. 2021;100(9):983-992. [16] 上官文姬,张跃辉,岳江,等.柚皮苷通过HIF-1α/VEGF信号促进H型血管抗骨质疏松的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2022,28(12):1755-1759. [17] CUI Y, GUO Y, KONG L, et al. A bone-targeted engineered exosome platform delivering siRNA to treat osteoporosis. Bioact Mater. 2021;10:207-221. [18] LIN X, XU F, ZHANG KW, et al. Acacetin Prevents Bone Loss by Disrupting Osteoclast Formation and Promoting Type H Vessel Formation in Ovariectomy-Induced Osteoporosis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:796227. [19] LI Z, LIU C, LIU X, et al. Aucubin Impeded Preosteoclast Fusion and Enhanced CD31hi EMCNhi Vessel Angiogenesis in Ovariectomized Mice. Stem Cells Int. 2022; 2022:5226771. [20] WANG Q, ZHOU J, WANG X, et al. Coupling induction of osteogenesis and type H vessels by pulsed electromagnetic fields in ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in mice. Bone. 2022;154:116211. [21] JIA J, HE R, YAO Z, et al. Daidzein alleviates osteoporosis by promoting osteogenesis and angiogenesis coupling. PeerJ. 2023;11: e16121. [22] CHENG C, DENG M, CHENG C, et al. FOXO1-mTOR pathway in vascular pericyte regulates the formation of type H vessels to control bone metabolism. J Orthop Translat. 2024;49:246-263. [23] CHEN W, JIN X, WANG T, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 interferes with the progression of diabetic osteoporosis by promoting type H angiogenesis modulating vasculogenic and osteogenic coupling. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1010937. [24] PENG Y, LV S, LI Y, et al. Glucocorticoids Disrupt Skeletal Angiogenesis Through Transrepression of NF-κB-Mediated Preosteoclast Pdgfb Transcription in Young Mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2020;35(6):1188-1202. [25] HUANG J, YIN H, RAO SS, et al. Harmine enhances type H vessel formation and prevents bone loss in ovariectomized mice. Theranostics. 2018;8(9):2435-2446. [26] CHEN X, LIU C, YU R, et al. Interaction between ferroptosis and TNF-α: Impact in obesity-related osteoporosis. FASEB J. 2023;37(6):e22947. [27] QIU J, LIU J, TIAN L, et al. Knockdown of LOX-1 ameliorates bone quality and generation of type H blood vessels in diabetic mice. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2024;752:109870. [28] ABDURAHMAN A, LI X, LI J, et al. Loading-driven PI3K/Akt signaling and erythropoiesis enhanced angiogenesis and osteogenesis in a postmenopausal osteoporosis mouse model. Bone. 2022;157:116346. [29] GAO B, LIN X, JING H, et al. Local delivery of tetramethylpyrazine eliminates the senescent phenotype of bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells and creates an anti-inflammatory and angiogenic environment in aging mice. Aging Cell. 2018;17(3):e12741. [30] SHANGGUAN Y, WU Z, XIE X, et al. Low-activity programming of the PDGFRβ/FAK pathway mediates H-type vessel dysplasia and high susceptibility to osteoporosis in female offspring rats after prenatal dexamethasone exposure. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021;185:114414. [31] CHEN Y, YU H, ZHU D, et al. miR-136-3p targets PTEN to regulate vascularization and bone formation and ameliorates alcohol-induced osteopenia. FASEB J. 2020; 34(4):5348-5362. [32] LU J, HU D, MA C, et al. Modified Qing’ e Pills exerts anti-osteoporosis effects and prevents bone loss by enhancing type H blood vessel formation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:998971. [33] SONG C, CAO J, LEI Y, et al. Nuciferine prevents bone loss by disrupting multinucleated osteoclast formation and promoting type H vessel formation. FASEB J. 2020;34(3):4798-4811. [34] YANG P, LV S, WANG Y, et al. Preservation of type H vessels and osteoblasts by enhanced preosteoclast platelet-derived growth factor type BB attenuates glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in growing mice. Bone. 2018; 114:1-13. [35] XIAO CL, LIU LL, TANG W, et al. Reduction of the trans-cortical vessel was associated with bone loss, another underlying mechanism of osteoporosis. Microvasc Res. 2024;152:104650. [36] WANG L, JIA P, SHAN Y, et al. Synergistic protection of bone vasculature and bone mass by desferrioxamine in osteoporotic mice. