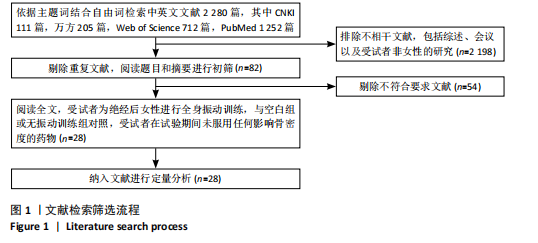
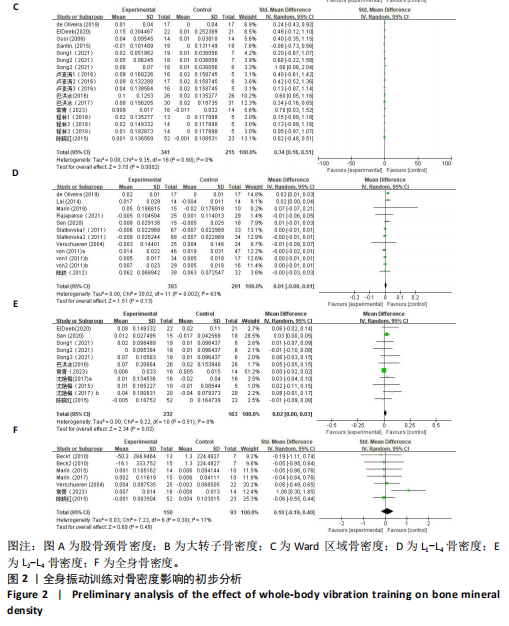
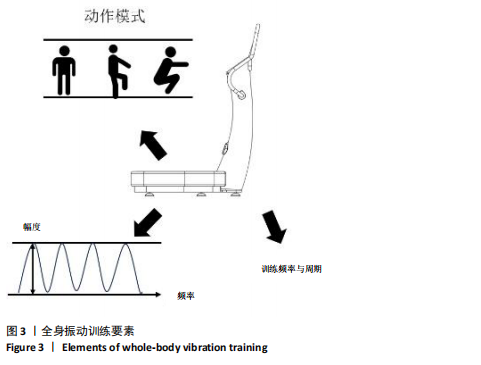
[1] WALKER MD, SHANE E. Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(21): 1979-1991.
[2] ZHAO R, ZHAO M, XU Z. The effects of differing resistance training modes on the preservation of bone mineral density in postmenopausal women: a meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int. 2015;26(5):1605-1618.
[3] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会.原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2017)[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(3):281-309.
[4] 刘刚,杨明辉,张京,等.《老年髋部骨折诊疗与管理指南(2022年版)》解读[J].骨科临床与研究杂志,2023,8(2):73-76.
[5] 吴志建,王竹影,胡冰倩,等.运动锻炼改善绝经后妇女骨密度效果的meta分析[J].中国康复医学杂志,2020,35(8):963-971.
[6] 王珍玉,夏渊,卢悦,等.不同抗阻训练方案对绝经后女性骨密度影响的网状Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023, 27(28):4586-4592.
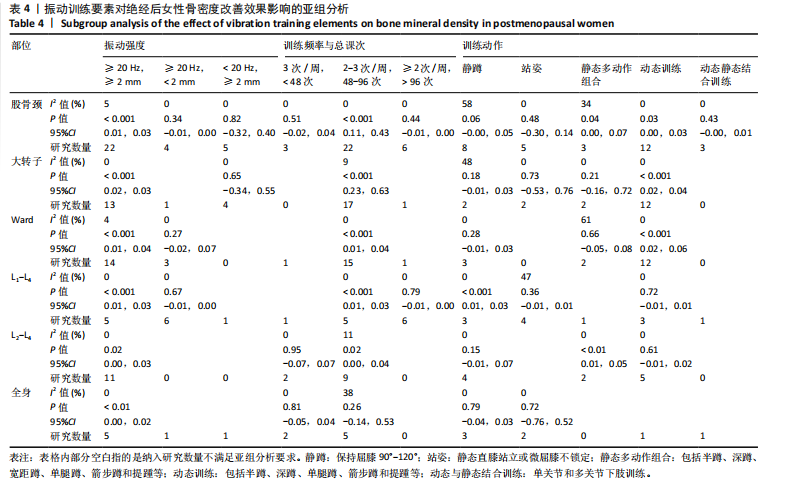
[7] 程林.不同频率全身振动训练对绝经期妇女血压和下肢骨密度影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(3):305-310+331.
[8] SINGH A, VARMA AR. Whole-Body Vibration Therapy as a Modality for Treatment of Senile and Postmenopausal Osteoporosis: A Review Article. Cureus. 2023;15(1): e33690.
[9] 曹丹炫,李斐,张勤,等.全身振动训练的应用效果与作用机制[J].武汉体育学院学报,2023,57(8):92-100.
