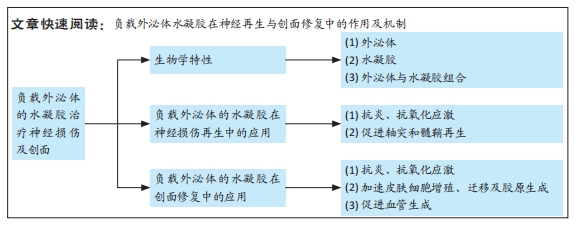
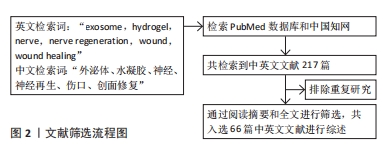
[1] KELLAWAY SC, ULLRICH MM, DZIEMIDOWICZ K, Electrospun drug-loaded scaffolds for nervous system repair. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2024;16(3):e1965.
[2] YAVUZ B, MUTLU EC, AHMED Z, et al. Applications of Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Nerve Regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(11):5863
[3] KARIMZADEH F, FARD ES, NADI A, et al. Advances in skin gene therapy: utilizing innovative dressing scaffolds for wound healing. A Comprehensive Review. J Mater Chem B. 2024;12(25):6033-6062.
[4] SUFIYAN M, KUSHWAHA P, AHMAD M, et al. Scaffold-Mediated Drug Delivery for Enhanced Wound Healing: A Review. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024;25(5):137.
[5] SABERIAN M, ABAK N. Hydrogel-mediated delivery of platelet-derived exosomes: Innovations in tissue engineering. Heliyon. 2024;10(2):e24584.
[6] 林慧洁,黄云,黄志华,等.载药外泌体在中枢神经系统疾病中的热点问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2025,29(23)5013-5021.
[7] AL-MADHAGI H. The Landscape of Exosomes Biogenesis to Clinical Applications. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024;19:3657-3675.
[8] FAN MH, PI JK, ZOU CY, et al. Hydrogel-exosome system in tissue engineering: A promising therapeutic strategy. Bioact Mater. 2024;38: 1-30.
[9] 唐海玉,李萌,袁志翔,等.纳米粒-水凝胶复合递药系统在肿瘤治疗中的研究进展[J].中国药学杂志,2024,59(10):857-867.
[10] MAESO L, ANTEZZNA PE, ARANA AGH, et al. Progress in the Use of Hydrogels for Antioxidant Delivery in Skin Wounds. Pharmaceutics. 2024;16(4):524.
[11] 伍志鑫,蒋雯雯,詹建辉,等.水凝胶:口腔颌面部组织缺损修复中的作用与问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2025,29(10):2178-2188.
[12] 蔡承建,蒋家超,罗萍,等.水生生物外泌体功能的研究进展[J].生物学杂志,2024,41(2):97-102.
[13] SHI L, ZHOU JY, YIN YK, et al. Advancing Tissue Damage Repair in Geriatric Diseases: Prospects of Combining Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes with Hydrogels. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024;19:3773-3804.
[14] NAZERIAN Y, NAZERIAN A, MOHAMADI-JAHANI F, et al. Hydrogel-encapsulated extracellular vesicles for the regeneration of spinal cord injury. Front Neurosci. 2023;17:1309172.
[15] HARLEY-TROXELL ME, STEINER R, ADVINCULA RC, et al. Interactions of Cells and Biomaterials for Nerve Tissue Engineering: Polymers and Fabrication. Polymers Basel. 2023;15(18):3685.
[16] WANG SJ, DU CZ, LI GL, Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: emerging concepts in the treatment of spinal cord injury. Am J Transl Res. 2023; 15(7):4425-4438.
[17] ZOU XD, DONG YZ, ALHASKAWI A, et al. Techniques and graft materials for repairing peripheral nerve defects. Front Neurol. 2023;14:1307883.
[18] ZHENG SS, WEI H, CHENG H, et al. Advances in nerve guidance conduits for peripheral nerve repair and regeneration. Am J Stem Cells. 2023;12(5):112-123.
[19] HU X, XU W, REN YL, et al. Spinal cord injury: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023; 8(1):245.
[20] NAMINI MS, DANESHIMEHR F, BEHESHTIZADEH N, et al. Cell-free therapy based on extracellular vesicles: a promising therapeutic strategy for peripheral nerve injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):254.
[21] XU XY, LIU RY, LI YP, et al. Spinal Cord Injury: From MicroRNAs to Exosomal MicroRNAs. Mol Neurobio. 2024;61(8):5974-5991
[22] GHOSH M, PEARSE DD. Schwann Cell-Derived Exosomal Vesicles: A Promising Therapy for the Injured Spinal Cord. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(24):17317.
