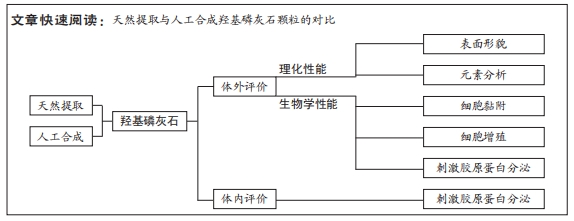
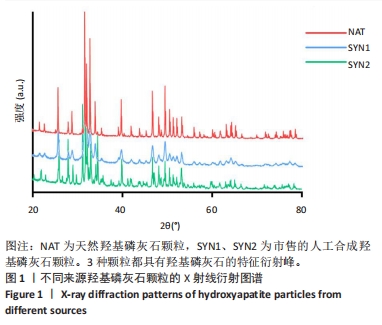
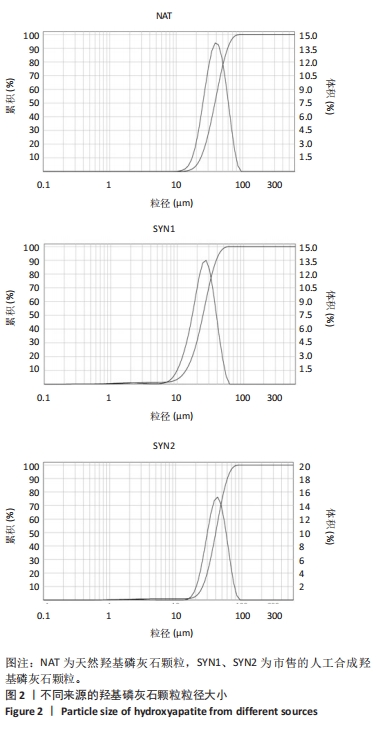
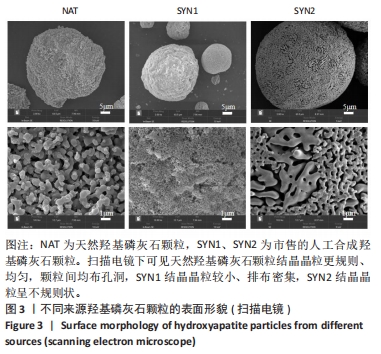
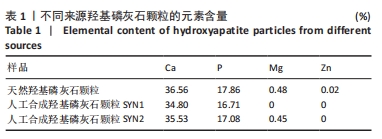
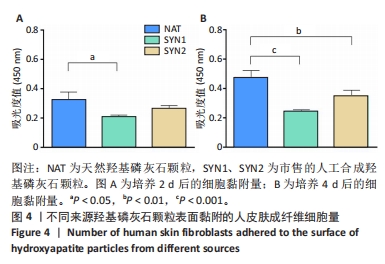
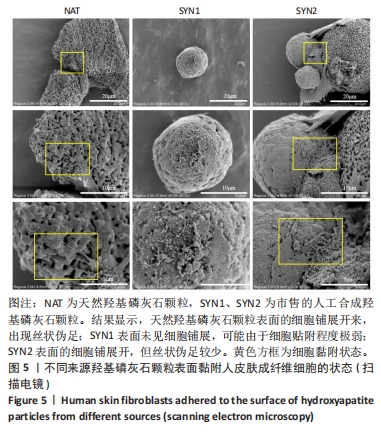
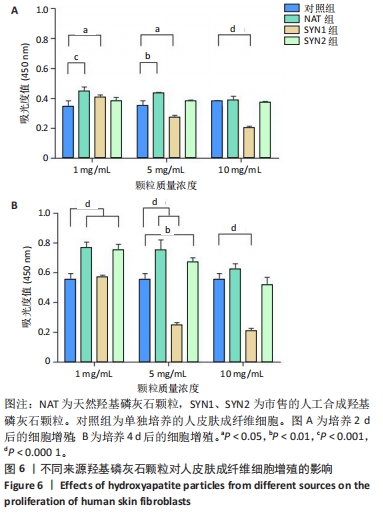
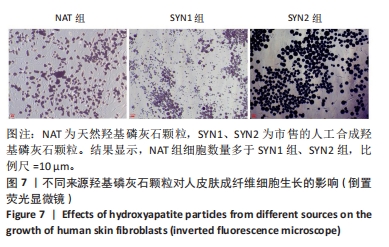
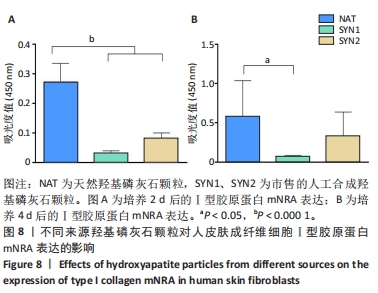
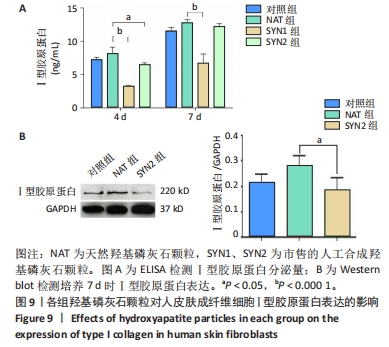
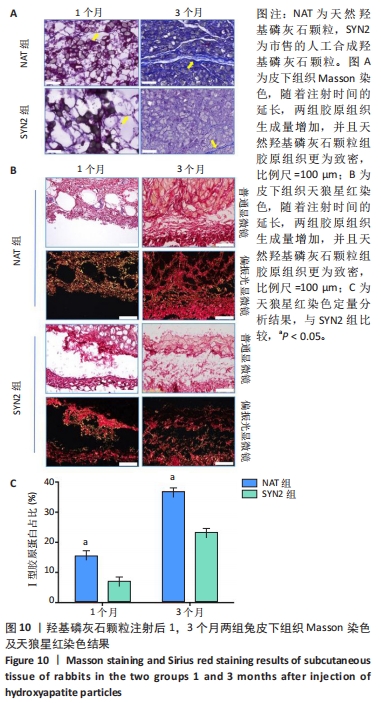
[1] HUSSAIN SH, LIMTHONGKUL B, HUMPHREYS TR. The biomechanical properties of the skin. Dermatol Surg. 2013;39(2):193-203.