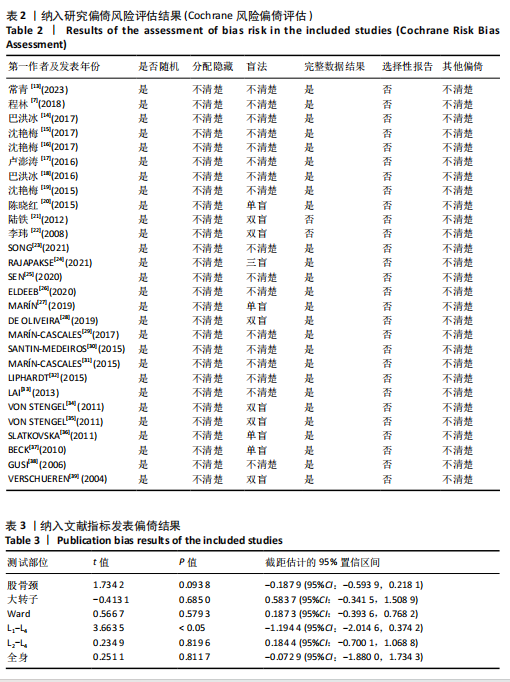
[10] HENDERSON LK, CRAIG JC, WILLIS NS, et al. How to write a Cochrane systematic review. Nephrology. 2010;15(6):617-624.
[11] ISHIGURO H, KODAMA S, HORIKAWA C, et al. In Search of the Ideal Resistance Training Program to Improve Glycemic Control and its Indication for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2016;46(1):67-77.
[12] 李贝贝,孟昭莉.运动干预对糖尿病前期人群糖脂代谢影响的网状Meta分析[J].中国体育科技,2023,59(1):92-103.
[13] 常青,周军,陈晓红,等.振动加蹲起训练对绝经后女性骨密度的影响[J].中国预防医学杂志,2023,24(1):23-28.
[14] 巴洪冰,程亮.高频全身振动训练及停练后对老年女性骨密度的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2017,23(4):428-430+463.
[15] 沈艳梅,安平,许鑫华,等.全身振动训练对骨质减少人群骨密度的影响[J].公共卫生与预防医学,2017,28(2):56-59.
[16] 沈艳梅,安平,许鑫华.全身振动训练对老年人肌肉-骨骼-关节的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2017,37(24):6171-6173.
[17] 卢澎涛.不同频率全身振动训练对老年女性骨密度及下肢肌力的影响[J].山东体育学院学报,2016,32(6):89-94.
[18] 巴洪冰,程亮.全身振动训练对老年女性骨密度的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2016,22(3):340-342.
[19] 沈艳梅,许鑫华.振动训练对35~49岁和50~65岁女性骨密度与平衡能力的影响[J].浙江体育科学,2015,37(3): 97-101+127.
[20] 陈晓红.振动训练对绝经后女性体成分的影响及与相关基因多态性的关联研究[D].北京:北京体育大学,2015.
[21] 陆铁,仲维佳,周君琳,等.全身振动对预防老年女性骨质疏松性骨折的作用[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2012,6(5):1113-1116.
[22] 李玮,钟菁,徐惠敏,等.全身振动对绝经后肥胖妇女抗骨折能力的影响[J].实用妇产科杂志,2008,24(11):667-670.
[23] SONG W, YANG Y. The Effect of Whole-Body Vibration Training with Different Amplitudes on Bone Mineral Density in Elderly Women. Isokinet Exerc Sci. 2021;29(4):413-418.
[24] RAJAPAKSE CS, JOHNCOLA AJ, BATZDORF AS, et al. Effect of Low-Intensity Vibration on Bone Strength, Microstructure, and Adiposity in Pre-Osteoporotic Postmenopausal Women: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. J Bone Miner Res. 2021;36(4):673-684.
[25] SEN EI, ESMAEILZADEH S, ESKIYURT N. Effects of whole-body vibration and high impact exercises on the bone metabolism and functional mobility in postmenopausal women. J Bone Miner Metab. 2020;38(3): 392-404.
[26] ELDEEB AM, ABDEL-AZIEM AA. Effect of Whole-Body Vibration Exercise on Power Profile and Bone Mineral Density in Postmenopausal Women With Osteoporosis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2020; 43(4):384-393.
[27] MARÍN-CASCALES E, RUBIO-ARIAS JÁ, ALCARAZ PE. Effects of Two Different Neuromuscular Training Protocols on Regional Bone Mass in Postmenopausal Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Front Physiol. 2019;10:846.
[28] DE OLIVEIRA LC, DE OLIVEIRA RG, DE ALMEIDA PIRES-OLIVEIRA DA. Effects of Whole-Body Vibration Versus Pilates Exercise on Bone Mineral Density in Postmenopausal Women: A Randomized and Controlled Clinical Trial. J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2019;42(2):E23-E31.
