[1] SING CW, LIN TC, BARTHOLOMEW S, et al. Global Epidemiology of Hip Fractures: Secular Trends in Incidence Rate, Post-Fracture Treatment, and All-Cause Mortality. J Bone Miner Res. 2023;38(8):1064-1075.
[2] T J, KWEK EBK. Are Intertrochanteric Fractures Evolving? Trends in the Elderly Population over a 10-Year Period. Clin Orthop Surg. 2022;14(1):13-20.
[3] MAFFULLI N, AICALE R. Proximal Femoral Fractures in the Elderly: A Few Things to Know, and Some to Forget. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022;58(10):1314.
[4] ZHANG C, FENG J, WANG S, et al. Incidence of and trends in hip fracture among adults in urban China: A nationwide retrospective cohort study. PLoS Med. 2020; 17(8):e1003180.
[5] LI L, FANG X, GAO J, et al. Comparison of InterTAN and PFNA internal fixation for elderly patients with intertrochanteric fracture: A retrospective cohort study. Pak J Med Sci. 2024;40(4):589-594.
[6] TANGKANJANAVELUKUL P, THAITALAY P, SRISUWAN S, et al. Feasibility biomechanical study of injectable Biphasic Calcium Phosphate bone cement augmentation of the proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) for the treatment of two intertrochanteric fractures using cadaveric femur. Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2024;10(4). doi: 10.1088/2057-1976/ad4e3c.
[7] 胡孙君,杜守超,熊文峰,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉内固定治疗高位股骨转子间骨折[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2021,35(3):307-311.
[8] 张晓萌,郁凯,王艳华,等.股骨转子间骨折术后内固定失效特点及其原因分析[J].中华创伤杂志,2021,37(5):429-436.
[9] CHEN XK, XIONG J, LIU YJ, et al. A rare complication of pelvic perforation by an excessive medial slide of the helical blade after treatment of an intertrochanteric fracture with proximal femoral nail anti-rotation: A case report and literature review. Chin J Traumatol. 2022;25(2):118-121.
[10] 郑利钦,林梓凌,李鹏飞,等.动态载荷下松质骨对骨质疏松性股骨颈骨折断裂力学影响的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(12):1887-1892.
[11] UGER JD, NAIK AJ, MURAKAMI AM, et al. Spatial assessment of femoral neck bone density and microstructure in hip osteoarthritis. Bone Rep. 2021;16:101155.
[12] BITTNER-FRANK M, REISINGER AG, ANDRIOTIS OG, et al. Cortical and trabecular mechanical properties in the femoral neck vary differently with changes in bone mineral density. JBMR Plus. 2024;8(6):ziae049.
[13] 张云林,汤梦露,周祥,等.女性年龄相关的股骨颈几何参数参考值[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2017,23(6):751-756.
[14] 李国海,张欣荣,韩莉,等.X线骨密度及股骨颈几何参数测量在不同海拔地区老年患者股骨结构评价的价值分析[J].中国医学物理学杂志,2020, 37(4):520-523.
[15] SONG H, HU SJ, DU SC, et al. Sub-Classification of AO/OTA-2018 Pertrochanteric Fractures Is Associated With Clinical Outcomes After Fixation of Intramedullary Nails. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2021;12:21514593211056739.
[16] LI M, ZHAO K, DING K, et al. Titanium Alloy Gamma Nail versus Biodegradable Magnesium Alloy Bionic Gamma Nail for Treating Intertrochanteric Fractures: A Finite Element Analysis. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(5):1513-1520.
[17] DING K, YANG W, WANG H, et al. Finite element analysis of biomechanical effects of residual varus/valgus malunion after femoral fracture on knee joint. Int Orthop. 2021;45(7):1827-1835.
[18] CUN Y, DOU C, TIAN S, et al. Traditional and bionic dynamic hip screw fixation for the treatment of intertrochanteric fracture: a finite element analysis. Int Orthop. 2020;44(3):551-559.
