[1] ZAN J, QIAN G, DENG F, et al. Dilemma and breakthrough of biodegradable poly-l-lactic acid in bone tissue repair. J Mater Res Technol. 2022;17:2369-2387.
[2] NORRIS BL, VANDERKARR M, SPARKS C, et al. Treatments, cost and healthcare utilization of patients with segmental bone defects. Injury. 2021;52(10):2935-2940.
[3] BALL AN, DONAHUE SW, WOJDA SJ, et al. The challenges of promoting osteogenesis in segmental bone defects and osteoporosis. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(6):1559-1572
[4] SADOWSKA JM, POWER RN, GENOUD KJ, et al. A multifunctional scaffold for bone infection treatment by delivery of microRNA therapeutics combined with antimicrobial nanoparticles. Adv Mater. 2024;36(6):2307639.
[5] MAUFFREY C, BARLOW BT, SMITH W. Management of segmental bone defects. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015;23(3):143-153.
[6] VALTANEN RS, YANG YP, GURTNER GC, et al. Synthetic and bone tissue engineering graft substitutes: what is the future? Injury. 2021;52 Suppl 2:S72-S77.
[7] SCHMIDT AH. Autologous bone graft: is it still the gold standard? Injury. 2021;52 Suppl 2:S18-S22.
[8] 张治博,王兆林,王志刚,等.Ilizarov骨搬移联合抗生素骨水泥促进胫骨大段骨缺损的对接点愈合[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(10):2038-2043.
[9] DAHL MT, MORRISON S. Segmental bone defects and the history of bone transport. J Orthop Trauma. 2021;35(Suppl 4):S1-S7.
[10] 赵越,许燕,周建平,等.骨组织工程中传统与仿生支架结构设计的差异[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(16):3458-3468.
[11] 朱昱衡,肖砚斌,李凌,等.3D打印聚醚醚酮假体重建锁骨恶性肿瘤切除后缺损[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2024,32(15): 1410-1414.
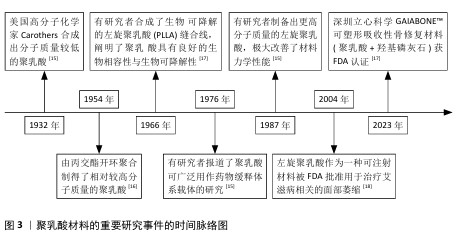
[12] 刘姿辰,禹宝庆.生物可降解聚乳酸用于骨修复的发展前景和研究价值[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(34):5552-5560.
[13] XIA D, WANG Y, WU R, et al. The effect of pore size on cell behavior in mesoporous bioglass scaffolds for bone regeneration. Appl Mater Today. 2022;29:101607.
[14] 董博,李效宇,李碧榕,等.3D打印支架修复感染性骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(29):4685-4690.
[15] 崔靖园,陈璨,杨洋,等.医用级聚乳酸合成及改性研究进展[J].化工新型材料, 2020,48(10): 268-272.
[16] 许明奕,逄宇帆,刑涛,等.聚乳酸合成方法的研究进展及市场分析[J].应用化工,2022,51(12):3614-3618,3624.
[17] 龚亚辉,王舒.新型生物医用材料聚乳酸产业及植入应用现状研究[J].当代化工研究,2024(6):24-26.
[18] 董诚挚,朱辉.注射用聚左旋乳酸在体表软组织充填中的应用现状[J].中国美容医学,2022,31(2):182-185.
[19] DAI W, LI S, JIA H, et al. Indirect 3D printing CDHA scaffolds with hierarchical porous structure to promote osteoinductivity and bone regeneration. J Mater Sci Technol. 2025;207:295-307.
[20] WANG C, WANG H, CHEN Q, et al. Polylactic acid scaffold with directional porous structure for large-segment bone repair. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;216:810-819.
[21] 章乐民.3D打印左旋聚乳酸复合骨植入物的成骨和抗菌性能研究[D].南昌:江西理工大学,2023.
[22] ZHENG Y, DENG F, WANG B, et al. Melt extrusion deposition (MED™) 3D printing technology-a paradigm shift in design and development of modified release drug products. Int J Pharm. 2021;1(60):120-135.
