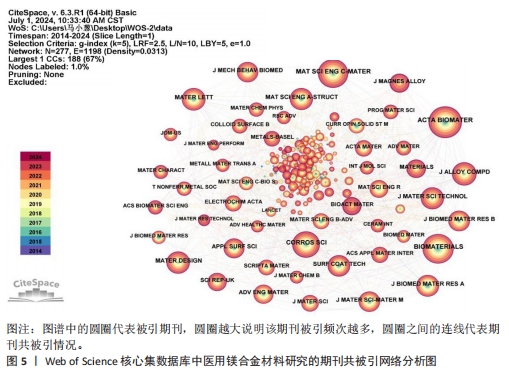
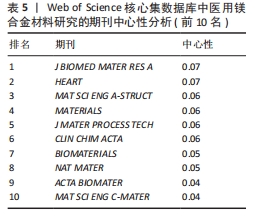
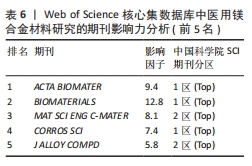
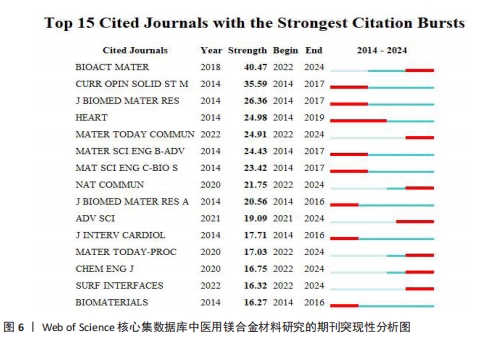
[1] WATANABE K, FUKUZAKI S, SUGINO A, et al. Cobalt-Chromium Alloy Has Superior Antibacterial Effect Than Titanium Alloy In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2021;46(17):E911-E915.
[2] BERNHARDT A, HELMHOLZ H, KILIAN D, et al. Impact of Degradable Magnesium Implants on Osteocytes in Single and Triple Cultures. Biomater Adv. 2022;134:112692.
[3] ANGRISANI N, VON DER AHE C, WILLUMEIT-RÖMER R, et al. Treatment of Osteoarthritis by Implantation of Mg-and WE43-cylinders-A Preclinical Study on Bone and Cartilage Changes and Their Influence on Pain Sensation in Rabbits. Bioact Mater. 2024;40:366-377.
[4] BERNHARDT A, HELMHOLZ H, KILIAN D, et al. Impact of Degradable Magnesium Implants on Osteocytes in Single and Triple Cultures. Biomater Adv. 2022;134:112692.
[5] ZHANG L, JIA GZ, TANG M, et al. Simultaneous Enhancement of Anti-corrosion, Biocompatibility, and Antimicrobial Activities by Hierarchically-structured Brushite/Ag3PO4-Coated Mg-based Scaffolds. Mater Sci Eng C. 2020;111:110779.
[6] 刘凯,马江,何新.基于Citespace的巴戟天研究进展和热点可视化分析[J].药物评价研究,2024,47(10):2399-2411.
[7] 张子旋,安逸,张馨文,等.基于CiteSpace对青藤碱在中医药研究应用现状的可视化分析[J].中国医药导报,2022,19(36):29-35.
[8] 陈悦,陈超美,刘则渊,等.CiteSpace知识图谱的方法论功能[J].科学学研究,2015, 33(2):242-253.
[9] 贺雅洁,王延博,杨硕.基于CiteSpace对中医药治疗子宫肌瘤的可视化分析[J].世界中西医结合杂志, 2022,17(12):2374-2380.
[10] 党小雯,黄海量,黄雷,等.生物医学领域碳纳米材料10年研究前沿与热点[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(4):752-760.
[11] 文跃然,王丹阳,刘颖.国内外医院薪酬研究分析对我国公立医院薪酬制度设计的启示:基于Citespace和Vosviewer的文献计量[J].中国卫生政策研究,2022,15(12):1-8.
[12] 李晓陵,高瑞雪,李昂,等.基于VOSviewer与CiteSpace的fMRI研究血管性认知障碍可视化分析[J]. 磁共振成像,2022,13(11):99-104.
[13] 谢恩礼,陶慧敏.血流限制训练在临床康复医学中的应用趋势[J].中国组织工程研究, 2024,28(2): 258-262.
[14] 梁杉,吉晓鹏,康英豪,等.基于CiteSpace的絮凝作用改善污泥脱水性能研究进展[J].应用化工,2023,52(11):3199-3204.
