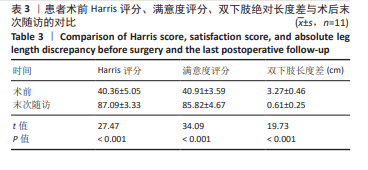
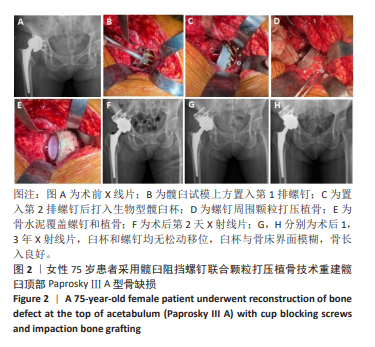
[1] BAINS SS, DUBIN JA, SALIB CG, et al. The Epidemiology of the Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty in the United States From 2016 to 2022. Arthroplast Today. 2024;30:101517.
[2] MOHAMMAD O, SHAARANI S, MOHAMMAD A, et al. Patients’ expectations surrounding revision total hip arthroplasty: a literature review. Arthroplasty. 2024;6(1):28.
[3] KIM YH, PARK JW. Eighteen-Year Follow-Up Study of 2 Alternative Bearing Surfaces Used in Total Hip Arthroplasty in the Same Young Patients. J Arthroplasty. 2020;35(3):824-830.
[4] MOLDOVAN F, MOLDOVAN L, BATAGA T. A Comprehensive Research on the Prevalence and Evolution Trend of Orthopedic Surgeries in Romania. Healthcare (Basel). 2023;11(13):1866.
[5] MURYLEV VY, KUKOVENKO GA, EFIMENKO O, et al. Does the interface between individual 3D acetabular implants and host bone influence the functional outcomes in patients with severe bone loss after revision surgery? SICOT J. 2024;10:42.
[6] YING J, CHENG L, LI J, et al. Treatment of Acetabular Bone Defect in Revision of Total Hip Arthroplasty Using 3D Printed Tantalum Acetabular Augment. Orthop Surg. 2023;15(5):1264-1271.
[7] BOZIC KJ, KURTZ SM, LAU E, et al. The epidemiology of revision total hip arthroplasty in the United States J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(1):128-133.
[8] 涂迪, 张德华, 韩大栋, 等. 髋关节置换髋臼骨缺损的评估与重建选择[J]. 生物骨科材料与临床研究,2023,20(3):78-83.
[9] WANG J, GUO F, YANG Q, et al. Statistical shape models quantify acetabular defects in hip revision surgery: implications for classification and surgical planning. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2024; 145(1):45.
[10] STRAHL A, BOESE CK, RIES C, et al. Outcome of different reconstruction options using allografts in revision total hip arthroplasty for severe acetabular bone loss: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023;143(10): 6403-6422.
[11] ANNAPAREDDY A, BOSE VC, KATARIYA AA, et al. Custom-Made 3D-Printed Augments and Cages: An Effective Solution for Managing Severe Acetabular Bone Los. J Orthop Case Rep. 2025;15(1):208-214.
[12] ZHANG J, KONG K, CHI Y, et al. Evaluation of the feasibility of acetabular cup pre-determination in revision total hip arthroplasty via X-ray of the bone stock of the anterosuperior acetabulum. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):597.
[13] ROOS BD, ROOS MV, CAMISA A, et al. Osseointegration and Success in Hip Arthroplasty Acetabular Revision Using Structured Homologous Graft: Average 9.6 Years Follow-up. Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2023; 58(3):523-531.
[14] XIONG L, LI H, HUANG X, et al. Both Acetabular and Femoral Reconstructions With Impaction Bone Grafting in Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty: Case Series and Literature Review. Arthroplast Today. 2023;24:101160.
[15] WANG Q, WANG Q, LIU P, et al. Clinical and radiological outcomes of jumbo cup in revision total hip arthroplasty: A systematic review. Front Surg. 2022;9:929103.
[16] ZHANG J, HUANG Y, ZHOU B, et al. Mid-Term Follow-Up of Acetabular Revision Arthroplasty Using Jumbo Cups. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(5):811-818.
[17] MANCINO F, CACCIOLA G, DI MATTEO V, et al. Reconstruction options and outcomes for acetabular bone loss in revision hip arthroplasty. Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2020;12(Suppl 1):8655.
[18] PERTICARINI L, ANDRIOLLO L, ROSSI S, et al. Severe acetabular bone loss management: is there still a role for titanium cages and cemented cups? Hip Int. 2025;351942269.
