[1] SABARI SS, BALASUBRAMANI K, IYER M, et al. Type 2 diabetes (T2DM) and parkinson’s disease (PD):a mechanistic approach. Mol Neurobiol. 2023;60(8):4547-4573.
[2] 糖尿病微循环障碍临床用药专家共识(2021年版)[J].中国医学前沿杂志,2021, 13(4):49-57.
[3] 朱欢,庹艳芳,文凡,等.常见代谢性疾病微循环功能变化及有氧运动干预效应[J].湖北体育科技,2024,43(3):87-93.
[4] 陈凯帆,林佳钏,王平.超声造影研究2型糖尿病骨骼肌微循环进展[J].中国介入影像与治疗学,2022,19(10):661-664.
[5] ZHANG X, DUAN Y, ZHANG X, et al. Adipsin alleviates cardiac microvascular injury in diabetic cardiomyopathy through Csk-dependent signaling mechanism. BMC Med. 2023;21(1):197-218.
[6] FUJJJ N, MCGARR GW, AMANO T, et al. Type 2 diabetes impairs vascular responsiveness to nitric oxide, but not the venoarteriolar reflex or post-occlusive reactive hyperaemia in forearm skin. Exp Dermatol. 2021; 30(12):1807-1813.
[7] RUSSELL RD, ROBERTS-THOMSON KM, HU D, et al. Impaired postprandial skeletal muscle vascular responses to a mixed meal challenge in normoglycaemic people with a parent with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2022;65(1):216-225.
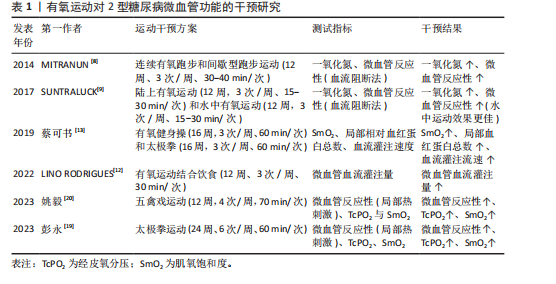
[8] MITRANUN W, DEEROCHANAWONG C, TANAKA H, et al. Continuous vs interval training on glycemic control and macro-and microvascular reactivity in type 2 diabetic patients. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2014;24(2):e69-e76.
[9] SUNTRALUCK S, TANAKA H, SUKSOM D, et al. The relative efficacy of land-based and water-based exercise training on macro- and micro-vascular functions in older patients with type 2 diabetes. J Aging Physical Acti. 2017; 25(3):446-452.
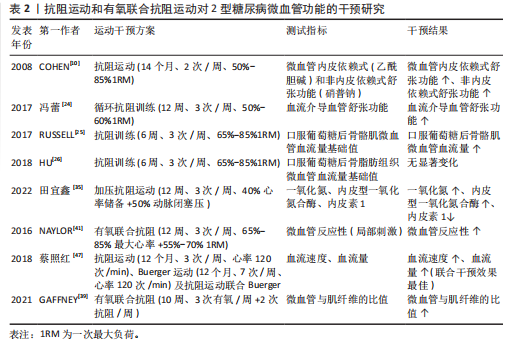
[10] COHEN ND, DUNSTAN DW, ROBINSON C, et al. Improved endothelial function following a 14-month resistance exercise training program in adults with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes ResClin Pract. 2008; 79(3):405-411.
[11] GAFFNEY K, LUCERO A, MACARTNEY-COXSON D, et al. Effects of whey protein on skeletal muscle microvascular and mitochondrial plasticity following 10 weeks of exercise training in men with type 2 diabetes. Applied Physiology, Nutrition. And Metabolism. 2021;46(8):915-924.
[12] LINO RODRIGUES K, VIEIRA DIAS DA SILVA V, NUNES GOULART DA SILVA PEREIRA E, et al. Aerobic exercise training improves microvascular function and oxidative stress parameters in diet-induced type 2 diabetic mice. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2022;15: 2991-3005.
[13] 蔡可书. 健身操和太极拳运动对中老年2型糖尿病患者下肢循环功能的影响[D].南京:南京体育学院,2019.
[14] 彭永,胡江平,朱欢.低负荷血流限制和高强度抗阻运动对男性运动青年大腿微循环功能的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2025,29(2):393-401.
[15] 朱欢,高炳宏.微血管反应性在耐力性运动员训练中的应用[J].中国运动医学杂志,2019,38(10):907-914.
[16] 朱欢,高炳宏.有氧运动对人体微血管反应性的作用及机制研究进展[J].生命科学,2020,32(8):855-863.