[15] HSU YC, LU YP, WANG SY, et al. Magnesium Alloys in Tumor Treatment: Current Research Status, Challenges and Future Prospects. J Magnesium Alloys. 2023;11(10):3399-3426.
[16] 郑玉峰,夏丹丹,谌雨农,等.增材制造可降解金属医用植入物[J].金属学报,2021, 57(11):1499-1520.
[17] TONG X, DONG Y, ZHOU R, et al. Enhanced Mechanical Properties, Corrosion Resistance, Cytocompatibility, Osteogenesis, and Antibacterial Performance of Biodegradable Mg-2Zn-0.5Ca-0.5Sr/Zr Alloys for Bone-implant Application. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;13(12): e2303975.
[18] ZHANG X, YANG C, YANG K. Novel Antibacterial Metals as Food Contact Materials: A review. Materials (Basel). 2023;16(8):3029.
[19] ERISEN DE, ZHANG YQ, ZHANG BC, et al. Biosafety and Biodegradation Studies of AZ31B Magnesium Alloy Carotid Artery stent in vitro and in vivo. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2022;110(1):239-248.
[20] 李一飞,周开宇,沈建通,等.基于关键词共现分析的我国先心病介入诊疗发展的可视化研究[J].临床儿科杂志,2012,30(7):631-637.
[21] 郭文,冷军,刘会敏,等.脑卒中后尿失禁10年研究文献的可视化分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(35):5676-5681.
[22] 李曌嫱,秦义,田元祥,等.针灸治疗腰椎间盘突出症的CiteSpace知识图谱可视化分析[J].中国针灸,2017,37(5):545-548.
[23] 陈文娟.数字资源评价研究特征、前沿与展望: 基于WOS数据库的文献计量学分析[J].图书馆学研究,2022(7):2-14.
[24] 高楠,周庆山.基于共被引方法的情报学前沿领域识别与演进趋势分析[J].现代情报, 2024,44(5):3-19.
[25] 王瑾茜,喻嵘,黄娟,等.基于CiteSpace的中性粒细胞在糖尿病领域研究进展可视化分析[J].中国比较医学杂志,2024,34(6):28-39.
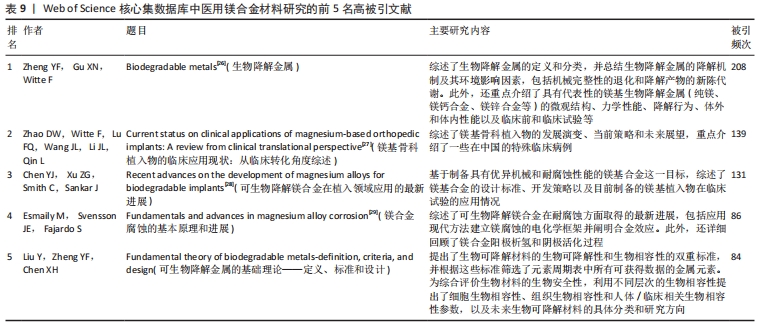
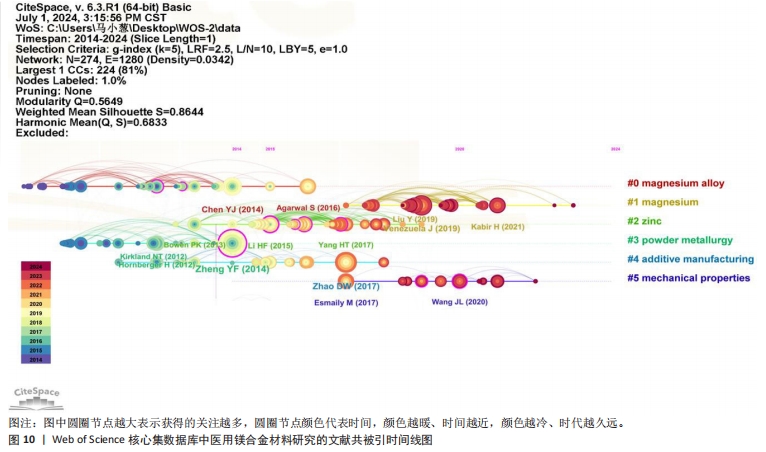
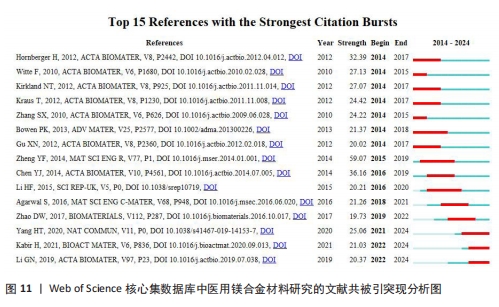
[26] ZHENG YF, GU XN, WITTE F. Biodegradable Metals. Mater Sci Eng R. 2014;77:1-34.