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(5):6642-6649. [37] HUANG T, LU Z, WANG Z, et al. Targeting adipocyte ESRRA promotes osteogenesis and vascular formation in adipocyte-rich bone marrow. Nat Commun. 2024; 15(1):3769. [38] LIN H, LIN R, HOU J, et al. Targeting endothelial PDGFR-β facilitates angiogenesis-associated bone formation through the PAK1/NICD axis. J Cell Physiol. 2024;239(8):e31291. [39] WANG S, YANG X, DING D, et al. The changes of bone vessels and their role in bone loss in tail-suspended rats. Acta Astronaut. 2021;189:368-378. [40] LIANG S, LING S, DU R, et al. The coupling of reduced type H vessels with unloading-induced bone loss and the protection role of Panax quinquefolium saponin in the male mice. Bone. 2021;143:115712. [41] LI YJ, GUO Q, YE MS, et al. YBX1 promotes type H vessel-dependent bone formation in an m5C-dependent manner. JCI Insight. 2024;9(4):e172345. [42] JIN X, SUN Y, BAI R, et al. Zhuang-Gu-Fang intervenes vasculogenic and osteogenic coupling in GK rats through Notch1/Noggin/VEGF pathway. Heliyon. 2024;10(6):e28014. [43] 胡晓惠,孙康晖,过丽强,等.基于H型血管生成益气化瘀方对去卵巢小鼠骨折愈合的机制研究[J].上海中医药大学学报,2024,38(6):75-81. [44] LENG S, CONG R, XIA Y, et al. Deferoxamine Accelerates Mandibular Condylar Neck Fracture Early Bone Healing by Promoting Type H Vessel Proliferation. J Oral Rehabil. 2025;52(1):17-26. [45] FENG SK, CHEN TH, LI HM, et al. Deficiency of Omentin-1 leads to delayed fracture healing through excessive inflammation and reduced CD31hiEmcnhi vessels. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021;534:111373. [46] LIU JH, YUE T, LUO ZW, et al. Akkermansia muciniphila promotes type H vessel formation and bone fracture healing by reducing gut permeability and inflammation. Dis Model Mech. 2020;13(11):dmm043620. [47] WANG L, HU R, XU P, et al. CD90’s role in vascularization and healing of rib fractures: insights from Dll4/notch regulation. Inflamm Res. 2024;73(12):2263-2277. [48] DING L, GU S, ZHOU B, et al. Ginsenoside Compound K Enhances Fracture Healing via Promoting Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:855393. [49] XU T, LUO Y, KONG F, et al. GIT1 is critical for formation of the CD31hiEmcnhi vessel subtype in coupling osteogenesis with angiogenesis via modulating preosteoclasts secretion of PDGF-BB. Bone. 2019;122:218-230. [50] LI X, FANG S, WANG S, et al. Hypoxia preconditioning of adipose stem cell-derived exosomes loaded in gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) promote type H angiogenesis and osteoporotic fracture repair. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024;22(1):112. [51] MI J, XU JK, YAO Z, et al. Implantable Electrical Stimulation at Dorsal Root Ganglions Accelerates Osteoporotic Fracture Healing via Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(1):e2103005. [52] RUAN Z, YIN H, WAN TF, et al. Metformin accelerates bone fracture healing by promoting type H vessel formation through inhibition of YAP1/TAZ expression. Bone Res. 2023;11(1):45. [53] ZHENG S, HU G, ZHENG J, et al. Osthole accelerates osteoporotic fracture healing by inducing the osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling of BMSCs via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Phytother Res. 2024;38(8):4022-4035. [54] TIAN S, ZOU Y, WANG J, et al. Protective effect of Du-Zhong-Wan against osteoporotic fracture by targeting the osteoblastogenesis and angiogenesis couple factor SLIT3. