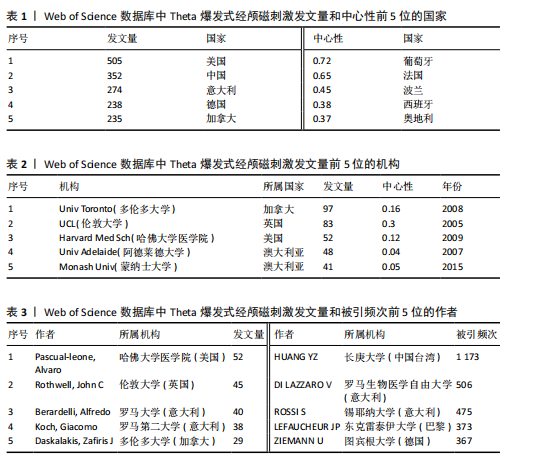
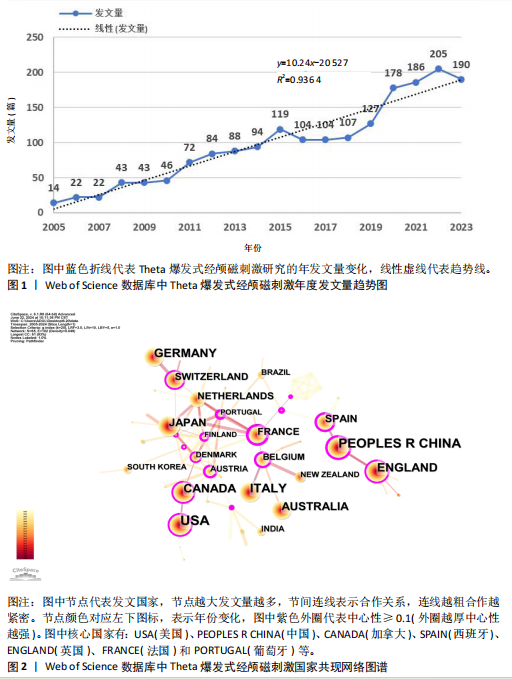
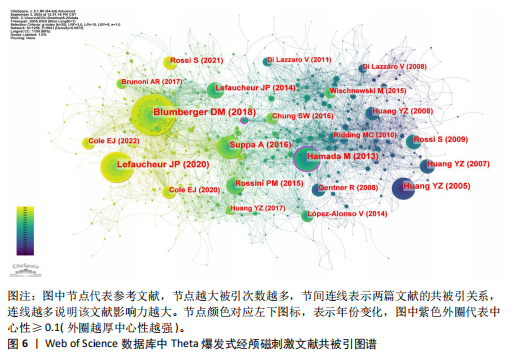
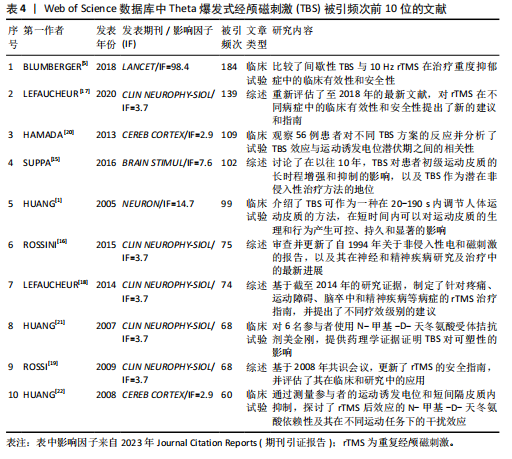
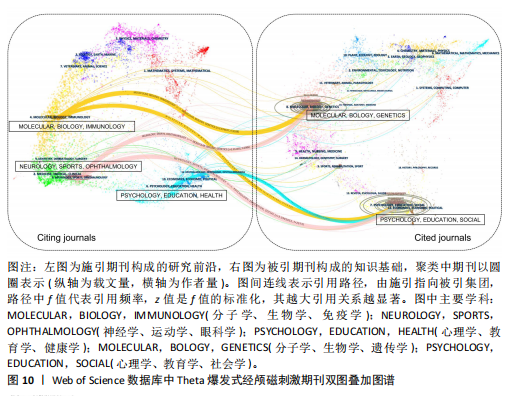
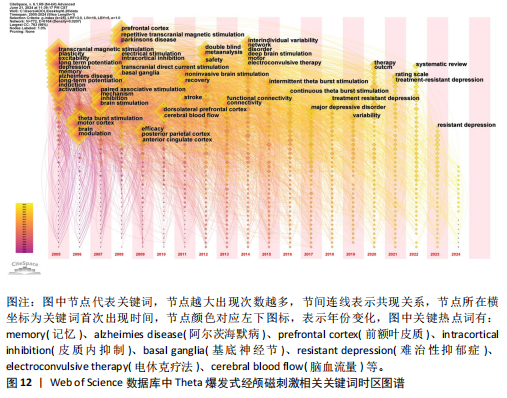
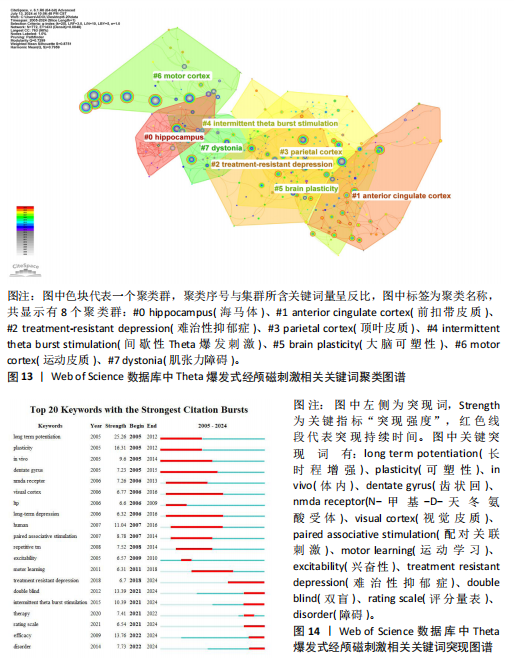
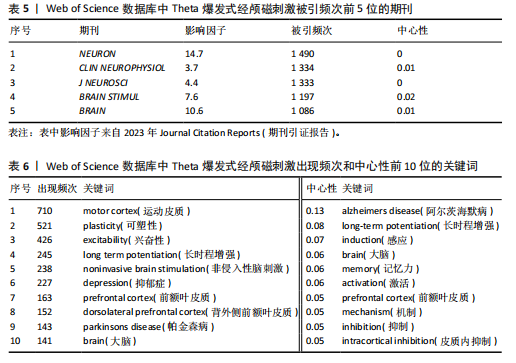
[13]
COLE E, O’SULLIVAN SJ, TIK M, et al. Accelerated theta burst stimulation: safety, efficacy, and future advancements. Biol Psychiatry. 2024;95(6):523-535.
[14] XU S, XU D, WEN L, et al. Integrating unified medical language system and kleinberg’s burst detection algorithm into research topics of medications for post-traumatic stress disorder. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020;14:3899-3913.
[15] SUPPA A, HUANG YZ, FUNKE K, et al. Ten years of theta burst stimulation in humans: established knowledge, unknowns and prospects. Brain Stimul. 2016;9(3):323-335.
[16] ROSSINI PM, BURKE D, CHEN R, et al. Non-invasive electrical and magnetic stimulation of the brain, spinal cord, roots and peripheral nerves: basic principles and procedures for routine clinical and research application. An updated report from an I.F.C.N. Committee. Clin Neurophysiol. 2015;126(6):1071-1107.
[17] LEFAUCHEUR JP, ALEMAN A, BAEKEN C, et al. Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS): an update (2014-2018). Clin Neurophysiol. 2020; 131(2):474-528.
[18] LEFAUCHEUR JP, ANDRE-OBADIA N, ANTAL A, et al. Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS). Clin Neurophysiol. 2014;125(11):2150-2206.
[19] ROSSI S, HALLETT M, ROSSINI PM, et al. Safety, ethical considerations, and application guidelines for the use of transcranial magnetic stimulation in clinical practice and research. Clin Neurophysiol. 2009;120(12):2008-2039.