[27] ZHAO DZ, WITTE F, LU FQ, et al. Current Status on Clinical Applications of Magnesium-based Orthopedic Implants: A Review from Clinical Translational Perspective. Biomaterials. 2017;112:287-302.
[28] CHEN Y, XU Z, SMITH C, et al. Recent Advances on The Development of Magnesium alloys for biodegradable implants. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(11):4561-4573.
[29] ESMAILY M, SVENSSON JE, FAJARDO S, et al. Fundamentals and Advances in Magnesium Alloy Corrosion. Prog Mater Sci. 2017;89:92-193.
[30] YANG H, JIA B, ZHANG Z, et al. Alloying Design of Biodegradable Zinc as Promising Bone Implants for Load-bearing Applications. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):401.
[31] KABIR H, MUNIR K, WEN C, et al. Recent Research and Progress of Biodegradable Zinc Alloys and Composites for Biomedical Applications: Biomechanical and Biocorrosion Perspectives. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(3):836-879.
[32] ROUT PK, ROY S, GANGULY S, et al. A Review on Properties of Magnesium-Based Alloys for Biomedical Applications. Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2022;8(4):042002.
[33] 王晶华,陈祺琪,顾金科.我国农业科技创新研究热点及演进态势:基于CiteSpace的可视化分析[J].科技管理研究,2022,42(22): 8-16.
[34] 邹婧,楚尧娟,杜秋争,等.酪氨酸激酶抑制剂在HER2阳性乳腺癌中应用的可视化分析[J].中国药房,2023,34(24):3036-3041.
[35] AGARWAL S, CURTIN J, DUFFY B, et al. Biodegradable Magnesium Alloys for Orthopedic Applications A Review on Corrosion, Biocompatibility and Surface Modifications. Mater Sci Eng C. 2016;68:948-963.
[36] LIU B, ZHANG X, XIAO GY, et al. Phosphate Chemical Conversion Coatings on Metallic Substrates for Biomedical Application: A review. Mater Sci Eng C. 2015;47:97-104.
[37] GARIMELLA A, RAMYA M, GHOSH SB, et al. Bioactive Fluorcanasite Reinforced Magnesium Alloy-based Porous Bio-nanocomposite Scaffolds with Tunable Mechanical Properties. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2023; 111(2):463-477.
[38] MARTYNENKO NS, ANISIMOVA NY, KISELEVSKIY MV, et al. In Vitro Biodegradation of Resorbable Magnesium Alloys Promising for Implant Development. Sovrem Tekhnologii Med. 2021;12(6):47-52.
[39] GNEDENKOV AS, FILONINA VS, SINEBRYUKHOV SL, et al. A Superior Corrosion Protection of Mg Alloy via Smart Nontoxic Hybrid Inhibitor-Containing Coatings. Molecules. 2023;28(6):2538.
[40] ANGRISANI N, AHE CVD, WILLUMEIT-RMER R, et al. Treatment of Osteoarthritis by Implantation of Mg-and WE43-cylinders-A Preclinical Study on Bone and Cartilage Changes and Their Influence on Pain Sensation in Rabbits. Bioact Mater. 2024;40:366-377.
[41] 许雅南,王伟强,杨帅康,等.铁基材料在生物可降解血管支架领域的研究进展[J].钢铁钒钛,2023, 44(4):158-166.
[42] 韩伟,张兴凯,郑玉峰,等.可降解铁基支架材料的研究进展[J].材料导报,2013, 27(S2):205-208.
[43] SU Y, COCKERILL I, WANG Y, et al. Zinc-Based Biomaterials for Regeneration and Therapy. Trends Biotechnol. 2019;37(4):428-441.
[44] JOSHI A, DIAS GJ, STAIGER MP. Surgically-Induced Deformation in Biodegradable Orthopaedic Implant Devices. Acta Biomater. 2022;154:667-675.
[45] LI W, QIAO W, LIU X, et al. Biomimicking Bone-Implant Interface Facilitates the Bioadaption of A New Degradable Magnesium Alloy to The Bone Tissue Microenvironment. Adv Sci. 2021;8(23):e2102035.
[46] CHEN Y, XIAO M, ZHAO H, et al. On the Antitumor Properties of Biomedical Magnesium Metal. J Mater Chem B. 2015;3(5): 849-858.
