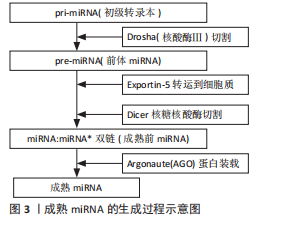
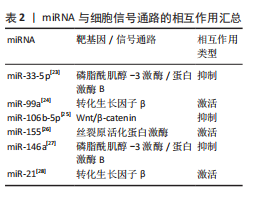
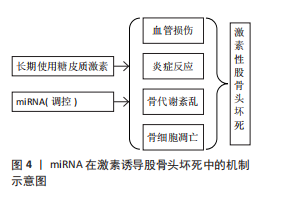
[1] 白锐,赵振群,刘万林,等.糖皮质激素诱导缺氧状态及程序性细胞死亡在股骨头坏死中调控机制[Z]. 内蒙古医科大学第二附属医院,2023.
[2] 孔令跃,刘万林,任逸众.激素性股骨头缺血坏死与Dickkopf-1及细胞凋亡的关系[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(28):4436-4441.
[3] TYC KM, WONG A, SCOTT RT JR, et al. Analysis of DNA variants in miRNAs and miRNA 3’UTR binding sites in female infertility patients. Lab Invest. 2021;101(4):503-512.
[4] BARTEL DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 200;116(2): 281-297.
[5] NOVINA CD, SHARP PA. The RNAi revolution. Nature. 2004;430(6996):161-164.
[6] LONG D, LEE R, WILLIAMS P, et al. Potent effect of target structure on microRNA function. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007;14(4):287-294.
[7] KOBAYASHI T, LU J, COBB BS, et al. Dicer-dependent pathways regulate chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(6):1949-1954.
[8] PALMIERI A, PEZZETTI F, BRUNELLI G, et al. Medpor regulates osteoblast’s microRNAs. Biomed Mater Eng. 2008;18(2):91-97.
[9] PALMIERI A, PEZZETTI F, SPINELLI G, et al. PerioGlas regulates osteoblast RNA interfering. J Prosthodont. 2008;17(7): 522-526.
[10] 白锐,刘万林.激素性股骨头缺血坏死病因学机制研究进展[J].内蒙古医学杂志,2010, 42(8):955-958.
[11] 赵振群,刘万林.激素性股骨头缺血坏死发病机理基因学研究进展[J].内蒙古医学杂志, 2010,42(7): 804-808.
[12] LIAN JB, STEIN GS, VAN WIJNEN AJ, et al. MicroRNA control of bone formation and homeostasis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2012;8(4): 212-227.
[13] TAIPALEENMÄKI H, BJERRE HOKLAND L, CHEN L, et al. Mechanisms in endocrinology: micro-RNAs: targets for enhancing osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Eur J Endocrinol. 2012;166(3):359-371.
[14] ALEČKOVIĆ M, KANG Y. Bone marrow stroma-derived miRNAs as regulators, biomarkers and therapeutic targets of bone metastasis. Bonekey Rep. 2015;4:671.
[15] 刘万林.自噬基因Beclin1与MAP1LC3在激素性股骨头缺血坏死中的作用及3-MA对其影响的实验研究 [D].呼和浩特:内蒙古医科大学第二附属医院,2018.
[16] 赵振群.低氧诱导因子-1与自噬相关基因MAP1LC3在激素性股骨头缺血坏死中作用的实验研究[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古医科大学第二附属医院,2018.
[17] DIENER C, KELLER A, MEESE E. Emerging concepts of miRNA therapeutics: from cells to clinic. Trends Genet. 2022;38(6):613-626.
[18] NOGAMI M, MIYAMOTO K, HAYAKAWA-YANO Y, et al. DGCR8-dependent efficient pri-miRNA processing of human pri-miR-9-2. J Biol Chem. 2021;296:100409.
[19] LI Z, IIDA J, SHIIMORI M, et al. Exportin-5 binding precedes 5’- and 3’-end processing of tRNA precursors in Drosophila. J Biol Chem. 2024;300(9):107632.