[23] LI QC, FU XY, HOU YH, et al. Engineering strategies and optimized delivery of exosomes for theranostic application in nerve tissue. Theranostics. 2023;13(12):4266-4286.
[24] ZHAO WQ, TU H, CHEN YX, et al. Functionalized hydrogels in neural injury repairing. Front Neurosci. 2023;17:1199299.
[25] 佟莹莹,金威洋,杨光华.水凝胶负载干细胞外泌体在组织再生领域的应用研究进展[J].生物工程学报,2023,39(4):1351-1362.
[26] YIN ZY, WAN BW, GONG G, et al. ROS: Executioner of regulating cell death in spinal cord injury. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1330678.
[27] PANG QM, CHEN SY, XU QJ, et al. Neuroinflammation and Scarring After Spinal Cord Injury: Therapeutic Roles of MSCs on Inflammation and Glial Scar. Front Immunol. 2021;12:751021.
[28] ZHU B, GU GJ, REN J, et al. Schwann Cell-Derived Exosomes and Methylprednisolone Composite Patch for Spinal Cord Injury Repair. ACS Nano. 2023;17(22):22928-22943.
[29] NIE R, ZHANG QY, FENG YZ, et al. Hydrogel-based immunoregulation of macrophages for tissue repair and regeneration. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024; 268(1):131643.
[30] YANG QF, SU SH, LIU SC, et al. Exosomes-loaded electroconductive nerve dressing for nerve regeneration and pain relief against diabetic peripheral nerve injury. Bioact Mater. 2023;26:194-215.
[31] LIU ZX, TONG H, LI J, et al. Low-Stiffness Hydrogels Promote Peripheral Nerve Regeneration Through the Rapid Release of Exosomes. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:922570.
[32] CHEN JC, WU JH, MU JF, et al. An antioxidative sophora exosome-encapsulated hydrogel promotes spinal cord repair by regulating oxidative stress microenvironment. Nanomedicine. 2023;47:102625.
[33] LI LM, ZHANG Y, MU JF, et al. Transplantation of Human Mesenchymal Stem-Cell-Derived Exosomes Immobilized in an Adhesive Hydrogel for Effective Treatment of Spinal Cord Injury. Nano Lett. 2020;20(6):4298-4305.
[34] 孙海涛,任春朋,杨永涛,等.外胚层间充质干细胞来源细胞外囊泡促进神经元轴突的伸长[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(23):4924-4930.
[35] MYATICH A, HAQUE A, SOLE C, et al. Clemastine in remyelination and protection of neurons and skeletal muscle after spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2023; 18(5):940-946.
[36] LIU B, ALIMI OA, WANG YF, et al., Differentiated mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes immobilized in decellularized sciatic nerve hydrogels for peripheral nerve repair. J Control Release. 2024;368:24-41.
[37] AFSARTALA Z, HADJIGHASSEM M, SHIRIAN S, et al., The Effect of Collagen and Fibrin Hydrogels Encapsulated with Adipose Tissue Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes for Treatment of Spinal Cord Injury in a Rat Model. Iran J Biotechnol. 2023;21(3):e3505.
[38] KOTAICH F, CAILLOL D, Bomont P. Neurofilaments in health and Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023;11:1275155.
[39] SUN Y, LIU QB, QIN YM, et al. Exosomes derived from CD271(+)CD56(+) bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell subpopoulation identified by single-cell RNA sequencing promote axon regeneration after spinal cord injury. Theranostics. 2024;14(2):510-527.
[40] LIU X, WU C, ZHANG Y, et al. Hyaluronan-based hydrogel integrating exosomes for traumatic brain injury repair by promoting angiogenesis and neurogenesis. Carbohydr Polym. 2023;306:120578.
[41] HERAS KL, GARCIA-ORUE I, RANCAN F, et al. Modulating the immune system towards a functional chronic wound healing: A biomaterials and Nanomedicine perspective. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2024;210:115342.
[42] SHARMA S, KISHEN A. Bioarchitectural Design of Bioactive Biopolymers: Structure-Function Paradigm for Diabetic Wound Healing. Biomimetics (Basel). 2024;9(5):275.
[43] ZHANG BY, BI YG, WANG K ,et al. Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Promising Therapeutic Opportunities for Diabetic Wound Healing. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024;19:4357-4375.
[44] XIE PL, XUE XD, LI XD. Recent Progress in Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes for Skin Wound Repair. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01328-3.
[45] 何梦君,王淞,钱卫,等. MXene水凝胶在皮肤创面中的应用研究[J].中国生物工程杂志,2024,44(4):76-87.