[23] 董谢平,裴国献.3D打印技术在骨科临床的应用与展望[J].陆军军医大学学报, 2022,44(15):1501-1507.
[24] WANG Z, WANG Y, YAN J, et al. Pharmaceutical electrospinning and 3D printing scaffold design for bone regeneration. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021; 174:504-534.
[25] XIONG S, ZHANG Y, ZENG J, et al. DLP fabrication of HA scaffold with customized porous structures to regulate immune microenvironment and macrophage polarization for enhancing bone regeneration. Mater Today Bio. 2024;24:100929.
[26] WANG W, LIU P, ZHANG B, et al. Fused deposition modeling printed PLA/Nano β-TCP composite bone tissue engineering scaffolds for promoting osteogenic induction function. Int J Nanomed. 2023; 18:5815-5830.
[27] DI W, SHUAI C, WANG Y, et al. A Chemotherapy-photothermal synergistic system in bifunctional bone scaffold: tumor therapy and bone repair. Mater Des. 2024. DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2024. 113269.
[28] 张雪琴,章宇轩,侯丹,等.光固化生物3D打印研究进展及其在生物医药领域的应用[J].中国科学:化学,2023,53(6): 958-973.
[29] 董栋,苏海军,李翔,等.光固化3D打印磷酸钙基生物陶瓷支架的研究进展[J].材料导报, 2023,37(18):66-74.
[30] KORDI O, BEHRAVESH AH, HASANNIA S,
et al. Additive manufacture of PLLA scaffolds reinforced with graphene oxide nano-particles via digital light processing (DLP). J Biomater Appl. 2023;38(4):484-499.
[31] GARZON-HERNANDEZ S, GARCIA-GONZALEZ D, JERUSALEM A, et al. Design of FDM 3D printed polymers: an experimental-modelling methodology for the prediction of mechanical properties. Mater Des. 2020;188:108414.
[32] ZHANG B, WANG L, SONG P, et al. 3D printed bone tissue regenerative PLA/HA scaffolds with comprehensive performance optimizations. Mater Des. 2021;201:109490.
[33] KOLLAMARAM G, CROKER DM, WALKER GM, et al. Low temperature fused deposition modeling (FDM) 3D printing of thermolabile drugs. Int J Pharm. 2018; 545(1-2):144-152.
[34] TABRIZ AG, KUOFIE H, SCOBLE J, et al. Selective Laser Sintering for printing pharmaceutical dosage forms. J Drug Deliv Sci Tec. 2023;86:104699.
[35] FENG P, SHEN S, SHUAI Y, et al. PLLA grafting draws GO from PGA phase to the interface in PLLA/PGA bone scaffold owing enhanced interfacial interaction. SM&T. 2023;35:e00566.
[36] SHUAI C, YANG W, FENG P, et al. Accelerated degradation of HAP/PLLA bone scaffold by PGA blending facilitates bioactivity and osteoconductivity. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(2): 490-502.
[37] XIONG W, YUAN L, HUANG J, et al. Direct osteogenesis and immunomodulation dual function via sustained release of naringin from the polymer scaffold. J Mater Chem B. 2023;11(45):10896-10907.
[38] RAHMATI M, MILLS DK, URBANSKA AM, et al. Electrospinning for tissue engineering applications. Prog Mater Sci. 2021;117:100721.
[39] MENG C, TANG D, LIU X, et al. Heterogeneous porous PLLA/PCL fibrous scaffold for bone tissue regeneration. Int Bio Macromol. 2023;235:123781.
[40] MENG C, LIU X, LI R, et al. 3D Poly (L-lactic acid) fibrous sponge with interconnected porous structure for bone tissue scaffold. Int Bio Macromol. 2024;268:131688.
[41] STELLA SMM, RAMA M, SRIDHAR TM,
et al. Optimization of biologically inspired electrospun scaffold for effective use in bone regenerative applications. Polymers. 2024;16(14):2023.
[42] MIRJALILI M, ZOHOORI S. Review for application of electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers technology in textile industry. J Nanostruct Chem. 2016;6: 207-213.
[43] LI Y, LI J, ZHONG Y, et al. pH-Responsive and nanoenzyme-loaded artificial nanocells relieved osteomyelitis efficiently by synergistic chemodynamic and cuproptosis therapy. Biomaterials. 2025;313:122762.
