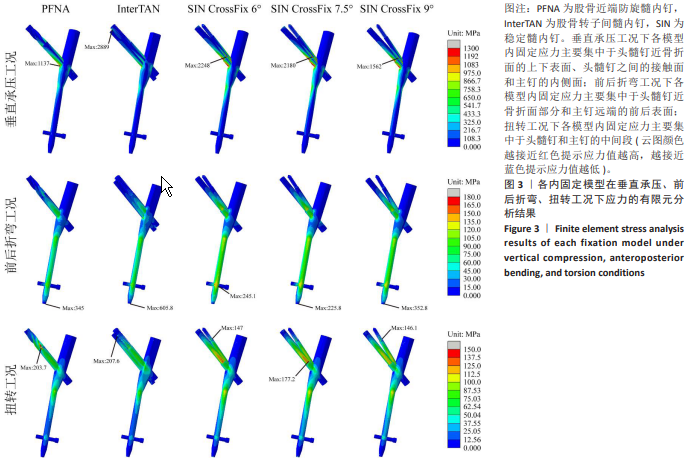
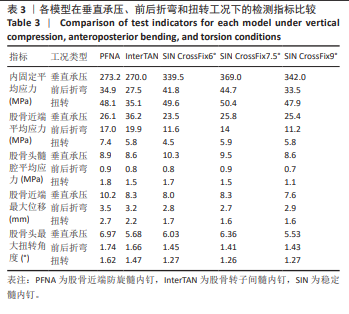
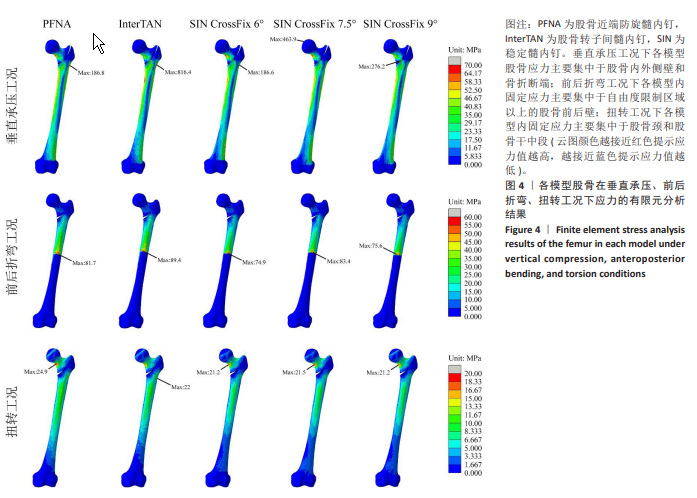
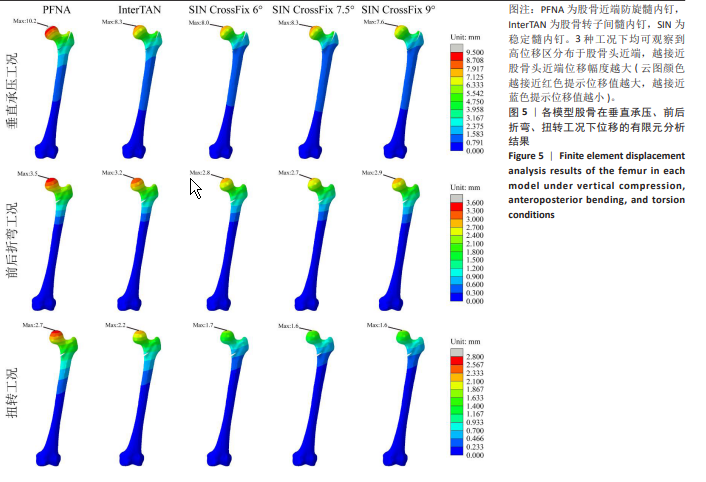
[1] HUANG Q, XU Y, XUE H, et al. Percutaneous reduction with double screwdrivers versus limited open reduction in the treatment of irreducible extracapsular hip fractures. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):429.
[2] BI C, ZHAO Y, MA Z, et al. Comparison of Proximal Anti-Rotation Intramedullary Nail and Femoral Head Replacement for the Treatment of Femoral Intertrochanteric Fractures in Elderly Patients. Altern Ther Health Med. 2023;29(5):268-273.
[3] 孙鸿朔, 张治博, 李孟奇, 等. 新型牵引床闭合复位髓内钉固定股骨粗隆间骨折[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2024,32(6):506-511.
[4] AN Y, JIANG D. Biomechanical effects of three internal fixation modes on femoral subtrochanteric spiral fractures in osteoporotic patients by finite element analysis. Zhongguo xiu fu chong jian wai ke za zhi. 2023;37(6):688-693.
[5] 徐志, 仲鹤鹤, 向浩, 等. 股骨干骨折3种不同固定方式的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(33):5271-5277.
[6] 李浩涛, 李力文, 张世民. 股骨转子间骨折后壁冠状面“香蕉样骨块”特点及其在头髓钉治疗中的研究进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2024,38(12):1517-1523.
[7] 王伟, 张金明, 杨占辉, 等. 有限切开复位钛缆环扎联合加长型髓内钉治疗股骨转子下骨折的效果[J]. 滨州医学院学报, 2023,46(4):312-314.
[8] 张巍, 唐佩福.老年髋部骨折治疗方法的选择与进展[J]. 中国骨伤, 2023,36(12):1111-1113.
[9] CHLEBECK JD, BIRCH CE, BLANKSTEIN M, et al. Nonoperative Geriatric Hip Fracture Treatment Is Associated With Increased Mortality: A Matched Cohort Study. J Orthop Trauma. 2019;33(7):346-350.