[19] ALTER TD, HADLEY ML, COUCH CG, et al. Highly Porous Acetabular Cup and Augment Constructs in Complex Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty: What Predicts 10-Year Implant Survivorship? J Arthroplasty. 2024; 39(9S1):S194-S202.
[20] 李锋侦,司文腾,田爱利,等.金属垫块结合Jumbo臼杯在人工髋关节翻修髋臼骨缺损重建中的应用研究[J].中国骨伤,2024,37(5): 464-469.
[21] SPRANZ D, MULLER LM, TREFZER R, et al. Reconstruction of severe acetabular defects (Paprosky type III A) in total hip arthroplasty using modular tantalum augments in combination with a cemented cup. Int Orthop. 2024;48(12):3083-3090.
[22] GUAN M, ZHOU G, LI X. A simple technique to strengthen the initial and mid-term to long-term stability of the cup during total hip arthroplasty in developmental dysplasia of the hip. Saudi Med J. 2018;39(4): 342-346.
[23] XU Z, LI Z, LI J, et al. Extra-articular Blocking Technique to Resolve Severe Acetabular Bone Defect in Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip. Orthop Surg. 2023;15(4):1187-1195.
[24] MAHOMED N, GANDHI R, DALTROY L, et al. The self-administered patient satisfaction scale for primary hip and knee arthroplasty. Arthritis. 2011;2011:591253.
[25] MARUYAMA M, TENSHO K, WAKABAYASHI S, et al. Standing versus supine radiographs to evaluate femoral head penetration in the polyethylene liner after total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014; 29(12):2415-2419.
[26] 陈斌斌, 赵蒙蒙, 范长生.我国髋关节置换患者的经济负担研究[J]. 中国卫生经济,2022,41(6):75-78.
[27] 陈衍霏, 孙爱斌, 邱惠, 等. 医护一体化引导式教育在基层医院全髋关节置换围术期的临床应用[J]. 基层医学论坛,2020,24(6): 743-745.
[28] 翁习生. 人工髋关节翻修术中髋臼骨缺损的重建方法[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2022,15(1):10-18.
[29] LI W, LIU D, LIU X, et al. Application of Intraoperative Individualized Cup Combination-Cup-on-Cup Technique in Severe Acetabular Defects. Orthop Surg. 2024;16(11):2853-2861.
[30] PAPROSKY WG, PERONA PG, LAWRENCE JM. Acetabular defect classification and surgical reconstruction in revision arthroplasty. A 6-year follow-up evaluation. J Arthroplasty. 1994;9(1):33-44.
[31] CHUNG BC, HECKMANN ND, GALLO MC, et al. Trabecular Metal Augments During Complex Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. Arthroplast Today. 2024;27:101435.
[32] SHETH NP, JONES SA, SANGHAVI SA, et al. How modular porous metal augments have changed the management of acetabular bone loss at primary or revision total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2024; 106-B(4):312-318.
[33] TRAM MK, TABBAA A, LAKRA A, et al. Patient Frailty is Correlated With Increased Adverse Events and Costs After Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2024;39(5):1151-1156.
[34] GUPTA P, QUAN T, PATEL CJ, et al. Extended length of stay in diabetic octogenarians following revision total hip arthroplasty. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2023;33(4):1217-1222.
[35] KWONG LM, JASTY M, HARRIS WH. High failure rate of bulk femoral head allografts in total hip acetabular reconstructions at 10 years. J Arthroplasty. 1993;8(4):341-346.
[36] LEE PT, RAZ G, SAFIR OA, et al. Long-term results for minor column allografts in revision hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010; 468(12):3295-3303.
[37] BROWN NM, MORRISON J, SPORER SM, et al. The Use of Structural Distal Femoral Allograft for Acetabular Reconstruction of Paprosky Type IIIA Defects at a Mean 21 Years of Follow-Up. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(3):680-683.
[38] 许志庆, 庄至坤, 龚志兵, 等. 结构性植骨应用于PaproskyⅢA型髋臼骨缺损髋关节翻修[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(36): 5787-5791.
[39] SALEH KJ, JAROSZYNSKI G, WOODGATE I, et al. Revision total hip arthroplasty with the use of structural acetabular allograft and reconstruction ring: a case series with a 10-year average follow-up. J Arthroplasty. 2000;15(8):951-958.
[40] CHEN HT, WU CT, HUANG TW, et al. Structural and Morselized Allografting Combined with a Cementless Cup for Acetabular Defects in Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty: A 4- to 14-Year Follow-Up. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:2364269.
[41] PANDEY AK, ZUKE WA, SURACE P, et al. Management of acetabular bone loss in revision total hip replacement: a narrative literature review. Ann Jt. 2024;9:21. |