[2] BASS LS, STACY S, MARIANO B, et al. Calcium hydroxylapatite (Radiesse) for treatment of nasolabial folds: Long-term safety and efficacy results. Aesthet Surg J. 2010;30(2):235-238.
[3] 张译心,罗倩,梁瀚文,等.注射用聚左旋乳酸微球体内可促胶原再生[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(34):5448-5453.
[4] AMIRI M, MEÇANI R, NIEHOT CD, et al. Skin regeneration-related mechanisms of Calcium Hydroxylapatite (CaHA): a systematic review. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023;10:1195934.
[5] 朱莎莎,岳述荣,林光明,等.微晶瓷在美容整形领域的应用简述[J].中国美容医学,2014,23(22):1944-1947.
[6] NOWAG B, CASABONA G, KIPPENBERGER S, et al. Calcium hydroxylapatite microspheres activate fibroblasts through direct contact to stimulate neocollagenesis. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2023;22:426-432.
[7] GUIDA S, GALADARI H. A systematic review of Radiesse/calcium hydroxylapatite and carboxymethylcellulose: evidence and recommendations for treatment of the face. Int J Dermatol. 2024; 63(2):150-160.
[8] NICOLA Z, ALBERTO C. Calcium hydroxylapatite treatment of human skin: evidence of collagen turnover through picrosirius red staining and circularly polarized microscopy. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2018;2018(11):29-35.
[9] GONZÁLEZ N, GOLDBERG DJ. Evaluating the effects of injected calcium hydroxylapatite on changes in human skin elastin and proteoglycan formation. Dermatol Surg. 2019;45(4):547-551.
[10] AMIRI M, MEÇANI R, LLANAJ E, et al. Calcium hydroxylapatite (CaHA) and aesthetic outcomes: A systematic review of controlled clinical trials. J Clin Med. 2024;13(6):1686.
[11] YUTSKOVSKAYA Y, KOGAN E, LESHUNOV E. A randomized, split-face, histomorphologic study comparing a volumetric calcium hydroxylapatite and a hyaluronic acid-based dermal filler. J Drugs Dermatol. 2014;13(9):1047-1052.
[12] NOWAG B, SCHÄFER D, HENGL T, et al. Biostimulating fillers and induction of inflammatory pathways: A preclinical investigation of macrophage response to calcium hydroxylapatite and poly-L lactic acid. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2024;23:99-106.
[13] MCCARTHY AD, HARTMANN C, DURKIN A, et al. A morphological analysis of calcium hydroxylapatite and poly-l-lactic acid biostimulator particles. Skin Res Technol. 2024;30(6):e13764.
[14] HU Y, LU H, YUAN X, et al. The histologic reaction and permanence of hyaluronic acid gel, calcium hydroxylapatite microspheres, and extracellular matrix bio gel. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2023;22(10):2685-2691.
[15] 李亚莹,白艳洁,曹婷.羟基磷灰石在硬组织修复中的应用进展[J].中国美容整形外科杂志,2020,31(3):190-193.
[16] 潘蕾,吴溯帆.羟基磷灰石在面部软组织填充中的应用[J].中华医学美学美容杂志,2010,16(1):66-68.
[17] 侯建飞,王福科,杨桂然,等.羟基磷灰石表面改性作为组织工程骨支架的应用优势[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(10):1610-1614.
[18] SHAW FL, HARRISON H, SPENCE K, et al. A detailed mammosphere assay protocol for the quantification of breast stem cell activity. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2012;17:111-117.
[19] GIORDO R, NASRALLAH GK, POSADINO AM, et al. Resveratrol-Elicited PKC Inhibition Counteracts NOX-Mediated Endothelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Human Retinal Endothelial Cells Exposed to High Glucose. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021;10(2):224.