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022;295: 115399. [55] CHEN X, HE W, SUN M, et al. STING inhibition accelerates the bone healing process while enhancing type H vessel formation. FASEB J. 2021;35(11):e21964. [56] WEI X, WANG J, DENG YY, et al. Tubiechong patching promotes tibia fracture healing in rats by regulating angiogenesis through the VEGF/ERK1/2 signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;301:115851. [57] SARKAR N, ZHAO J, ZHANG NY, et al. 3D printed O2-generating scaffolds enhance osteoprogenitor- and type H vessel recruitment during bone healing. Acta Biomater. 2024;185:126-143. [58] YAN C, ZHANG P, QIN Q, et al. 3D-printed bone regeneration scaffolds modulate bone metabolic homeostasis through vascularization for osteoporotic bone defects. Biomaterials. 2024;311:122699. [59] 汤勇,罗科宇,陈玥琦,等.层粘连蛋白α4链功能肽修饰脱钙骨基质支架诱导H型血管及骨生成促进骨缺损修复的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2020,34(12):1594-1601. [60] LI S, SONG C, YANG S, et al. Supercritical CO2 foamed composite scaffolds incorporating bioactive lipids promote vascularized bone regeneration via Hif-1α upregulation and enhanced type H vessel formation. Acta Biomater. 2019;94:253-267. [61] 周航,刘宏梽,林敏敏,等.高压氧通过激活Prrx1+骨骼干细胞中的力学敏感蛋白Piezo1促进骨修复[J].医用生物力学,2024,39(S1):258. [62] WEI X, ZHOU W, TANG Z, et al. Magnesium surface-activated 3D printed porous PEEK scaffolds for in vivo osseointegration by promoting angiogenesis and osteogenesis. Bioact Mater. 2022;20:16-28. [63] 刘超.生物力学调控血管生成与成骨偶联促进骨组织再生的研究[J].医用生物力学,2024,39(S1):14. [64] YANG C, LIU Y, WANG Z, et al. Controlled mechanical loading improves bone regeneration by regulating type H vessels in a S1Pr1-dependent manner. FASEB J. 2022;36(10):e22530. [65] LIU Z, LIU H, LIU S, et al. SIRT1 activation promotes bone repair by enhancing the coupling of type H vessel formation and osteogenesis. Cell Prolif. 2024;57(6):e13596. [66] QIU M, LI C, CAI Z, et al. 3D Biomimetic Calcified Cartilaginous Callus that Induces Type H Vessels Formation and Osteoclastogenesis. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023; 10(16):e2207089. [67] WANG J, GAO Y, CHENG P, et al. CD31hiEmcnhi Vessels Support New Trabecular Bone Formation at the Frontier Growth Area in the Bone Defect Repair Process. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):4990. [68] LIU Y, WANG Y, LIN M, et al. Cellular Scale Curvature in Bioceramic Scaffolds Enhanced Bone Regeneration by Regulating Skeletal Stem Cells and Vascularization. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;13(29):e2401667. [69] HU Y, LI H. Comparison of part-time and full-time mandibular advancement: enlightenment based on type H vessel coupling osteogenesis. Clin Oral Investig. 2023;27(7):3695-3703. [70] LU W, XU Y, LUO H, et al. Comprehensive process optimization for rapidly vascularized osseointegration by dual ions effects. Chem Eng J. 2024;497:154520. [71] YAO H, GUO J, ZHU W, et al. Controlled Release of Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 Augments the Coupling of Angiogenesis and Osteogenesis for Accelerating Mandibular Defect Repair. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(11):2397. [72] XU D, QIAN J, GUAN X, et al. Copper-Containing Alloy as Immunoregulatory Material in Bone Regeneration via Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;8:620629. [73] XIANG H, DAI X, XU W, et al. Cryogenic 3D printing of bifunctional silicate nanoclay incorporated scaffolds for promoted angiogenesis and bone regeneration. Materials Design. 2022;223:111220. [74] 张武阳,李登科,王一名,等.Ctsk基因敲除调控H型血管参与小鼠牙槽窝愈合的研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2024, 40(3):330-336. [75] ZHAI Y, ZHOU Z, XING X, et al. Differential bone and vessel type formation at superior and dura periosteum during cranial bone defect repair. Bone Res. 2025;13(1):8. [76] LIU L, ZHOU N, FU S, et al. Endothelial cell-derived exosomes trigger a positive feedback loop in osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling via up-regulating zinc finger and BTB domain containing 16 in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024;22(1):721. [77] MA Y, SUN L, ZHANG J, et al. Exosomal mRNAs for Angiogenic-Osteogenic Coupled Bone Repair. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(33):e2302622. [78] HE Y, WANG W, LIN S, et al. Fabrication of a bio-instructive scaffold conferred with a favorable microenvironment allowing for superior implant osseointegration and accelerated in situ vascularized bone regeneration via type H vessel formation. Bioact Mater. 2021;9:491-507. [79] DAI K, SHEN T, YU Y, et al. Generation of rhBMP-2-induced juvenile ossicles in aged mice. Biomaterials. 2020;258:120284. [80] CHEN J, LI M, LIU AQ, et al. Gli1+ Cells Couple with Type H Vessels and Are Required for Type H Vessel Formation. Stem Cell Reports. 2020;15(1):110-124. [81] YAN ZQ, WANG XK, ZHOU Y, et al. H-type blood vessels participate in alveolar bone remodeling during murine tooth extraction healing. Oral Dis. 2020;26(5):998-1009. [82] WEI J, DUAN D, JING Y, et al. Heparin-conjugated injectable hydrogels with sustained releasing capability for promotion of H-type vessel formation and rat femoral bone defects repair. Materials Design. 2023;235:112407. [83] XIANG X, PATHAK JL, WU W, et al. Human serum-derived exosomes modulate macrophage inflammation to promote VCAM1-mediated angiogenesis and bone regeneration. J Cell Mol Med. 2023;27(8): 1131-1143. [84] LU W, ZENG M, LIU W, et al. Human urine-derived stem cell exosomes delivered via injectable GelMA templated hydrogel accelerate bone regeneration. Mater Today Bio. 2023;19:100569. [85] MARGER L, LIAUDET N, SCHERRER SS, et al. Identification of Type-H-like Blood Vessels in a Dynamic and Controlled Model of Osteogenesis in Rabbit Calvarium. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(13):4703. [86] ZENG Y, HUANG C, DUAN D, et al. Injectable temperature-sensitive hydrogel system incorporating deferoxamine-loaded microspheres promotes H-type blood vessel-related bone repair of a critical size femoral defect. Acta Biomater. 2022; 153:108-123. [87] BAI J, LI L, KOU N, et al. Low level laser therapy promotes bone regeneration by coupling angiogenesis and osteogenesis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):432. [88] JIN S, WEN J, ZHANG Y, et al. M2 macrophage-derived exosome-functionalized topological scaffolds regulate the foreign body response and the coupling of angio/osteoclasto/osteogenesis. Acta Biomater. 2024;177:91-106. [89] KOHARA Y, KITAZAWA R, HARAGUCHI R, et al. Macrophages are requisite for angiogenesis of type H vessels during bone regeneration in mice. Bone. 2022;154:116200. [90] GUO J, YAO H, CHANG L, et al. Magnesium Nanocomposite Hydrogel Reverses the Pathologies to Enhance Mandible Regeneration. Adv Mater. 2025;37(2): e2312920. [91] YOU J, LI Y, WANG C, et al. Mild Thermotherapy-Assisted GelMA/HA/MPDA@Roxadustat 3D-Printed Scaffolds with Combined Angiogenesis-Osteogenesis Functions for Bone Regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;13(22):e2400545. [92] HE WZ, YANG M, JIANG Y, et al. miR-188-3p targets skeletal endothelium coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis during ageing. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(5):494. [93] YANG M, LI CJ, XIAO Y, et al. Ophiopogonin D promotes bone regeneration by stimulating CD31hi EMCNhi vessel formation. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(3):e12784. [94] CHEN K, LIAO S, LI Y, et al. Osteoblast-derived EGFL6 couples angiogenesis to osteogenesis during bone repair. Theranostics. 2021;11(20):9738-9751. [95] TANG Y, LUO K, CHEN Y, et al. Phosphorylation inhibition of protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B tyrosine-152 induces bone regeneration coupled with angiogenesis for bone tissue engineering. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(7):2039-2057. [96] OKADA K, NIWA Y, FUKUHARA K, et al. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 is involved in glucocorticoid-induced decreases in angiogenesis during bone repair in mice. J Bone Miner Metab. 