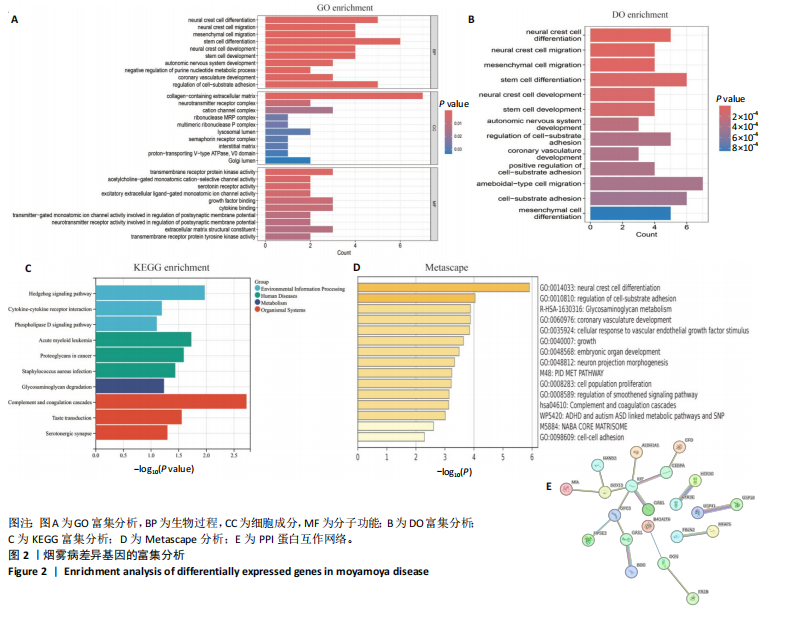
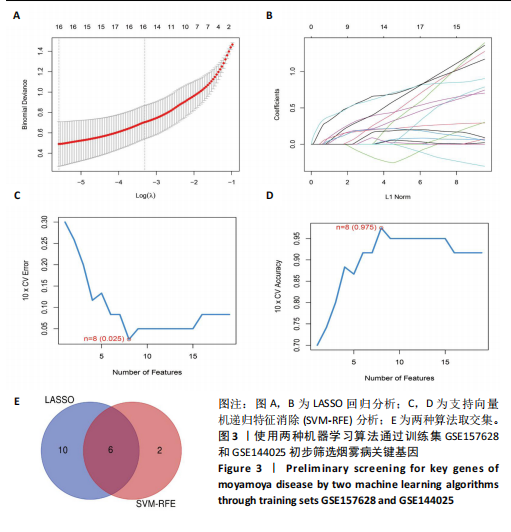
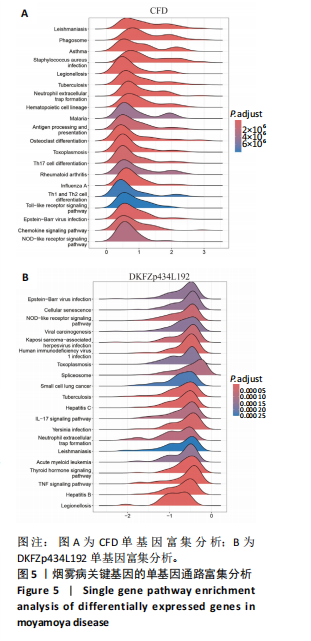
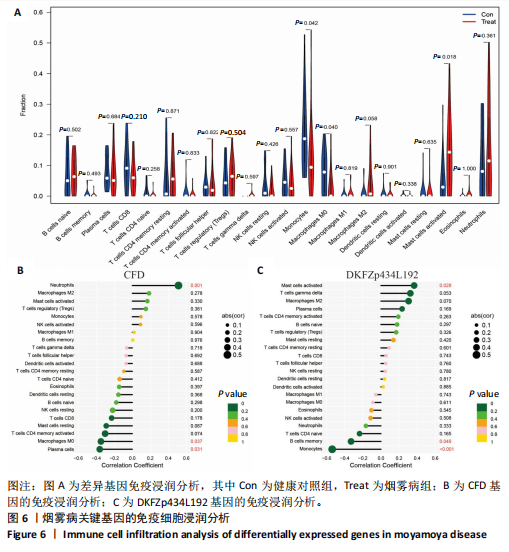
[1] FUJIMURA M, TOMINAGA T, KURODA S, et al. 2021 Japanese Guidelines for the Management of Moyamoya Disease: Guidelines from the Research Committee on Moyamoya Disease and Japan Stroke Society. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2022;62(4):165-170.
[2] KURODA S, FUJIMURA M, TAKAHASHI J, et al. Diagnostic Criteria for Moyamoya Disease - 2021 Revised Version. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2022;62(7):307-312.
[3] KURODA S, HOUKIN K. Moyamoya disease: current concepts and future perspectives. Lancet Neurol. 2008;7(11):1056-1066.
