[1] 王红,丁勇,田娟.早期康复训练对人工全髋关节置换术后康复诸因素的影响[J].中国临床康复,2003,7(8):1326.
[2] CHOU R, GORDON DB, DE LEON-CASASOLA OA, et al. Management of Postoperative Pain: A Clinical Practice Guideline From the American Pain Society, the American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, and the American Society of Anesthesiologists’ Committee on Regional Anesthesia, Executive Committee, and Administrative Council. J Pain. 2016;17(2):131-157.
[3] HADLANDSMYTH K, ZIMMERMAN MB, WAJID R, et al. Longitudinal Postoperative Course of Pain and Dysfunction Following Total Knee Arthroplasty. Clin J Pain. 2018; 34(4):332-338.
[4] WU T, HUANG W, QI J, et al. Research trends and frontiers on antiphospholipid syndrome: A 10-year bibliometric analysis (2012-2021). Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1035229.
[5] 周宗科,翁习生,向兵,等.中国髋、膝关节置换术加速康复:围术期贫血诊治专家共识[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2016,9(1):10-15.
[6] ABRECHT CR, CORNELIUS M, WU A, et al. Prediction of Pain and Opioid Utilization in the Perioperative Period in Patients Undergoing Primary Knee Arthroplasty: Psychophysical and Psychosocial Factors. Pain Med. 2019;20(1):161-171.
[7] NANDI M, SCHREIBER KL, MARTEL MO, et al. Sex differences in negative affect and postoperative pain in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. Biol Sex Differ. 2019;10(1):23.
[8] OWENS MA, MUN CJ, HAMILTON KR, et al. Presurgical sleep and pain behaviors predict insomnia symptoms and pain after total knee arthroplasty: a 12-month longitudinal, observational study. Pain Med. 2023;24(11):1224-1233.
[9] HAMILTON KR, HUGHES AJ, CAMPBELL CM, et al. Perioperative insomnia trajectories and functional outcomes after total knee arthroplasty. Pain. 2023;164(12):2769-2779.
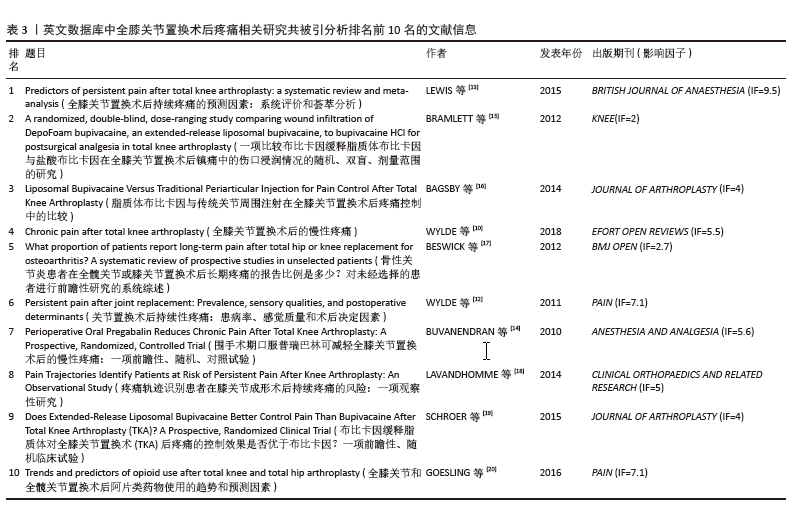
[10] WYLDE V, BESWICK A, BRUCE J, et al. Chronic pain after total knee arthroplasty. EFORT Open Rev. 2018;3(8):461-470.
[11] WYLDE V, BERTRAM W, BESWICK AD, et al. Clinical- and cost-effectiveness of the STAR care pathway compared to usual care for patients with chronic pain after total knee replacement: study protocol for a UK randomised controlled trial. Trials. 2018;19(1):132.
[12] WYLDE V, HEWLETT S, LEARMONTH ID, et al. Persistent pain after joint replacement: Prevalence, sensory qualities, and postoperative determinants. Pain. 2011;152(3):566-572.
[13] LEWIS GN, RICE DA, MCNAIR PJ, et al. Predictors of persistent pain after total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth. 2015;114(4):551-561.
[14] BUVANENDRAN A, KROIN JS, DELLA VALLE CJ, et al. Perioperative Oral Pregabalin Reduces Chronic Pain After Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Prospective, Randomized, Controlled Trial. Anesth Analg. 2010;110(1):199-207.
