[1] SAINI V, GUADA L, YAVAGAL DR. Global Epidemiology of Stroke and Access to Acute Ischemic Stroke Interventions. Neurology. 2021;97(20 Suppl 2):S6-S16.
[2] CHEN Y, SU W, GUI CF, et al. Effectiveness of cerebellar vermis intermittent theta-burst stimulation in improving trunk control and balance function for patients with subacute stroke: a randomised controlled trial protocol. BMJ Open. 2023;13(1):e066356.
[3] GITTLER M, DAVIS AM. Guidelines for Adult Stroke Rehabilitation and Recovery. JAMA. 2018;319(8):820-821.
[4] MEAD GE, HSIEH CF, LEE R, et al. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors for stroke recovery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke. 2013;44(3):844-850.
[5] LANGHAMMER B, STANGHELLE JK. Can physiotherapy after stroke based on the Bobath concept result in improved quality of movement compared to the motor relearning programme. Physiother Res Int. 2011;16(2):69-80.
[6] WOODFORD H, PRICE C. EMG biofeedback for the recovery of motor function after stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007; 2007(2):CD004585.
[7] NATHOU C, DUPREY E, SIMON G, et al. Effects of low- and high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on long-latency auditory evoked potentials. Neurosci Lett. 2018;686:198-204.
[8] DUAN X, HUANG D, ZHONG H, et al. Efficacy of rTMS in treating functional impairment in post-stroke patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurol Sci. 2024;45(8): 3887-3899.
[9] 夏渊,卢悦,李爱玲,等.θ节律刺激对脑卒中后患者上肢运动功能和日常生活能力影响的Meta分析[J].中国医学物理学杂志,2022,39(3):341-348.
[10] CHUNG SW, HOY KE, FITZGERALD PB. Theta-burst stimulation: a new form of TMS treatment for depression? Depress Anxiety. 2015;32(3):182-192.
[11] CARDENAS-MORALES L, NOWAK DA, KAMMER T, et al. Mechanisms and applications of theta-burst rTMS on the human motor cortex. Brain Topogr. 2010; 22(4):294-306.
[12] GUTIÉRREZ-MUTO AM, CASTILLA J, FREIRE M, et al. Theta burst stimulation: Technical aspects about TMS devices. Brain Stimul. 2020;13(3):562-564.
[13] KOCH G, ESPOSITO R, MOTTA C, et al. Improving visuo-motor learning with cerebellar theta burst stimulation: Behavioral and neurophysiological evidence. Neuroimage. 2020;208:116424.
[14] LIN LF, CHANG KH, HUANG YZ, et al. Simultaneous stimulation in bilateral leg motor areas with intermittent theta burst stimulation to improve functional performance after stroke: a feasibility pilot study. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2019; 55(2):162-168.
[15] 陈伟群,王新德.全国第五届脑血管病学术会议纪要[J].中华神经科杂志,2000, 33(4):252.
[16] HIGGINS JP, ALTMAN DG, GOTZSCHE PC, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2011;343:d5928.
[17] MAHER CG, SHERRINGTON C, HERBERT RD, et al. Reliability of the PEDro scale for rating quality of randomized controlled trials. Phys Ther. 2003;83(8):713-721.
[18] 陈静,石明芳,陈君,等.小脑间歇性θ短阵脉冲刺激联合物理治疗对脑卒中患者平衡功能和步态的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2023,45(5):402-407.
[19] 邓罗义,陈彦,曾妮,等.健侧小脑间歇性θ短阵脉冲刺激康复治疗对脑卒中患者下肢步行功能的影响[J].实用医学杂志,2024,40(13):1797-1802.
[20] 孔晴,郭壮丽,高呈飞,等.小脑间歇性θ脉冲刺激对脑卒中后下肢功能障碍患者步行功能的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2024,46(3):226-231.
[21] 毛佳宁,张皓,崔利华.小脑经颅磁刺激对脑卒中偏瘫患者平衡及运动功能的影响[J].神经损伤与功能重建,2024, 19(10):574-578+604.
[22] 彭瑾,谢珊,查益,等.间歇性θ短阵脉冲刺激小脑蚓部对脑卒中患者下肢运动功能障碍的影响[J].神经损伤与功能重建,2025,20(1):21-25.