[4] UCHINO K, JOHNSTON SC, BECKER KJ, et al. Moyamoya disease in Washington State and California. Neurology. 2005;65(6):956-958.
[5] KIM JS. Moyamoya Disease: Epidemiology, Clinical Features, and Diagnosis. J Stroke. 2016;18(1):2-11.
[6] GONZALEZ NR, AMIN-HANJANI S, BANG OY, et al. Adult Moyamoya Disease and Syndrome: Current Perspectives and Future Directions: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2023;54(10):e465-e479.
[7] LI J, JIN M, SUN X, et al. Imaging of Moyamoya Disease and Moyamoya Syndrome: Current Status. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2019;43(2): 257-263.
[8] YANG H, HUANG G, LI X, et al. High-resolution magnetic resonance vessel wall imaging provides new insights into Moyamoya disease. Front Neurosci. 2024;18:1375645.
[9] 中华医学会神经外科学分会.烟雾病和烟雾综合征诊断与治疗中国专家共识(2024版)[J].中华神经外科杂志,2024,40(3):220-229.
[10] PORRAS JL, YANG W, XU R, et al. Effectiveness of Ipsilateral Stroke Prevention Between Conservative Management and Indirect Revascularization for Moyamoya Disease in a North American Cohort. World Neurosurg. 2018;110:e928-e936.
[11] SMITH ER, SCOTT RM. Surgical management of moyamoya syndrome. Skull Base. 2005;15(1):15-26.
[12] RAMESH V, BERNARDI B, STAFA A, et al. Intracerebral large artery disease in Aicardi-Goutières syndrome implicates SAMHD1 in vascular homeostasis. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2010;52(8):725-732.
[13] KIM T, OH CW, BANG JS, et al. Moyamoya Disease: Treatment and Outcomes. J Stroke. 2016;18(1):21-30.
[14] BAO XY, DUAN L. Chinese expert consensus on the treatment of MMD. Chin Neurosurg J. 2023;9(1):5.
[15] 杨培中.EDAS联合通窍益髓汤治疗缺血型烟雾病的临床疗效分析[D].济南:山东中医药大学,2017.
[16] 王馨慧,王苏童,吕穆杰,等.黄芪桂枝五物汤调节M1/M2巨噬细胞改善炎症反应的分子机制研究[J]. 北京中医药大学学报,2023, 46(6):801-810.
[17] YUN W, DAN W, LIU J, et al. Investigation of the Mechanism of Traditional Chinese Medicines in Angiogenesis through Network Pharmacology and Data Mining. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021;2021:5539970.
[18] VANCURA J, BOYD NK, VOGEL BN, et al. Rapidly progressive moyamoya vasculopathy stabilized with immunotherapy in aicardi-goutières syndrome. J Neurol. 2024;271(2):1019-1022.
[19] HE S, ZHOU Z, ZHANG J, et al. Differential WNT4 expression among various subtypes of moyamoya disease results in alterations of microtubule stability. Clin Transl Med. 2024;14(8):e1797.
[20] JIN F, DUAN C. Identification of immune-infiltrated hub genes as potential biomarkers of Moyamoya disease by bioinformatics analysis. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022;17(1):80.
[21] ZHOU Z, WANG Y, ZHANG J, et al. Characterization of PANoptosis-related genes and the immune landscape in moyamoya disease. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):10278.
[22] HAN Z, ZHANG J, SU Y, et al. Identification of oxidative phosphorylation-related genes in moyamoya disease by combining bulk RNA-sequencing analysis and machine learning. Front Genet. 2024;15:1417329.
[23] LI W, ZHAO X, FU J, et al. Identification of lysosome-related hub genes as potential biomarkers and immune infiltrations of moyamoya disease by multiple bioinformatics methods and machine-learning strategies. Heliyon. 2024;10(14):e34432.
[24] LI J, HE Q, ZHENG Z, et al. Comprehensive Analysis and In Vitro Verification of Endothelial-Mesenchymal Transition-Related Genes in Moyamoya Disease. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04423-x.
[25] XU Y, CHEN B, GUO Z, et al. Identification of diagnostic markers for moyamoya disease by combining bulk RNA-sequencing analysis and machine learning. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):5931.
[26] Research Committee on the Pathology and Treatment of Spontaneous Occlusion of the CoW, Health Labour Sciences Research Grant for Research on Measures for Infractable Diseases. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of moyamoya disease (spontaneous occlusion of the circle of Willis). Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2012;52(5):245-266.
[27] KAMADA F, AOKI Y, NARISAWA A, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies RNF213 as the first Moyamoya disease gene. J Hum Genet. 2011;56(1):34-40.
[28] LI J, HE Q, LIU C, et al. Integrated analysis of the association between methionine cycle and risk of moyamoya disease. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2023;29(11):3212-3227.
[29] HE S, ZHANG J, LIU Z, et al. Upregulated Cytoskeletal Proteins Promote Pathological Angiogenesis in Moyamoya Disease. Stroke. 2023;54(12): 3153-3164.