[20] 郑鸿浩.可降解聚合物微球的表面拓扑结构调控及其对细胞粘附和功能的影响研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2018.
[21] ANA BF, STEFANIE GL, MARKUS R, et al. Differential regulation of osteogenic differentiation of stem cells on surface roughness gradients. Biomaterials. 2014;35(33):9023-9032.
[22] CHEN W, SHAO Y, LI X, et al. Nanotopographical surfaces for stem cell fate control: Engineering mechanobiology from the bottom. Nano Today. 2014;9(6):759-784.
[23] WANG L, LUO Q, ZHANG X, et al. Co-implantation of magnesium and zinc ions into titanium regulates the behaviors of human gingival fibroblasts, Bioact Mater. 2021;6:(1):64-74.
[24] GAO J, WANG M, SHI C, et al. Synthesis of trace element Si and Sr codoping hydroxyapatite with non-cytotoxicity and enhanced cell proliferation and differentiation. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2016;174(1): 208-217.
[25] MUENCH LN, TAMBURINI L, KRISCENSKI D, et al. The effect of augmenting suture material with magnesium and platelet-rich plasma on the in vitro adhesion and proliferation potential of subacromial bursa-derived progenitor cells. JSES Int. 2023;26;7(6):2367-2372.
[26] 许德田.口服胶原蛋白水解产物对皮肤的作用[J].中国美容医学, 2013,22(3):410-413.
[27] 任荣鑫,马小兵,鲍世威,等.面部注射填充材料的临床应用进展[J].中国美容整形外科杂志,2021,32(2):96-98.
[28] DURAIRAJ K, BAKER O, YAMBAO M, et al. Safety and efficacy of diluted calcium hydroxylapatite for the treatment of cellulite dimpling on the buttocks: Results from an Open-Label, Investigator-Initiated, Single-Center, Prospective Clinical Study. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024; 48(9):1797-1806.
[29] MELFA F, MCCARTHY A, AGUILERA SB, et al. Guided SEFFI and CaHA: A retrospective observational study of an innovative protocol for regenerative aesthetics. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(15):4381.
[30] BAY AS, ALEC MC, SAAMI K, et al. The role of calcium hydroxylapatite (Radiesse) as a regenerative aesthetic treatment: a narrative review. Aesthet Surg J. 2023;43(10):1063-1090.
[31] 姚然,贾有胜,张曼,等.三例面部注射可降解稀释复合纳米羟基磷灰石钙的螺旋CT分析[J].中国美容整形外科杂志,2024,35(1): 62-64.
[32] VISCOMI B, FARIA G, HERNANDEZ CA, et al. Contouring Plus: A comprehensive approach of the lower third of the face with calcium hydroxylapatite and hyaluronic acid. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2023;16:911-924.
[33] FIRDAUS HUSSIN MS, ABDULLAH HZ, IDRIS MI, et al. Extraction of natural hydroxyapatite for biomedical applications-A review. Heliyon. 2022;8(8):e10356.
[34] ANSELME K. Osteoblast adhesion on biomaterials. Biomaterials. 2000;21(7):667-681.
[35] WALTHERS CM, NAZEMI AK, PATEL SL, et al. The effect of scaffold macroporosity on angiogenesis and cell survival in tissue-engineered smooth muscle. Biomaterials. 2014;35(19):5129-5137.
[36] KLENKE FM, LIU Y, YUAN H, et al. Impact of pore size on the vascularization and osseointegration of ceramic bone substitutes in vivo. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008;85(3):777-786.
[37] 王央玲,黄海桃,符火.微量元素对合并糖脂代谢异常子痫前期患者内皮祖细胞增殖及迁移活性的影响[J].中国计划生育学杂志, 2022,30(9):1950-1954.
[38] WAAS WF, DALBY KN. Physiological concentrations of divalent magnesium ion activate the serine/threonine specific protein kinase ERK2. Biochemistry. 2003;42(10):2960-2970.
[39] KAMBE T. An overview of a wide range of functions of ZnT and Zip Zinc transporters in the secretory pathway. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2011;75(6):1036-1043.
[40] NOAM L, MICHAL H. How cellular Zn2+ signaling drives physiological functions. Cell Calcium. 2018;75:53-63.
[41] FUKADA T, CIVIC N, FURUICHI T, et al. The Zinc transporter SLC39A13/ZIP13 is required for connective tissue development; its involvement in BMP/TGF-β signaling pathways. PLoS One. 2008;3(11):e3642.
[42] HASSAN N, KRIEG T, ZINSER M, et al. An overview of scaffolds and biomaterials for skin expansion and soft tissue regeneration: insights on Zinc and Magnesium as new potential key elements. Polymers(Basel). 2023;15(19):3854.
[43] HAN J, ANDRÉE L, DENG D, et al. Biofunctionalization of dental abutments by a zinc/chitosan/gelatin coating to optimize fibroblast behavior and antibacterial properties. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2024; 112(11):1873-1892. |