[20] MCGEARY SE, LIN KS, SHI CY, et al. The biochemical basis of microRNA targeting efficacy. Science. 2019;366(6472):eaav1741.
[21] NEWMAN MA, THOMSON JM, HAMMOND SM. Lin-28 interaction with the Let-7 precursor loop mediates regulated microRNA processing. RNA. 2008;14(8):1539-1549.
[22] RYBAK A, FUCHS H, SMIRNOVA L, et al. A feedback loop comprising lin-28 and let-7 controls pre-let-7 maturation during neural stem-cell commitment. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10(8):987-993.
[23] ZHAO L, HUANG J, ZHU Y, et al. miR-33-5p knockdown attenuates abdominal aortic aneurysm progression via promoting target adenosine triphosphate-binding cassette transporter A1 expression and activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Perfusion. 2020;35(1):57-65.
[24] EMMRICH S, RASCHE M, SCHÖNING J, et al. miR-99a/100~125b tricistrons regulate hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell homeostasis by shifting the balance between TGFβ and Wnt signaling. Genes Dev. 2014; 28(8):858-874.
[25] RONG L, XU Y, ZHANG K, et al. HNRNPA2B1 inhibited SFRP2 and activated Wnt-β/catenin via m6A-mediated miR-106b-5p processing to aggravate stemness in lung adenocarcinoma. Pathol Res Pract. 2022; 233:153794.
[26] XU Y, ZHANG C, CAI D, et al. Exosomal miR-155-5p drives widespread macrophage M1 polarization in hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae-induced acute lung injury via the MSK1/p38-MAPK axis. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023;28(1):92.
[27] XIA C, ZHU K, ZHANG Y, et al. Serum exosome-derived miR-146a-3p promotes macrophage M2 polarization in allergic rhinitis by targeting VAV3 via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023; 124(Pt B):110997.
[28] ZEBOUDJ L, SIDERIS-LAMPRETSAS G, SILVA R, et al. Silencing miR-21-5p in sensory neurons reverses neuropathic allodynia via activation of TGF-β-related pathway in macrophages. J Clin Invest. 2023;133(11):e164472.
[29] ONYIDO EK, SWEENEY E, NATERI AS. Wnt-signalling pathways and microRNAs network in carcinogenesis: experimental and bioinformatics approaches. Mol Cancer. 2016; 15(1):56.
[30] WANG Z, LI Y, KONG D, et al. Cross-talk between miRNA and Notch signaling pathways in tumor development and progression. Cancer Lett. 2010;292(2):141-148.
[31] 李文超,肖骋风,曾朝阳,等.微RNA的发现及其意义:2024年诺贝尔生理学或医学奖的启示[J].生物化学与生物物理进展, 2024,51(12):3061-3072.
[32] THOMSON DW, DINGER ME. Endogenous microRNA sponges: evidence and controversy. Nat Rev Genet. 2016;17(5):272-283.
[33] 赵健志,李欢欢,刘柯欣,等.microRNA与靶基因相互调控机制的研究进展[J].科学通报,2021,66(24):3123-3140.
[34] LI H, QU L. Correlation of miRNA-21 and blood Cr levels with tumor infiltration and distant metastasis in renal cancer patients. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2022;68(5):117-123.
[35] DIAO W, QIAN Q, SHENG G, et al. Triclosan targets miR-144 abnormal expression to induce neurodevelopmental toxicity mediated by activating PKC/MAPK signaling pathway. J Hazard Mater. 2022;431:128560.
[36] NING W, LI S, YANG W, et al. Blocking exosomal miRNA-153-3p derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells ameliorates hypoxia-induced myocardial and microvascular damage by targeting the ANGPT1-mediated VEGF/PI3k/Akt/eNOS pathway. Cell Signal. 2021;77:109812.
[37] TANG L, LU W, HUANG J, et al. miR-144 promotes the proliferation and differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells by downregulating the expression of SFRP1. Mol Med Rep. 2019;20(1):270-280.