[44] SHUAI C, SHI X, WANG K, et al. Ag-doped CNT/HAP nanohybrids in a PLLA bone scaffold show significant antibacterial activity. Bio-Des Manuf. 2024;7(2):
105-120.
[45] LI B, YANG H, SONG H, et al. Composite PLLA/Ag@ SiO2 microspheres for bone regeneration in infected bone defects. Ceram Int. 2023;49(18):30424-30435.
[46] QIAO Z, ZHANG W, JIANG H, et al. 3D-printed composite scaffold with anti-infection and osteogenesis potential against infected bone defects. RSC Adv. 2022;12(18):
11008-11020.
[47] GUO W, LIU W, XU L, et al. Halloysite nanotubes loaded with nano silver for the sustained-release of antibacterial polymer nanocomposite scaffolds. J Mater Sci Technol. 2020;46:237-247.
[48] LIU X, LIU Y, QIANG L, et al. Multifunctional 3D-printed bioceramic scaffolds: recent strategies for osteosarcoma treatment. J Tissue Eng. 2023;14:20417314231170371.
[49] REN Y, CHEN C, ZHANG M, et al. Application of nanostructure-loaded hydrogels for cancer treatment and tissue regeneration. Appl Mater Today. 2024;37:102086.
[50] DI W, SHUAI Y, BO W, et al. A bifunctional zoledronate sustained-release system in scaffold: Tumor therapy and bone repair. Colloids Surf B. 2023;222:113064.
[51] SZYMANSKI W. Beyond photodynamic therapy: light-activated cancer chemotherapy. Curr Med Chem. 2017; 24(42):4905-4950.
[52] QIAN G, WANG J, YANG L, et al. A pH-responsive CaO2@ ZIF-67 system endows a scaffold with chemodynamic therapy properties. J Mater Sci. 2023;58(3):1214-1228.
[53] LEE HJ, JEON JH, KIM CH, et al. Photosynthetic microporous bioactive glass ceramic beads for treating avascular osteonecrosis. J Ind Eng Chem. 2023;122:551-561.
[54] MA C, ANDRE G, EDWARDS D, et al. A rat model of ischemic osteonecrosis for investigating local therapeutics using biomaterials. Acta Biomater. 2021;132:260-271.
[55] YANG F, XU C, ZHANG W, et al. Biodegradable magnesium incorporated microspheres enable immunomodulation and spatiotemporal drug release for the treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Compos Part B-Eng. 2023; 250:110430.
[56] YANG Y, YAO Z, SUN Y, et al. 3D-printed manganese dioxide incorporated scaffold promotes osteogenic-angiogenic coupling for refractory bone defect by remodeling osteo-regenerative microenvironment. Bioact Mater. 2025;44:354-370.
[57] FENG G, ZHANG P, HUANG J, et al. Sequential release of Panax notoginseng saponins and osteopractic total flavone from poly (L-lactic acid) scaffold for treating glucocorticoid-associated osteonecrosis of femoral head. J Funct Biomater. 2023;14(1):31.
[58] HWANG SH, CHO PG, KIM K, et al. What are the risk factors for a second osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture? Spine J. 2023;23(11):1586-1592.
[59] KATTHAGEN JC, SCHWARZE M, WARNHOFF M, et al. Influence of plate material and screw design on stiffness and ultimate load of locked plating in osteoporotic proximal humeral fractures. Injury. 2016;47(3): 617-624.
[60] ORYAN A, HASSANAJILI S, SAHVIEH S. Zoledronate loaded polylactic acid/polycaprolactone/hydroxyapatite scaffold accelerates regeneration and led to enhance structural performance and functional ability of the radial bone defect in rat. Iran J Vet Res. 2023;24(2):122.
[61] DRAKE MT, CLARKE BL, LEWIECKI EM. The pathophysiology and treatment of osteoporosis. Clin Ther. 2015;37(8): 1837-1850.
[62] YAN C, ZHANG P, QIN Q, et al. 3D-printed bone regeneration scaffolds modulate bone metabolic homeostasis through vascularization for osteoporotic bone defects. Biomaterlals. 2024;311:122699. |