[20] HAMADA M, MURASE N, HASAN A, et al. The role of interneuron networks in driving human motor cortical plasticity. Cereb Cortex. 2013;23(7):1593-1605.
[21] HUANG YZ, CHEN RS, ROTHWELL JC, et al. The after-effect of human theta burst stimulation is NMDA receptor dependent. Clin Neurophysiol. 2007;118(5):1028-1032.
[22] HUANG YZ, ROTHWELL JC, EDWARDS MJ, et al. Effect of physiological activity on an NMDA-dependent form of cortical plasticity in human. Cereb Cortex. 2008;18(3):563-570.
[23] NETTEKOVEN C, VOLZ LJ, KUTSCHA M, et al. Dose-dependent effects of theta burst rTMS on cortical excitability and resting-state connectivity of the human motor system. J Neurosci. 2014;34(20):6849-6859.
[24] TALELLI P, WALLACE A, DILEONE M, et al. Theta burst stimulation in the rehabilitation of the upper limb: a semirandomized, placebo-controlled trial in chronic stroke patients. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2012;26(8):976-987.
[25] KOCH G, BONNI S, CASULA EP, et al. Effect of cerebellar stimulation on gait and balance recovery in patients with hemiparetic stroke: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Neurol. 2019;76(2):170-178.
[26] LOWE CJ, MANOCCHIO F, SAFATI AB, et al. The effects of theta burst stimulation (TBS) targeting the prefrontal cortex on executive functioning: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuropsychologia. 2018;111(4):344-359.
[27] KOCH G, BRUSA L, CARRILLO F, et al. Cerebellar magnetic stimulation decreases levodopa-induced dyskinesias in Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2009;73(2):113-119.