[15] BRAMLETT K, ONEL E, VISCUSI ER, et al. A randomized, double-blind, dose-ranging study comparing wound infiltration of DepoFoam bupivacaine, an extended-release liposomal bupivacaine, to bupivacaine HCl for postsurgical analgesia in total knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2012;19(5):530-536.
[16] BAGSBY DT, IRELAND PH, MENEGHINI RM. Liposomal Bupivacaine Versus Traditional Periarticular Injection for Pain Control After Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(8):1687-1690.
[17] BESWICK AD, WYLDE V, GOOBERMAN-HILL R, et al. What proportion of patients report long-term pain after total hip or knee replacement for osteoarthritis? A systematic review of prospective studies in unselected patients. BMJ Open. 2012;2(1):e000435.
[18] LAVAND’HOMME PM, GROSU I, FRANCE MN, et al. Pain Trajectories Identify Patients at Risk of Persistent Pain After Knee Arthroplasty: An Observational Study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(5):1409-1415.
[19] SCHROER WC, DIESFELD PG, LEMARR AR, et al. Does Extended-Release Liposomal Bupivacaine Better Control Pain Than Bupivacaine After Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA)? A Prospective, Randomized Clinical Trial. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(9):64-67.
[20] GOESLING J, MOSER SE, ZAIDI B, et al. Trends and predictors of opioid use after total knee and total hip arthroplasty. Pain. 2016;157(6):1259-1265.
[21] ZHANG Z, SONG K, YAO Y, et al. Incidence and Risk Factors for Post-Thrombotic Syndrome in Patients With Deep Vein Thrombosis Following Total Knee and Hip Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(3): 560-563.
[22] LI JW, MA YS, XIAO LK. Postoperative Pain Management in Total Knee Arthroplasty. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(5):755-761.
[23] 王宁,罗汉民.超前镇痛护理模式在膝关节置换术患者围手术期的应用[J].中国当代医药,2023,30(18):170-173.
[24] 赖迎秋.膝关节置换术患者实施疼痛评估及护理干预对其术后活动能力的影响研究[J].中国社区医师,2019,35(35): 137+139.
[25] 王伟,姜晨轶,丁小萍.改良疼痛评估方法在全膝关节置换术后病人中的应用[J].护理研究,2017,31(11):1402-1403.
[26] 姜俪凡,冯艺,安海燕.人工全膝关节置换术康复锻炼期镇痛方式对关节功能恢复的影响[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2014, 20(2):90-94.
[27] 王旭,高玉华,郭斌,等.罗哌卡因复合舒芬太尼或地佐辛连续股神经阻滞在全膝关节置换术后镇痛中的应用[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2016,32(3):258-261.
[28] 崔翔.不同浓度罗哌卡因收肌管阻滞结合股外侧皮神经阻滞用于全膝关节置换术后的镇痛效果研究[D].太原:山西医科大学,2023.
[29] 吴明珑,田薇,刘洪娟.人工全膝关节置换术后最佳冰敷时间及频率的研究[J].骨科,2015,6(3):159-161.
[30] 蔡立柏,刘延锦,李英,等.多学科协作干预方案在全膝关节置换术后恐动症患者中的应用研究[J].中华护理杂志, 2020,55(4):494-499.
[31] 王博,老年全膝关节置换术患者恐动症状况及其与心理韧性、家庭关怀的关系研究[D].济南:山东中医药大学,2020.
[32] 赵传伟.耳穴压豆联合穴位贴敷改善全膝关节置换术后疼痛的临床研究[D].北京:中国中医科学院,2022.
[33] 杨勇,尹吉恒,韩丽.TKA术后患肢穴位电针刺治疗对术后疼痛及康复的影响[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2017,17(35): 24-25+27.
[34] 北京医学会骨科专业委员会关节外科学组,中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组.中国全膝关节置换术围手术期疼痛管理指南(2022)[J].协和医学杂志,2022, 13(6):965-985.
[35] ASO K, IKEUCHI M, TAKAYA S, et al. Chronic postsurgical pain after total knee arthroplasty: A prospective cohort study in Japanese population. Mod Rheumatol. 2021;31(5):1038-1044.
[36] GROSU I, LAVAND’HOMME P, THIENPONT E. Pain after knee arthroplasty: an unresolved issue. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22(8):1744-1758.
[37] RAJA SN, CARR DB, COHEN M, et al. The revised International Association for the Study of Pain definition of pain: concepts, challenges, and compromises. Pain. 2020; 161(9):1976-1982.
[38] HAH JM, CRAMER E, HILMOE H, et al. Factors Associated With Acute Pain Estimation, Postoperative Pain Resolution, Opioid Cessation, and Recovery Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(3):e190168.