[30] YIN Z, GE P, ZENG C, et al. Association of lysine pathway metabolites with moyamoya disease. Clin Nutr. 2024;43(3):787-795.
[31] GÓMEZ-BANOY N, GUSEH JS, LI G, et al. Adipsin preserves beta cells in diabetic mice and associates with protection from type 2 diabetes in humans. Nat Med. 2019;25(11):1739-1747.
[32] ABHINAV K, LEE AG, PENDHARKAR AV, et al. Comprehensive Profiling of Secreted Factors in the Cerebrospinal Fluid of Moyamoya Disease Patients. Transl Stroke Res. 2024;15(2):399-408.
[33] CHEN X, SONG C, MA X, et al. High lipoprotein(a) concentration is associated with moyamoya disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2024;23(1):21.
[34] DEB-CHATTERJI M, KELLER CW, KOCH S, et al. Profiling Complement System Components in Primary CNS Vasculitis. Cells. 2021;10(5):1139.
[35] VOLANAKIS JE, NARAYANA SV. Complement factor D, a novel serine protease. Protein Sci. 1996;5(4):553-564.
[36] MULLARD A. FDA approves first complement factor D inhibitor. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024;23(5):329.
[37] GU SX, YAROVINSKY TO, HWA J. Fishing for “complements” with vascular organoid models of microvascular disease. Cell Stem Cell. 2023;30(10):1285-1286.
[38] JIN S, REESINK KD, KROON AA, et al. Complement factors D and C3 cross-sectionally associate with arterial stiffness, but not independently of metabolic risk factors: The Maastricht Study. J Hypertens. 2022; 40(11):2161-2170.
[39] KAWAKAMI E, SAIKI N, YONEYAMA Y, et al. Complement factor D targeting protects endotheliopathy in organoid and monkey models of COVID-19. Cell Stem Cell. 2023;30(10):1315-1330.e10.
[40] ITO S, HASHIMOTO H, YAMAKAWA H, et al. The complement C3-complement factor D-C3a receptor signalling axis regulates cardiac remodelling in right ventricular failure. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):5409.
[41] RICKLIN D, REIS ES, LAMBRIS JD. Complement in disease: a defence system turning offensive. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016;12(7):383-401.
[42] KATO M, KUDO Y, HATASE M, et al. Moyamoya Disease Associated with a Deficiency of Complement Component 6. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2022;31(8):106601.
[43] LIU XM, RUAN XZ, CAI Z, et al. Moyamoya disease caused by leptospiral cerebral arteritis. Chin Med J (Engl). 1980;93(9):599-604.
[44] SUZUKI J, KODAMA N. Moyamoya disease--a review. Stroke. 1983;14(1): 104-109.
[45] TAKAYANAGI K, KANAMORI F, ISHII K, et al. Higher abundance of Campylobacter in the oral microbiome of Japanese patients with moyamoya disease. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):18545.
[46] GE P, TAO C, WANG W, et al. Circulating immune cell landscape and T-cell abnormalities in patients with moyamoya disease. Clin Transl Med. 2024;14(4):e1647.
[47] KIM JH, JEON H, KIM M, et al. Chemical and perfusion markers as predictors of moyamoya disease progression and complication types. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):56.
[48] LI H, CAO X, GU X, et al. GM-CSF Promotes the Development of Dysfunctional Vascular Networks in Moyamoya Disease. Neurosci Bull. 2024;40(4):451-465.
[49] LIU C, GE P, ZHANG B, et al. Mass cytometry revealed the circulating immune cell landscape across different Suzuki stages of Moyamoya disease. Immunol Res. 2024;72(4):654-664.
[50] WU J, LU AD, ZHANG LP, et al. Study of clinical outcome and prognosis in pediatric core binding factor-acute myeloid leukemia. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2019;40(1):52-57.
[51] GORLA G, CARROZZINI T, POLLACI G, et al. Increase of Circulating Endothelial Progenitor Cells and Released Angiogenic Factors in Children with Moyamoya Arteriopathy. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(2):1233.
[52] 陈宝田.陈宝田教授经方临床应用[M].广州:广东科技出版社, 2014.
[53] 黄仕营, 谢炜.陈宝田教授时方临床应用[M].北京:科学出版社, 2017.
[54] 骆文婷,陈泽伟,伍志勇,等.补黄四五汤治疗周围性面瘫的疗效及安全性[J].暨南大学学报(自然科学与医学版),2018,39(4):332-338.
[55] BERSANO A, GUEY S, BEDINI G, et al. Research Progresses in Understanding the Pathophysiology of Moyamoya Disease. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2016;41(3-4):105-118.
[56] BEDINI G, BLECHARZ KG, NAVA S, et al. Vasculogenic and Angiogenic Pathways in Moyamoya Disease. Curr Med Chem. 2016;23(4):315-345.
|