[19] 丁凯,陈伟,杨伟杰,等.股骨骨折后残留内/外翻畸形愈合对膝关节生物力学影响的有限元分析[J].中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志,2020,6(5):257-264.
[20] TUCKER SM, WEE H, FOX E, et al. Parametric Finite Element Analysis of Intramedullary Nail Fixation of Proximal Femur Fractures. J Orthop Res. 2019; 37(11):2358-2366.
[21] BURKHART TA, ANDREWS DM, DUNNING CE. Finite element modeling mesh quality, energy balance and validation methods: a review with recommendations associated with the modeling of bone tissue. J Biomech. 2013;46(9):1477-1488.
[22] CUI Y, XING W, PAN Z, et al. Characterization of novel intramedullary nailing method for treating femoral shaft fracture through finite element analysis. Exp Ther Med. 2020;20(2):748-753.
[23] WANG Y, CHEN W, ZHANG L, et al. Finite Element Analysis of Proximal Femur Bionic Nail (PFBN) Compared with Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation and InterTan in Treatment of Intertrochanteric Fractures. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(9):2245-2255.
[24] SING CW, LIN TC, BARTHOLOMEW S, et al. Global Epidemiology of Hip Fractures: Secular Trends in Incidence Rate, Post-Fracture Treatment, and All-Cause Mortality. J Bone Miner Res. 2023;38(8):1064-1075.
[25] 李兴国,邓叶龙,刘朝晖,等.中国老年髋部骨折流行性病学特征分析[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2021,27(7):601-606.
[26] HAGINO H. Current and Future Burden of Hip and Vertebral Fractures in Asia. Yonago Acta Med. 2021;64(2):147-154.
[27] SEONG YJ, SHIN WC, MOON NH, et al. Timing of Hip-fracture Surgery in Elderly Patients: Literature Review and Recommendations. Hip Pelvis. 2020;32(1):11-16.
[28] ANDALIB A, ETEMADIFAR M, YAVARI P. Clinical Outcomes of Intramedullary and Extramedullary Fixation in Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2020;8(2):190-197.
[29] ZEELENBERG ML, NUGTEREN LHT, PLAISIER AC, et al. Extramedullary versus intramedullary fixation of stable trochanteric femoral fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023;143(8):5065-5083.
[30] LU GL, LI SJ, LI WX. Biomechanical study of extramedullary and intramedullary fixation in the treatment of unstable intertrochanteric reversed-tilt fractures of the femur. Ann Transl Med. 2022;10(4):191.
[31] YU F, TANG YW, WANG J, et al. Does intramedullary nail have advantages over dynamic hip screw for the treatment of AO/OTA31A1-A3? A meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):588.
[32] CHENG YX, SHENG X. Optimal surgical methods to treat intertrochanteric fracture: a Bayesian network meta-analysis based on 36 randomized controlled trials. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):402.
[33] ZHENG L, WONG DW, CHEN X, et al. Risk of proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) implant failure upon different lateral femoral wall thickness in intertrochanteric fracture: a finite element analysis. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2022;25(5):512-520.
[34] XU R, RU J, JI F, et al. Comparison of efficacy, complications and TGF-β2 expression between DHS and PFNA in elderly patients with osteoporotic femoral intertrochanteric fracture. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(1):394-399.
|






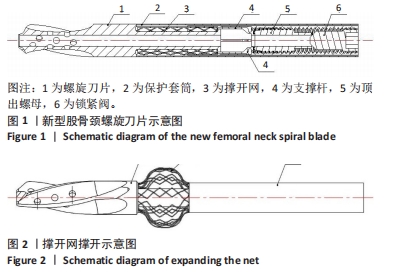 此次研究通过有限元方法对NFNSB和PFNA固定股骨转子间骨折的力学特性进行对比分析,从而得出结论,为新型内固定系统设计提供理论参考。
此次研究通过有限元方法对NFNSB和PFNA固定股骨转子间骨折的力学特性进行对比分析,从而得出结论,为新型内固定系统设计提供理论参考。