2024;42(3):282-289. [97] ZHOU C, HU G, LI Y, et al. Polydatin accelerates osteoporotic bone repair by inducing the osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via the PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway. Int J Surg. 2025;111(1):411-425. [98] KAIDA N, MATSUNAGA S, TACHIKI C, et al. Ridge preservation using octacalcium phosphate collagen to induce new bone containing a vascular network of mainly Type H vessels. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):25335. [99] ZHOU J, LI Y, HE J, et al. ROS Scavenging Graphene-Based Hydrogel Enhances Type H Vessel Formation and Vascularized Bone Regeneration via ZEB1/Notch1 Mediation. Macromol Biosci. 2023;23(4):e2200502. [100] SUN Y, LIU X, ZENG X, et al. Simvastatin-loaded sulfonated PEEK enhances angiogenesis and osteogenesis via miR-29cb2-mediated HIF-3α downregulation. Chem Eng J. 2022;448:137738. [101] 杨启恒,刘士博,刘航航,等.SIRT1调控BMSCs成骨分化与H型血管生成促进骨质疏松骨缺损愈合的研究[J].口腔医学研究,2024,40(9):785-792. [102] STEFANOWSKI J, LANG A, RAUCH A, et al. Spatial Distribution of Macrophages During Callus Formation and Maturation Reveals Close Crosstalk Between Macrophages and Newly Forming Vessels. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2588. [103] GAO L, CHEN W, LI L, et al. Targeting soluble epoxide hydrolase promotes osteogenic-angiogenic coupling via activating SLIT3/HIF-1α signalling pathway. Cell Prolif. 2023; 56(7):e13403. [104] JIANG L, SHENG K, WANG C, et al. The Effect of MMP-2 Inhibitor 1 on Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis During Bone Regeneration. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;8:596783. [105] 申震,陈泽华,郭英,等.骨碎补总黄酮对牵张成骨模型大鼠中H血管及成血管-成骨偶联的作用[J].中华中医药杂志, 2022,37(3):1352-1356. [106] JIANG W, HONG S, LIU K, et al. A tetrahedral DNA nanostructure-mediated miRNA inhibitor delivery system: Type H vessel-related bone healing during distraction osteogenesis. Chem Eng J. 2024;496: 153863. [107] SHEN J, SUN Y, LIU X, et al. EGFL6 regulates angiogenesis and osteogenesis in distraction osteogenesis via Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):415. [108] DANIEL M, SHEPPARD N, CARLOS G, et al. H Vessel Formation as a Marker for Enhanced Bone Healing in Irradiated Distraction Osteogenesis. Semin Plast Surg. 2024;38(1):31-38. [109] SHEN Z, CHEN Z, LI Z, et al. Total Flavonoids of Rhizoma Drynariae Enhances Angiogenic-Osteogenic Coupling During Distraction Osteogenesis by Promoting Type H Vessel Formation Through PDGF-BB/PDGFR-β Instead of HIF-1α/ VEGF Axis. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:503524. [110] SHEN Z, DONG W, CHEN Z, et al. Total flavonoids of Rhizoma Drynariae enhances CD31hiEmcnhi vessel formation and subsequent bone regeneration in rat models of distraction osteogenesis by activating PDGF‑BB/VEGF/RUNX2/OSX signaling axis. Int J Mol Med. 2022;50(3):112. [111] LI D, ZHAO D, ZENG Z, et al. Ternary regulation mechanism of Rhizoma drynariae total flavonoids on induced membrane formation and bone remodeling in Masquelet technique. PLoS One. 2022; 17(12):e0278688. [112] 申震,黄梓越,和智娟,等.骨诱导膜中H型血管动态表达及耦合骨生成修复大段骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2025, 29(28):5950-5956. [113] 张兆坤,赵俊杰,王玺玉,等.股骨头坏死中骨微血管内皮细胞对氧化应激性损伤的修复机制[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2024,17(10):950-956. [114] 田佳庆,刘良燕,彭鹏,等.基于“成骨-成血管”理论探讨全身振动疗法治疗激素性股骨头坏死的效果及作用机制[J].中医正骨,2024,36(9):59-68+82. [115] 于海洋,卢增鹏,汪海燕,等.激素性股骨头坏死中Hif-1α/VEGF信号轴和H型血管改变的实验研究[J].中国实验动物学报,2022,30(6):759-766. [116] 于海洋,卢增鹏,汪海燕,等.生骨再造丸对激素性股骨头坏死大鼠H型血管生成的影响[J].中国中医药信息杂志, 2023,30(5):91-96. [117] 宋红梅,谢文博,林菲菲,等.温阳补肾方对激素性股骨头坏死模型兔血清中成骨、成血管因子及H型血管标志物的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2023, 31(10):6-11. [118] 向炜,邱成,张小敏,等.银杏叶提取物促进大鼠激素性股骨头坏死中H亚型微血管形成的实验研究[J].