[23] 王佳,王先斌,宋宁,等.不同经颅磁刺激模式对脑卒中后下肢运动障碍患者肢体运动功能的影响[J].贵州医科大学学报,2023,48(6):702-709.
[24] 王淑睿,李丽.小脑间歇性θ短阵快速脉冲刺激对脑卒中患者下肢运动功能的影响[J].中国康复理论与实践,2022, 28(10):1205-1210.
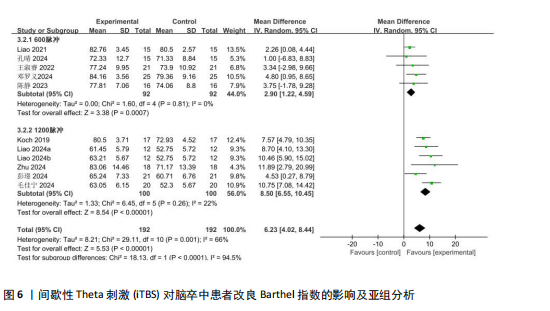
[25] ZHU PA, LI ZL, LU QQ, et al. Can cerebellar theta-burst stimulation improve balance function and gait in stroke patients? A randomized controlled trial. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2024;60(3):391-399.
[26] KOCH G, BONNÌ S, CASULA EP, et al. Effect of Cerebellar Stimulation on Gait and Balance Recovery in Patients With Hemiparetic Stroke: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2019;76(2):170-178.
[27] LIAO LY, XIE YJ, CHEN Y, et al. Cerebellar Theta-Burst Stimulation Combined With Physiotherapy in Subacute and Chronic Stroke Patients: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2021;35(1):23-32.
[28] LIAO LY, ZHU Y, PENG QY, et al. Intermittent Theta-Burst Stimulation for Stroke: Primary Motor Cortex Versus Cerebellar Stimulation: A Randomized Sham-Controlled Trial. Stroke. 2024;55(1):156-165.
[29] XIE YJ, WEI QC, CHEN Y, et al. Cerebellar Theta Burst Stimulation on Walking Function in Stroke Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Front Neurosci. 2021;15:688569.
[30] MCKENNEY K, ELDER AS, ELDER C, et al. Myofascial release as a treatment for orthopaedic conditions: a systematic review. J Athl Train. 2013;48(4):522-527.
[31] SMITH MC, BYBLOW WD, BARBER PA, et al. Proportional Recovery From Lower Limb Motor Impairment After Stroke. Stroke. 2017;48(5):1400-1403.
[32] CHEN K, SUN M, ZHUANG H. Effect of theta burst stimulation on lower extremity motor function improvement and balance recovery in patients with stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024;103(44):e40098.
[33] JEMNA N, ZDRENGHEA AC, FRUNZA G, et al. Theta-burst stimulation as a therapeutic tool in neurological pathology: a systematic review. Neurol Sci. 2024;45(3):911-940.
[34] WANG CP, TSAI PY, YANG TF, et al. Differential effect of conditioning sequences in coupling inhibitory/facilitatory repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for poststroke motor recovery. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2014;20(4):355-363.
[35] BALASUBRAMANIAN CK, LI CY, BOWDEN MG, et al. Dimensionality and Item-Difficulty Hierarchy of the Lower Extremity Fugl-Meyer Assessment in Individuals With Subacute and Chronic Stroke. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2016;97(4):582-589.
[36] DI LAZZARO V, DILEONE M, PROFICE P, et al. Direct demonstration that repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation can enhance corticospinal excitability in stroke. Stroke. 2006;37(11):2850-2853.
[37] HUANG YZ, EDWARDS MJ, ROUNIS E, et al. Theta burst stimulation of the human motor cortex. Neuron. 2005;45(2):201-206.
[38] FUNKE K, BENALI A. Modulation of cortical inhibition by rTMS - findings obtained from animal models. J Physiol. 2011;589(Pt 18): 4423-4435.
[39] REHME AK, EICKHOFF SB, ROTTSCHY C, et al. Activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis of motor-related neural activity after stroke. Neuroimage. 2012;59(3):2771-2782.