[38] HUANG M, WANG Y, WANG Z, et al. miR-134-5p inhibits osteoclastogenesis through a novel miR-134-5p/Itgb1/MAPK pathway. J Biol Chem. 2022;298(7):102116.
[39] GHINI F, RUBOLINO C, CLIMENT M, et al. Endogenous transcripts control miRNA levels and activity in mammalian cells by target-directed miRNA degradation. Nat Commun. 2018; 9(1):3119.
[40] FENG H, YUAN X, WU S, et al. Effects of writers, erasers and readers within miRNA-related m6A modification in cancers. Cell Prolif. 2023;56(1):e13340.
[41] KUREEL J, DIXIT M, TYAGI AM, et al. miR-542-3p suppresses osteoblast cell proliferation and differentiation, targets BMP-7 signaling and inhibits bone formation. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5(2):e1050.
[42] ZHANG Z, JIN A, YAN D. MicroRNA-206 contributes to the progression of steroid‑induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head by inducing osteoblast apoptosis by suppressing programmed cell death 4. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(1):801-808.
[43] 刘佳,胡桃红,袁敏,等.微小RNA调控血管内皮细胞凋亡机制的研究进展[J].解放军医学院学报,2018,39(9):826-829.
[44] 张斌,谢满江.力学敏感性microRNA在微重力环境致血管平滑肌细胞表型转换中的作用[J].心脏杂志,2019,31(2):190-194.
[45] YANG D, YANG Z, CHEN L, et al. Dihydromyricetin increases endothelial nitric oxide production and inhibits atherosclerosis through microRNA-21 in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(10): 5911-5925.
[46] JIANG F, CHEN Q, WANG W, et al. Hepatocyte-derived extracellular vesicles promote endothelial inflammation and atherogenesis via microRNA-1. J Hepatol. 2020;72(1):156-166.
[47] JIANG C, LIN Y, SHAN H, et al. miR-146a Protects against Staphylococcus aureus-Induced Osteomyelitis by Regulating Inflammation and Osteogenesis. ACS Infect Dis. 2022;8(5):918-927.
[48] SUN J, LIAO Z, LI Z, et al. Down-regulation miR-146a-5p in Schwann cell-derived exosomes induced macrophage M1 polarization by impairing the inhibition on TRAF6/NF-κB pathway after peripheral nerve injury. Exp Neurol. 2023;362:114295.
[49] XIAO L, LIU Y, WANG N. New paradigms in inflammatory signaling in vascular endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014; 306(3):H317-325.
[50] 刘丹丹,秦合伟,高洋,等.中药通过miRNA调控血管内皮细胞损伤防治动脉粥样硬化的作用机制研究进展[J].中国药房, 2023,34(12):1524-1528.
[51] 韩杰,林智宇,徐志为,等.miRNA通过骨代谢机制干预股骨头坏死[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(32): 5238-5248.
[52] YING W, RIOPEL M, BANDYOPADHYAY G, et al. Adipose Tissue Macrophage-Derived Exosomal miRNAs Can Modulate In Vivo and In Vitro Insulin Sensitivity. Cell. 2017;171(2):372-384.e312.
[53] YANG C, LIU X, ZHAO K, et al. miRNA-21 promotes osteogenesis via the PTEN/PI3K/Akt/HIF-1α pathway and enhances bone regeneration in critical size defects. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019; 10(1):65.
[54] WANG H, SUN Z, WANG Y, et al. miR-33-5p, a novel mechano-sensitive microRNA promotes osteoblast differentiation by targeting Hmga2. Sci Rep. 2016;6:23170.
[55] WANG H, HU Z, SHI F, et al. Osteoblast-targeted delivery of miR-33-5p attenuates osteopenia development induced by mechanical unloading in mice. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(2):170.
[56] CHEN Z, HUAI Y, CHEN G, et al. MiR-138-5p Targets MACF1 to Aggravate Aging-related Bone Loss. Int J Biol Sci. 2022;18(13): 4837-4852.