[17] 陈友强,程瑞豪,贺缨,等.基于皮肤温度信号的糖尿病患者血管舒张功能评价[J].医用生物力学,2023,38(2):368-374.
[18] FUCHS D, DUPON PP, SCHAAP LA, et al. The association between diabetes and dermal microvascular dysfunction non-invasively assessed by laser Doppler with local thermal hyperemia: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017;16(1):11-22.
[19] 彭永,朱欢,刘尧峰,等.24周太极拳结合弹力带抗阻运动对2型糖尿病患者足背微循环功能的影响[J].首都体育学院学报, 2023,35(1):77-85.
[20] 姚毅. 12周五禽戏运动对2型糖尿病患者微循环功能的影响及可能机制研究[D].恩施:湖北民族大学,2023.
[21] 肖哲,朱欢,胡江平,等.10周有氧运动和有氧结合抗阻运动对肥胖大学生微循环功能的影响及机制研究[J].中国全科医学, 2022,25(19):2349-2355+2362.
[22] PRIMER KR, PSALTIS PJ, TAN JTM, et al. The role of high-density lipoproteins in endothelial cell metabolism and diabetes-impaired angiogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(10):3633-3653.
[23] 文凡,朱欢,王康锋,等.水中运动疗法对常见慢性病干预效果的研究进展[J].体育科技文献通报,2024,32(2): 236-241.
[24] 冯蕾,周素珍,赵占胜,等.循环运动训练对2型糖尿病妇女心肺适能及血流介导的血管舒张功能的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志,2017,32(6):680-685.
[25] RUSSELL RD, HU D, GREENAWAY T, et al. Skeletal muscle microvascular-linked improve ments in glycemic control from resistance training in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(9): 1256 -1263.
[26] HU D, RUSSELL RD, REMASH D, et al. Are the metabolic benefits of resistance training in type 2 diabetes linked to improvements in adipose tissue microvascular blood flow. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2018;315(6): E1242-E1250.
[27] HU D, REMASH D, RUSSELL RD, et al. Impairments in adipose tissue microcirculation in type 2 diabetes mellitus assessed by real-time contrast-enhanced ultrasound. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018;11(4): e007074-e007088.
[28] KAMBIČ T. Blood flow restriction training: You can occlude your veins, but not your oxygen transport. J Physiol. 2020;598(18):3825-3826.
[29] SAATMANN N, ZAHARIA OP, LOENNEKE JP, et al. Effects of blood flow restriction exercise and possible applications in type 2 diabetes. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2021;32(2):106-117.
[30] ŞAHIN E, AYAZ T, SAGLAM M, et al. Acute effects of blood flow restricted aerobic exercise in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Medicine(Baltimore). 2024;103(31): e39031-e39037.
[31] DA CUNHA NASCIMENTO D, SCHOENFELD BJ, PRESTES J, et al. Potential implications of blood flow restriction exercise on vascular health:a brief review. Sports Med. 2020;50(1):73-81.
[32] MAGA M, WACHSMANN-MAGA A, BATKO K, et al. Impact of blood-flow-restricted training on arterial Functions and angiogenesis-a systematic review with meta-analysis. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(6):1601-1619.
[33] GARCIA NF, DE MORAES C, REBELO MA, et al. Low load strength training, associated with or without blood flow restriction increased no production and decreased production of reactive oxygen species in rats aorta. Life Sci. 2022;294:120350-120358.
[34] 刘申,姬卫秀,唐佳福,等.加压训练对心血管系统的作用研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志,2023,42(5):401-406.
[35] 田宜鑫.血流限制训练对Ⅱ型糖尿病患者糖脂代谢指标和血管内皮因子的影响[D].南京:南京体育学院,2022.
[36] 魏佳,李博,冯连世,等.血流限制训练的方法学因素及潜在安全性问题[J].中国体育科技,2019,55(3):3-12.
[37] 范紫菡,吴迎.缺血处理在运动训练中的应用:效果、机制及问题[J].中国运动医学杂志,2024,43(9):753-766.
[38] 逯莉莉.血流限制联合四肢联动训练对2型糖尿病患者干预效果的观察[D].天津: 天津体育学院,2022.
[39] GAFFNEY K, LUCERO A, MACARTNEY-COXSON D, et al. Effects of whey protein on skeletal muscle microvascular and mitochondrial plasticity following 10 weeks of exercise training in men with type 2 diabetes. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, And Metabolism. 2021;46(8):915-924.