[40] LUFT AR, FORRESTER L, MACKO RF, et al. Brain activation of lower extremity movement in chronically impaired stroke survivors. Neuroimage. 2005;26(1):184-194.
[41] BODDINGTON LJ, REYNOLDS JNJ. Targeting interhemispheric inhibition with neuromodulation to enhance stroke rehabilitation. Brain Stimul. 2017;10(2): 214-222.
[42] ACOBS JV, HORAK FB. Cortical control of postural responses. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2007;114(10):1339-1348.
[43] NEULS PD, CLARK TL, VAN HEUKLON NC, et al. Usefulness of the Berg Balance Scale to predict falls in the elderly. J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2011;34(1):3-10.
[44] SPAMPINATO DA, CELNIK PA, ROTHWELL JC. Cerebellar-Motor Cortex Connectivity: One or Two Different Networks? J Neurosci. 2020;40(21):4230-4239.
[45] HANAKAWA T, HOTTA F, NAKAMURA T, et al. Macrostructural Cerebellar Neuroplasticity Correlates With Motor Recovery After Stroke. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2023; 37(11-12):775-785.
[46] XIA Y, TANG X, HU R, et al. Cerebellum-Cerebrum paired target magnetic stimulation on balance function and brain network of patients with stroke: A functional near-infrared spectroscopy pilot study. Front Neurol. 2022;13:1071328.
[47] TAN HX, WEI QC, CHEN Y, et al. The Immediate Effects of Intermittent Theta Burst Stimulation of the Cerebellar Vermis on Cerebral Cortical Excitability During a Balance Task in Healthy Individuals: A Pilot Study. Front Hum Neurosci. 2021;15: 748241.
[48] CASULA EP, PELLICCIARI MC, PONZO V, et al. Cerebellar theta burst stimulation modulates the neural activity of interconnected parietal and motor areas. Sci Rep. 2016;6:36191.
[49] DIAO X, LU Q, QIAO L, et al. Cortical Inhibition State-Dependent iTBS Induced Neural Plasticity. Front Neurosci. 2022;16:788538.
[50] WANG YC, CHANG PF, CHEN YM, et al. Comparison of responsiveness of the Barthel Index and modified Barthel Index in patients with stroke. Disabil Rehabil. 2023;45(6):1097-1102.
[51] CHUNG SW, HILL AT, ROGASCH NC, et al. Use of theta-burst stimulation in changing excitability of motor cortex: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2016;63:43-64.
[52] NETTEKOVEN C, VOLZ LJ, KUTSCHA M, et al. Dose-dependent effects of theta burst rTMS on cortical excitability and resting-state connectivity of the human motor system. J Neurosci. 2014;34(20):6849-6859.
[53] YU F, TANG X, HU R, et al. The After-Effect of Accelerated Intermittent Theta Burst Stimulation at Different Session Intervals. Front Neurosci. 2020;14:576.
[54] WILLIAMS NR, SUDHEIMER KD, BENTZLEY BS, et al. High-dose spaced theta-burst TMS as a rapid-acting antidepressant in highly refractory depression. Brain. 2018; 141(3):e18.
[55] ANIL S, LU H, ROTTER S, et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) triggers dose-dependent homeostatic rewiring in recurrent neuronal networks. PLoS Comput Biol. 2023;19(11):e1011027.
[56] 黄如训,郭玉璞. 2000年广州全国脑血管病专题研讨会脑卒中的分型分期治疗(建议草案)[J]. 现代实用医学,2003,15(9): 592-594.
[57] WANG L, HUANG G, ZHANG L, et al. Effects of the Intermittent Theta Burst Stimulation of the Cerebellar Vermis on Balance Recovery After Stroke: A Study Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:881311.
[58] LI D, CHENG A, ZHANG Z, et al. Effects of low-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation combined with cerebellar continuous theta burst stimulation on spasticity and limb dyskinesia in patients with stroke. BMC Neurol. 2021; 21(1):369.
[59] CABRAL DF, FRIED P, KOCH S, et al. Efficacy of mechanisms of neuroplasticity after a stroke. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2022; 40(2):73-84.
|