[47] 郑玉峰.可降解金属研究前沿进展[J].材料科学与工艺,2023,31(2):1-14.
[48] 孟帅举,王孟璐,宋金龙,等.Cu对铸态Mg-Bi-Sn系合金微观组织与力学性能的影响[J].中国有色金属学报,2024,34(10):3352-3365.
[49] 贾澳,魏珂正,徐媛媛,等.Al、Zn元素添加对Mg-Cu合金微观组织和力学性能的影响[J].材料热处理学报,2024,45(8):58-65.
[50] RAPIEJKO C, MIKUSEK D, JANUSZEWICZ B,
et al. Refinement of The Magnesium-Aluminium Alloy Microstructure with Zirconium. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(24):8982.
[51] ALATEYAH AL, ALAWAD MO, AUOHANI TA, et al. Influence of UItra Fine-grained Microstructure and Texture Evolution of ECAP ed ZK30 Magnesium Alloy on The Corrosion Behavior in Different Corrosive Agents. Materials. 2022;15(16):5515.
[52] MOHAMED A, ELAZIZ A, BREITINGER HG. Study of The Degradation Behavior and The Biocompatibility of Mg-0.8Ca Alloy for Orthopedic Implant Applications. J Magnesium Alloys. 2019;7(2):249-257.
[53] YANG X, CHEN S, ZHANG S, et al. Intracellular Zinc Protects Kv7 K+ Channels from Ca2+ Calmodulin-Mediated Inhibition. J Biol Chem. 2023;299(2):102819.
[54] GONG XL, CHEN JH, YAN HG, et al. Effects of Minor Sr Addition on Biocorrosion and Stress Corrosion Cracking of As-Cast Mg-4Zn Alloys. Corrosion. 2020;76(1):71-81.
[55] TALTAVULL C, TORRES B, LOPEZ A J, et al. Selective Laser Surface Melting of a Magnesium-Aluminum Alloy. Mater Lett. 2012;85:98-101.
[56] HE M, LU W, YU D, et al. Corrosion Behavior and Biocompatibility of Na2EDTA-Induced Nacre Coatings on AZ91D Alloys Prepared via Hydrothermal Treatment. Front Chem. 2022; 9:810886.
[57] KOZINA I, KRAWIEC H, STAROWICZ M, et al. Corrosion Resistance of MgZn Alloy Covered by Chitosan-Based Coatings. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(15):8301.
[58] WU Y, ZHU B, ZHANG X, et al. Preparation and Characterization of Y-doped Microarc Oxidation Coating on AZ31 Magnesium Alloys. J Biomater Appl. 2022;37(5):930-941.
[59] 王嘉昀,吴俏兰,高祖,等.基于科学知识图谱的桔梗研究热点与趋势分析[J].中医药导报,2023,29(10):110-118.
[60] LI W, QIAO W, LIU X, et al. Biomimicking Bone-Implant Interface Facilitates the Bioadaption of a New Degradable Magnesium Alloy to the Bone Tissue Microenvironment. Adv Sci. 2021;8(23):e2102035.
[61] HWANG SW, TAO H, KIM DH, et al. A Physically Transient Form of Silicon Electronics. Science. 2012;337(6102):1640-1644.
[62] WANG XH, NI JS, CAO NL, et al. In Vivo Evaluation of Mg-6Zn and Titanium Alloys on Collagen Metabolism in the Healing of Intestinal Anastomosis. Sci Rep. 2017;7:44919.
[63] BAO G, FAN Q, GE D, et al. In Vitro and In Vivo Studies to Evaluate the Feasibility of Zn-0.1Li and Zn-0.8Mg Application in the Uterine Cavity Microenvironment Compared to Pure Zinc. Acta Biomater. 2021;123:393-406.
[64] YU T, ZHENG L, CHEN G, et al. A Study to Compare the Efficacy of a Biodegradable Dynamic Fixation System with Titanium Devices in Posterior Spinal Fusion between Articular Processes in a Canine Model. J Biomech Eng. 2021;143(3):031010.
[65] REYES RL, GHIM MS, KANG NU, et al. Development and Assessment of Modified-Honeycomb-Structure Scaffold for Bone Tissue Engineering. Addit Manuf. 2022;54:102740.
[66] TORRONI A, XIANG CC, WITEK L, et al. Histo-Morphologic Characteristics of Intra-osseous Implants of WE43 Mg Alloys With and Without Heat Treatment in an in Vivo Cranial Bone Sheep Model. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2018;3(46):473-478. |