[40] JORGE ML, DE OLIVEIRA VN, RESENDE NM, et al. The effects of aerobic, resistance, and combined exercise on metabolic control, inflammatory markers, adipocytokines, and muscle insulin signaling in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus - ScienceDirect. Metabolism. 2011;60(9):1244-1252.
[41] NAYLOR LH, DAVISEA, KALIC RJ, et al. Exercise training improves vascular function in adolescents with type 2 diabetes. Physiol Rep. 2016;4(4):e12713-e12724.
[42] ZHAO YC, GUO W, GAO BH, et al. Hypoxic training upregulates mitochondrial turnover and angiogenesis of skeletal muscle in mice. Life Sci. 2022;291:119340-119347.
[43] MA C, ZHAO Y, DING X, et al. The role of Sirt3 in the changes of skeletal muscle mitophagy induced by hypoxic training. Gen Physiol Biophys. 2022;41(5):447-455.
[44] MA C, ZHAO Y, DING X, et al. Hypoxic training ameliorates skeletal muscle microcirculation vascular function in a sirt3-dependentmanner. Frontiers in Phy. 2022;13:921763-921771.
[45] SUN Q, JIA H, CHENG S, et al. Metformin alleviates epirubicin-induced endothelial impairment by restoring mitochondrial homeostasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;24(1):343-357.
[46] 林建健,宋洁.运动调控线粒体动力学变化的研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究, 2024,28(11):1767-1771.
[47] 蔡照红,江培兰,鲍红丹,等.抗阻运动联合Buerger运动在2型糖尿病下肢血管病变治疗中的应用[J].中国基层医药,2018,25(18):2354-2358.
[48] 时文霞,谢军,何玉凤,等.血管内皮功能障碍运动干预的血流剪切力作用机制研究进展[J].中国体育科技,2024, 60(3):51-64.
[49] 段艺杰,任韦燕,叶文强,等.日常运动对行走刺激下糖尿病足部微循环响应的影响[J].医用生物力学,2021, 36(S1):133.
[50] SÖRENSEN BM, VAN DER HEIDE FCT, HOUBEN AJHM, et al. Higher levels of daily physical activity are associated with better skin microvascular function in type 2 diabetes-The Maastricht Study. Microcirculation. 2020;27(4): e12611-e12623.
[51] MORTENSEN SP, WINDING KM, IEPSEN UW, et al. The effect of two exercise modalities on skeletal muscle capillary ultrastructure in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2019;29(3):360-368.
[52] ZINN S, NELIS P, MINNEBECK K, et al. Effect of high-intensity interval training in patients with type 1 diabetes on physical fitness and retinal microvascular perfusion determined by optical coherence tomography angiography. Microvasc Res. 2020;132: 104057-104065.
[53] ANDERSEN TR, SCHMIDT JF, THOMASSEN M, et al. A preliminary study: effects of football training on glucose control, body composition, and performance in men with type 2 diabetes. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2014; 24(Supplement):43-56.
[54] MACHADO MV, VIEIRA AB, DA CONCEIÇÃO F, et al. Exercise training dose differentially alters muscle and heart capillary density and metabolic functions in an obese rat with metabolic syndrome. Exp Physiol. 2017; 102(12):1716-1728.
[55] 胥祉涵,王世强,李丹,等.2022年美国运动医学会《2型糖尿病患者的运动/身体活动指南》解读及启示[J].中国全科医学,2022,25(25):3083-3088.
[56] 《2型糖尿病患者体重管理专家共识》专家组.2型糖尿病患者体重管理专家共识(2024年版)[J].国际内分泌代谢杂志,2024, 44(5):359-370.
[57] 周术锋,肖哲,朱欢,等.12周有氧运动对习惯久坐大学生微循环功能的影响[J].中国学校卫生,2021,42(9):1332-1335+1339.
[58] BORGES JP, NASCIMENT AR, LOPES GO, et al. The impact of exercise frequency upon microvascular endothelium function and oxidative stress among patients with coronary artery disease. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2018;38(5):840-846.
[59] BORGES JP, LOPES GO, VERRI V, et al. A novel effective method for the assessment of microva-scular function in male patients with coronary artery disease: a pilot studyusing laser speck-le contrast imaging. Braz JMed Biol Res. 2016;49(10): e5541-e5547.
[60] KANALEY JA, COLBERG SR, CORCORAN MH, et al. Exercise/Physical activity in individuals with type 2 diabetes: a consensus statement from the american college of sports medicine. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2022;54(2):353-368.
|