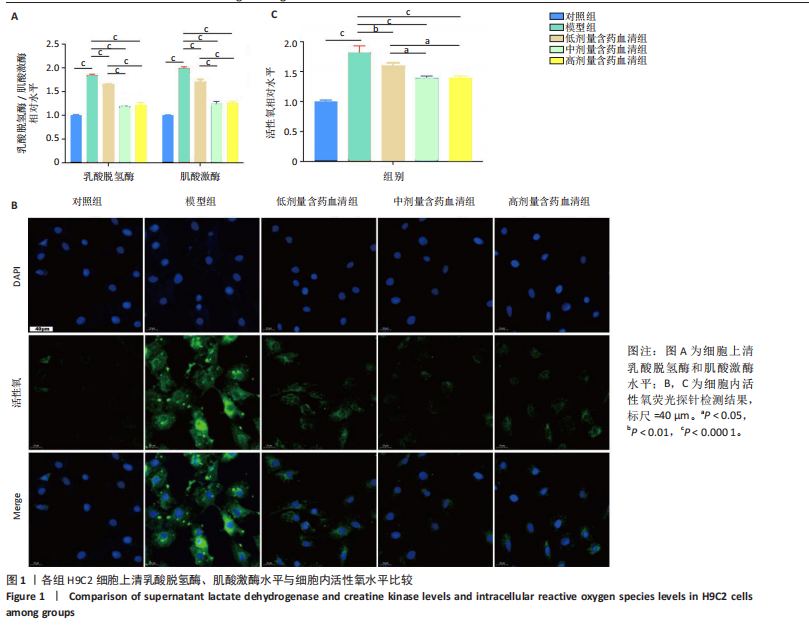
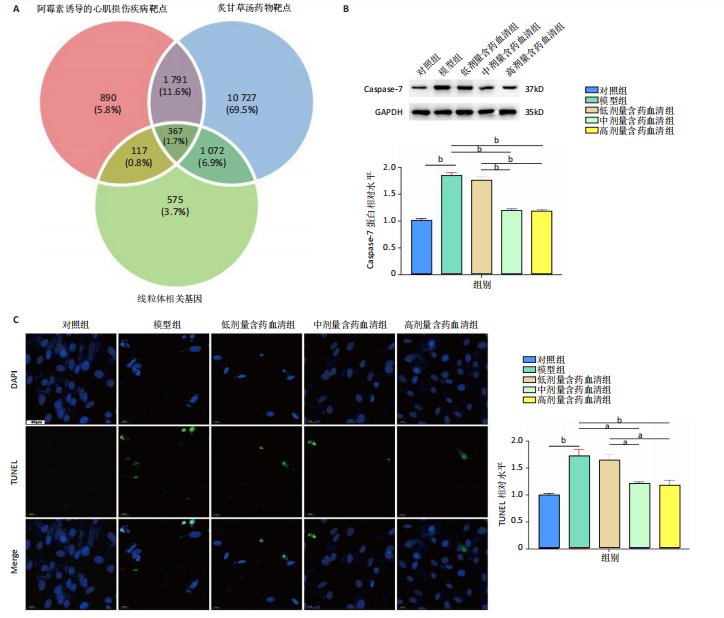
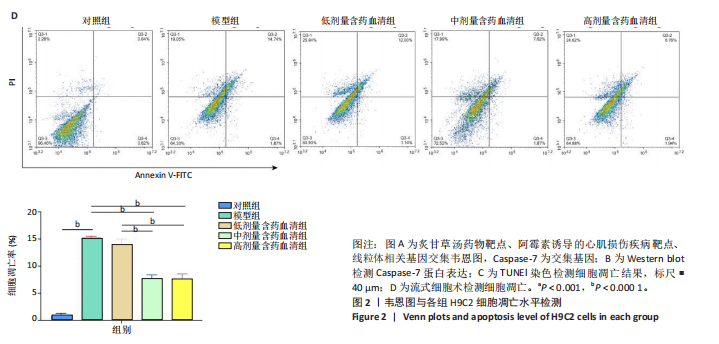
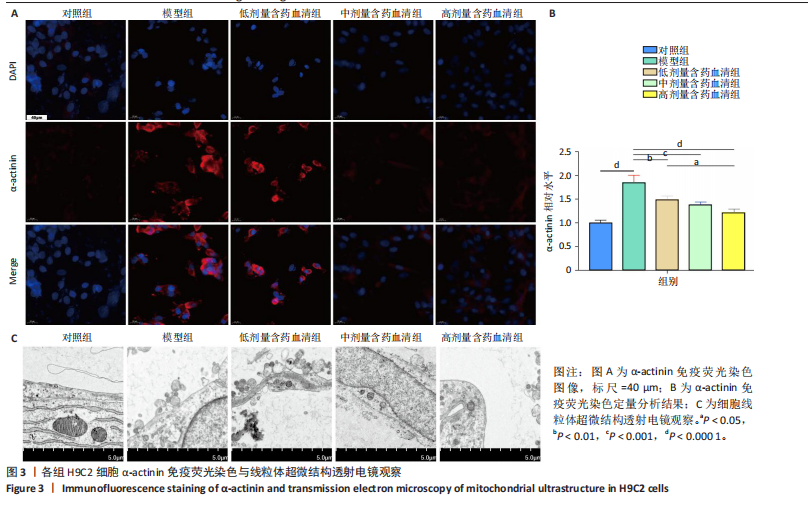
[1] MILLER KD, NOGUEIRA L, DEVASIA T, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72(5):409-436.