中国现代医学杂志,2024,34(7):34-41. [119] TIAN JQ, WEI TF, WEI YR, et al. Effect of whole body vibration therapy in the rat model of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023;11:1251634. [120] SHAO W, WANG B, WANG P, et al. Inhibition of sympathetic tone via hypothalamic descending pathway propagates glucocorticoid-induced endothelial impairment and osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Bone Res. 2024;12(1):64. [121] CAO H, SHI K, LONG J, et al. PDGF-BB prevents destructive repair and promotes reparative osteogenesis of steroid-associated osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rabbits. Bone. 2023;167:116645. [122] 章家皓,田佳庆,王帅,等.补肾强筋胶囊对膝骨关节炎大鼠膝关节软骨下骨质的影响及其作用机制的实验研究[J].中医正骨,2024,36(8):19-26. [123] 江自鲜,陆玉春,李朝梦,等.斯赤列提取物抑制骨关节炎模型大鼠的异常血管新生[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(34): 5458-5466. [124] 段宇辰,何睿,陈晓华,等.脱落乳牙牙髓干细胞来源外泌体对大鼠TMJ OA软骨下骨稳态的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志, 2024,40(3):315-322. [125] WU H, XU T, CHEN Z, et al. Specific inhibition of FAK signaling attenuates subchondral bone deterioration and articular cartilage degeneration during osteoarthritis pathogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(11):8653-8666. [126] LI Y, MU W, XU B, et al. Artesunate, an Anti-Malaria Agent, Attenuates Experimental Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting Bone Resorption and CD31hiEmcnhi Vessel Formation in Subchondral Bone. Front Pharmacol. 2019; 10:685. [127] LI J, DING Z, LI Y, et al. BMSCs-Derived Exosomes Ameliorate Pain Via Abrogation of Aberrant Nerve Invasion in Subchondral Bone in Lumbar Facet Joint Osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(3):670-679. [128] HU Y, WU H, XU T, et al. Defactinib attenuates osteoarthritis by inhibiting positive feedback loop between H-type vessels and MSCs in subchondral bone. J Orthop Translat. 2020;24:12-22. [129] FANG C, GUO JW, WANG YJ, et al. Diterbutyl phthalate attenuates osteoarthritis in ACLT mice via suppressing ERK/c-fos/NFATc1 pathway, and subsequently inhibiting subchondral osteoclast fusion. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022;43(5):1299-1310. [130] CUI Z, WU H, XIAO Y, et al. Endothelial PDGF-BB/PDGFR-β signaling promotes osteoarthritis by enhancing angiogenesis-dependent abnormal subchondral bone formation. Bone Res. 2022;10(1):58. [131] CUI Z, CRANE J, XIE H, et al. Halofuginone attenuates osteoarthritis by inhibition of TGF-β activity and H-type vessel formation in subchondral bone. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(9):1714-1721. [132] ZHAO J, SUN Y, SHENG X, et al. Hypoxia-treated adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes attenuate lumbar facet joint osteoarthritis. Mol Med. 2023; 29(1):120. [133] LIN C, CHEN Z, GUO D, et al. Increased expression of osteopontin in subchondral bone promotes bone turnover and remodeling, and accelerates the progression of OA in a mouse model. Aging (Albany NY). 2022;14(1):253-271. [134] QIN H, ZHAO X, HU YJ, et al. Inhibition of SDF-1/CXCR4 Axis to Alleviate Abnormal Bone Formation and Angiogenesis Could Improve the Subchondral Bone Microenvironment in Osteoarthritis. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:8852574. [135] LI P, FENG K, ZHAN X. Inhibition of Slit3/Robo1 signaling alleviates osteoarthritis in mice by reducing abnormal H-type vessel formation in subchondral bone. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2024; 46(6):935-946. [136] WANG J, YU W, ZHANG Y, et al. Mechanism of hyperbaric oxygen therapy downregulating H-type angiogenesis in subchondral bone of knee osteoarthritis through the PHD2/HIF-1α pathway. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025;20(1):79. [137] LIU X, GUO Q, WANG L, et al. Metformin attenuates high-fat diet induced metabolic syndrome related osteoarthritis through inhibition of prostaglandins. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023;11:1184524. [138] LIU Y, DA W, XU MJ, et al. Single-cell transcriptomics reveals novel chondrocyte and osteoblast subtypes and their role in knee osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025;10(1):40. [139] ZOU Y, WANG Z, SHI H, et al. Soybean Isoflavones Alleviate Osteoarthritis Through Modulation of the TSC1/mTORC1 Signaling Pathway to Reduce Intrachondral Angiogenesis. Immunol Invest. 2024;53(8): 1439-1455. [140] LI HZ, HAN D, AO RF, et al. Tanshinone IIA attenuates osteoarthritis via inhibiting aberrant angiogenesis in subchondral bone. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2024;753:109904. [141] WANG R, XU B. TGFβ1-modified MSC-derived exosome attenuates osteoarthritis by inhibiting PDGF-BB secretion and H-type vessel activity in the subchondral bone. Acta Histochem. 2022;124(7):151933. [142] ZHANG K, YU J, LI J, et al. The Combined Intraosseous Administration of Orthobiologics Outperformed Isolated Intra-articular Injections in Alleviating Pain and Cartilage Degeneration in a Rat Model of MIA-Induced Knee Osteoarthritis. Am J Sports Med. 2024;52(1):140-154. [143] LU J, ZHANG H, CAI D, et al. Positive-Feedback Regulation of Subchondral H-Type Vessel Formation by Chondrocyte Promotes Osteoarthritis Development in Mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2018;33(5):909-920. [144] SINGH A, VEERIAH V, XI P, et al. Angiocrine signals regulate quiescence and therapy resistance in bone metastasis. JCI Insight. 2019;4(13):e125679. [145] YIP RKH, RIMES JS, CAPALDO BD, et al. Mammary tumour cells remodel the bone marrow vascular microenvironment to support metastasis. Nat Commun. 2021; 12(1):6920. [146] CHEN YX, LUO YP, HOU XD, et al. Natural Affinity Driven Modification by Silicene to Construct a “Thermal Switch” for Tumorous Bone Loss. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024;11(35):e2404534. [147] 赵常红,关彩萍.H型血管在骨构建和重塑中的作用机制[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2023,16(4):404-412. [148] XIE H, CUI Z, WANG L, et al. PDGF-BB secreted by preosteoclasts induces angiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis. Nat Med. 2014;20(11):1270-1278. [149] 李高志,石菲,张舒,等.血管新生与骨形成偶联、骨骼疾病发生及治疗中H型血管的作用机制研究进展[J].山东医药,2021,61(3):91-94. [150] 樊佳煊,曹林忠.H型血管内皮细胞铁死亡对骨稳态影响及相关机制的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2024,30(10):1449-1454. [151] GUBIN AV, BORZUNOV DY, MARCHENKOVA LO, et al. Contribution of G.A. Ilizarov to bone reconstruction: historical achievements and state of the art. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2016;11(3):145-152. [152] 赵芝鹤,张于凡,张文慧,等.经缝牵引成骨动物模型制备及早期组织学变化研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2024,40(2): 173-179. [153] 申震,姜自伟,李定,等.基于牵张成骨技术比较两种补肾法在成血管-成骨偶联机制中的作用差异[J].中华中医药杂志,2019,34(5):2150-2155. [154] MASQUELET AC. La technique de la membrane induite dans les reconstructions osseuses segmentaires: développement et perspectives. Bull Acad Natl Med. 2017; 201(1-3):439-453. [155] 李定,李悦,黄枫,等.骨碎补总黄酮在诱导膜技术中对骨缺损区域血管形成和成骨质量的影响[J].中华中医药杂志, 2019,34(11):5086-5089. [156] 申震,姜自伟,李定,等.基于Masquelet诱导膜技术比较不同固定方式构建的胫骨大段骨缺损模型[J].中国实验动物学报,2018,26(6):673-680. [157] WEINSTEIN RS, HOGAN EA, BORRELLI MJ, et al. The Pathophysiological Sequence of Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head in Male Mice. Endocrinology. 2017;158(11):3817-3831. |
| [1] | 陈秋函, 杨 龙, 袁代柱, 吴展羽, 邹梓豪, 叶 川. 膝关节周围截骨治疗膝骨关节炎:治疗策略的优化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2303-2312. |
| [2] | 张子峥, 罗 旺, 刘长路. 膝内侧间室骨关节炎单髁置换中有限元分析的应用价值[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2313-2322. |
| [3] | 赵非凡, 曹玉净. 股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗股骨转子间骨折内固定失效的危险因素与应对策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2323-2333. |
| [4] | 陈惠挺, 曾伟权, 周剑鸿, 王 杰, 庄聪颖, 陈培友, 梁泽乾, 邓伟明. 椎体成形中拖尾锚定治疗伴裂隙征骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2145-2152. |
| [5] | 曾 轩, 翁 汭, 叶仕成, 唐佳栋, 莫 凌, 李文超. 两种腰椎旋扳手法治疗腰椎间盘突出症:生物力学差异的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2153-2161. |
| [6] | 程旗圣, 居来提·买提肉孜, 肖 扬, 张陈伟, 帕尔哈提·热西提. 新型变径螺钉在腰椎改良皮质骨轨迹中的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2162-2171. |