[29] MARÍN-CASCALES E, ALCARAZ PE, RUBIO-ARIAS JA. Effects of 24 Weeks of Whole Body Vibration Versus Multicomponent Training on Muscle Strength and Body Composition in Postmenopausal Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Rejuvenation Res. 2017;20(3):193-201.
[30] SANTIN-MEDEIROS F, SANTOS-LOZANO A, REY-LÓPEZ JP, et al. Effects of eight months of whole body vibration training on hip bone mass in older women. Nutr Hosp. 2015;31(4):1654-1659.
[31] MARÍN-CASCALES E, RUBIO-ARIAS JA, ROMERO-ARENAS S, et al. Effect of 12 Weeks of Whole-Body Vibration Versus Multi-Component Training in Post-Menopausal Women. Rejuvenation Res. 2015;18(6):508-516.
[32] LIPHARDT AM, SCHIPILOW J, HANLEY DA, et al. Bone quality in osteopenic postmenopausal women is not improved after 12 months of whole-body vibration training. Osteoporos Int. 2015;26(3):911-920.
[33] LAI CL, TSENG SY, CHEN CN, et al. Effect of 6 months of whole body vibration on lumbar spine bone density in postmenopausal women: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Interv Aging. 2013;8:1603-1609.
[34] VON STENGEL S, KEMMLER W, BEBENEK M, et al. Effects of whole-body vibration training on different devices on bone mineral density. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011; 43(6):1071-1079.
[35] VON STENGEL S, KEMMLER W, ENGELKE K, et al. Effects of whole body vibration on bone mineral density and falls: results of the randomized controlled ELVIS study with postmenopausal women. Osteoporos Int. 2011;22(1):317-325.
[36] SLATKOVSKA L, ALIBHAI SM, BEYENE J, et al. Effect of 12 months of whole-body vibration therapy on bone density and structure in postmenopausal women: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2011;155(10):668-679.
[37] BECK BR, NORLING TL. The effect of 8 mos of twice-weekly low- or higher intensity whole body vibration on risk factors for postmenopausal hip fracture. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2010;89(12):997-1009.
[38] GUSI N, RAIMUNDO A, LEAL A. Low-frequency vibratory exercise reduces the risk of bone fracture more than walking: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2006;7:92.
[39] VERSCHUEREN SM, ROELANTS M, DELECLUSE C, et al. Effect of 6-month whole body vibration training on hip density, muscle strength, and postural control in postmenopausal women: a randomized controlled pilot study. J Bone Miner Res. 2004;19(3):352-359.
[40] MUNERA M, BERTUCCI W, DUC S, et al. Transmission of whole body vibration to the lower body in static and dynamic half-squat exercises. Sports Biomech. 2016;15(4):409-428.
[41] TANKISHEVA E, JONKERS I, BOONEN S, et al. Transmission of whole-body vibration and its effect on muscle activation. J Strength Cond Res. 2013;27(9):2533-2541.
[42] NAWAYSEH N. Transmission of vibration from a vibrating plate to the head of standing people. Sports Biomech. 2019; 18(5):482-500.
[43] SPAIN L, YANG L, WILKINSON JM, et al. Transmission of whole body vibration - Comparison of three vibration platforms in healthy subjects. Bone. 2021;144:115802.
[44] YE X, GU Y, BAI Y, et al. Does Low-Magnitude High-Frequency Vibration (LMHFV) Worth for Clinical Trial on Dental Implant? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on Animal Studies. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:626892.
[45] STEPPE L, LIEDERT A, IGNATIUS A, et al. Influence of Low-Magnitude High-Frequency Vibration on Bone Cells and Bone Regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:595139.
[46] BONANNI R, CARIATI I, ROMAGNOLI C, et al. Whole Body Vibration: A Valid Alternative Strategy to Exercise? J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. 2022;7(4):99.
[47] FERNANDEZ P, PASQUALINI M, LOCRELLE H, et al. The effects of combined amplitude and high-frequency vibration on physically inactive osteopenic postmenopausal women. Front Physiol. 2022;13:952140.
[48] LYNCH MA, BRODT MD, SILVA MJ. Skeletal effects of whole-body vibration in adult and aged mice. J Orthop Res. 2010;28(2):241-247.
[49] OSUGI T, IWAMOTO J, YAMAZAKI M, et al. Effect of a combination of whole body vibration exercise and squat training on body balance, muscle power, and walking ability in the elderly. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2014;10:131-138.
[50] RITTWEGER J, JUST K, KAUTZSCH K, et al. Treatment of chronic lower back pain with lumbar extension and whole-body vibration exercise: a randomized controlled trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(17):1829-1834. |