[2] DEMPKE W, ZIELINSKI R, WINKLER C, et al. Anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity - are we about to clear this hurdle? Eur J Cancer. 2023; 185:94-104.
[3] CAMILLI M, CIPOLLA CM, DENT S, et al. Anthracycline Cardiotoxicity in Adult Cancer Patients: JACC: CardioOncology State-of-the-Art Review. JACC CardioOncol. 2024;6(5):655-677.
[4] SWAIN SM, WHALEY FS, EWER MS. Congestive heart failure in patients treated with doxorubicin: a retrospective analysis of three trials. Cancer. 2003;97(11):2869-2879.
[5] ELFADADNY A, RAGAB RF, HAMADA R, et al. Natural bioactive compounds-doxorubicin combinations targeting topoisomerase II-alpha: Anticancer efficacy and safety. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2023; 461:116405.
[6] TAI P, CHEN X, JIA G, et al. WGX50 mitigates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity through inhibition of mitochondrial ROS and ferroptosis. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):823.
[7] WU BB, LEUNG KT, POON EN. Mitochondrial-Targeted Therapy for Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1912.
[8] HENRIKSEN PA. Anthracycline cardiotoxicity: an update on mechanisms, monitoring and prevention. Heart. 2018;104(12):971-977.
[9] WU L, WANG L, DU Y, et al. Mitochondrial quality control mechanisms as therapeutic targets in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2023;44(1):34-49.
[10] KITAKATA H, ENDO J, IKURA H, et al. Therapeutic Targets for DOX-Induced Cardiomyopathy: Role of Apoptosis vs. Ferroptosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):l1414.
[11] 丁纯志,陈群,赵景胜.炙甘草汤防治阿霉素心脏毒性的疗效观察[J].北京中医药大学学报,2001,24(3):59-60.
[12] ZHOU J, LIU Y, WEI X, et al. Glycnsisitin A: A promising bicyclic peptide against heart failure that facilitates TFRC-mediated uptake of iron in cardiomyocytes. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024;14(7):3125-3139.
[13] 张仲景.伤寒论[M].王叔和,钱超尘,郝万山整理,北京:人民卫生出版社,2005:2.
[14] FU J, CHENG L, ZHANG J, et al. Isoliquiritin targeting m5C RNA methylation improves mitophagy in doxorubicin-induced myocardial cardiotoxicity. Phytomedicine. 2024;136:156293.
[15] GAO F, LIANG T, LU YW, et al. Reduced Mitochondrial Protein Translation Promotes Cardiomyocyte Proliferation and Heart Regeneration. Circulation. 2023;148(23):1887-1906.
[16] YU M, CAI Z, ZHANG J, et al. Aberrant NSUN2-mediated m5C modification of exosomal LncRNA MALAT1 induced RANKL-mediated bone destruction in multiple myeloma. Commun Biol. 2024;7(1):1249.
[17] WALLACE KB, SARDAO VA, OLIVEIRA PJ. Mitochondrial Determinants of Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyopathy. Circ Res. 2020;126(7):926-941.
[18] SANGWENI NF, GABUZA K, HUISAMEN B, et al. Molecular insights into the pathophysiology of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: a graphical representation. Arch Toxicol. 2022;96(6):1541-1550.
[19] ARRIGONI R, JIRILLO E, CAIATI C. Pathophysiology of Doxorubicin-Mediated Cardiotoxicity. Toxics. 2025;13(4):277.
[20] AL-MAAMARI A, SULTAN M, WU S, et al. Activation of sigma 1 receptor attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by alleviating oxidative stress, mitochondria dysfunction, ER stress-related apoptosis, and autophagy impairment. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025;310(Pt 4):143549.
[21] SONG L, QIU Q, JU F, et al. Mechanisms of doxorubicin-induced cardiac inflammation and fibrosis; therapeutic targets and approaches. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2024;761:110140.
[22] ZHANG S, LIU X, BAWA-KHALFE T, et al. Identification of the molecular basis of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Nat Med. 2012;18(11): 1639-1642.
[23] KALYANARAMAN B. Teaching the basics of the mechanism of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: Have we been barking up the wrong tree? Redox Biol. 2020;29:101394.
[24] WU L, SOWERS JR, ZHANG Y, et al. Targeting DNA damage response in cardiovascular diseases: from pathophysiology to therapeutic implications. Cardiovasc Res. 2023;119(3):691-709.