| [7] | 刘文龙, 董 磊, 肖争争, 聂 宇. 骨质疏松患者行固定平台单髁置换后胫骨假体松动的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2191-2198. |
| [8] | 饶敬澄, 李豫皖, 郑红兵, 徐 志, 朱爱祥, 史 册, 王 冰, 杨 春, 孔祥如, 朱大伟. 新型股骨近端稳定髓内钉与传统髓内钉生物力学的差异[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2217-2225. |
| [9] | 陈 龙, 王小阵, 席金涛, 鲁齐林. 短节段置钉联合可扩张聚醚醚酮置换体在骨质疏松椎体中的生物力学性能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2226-2235. |
| [10] | 张 楠, 孟庆华, 鲍春雨. 踝关节有限元模型的特性及临床应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2343-2349. |
| [11] | 蒋祥龙, 厉中山, 车同同. 低频脉冲电磁场在肌肉修复与增长中的应用效果和作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2350-2360. |
| [12] | 周道斌, 王科豪, 谢 洋, 宁仁德. 掌侧锁定钢板与联合背侧钢板固定桡骨远端骨折尺背侧骨折块的生物力学特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2255-2261. |
| [13] | 王泊凯, 王志强, 周宏艳, 李骏然, 武一恒, 赵洪波. 青少年胫骨远端三平面骨折的骨折地图绘制与成像分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(9): 2248-2254. |
| [14] | 刘大为, 崔颖颖, 王方辉, 王子轩, 陈宇涵, 李友瑞, 张荣和. 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯介导活性氧双向调控及在纳米材料中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2101-2112. |
| [15] | 吴妍廷, 李 宇, 廖金凤. 氧化镁纳米粒调控成骨与血管生成相关基因表达促进骨缺损愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1885-1895. |
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1 资料来源
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者于2024年8月进行首次检索,2025年2月进行检索补充。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 2014年1月至2025年2月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 中文数据库:CNKI、维普、万方数据库;英文数据库:PubMed、Scopus、Web of Science。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词:H型血管,CD31hiEmcnhi,“H”型血管,成血管-成骨偶联,血管生成-成骨偶联,H亚型血管,H型微血管,成骨-成血管,骨骼,骨头;英文检索词:H-type vascular,CD31hiEmcnhi,type H vessel,H‐type vessel,angiogenic-osteogenic coupling,angiogenic-osteogenic,Subtype H vessels,Type H microvessels,“type H” capillaries,bone,bones,skeleton。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 综述、基础研究、临床试验、研究原著。
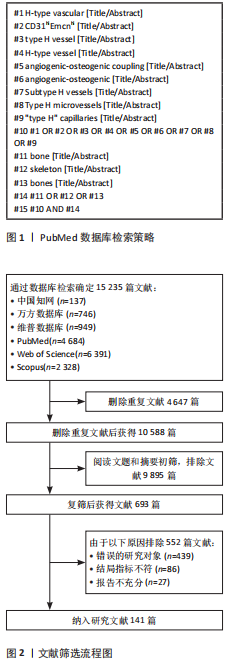
1.1.6 检索策略 以PubMed数据库检索策略为例,见图1。
1.1.7 检索文献量 初步检索到文献15 235篇,包括CNKI 137篇,万方数据库746篇,维普数据库949篇,PubMed数据库4 684篇,Web of Science数据库6 391篇,Scopus数据库2 328篇,共计中文文献1 832篇,英文文献13 403篇。
1.2 纳入与排除标准
纳入标准:①公开发表的研究;②涉及H型血管且与骨骼疾病动物模型相关的研究;③中文或英文文献;④可开放获取文献(不包含预印本或灰色文献)。
排除标准:①以英文或中文以外语言撰写的文章;②重复出版物;③题录、会议论文、信函等。
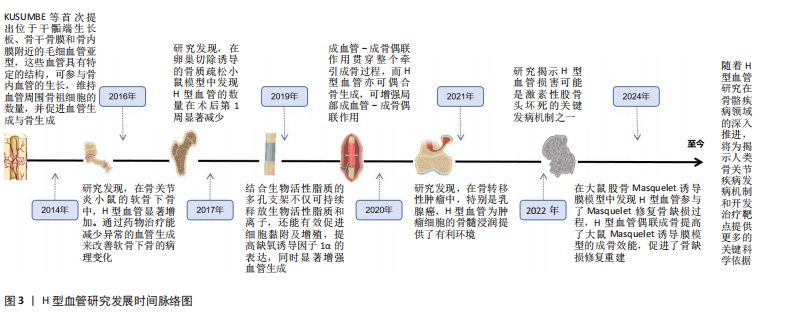
1.3 资料整合 最初检索得到15 235篇文献,排除重复文献4 647篇,阅读标题和摘要,排除不符合纳入标准的文献9 892篇,然后阅读全文,因结局指标、研究对象不符、报告不充分等原因排除552篇文献,最终纳入141篇文献进行模型归类分析[6-146],见表1。文献筛选流程如图2所示,另外引用了16篇经典综述文献。
Summary and prospects
3.1 既往他人在该领域研究的贡献和存在的问题 H型血管在骨代谢与骨骼疾病领域的生物学功能已成为当代骨科研究的前沿热点。现有研究广泛探讨了H型血管在多种骨骼疾病动物模型中的生成机制与骨代谢调控过程,揭示了其作为骨组织微环境关键调控因子的重要科学价值。文献证据表明,H型血管通过精密调控血管生成与成骨过程的耦合,在骨组织的生理稳态维持与病理转变中发挥着关键的生物学功能。在不同骨骼疾病的病理进程中,H型血管呈现出差异化的调控模式:在骨质疏松症、骨折、骨坏死等退行性骨骼疾病中,通过促进H型血管表达,可显著改善骨微环境的血管重塑与骨再生能力;而在骨关节炎、骨肿瘤等恶性骨骼疾病中,选择性抑制H型血管表达则成为潜在的治疗干预策略。
尽管H型血管研究领域近年来呈现快速发展态势,但由于该概念提出时间相对较短,现有研究仍处于探索阶段。当前研究面临的主要挑战集中于对H型血管复杂调控机制的深入阐释,尤其是从基础研究向临床转化应用的系统性转变过程中。研究对象的相对局限,以及对其精确作用机制的理解仍存不足,这些都成为限制进一步研究的关键瓶颈。因此,深入开展多尺度、多维度的H型血管功能研究,构建其在骨骼疾病中的精确调控网络,已成为骨科学研究的重要方向。
3.2 该综述区别于他人他篇的特点 通过系统性文献分析,深入探讨不同骨骼疾病动物模型中H型血管的分子生物学机制与调控网络,旨在构建H型血管在骨骼疾病病理生理过程中的综合性理论框架,为理解复杂骨微环境的动态调控机制提供创新性学术视角。不同于传统的单一疾病模型研究,此综述采用跨疾病、多维度的整合性研究范式,全面解析H型血管在骨骼疾病中的异质性功能特征及其潜在价值。研究不仅深入挖掘了H型血管在骨代谢调控中的分子机制,还系统阐释了H型血管在不同骨骼疾病中作为潜在治疗靶点的科学价值。
3.3 综述的意义 此综述阐述了围绕H型血管开展的基础研究的进展与未来方向,通过对相关研究文献的系统梳理和深入解析,为该领域的学术发展提供相应的理论基础和研究指引。
3.4 对未来的建议 未来的研究应加强对H型血管在不同病理状态下的动态监测,探索其在临床中的应用,并开展多靶点干预策略的研究,以改善H型血管功能并促进骨骼健康。同时,应积极推动基础研究与临床实践的结合,促进H型血管相关治疗方法的转化与应用,以期为复杂骨骼疾病的治疗提供新的思路和方法。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
在骨骼疾病研究领域,H型血管的生成及其在骨代谢中的作用已成为一个重要的研究热点。近年来,越来越多的研究集中于H型血管在不同骨骼疾病动物模型中的生物学功能,特别是在骨质疏松、骨折和骨关节炎等疾病中的作用机制。这些研究表明,H型血管不仅在骨内血管生成中发挥关键作用,还与骨代谢密切相关,能够作为评估骨量水平的早期标志物。目前,H型血管的研究主要集中在其生成机制和调控网络的探索。文献显示,H型血管通过调控血管生成与成骨过程的耦合,影响骨组织的生理稳态与病理转变。然而,目前有关H型血管在人体骨骼疾病中的具体机制仍需进一步研究,尤其是在临床转化方面的应用。未来研究应集中于对H型血管在不同病理状态下的动态监测,以及开发多靶点干预策略以改善其功能并促进骨骼健康。同时,推动基础研究与临床实践的结合,将为复杂骨骼疾病的治疗提供新的思路和方法。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||