[46] BICER M. Revolutionizing dermatology: harnessing mesenchymal stem/stromal cells and exosomes in 3D platform for skin regeneration. Arch Dermatol Res. 2024;316(6):242.
[47] CAI FY, WANG P, CHEN WJ, et al. The physiological phenomenon and regulation of macrophage polarization in diabetic wound. Mol Biol Rep. 2023;50(11):9469-9477.
[48] MAESO L, ANTEZANA PE, HVOZDA AA, et al. Progress in the Use of Hydrogels for Antioxidant Delivery in Skin Wounds. Pharmaceutics. 2024;16(4):524.
[49] SHI Y, WANG S, WANG K, et al. Relieving Macrophage Dysfunction by Inhibiting SREBP2 Activity: A Hypoxic Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Exosomes Loaded Multifunctional Hydrogel for Accelerated Diabetic Wound Healing. Small. 2024; 20(25):e2309276.
[50] GENG XR, QI Y, LIU XT, et al. A multifunctional antibacterial and self-healing hydrogel laden with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for accelerating diabetic wound healing. Biomater Adv. 2022;133:112613.
[51] ZHOU Y, ZHANG XL, LU ST, et al., Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes encapsulated in pluronic F127 hydrogel promote wound healing and regeneration. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022; 13(1):407.
[52] HAN CX, LIU F, ZHANG Y, et al. Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Exosomes Delivered Using Silk Fibroin and Sericin Composite Hydrogel Promote Wound Healing. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:713021.
[53] XIANG KT, CHEN J, GUO JH, et al. Multifunctional ADM hydrogel containing endothelial cell-exosomes for diabetic wound healing. Mater Today Bio. 2023; 23:100863.
[54] JIANG T, LIU S, WU JH, et al. ADSC-exo@MMP-PEG smart hydrogel promotes diabetic wound healing by optimizing cellular functions and relieving oxidative stress. Mater Today Bio. 2022;16:100365.
[55] 刘唱,罗银利,金哲虎,等.microRNA调控角质形成细胞促进皮肤创伤愈合的研究进展[J].中国皮肤性病学杂志,2023,37(10):1201-1210.
[56] GARDEAZABAL L, IZETA A. Elastin and collagen fibres in cutaneous wound healing. Exp Dermatol. 2024;33(3):e15052.
[57] ZHANG YB, ZOUBOULIS CC, XIAO ZB. Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells activate sebocytes through the PI3K/AKT/SREBP-1 pathway to accelerate wound healing. Cell Tissue Res. 2024;396(3):329-342.
[58] LIU Y, LIU YE, ZHAO Y, et al. Application of adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes-loaded beta-chitin nanofiber hydrogel for wound healing. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2022;60(2):167-178.
[59] ZHENG Z, BU Z, WANG S, et al. Extracellular matrix hydrogels with fibroblast growth factor 2 containing exosomes for reconstructing skin microstructures.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024;22(1):438.
[60] SHANG S, ZHUANG K, CHEN J, et al. A bioactive composite hydrogel dressing that promotes healing of both acute and chronic diabetic skin wounds. Bioact Mater. 2024;34:298-310.
[61] SHI ZJ, YAO C, SHUI YJ, et al. Research progress on the mechanism of angiogenesis in wound repair and regeneration. Front Physiol. 2023;14:1284981.
[62] ZHANG Y, LI M, WANG YC, et al. Exosome/metformin-loaded self-healing conductive hydrogel rescues microvascular dysfunction and promotes chronic diabetic wound healing by inhibiting mitochondrial fission. Bioact Mater. 2023;26:323-336.
[63] HU N, CAI ZW, JIANG XD, et al. Hypoxia-pretreated ADSC-derived exosome-embedded hydrogels promote angiogenesis and accelerate diabetic wound healing. Acta Biomater. 2023;157:175-186.
[64] WANG YX, CAO Z, WEI Q, et al. VH298-loaded extracellular vesicles released from gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel facilitate diabetic wound healing by HIF-1alpha-mediated enhancement of angiogenesis. Acta Biomater. 2022;147:342-355.
[65] LI M, KE QF, TAO SC, et al. Fabrication of hydroxyapatite/chitosan composite hydrogels loaded with exosomes derived from miR-126-3p overexpressed synovial mesenchymal stem cells for diabetic chronic wound healing. J Mater Chem B. 2016;4(42):6830-6841.
[66] ZHANG QQ, SU P, ZHAO F, et al. Enhancing Skin Injury Repair: Combined Application of PF-127 Hydrogel and hADSC-Exos Containing miR-148a-3p. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2024;10(4):2235-2250. |