[10] USAMI T, TAKADA N, KOSUWON W, et al. A Lateral Fracture Line Affects Femoral Trochanteric Fracture Instability and Swing Motion of the Intramedullary Nail: A Biomechanical Study. JB JS Open Access. 2024; 9(1):2300118.
[11] CHEN X, HU Y, GENG Z, et al. The “Three in One” Bone Repair Strategy for Osteoporotic Fractures. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:910602.
[12] SONG H, CHANG SM, HU SJ, et al. Low filling ratio of the distal nail segment to the medullary canal is a risk factor for loss of anteromedial cortical support: a case control study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):27.
[13] TANG Z, LV Y, ZHU Z, et al. Biomechanical characteristic differences of two new types of intramedullary nail devices in the treatment of comminuted intertrochanteric fractures of femur: a comparative study based on finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024;19(1):583.
[14] 杨青, 牛宇飞, 苏静亮, 等. InterTan结合重建钢板治疗老年股骨转子间骨折PFNA内固定术后髓钉断裂的疗效分析[J]. 生物骨科材料与临床研究,2024,21(3):58-63.
[15] 缪建云, 徐维臻, 翟文亮, 等. 髓内钉联合髓外固定治疗伴有冠状面骨折的股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效观察[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2025,33(1):74-77.
[16] LI J, ZHANG L, ZHANG H, et al. Effect of reduction quality on post-operative outcomes in 31-A2 intertrochanteric fractures following intramedullary fixation: a retrospective study based on computerised tomography findings. Int Orthop. 2019;43(8):1951-1959.
[17] 史文骥, 毛宾尧, 赵艳. 股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗老年股骨转子间骨折疗效及并发症探讨[J]. 中国骨伤,2021,34(10):906-910.
[18] WANG Y, CHEN W, ZHANG L, et al. Finite Element Analysis of Proximal Femur Bionic Nail (PFBN) Compared with Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation and InterTan in Treatment of Intertrochanteric Fractures. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(9):2245-2255.
[19] 徐志, 刘子铭, 李豫皖, 等. 多孔结构设计人工踝关节衬垫生物力学的优化方案[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(30):4817-4824.
[20] 徐志, 李豫皖, 刘子铭, 等. 五种内固定方式治疗SeinsheimerⅤ型股骨转子下骨折的生物力学特性比较[J].中华骨科杂志,2024,44(9):616-625.
[21] LI J, YIN P, ZHANG L, et al. Medial anatomical buttress plate in treating displaced femoral neck fracture a finite element analysis. Injury. 2019; 50(11):1895-1900.
[22] WANG Q, SUN L, LIU L, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of the modified proximal femoral nail for the treatment of reverse obliquity intertrochanteric fractures. Sci Rep. 2025;15(1):3261.
[23] HOHENDORFF B, MEYER P, MENEZES D, et al. Treatment results and complications after PFN osteosynthesis. Unfallchirurg. 2005;108(11):938, 940-946.
[24] BONNAIRE F, LEIN T, FÜLLING T, et al. Reduced complication rates for unstable trochanteric fractures managed with third-generation nails: Gamma 3 nail versus PFNA. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2020;46(5):955-962.
[25] 孟永标, 杨跃芬, 吴生华, 等. 股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折合并膝骨关节炎的效果[J]. 浙江创伤外科,2025,30(2):238-241.
[26] MURUGAN PB, MOHIDEEN S, PRADEEP E, et al. Comparison of functional and radiological outcome of unstable intertrochanteric femur fractures treated using PFN and PFNA in patients with osteoporosis. J Orthop Case Rep. 2024; 14(10):219-224.
[27] 田可为, 陈勤, 陈柯, 等. 股骨近端防旋髓内钉内固定术后尾帽退出并发症临床报道[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2023,37(2):252-254.
[28] 冯皓, 张斌, 聂涛. 三种术式治疗老年不稳定股骨粗隆间骨折术后并发症及远期疗效[J].中国老年学杂志,2021,41(9):1850-1853.
[29] LU X, GOU W, WU S, et al. Complication Rates and Survival of Nonagenarians after Hip Hemiarthroplasty versus Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation for Intertrochanteric Fractures: A 15-Year Retrospective Cohort Study of 113 Cases. Orthop Surg. 2023;15(12):3231-3242.
[30] ZHU Z, ZHAO Z, WANG X, et al. A comparison of functional and radiological outcome of combine compression antegrade intertrochanteric nail (InterTan) and proximal femoral nail anti-rotation II (PFNA-II) in elderly patients with intertrochanteric fractures. Pak J Med Sci. 2023;39(1):96-100.
[31] 金立昆, 李晔, 张杰, 等. 不同髓内固定方式治疗股骨转子间骨折的临床观察[J]. 中国骨伤,2024,37(3):293-299.
[32] 傅宏沛, 周云烽, 贾俊杰, 等. PFBN、InterTan、PFNA髓内钉内固定治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折早期疗效比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2023,38(10):1058-1061.
[33] 杨冬松, 王琼, 陈许冬, 等. 股骨近端仿生髓内钉治疗外侧壁破裂型老年股骨转子间骨折的近期疗效观察[J]. 创伤外科杂志,2025,27(1):34-37.
[34] BAI H, LIU L, DUAN N, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of three implants for treating unstable femoral intertrochanteric fractures: finite element analysis in axial, bending and torsion loads. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023; 11:1279067.
[35] TANG Z, LV Y, ZHU Z, et al. Biomechanical characteristic differences of two new types of intramedullary nail devices in the treatment of comminuted intertrochanteric fractures of femur: a comparative study based on finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024;19(1):583. |