[57] CHEN Z, ZHAO F, LIANG C, et al. Silencing of miR-138-5p sensitizes bone anabolic action to mechanical stimuli. Theranostics. 2020; 10(26):12263-12278.
[58] CHUNLEI H, CHANG Z, SHENG L, et al. Down-regulation of MiR-138-5p Protects Chondrocytes ATDC5 and CHON-001 from IL-1 β-induced Inflammation Via Up-regulating SOX9. Curr Pharm Des. 2020;25(43):4613-4621.
[59] 赵园园,代思明,张跃,等.miRNAs对骨关节炎调控的研究进展[J].中华医学杂志, 2019,99(3):235-237.
[60] HAO Y, LU C, ZHANG B, et al. CircPVT1 up-regulation attenuates steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head through regulating miR-21-5p-mediated Smad7/TGFβ signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2021; 25(10):4608-4622.
[61] KIM H, WRANN CD, JEDRYCHOWSKI M, et al.
Irisin Mediates Effects on Bone and Fat via αV Integrin Receptors. Cell. 2018;175(7):1756-1768.e17.
[62] 赵振群,张志峰,刘万林,等.激素性股骨头坏死过程中低氧诱导因子1α与骨细胞凋亡[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(51):8201-8207.
[63] ZHAO G, GU W. Effects of miR-146a-5p on chondrocyte interleukin-1β-induced inflammation and apoptosis involving thioredoxin interacting protein regulation. J Int Med Res. 2020;48(11): 300060520969550.
[64] 宋熙雯,唐燚,宋朝卉,等.低氧状态下HIF-1α对骨细胞凋亡的影响[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2020,30(6):369-375.
[65] ZHOU D, YANG D. [miRNA Is Involved in the Pathogenesis of Multiple Diseases by Targeting Osteoprotegerin]. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024;55(3):777-782.
[66] 李文娜,秦怡,彭伟盼.MicroRNA检测方法研究进展[J].传感器与微系统,2024,43(3):1-5+13.
[67] What will it take to get miRNA therapies to market? Nat Biotechnol. 2024;42(11):1623-1624.
[68] AKHLAGHIPOUR I, TAGHEHCHIAN N, ZANGOUEI AS, et al. MicroRNA-377: A therapeutic and diagnostic tumor marker. Int J Biol Macromol 2023;226:1226-1235.
[69] GAHLAWAT AW, WITTE T, SINN P, et al. Circulating cf-miRNA as a more appropriate surrogate liquid biopsy marker than cfDNA for ovarian cancer. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1): 5503.
[70] SWELLAM M, ZAHRAN RFK, GHONEM SA, et al. Serum MiRNA-27a as potential diagnostic nucleic marker for breast cancer. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2021;127(1):90-96.
[71] ZHANG M, BAI X, ZENG X, et al. circRNA-miRNA-mRNA in breast cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 2021;523:120-130.
[72] WANG X, GUO B, LI Q, et al. miR-214 targets ATF4 to inhibit bone formation. Nat Med. 2013;19(1):93-100.
[73] WIGGINS JF, RUFFINO L, KELNAR K, et al. Development of a lung cancer therapeutic based on the tumor suppressor microRNA-34. Cancer Res. 2010;70(14): 5923-5930.
[74] TRANG P, WIGGINS JF, DAIGE CL, et al. Systemic delivery of tumor suppressor microRNA mimics using a neutral lipid emulsion inhibits lung tumors in mice. Mol Ther.2011;19(6):1116-1122.
[75] ZHU X, LIU Q, ZHU F, et al. An engineered cellular carrier delivers miR-138-5p to enhance mitophagy and protect hypoxic-injured neurons via the DNMT3A/Rhebl1 axis. Acta biomater. 2024;186:424-438.
[76] FEI Y, YU X, LIU P, et al. Simplified Lipid Nanoparticles for Tissue- And Cell-Targeted mRNA Delivery Facilitate Precision Tumor Therapy in a Lung Metastasis Mouse Model. Adv Mater. 2024;36(48):e2409812.
|