[25] 杨洁文,徐叶峰,严卿莹.炙甘草汤干预阿霉素致大鼠心肌损害的能量代谢研究[J].浙江中医杂志,2021,56(4):258-260.
[26] DUTTA B, LOO S, KAM A, et al. Cell-Permeable Microprotein from Panax Ginseng Protects Against Doxorubicin-Induced Oxidative Stress and Cardiotoxicity. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025;14(4):493.
[27] KONG CY, GUO Z, SONG P, et al. Underlying the Mechanisms of Doxorubicin-Induced Acute Cardiotoxicity: Oxidative Stress and Cell Death. Int J Biol Sci. 2022;18(2):760-770.
[28] RAWAT PS, JAISWAL A, KHURANA A, et al. Doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: An update on the molecular mechanism and novel therapeutic strategies for effective management. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;139:111708.
[29] WANG X, LIU Z, LIN C. Metal ions-induced programmed cell death: how does oxidative stress regulate cell death? Life Sci. 2025;374:123688.
[30] DAN DUNN J, ALVAREZ LA, ZHANG X, et al. Reactive oxygen species and mitochondria: A nexus of cellular homeostasis. Redox Biol. 2015;6:472-485.
[31] SONGBO M, LANG H, XINYONG C, et al. Oxidative stress injury in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Toxicol Lett. 2019;307:41-48.
[32] TANAKA Y, NAGOSHI T, YOSHII A, et al. Xanthine oxidase inhibition attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in mice. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021;162:298-308.
[33] YANG L, GUAN J, LUO S, et al. Angiotensin IV ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by increasing glutathione peroxidase 4 and alleviating ferroptosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2023;479:116713.
[34] WU S, LAN J, LI L, et al. Sirt6 protects cardiomyocytes against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by inhibiting P53/Fas-dependent cell death and augmenting endogenous antioxidant defense mechanisms. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023;39(1):237-258.
[35] WANG T, XING G, FU T, et al. Role of mitochondria in doxorubicin-mediated cardiotoxicity: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic strategies. Int J Med Sci. 2024;21(5):809-816.
[36] WENNINGMANN N, KNAPP M, ANDE A, et al. Insights into Doxorubicin-induced Cardiotoxicity: Molecular Mechanisms, Preventive Strategies, and Early Monitoring. Mol Pharmacol. 2019;96(2):219-232.
[37] SCHIRONE L, D’AMBROSIO L, FORTE M, et al. Mitochondria and Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyopathy: A Complex Interplay. Cells. 2022;11(13):2000.
[38] AHMAD N, ULLAH A, CHU P, et al. Doxorubicin induced cardio toxicity through sirtuins mediated mitochondrial disruption. Chem Biol Interact. 2022;365:110028.
[39] SUN Y, XIAO L, CHEN L, et al. Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiac Remodeling: Mechanisms and Mitigation Strategies. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2025. doi: 10.1007/s10557-025-07673-6.
[40] CHRISTIDI E, BRUNHAM LR. Regulated cell death pathways in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(4):339.
[41] KITAKATA H, ENDO J, IKURA H, et al. Therapeutic Targets for DOX-Induced Cardiomyopathy: Role of Apoptosis vs. Ferroptosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1414.
[42] YANG H, LI S, LI W, et al. Actinomycin D synergizes with Doxorubicin in triple-negative breast cancer by inducing P53-dependent cell apoptosis. Carcinogenesis. 2024;45(4):262-273.
[43] ARIES A, PARADIS P, LEFEBVRE C, et al. Essential role of GATA-4 in cell survival and drug-induced cardiotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(18):6975-6980.
[44] LI S, LIU H, LIN Z, et al. Isoorientin attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiac injury via the activation of MAPK, Akt, and Caspase-dependent signaling pathways. Phytomedicine. 2022;101:154105.
[45] DAS J, GHOSH J, MANNA P, et al. Taurine suppresses doxorubicin-triggered oxidative stress and cardiac apoptosis in rat via up-regulation of PI3-K/Akt and inhibition of p53, p38-JNK. Biochem Pharmacol. 2011;81(7):891-909.
[46] AN J, LI P, LI J, et al. ARC is a critical cardiomyocyte survival switch in doxorubicin cardiotoxicity. J Mol Med (Berl). 2009;87(4):401-410.
[47] LAMKANFI M, KANNEGANTI TD. Caspase-7: a protease involved in apoptosis and inflammation. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010; 42(1):21-24.
[48] CHRISTGEN S, TWEEDELL RE, KANNEGANTI TD. Programming inflammatory cell death for therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 2022;232:108010.
[49] SAHOO G, SAMAL D, KHANDAYATARAY P, et al. A Review on Caspases: Key Regulators of Biological Activities and Apoptosis. Mol Neurobiol. 2023;60(10):5805-5837. |