[39] SPRINGBORG AH, KEHLET H, NIELSEN NI, et al. Predictors of subacute postoperative pain after total knee arthroplasty: A secondary analysis of two randomized trials. Eur J Pain. 2025;29(1):e4703.
[40] BURNS LC, RITVO SE, FERGUSON MK, et al. Pain catastrophizing as a risk factor for chronic pain after total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review. J Pain Res. 2015;8: 21-32.
[41] SCHWARZKOPF R, DREXLER M, MA MW, et al. Is There a Benefit for Liposomal Bupivacaine Compared to a Traditional Periarticular Injection in Total Knee Arthroplasty Patients With a History of Chronic Opioid Use? J Arthroplasty. 2016; 31(8):1702-1705.
[42] WHALE K, WYLDE V, BESWICK A, et al. Effectiveness and reporting standards of psychological interventions for improving short-term and long-term pain outcomes after total knee replacement: a systematic review. BMJ Open. 2019;9(12):e029742.
[43] KRAEKEL SM, CABARCAS BC, SALOMON KI, et al. Impact of State Opioid Regulation on Postoperative Opioid Prescribing Patterns for Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Retrospective Analysis. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2023;31(5):258-264.
[44] ABDALLAH FW, GILRON I, FILLINGIM RB, et al. AAAPT Diagnostic Criteria for Acute Knee Arthroplasty Pain. Pain Med. 2020;21(5):1049-1060.
[45] SPRINGBORG AH, VISBY L, KEHLET H, et al. Psychological predictors of acute postoperative pain after total knee and hip arthroplasty: A systematic review. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2023;67(10): 1322-1337.
[46] GOLLADAY GJ, BALCH KR, DALURY DF, et al. Oral Multimodal Analgesia for Total Joint Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2017; 32(9):S69-S73.
[47] MEMTSOUDIS SG, POERAN J, ZUBIZARRETA N, et al. Association of Multimodal Pain Management Strategies with Perioperative Outcomes and Resource Utilization A Population-based Study. Anesthesiology. 2018;128(5):891-902.
[48] SUN H, HUANG ZY, ZHANG ZQ, et al. A Meta-Analysis Comparing Liposomal Bupivacaine and Traditional Periarticular Injection for Pain Control after Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2019;32(3):251-258.
[49] JIANG H, MA Q, DONG J, et al. The effect of liposomal bupivacaine for surgical wound infiltration: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Int Wound J. 2023;20(5):1591-1608.
[50] LIU Y, ZENG Y, ZENG JF, et al. The efficacy of liposomal bupivacaine compared with traditional peri-articular injection for pain control following total knee arthroplasty: an updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):306.
[51] 马国续.收肌管阻滞与股神经阻滞在全膝关节置换快速康复中的临床疗效分析[D].银川:宁夏医科大学,2019.
[52] 李潞,汪文静,王海丽. 超声引导下收肌管阻滞联合坐骨神经阻滞在膝关节置换术后的镇痛效果[J].海军医学杂志, 2022,43(5):505-508.
[53] 刘羡,周琴,李仁华.腘丛神经阻滞对全膝关节置换术患者术后镇痛、应激反应及功能恢复的影响[J].医学理论与实践, 2023,36(24):4206-4209.
[54] SUN EC, BATEMAN BT, MEMTSOUDIS SG, et al. Lack of Association Between the Use of Nerve Blockade and the Risk of Postoperative Chronic Opioid Use Among Patients Undergoing Total Knee Arthroplasty: Evidence From the Marketscan Database. Anesth Analg. 2017;125(3):999-1007.
[55] SWISHER MW, BALL ST, GONZALES FB, et al. A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study Using Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Cryoneurolysis of the Infrapatellar Branch of the Saphenous Nerve for Analgesia Following Total Knee Arthroplasty. Pain Ther. 2022;11(4):1299-1307.
[56] 白天宇.经皮穴位电刺激联合多模式镇痛改善TKA术后疼痛加速康复的临床研究[D].北京:中国中医科学院,2023.
[57] 钟伟华,苟凌云,廖明军,等.耳穴压丸法辅助镇痛对原发性全膝关节置换术后下肢疼痛和膝关节功能的影响[J].亚太传统医药,2023,19(3):88-93.
[58] 张坤鹏,陈先进.血府逐瘀汤在全膝关节置换术后肿痛治疗中的应用效果[J].中国社区医师,2023,39(1):63-65.
[59] 李凯明,金添,申杨勇,等.经皮穴位电刺激对膝关节置换患者生存质量中远期疗效评价[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2023, 25(10):59-63.
|