[28] TALELLI P, GREENWOOD RJ, ROTHWELL JC. Exploring theta burst stimulation as an intervention to improve motor recovery in chronic stroke. Clin Neurophysiol. 2007; 118(2):333-342.
[29] JANNATI A, OBERMAN LM, ROTENBERG A, et al. Assessing the mechanisms of brain plasticity by transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2023; 48(1):191-208.
[30] CAPPON D, den BOER T, JORDAN C, et al. Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) for geriatric depression. Ageing Res Rev. 2022;74(2):101531.
[31] MENARDI A, ROSSI S, KOCH G, et al. Toward noninvasive brain stimulation 2.0 in Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res Rev. 2022;75(3):101555.
[32] SABBAGH M, SADOWSKY C, TOUSI B, et al. Effects of a combined transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and cognitive training intervention in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2020;16(4):641-650.
[33] SEYBERT C, COTOVIO G, RODRIGUES DSD, et al. Replicability of motor cortex-excitability modulation by intermittent theta burst stimulation. Clin Neurophysiol. 2023;152(8):22-33.
[34] SOLOMON EA, SPERLING MR, SHARAN AD, et al. Theta-burst stimulation entrains frequency-specific oscillatory responses. Brain Stimul. 2021;14(5):1271-1284.
[35] LI J, REN M, WANG W, et al. Human Theta burst stimulation combined with subsequent electroacupuncture increases corticospinal excitability. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020; 2020(1):8824530.
[36] QIU S, WANG S, PENG W, et al. Continuous theta-burst stimulation modulates resting-state EEG microstates in healthy subjects. Cogn Neurodyn. 2022;16(3):621-631.
[37] VINK J, VAN LIESHOUT E, OTTE WM, et al. Continuous theta-burst stimulation of the contralesional primary motor cortex for promotion of upper limb recovery after stroke: a randomized controlled trial. Stroke. 2023;54(8):1962-1971.
[38] RASHID-LOPEZ R, MACIAS-GARCIA P, SANCHEZ-FERNANDEZ FL, et al. Neuroimaging and serum biomarkers of neurodegeneration and neuroplasticity in Parkinson’s disease patients treated by intermittent theta-burst stimulation over the bilateral primary motor area: a randomized, double-blind, sham-controlled, crossover trial study. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023;15:1258315.
[39] ZAVOROTNYY M, ZOLLNER R, REKATE H, et al. Intermittent theta-burst stimulation moderates interaction between increment of N-Acetyl-Aspartate in anterior cingulate and improvement of unipolar depression. Brain Stimul. 2020;13(4):943-952.
[40] CHANG CH, LIU CY, CHEN SJ, et al. Accelerated theta-burst transcranial magnetic stimulation of the bilateral dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in a patient with post-traumatic stress disorder and major depressive disorder: case report. Front Psychiatry. 2023;14:1061088.
[41] POORGANJI M, GOEKE K, ZOMORRODI R, et al. The use of theta burst stimulation in patients with schizophrenia-A systematic review. Schizophr Res. 2023;261(11):245-255.
[42] NGETICH R, JIN D, LI W, et al. Enhancing visuospatial working memory performance using intermittent theta-burst stimulation over the right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Front Hum Neurosci. 2022;16:752519.
[43] JIN X, XU CY, FEI JF, et al. Alzheimer’s disease with depressive symptoms: clinical effect of intermittent theta burst stimulation repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. World J Psychiatry. 2024;14(8):1216-1223.
[44] NEUTEBOOM D, ZANTVOORD JB, GOYA-MALDONADO R, et al. Accelerated intermittent theta burst stimulation in major depressive disorder: a systematic review. Psychiatry Res. 2023;327(9):115429.
[45] CAI DB, QIN ZJ, LAN XJ, et al. Accelerated intermittent theta burst stimulation for major depressive disorder or bipolar depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Asian J Psychiatr. 2023; 85(7):103618.
[46] TSAI PY, LIN WS, TSAI KT, et al. High-frequency versus theta burst transcranial magnetic stimulation for the treatment of poststroke cognitive impairment in humans. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2020;45(4):262-270.
[47] FENG Y, HUANG Z, MA X, et al. Intermittent theta-burst stimulation alleviates hypoxia-ischemia-caused myelin damage and neurologic disability. Exp Neurol. 2024; 378(8):114821.
[48] WU Y, WANG L, YU F, et al. Intermittent theta burst stimulation (iTBS) as an optimal treatment for schizophrenia risk decision: an ERSP study. Front Psychiatry. 2021;12:594102.
[49] GOH KK, CHEN CH, WU TH, et al. Efficacy and safety of intermittent theta-burst stimulation in patients with schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of randomized sham-controlled trials. Front Pharmacol. 2022; 13:944437.
[50] STEKIC A, ZELJKOVIC M, ZARIC KM, et al. Intermittent theta burst stimulation ameliorates cognitive deficit and attenuates neuroinflammation via PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in Alzheimer’s-Like disease model. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:889983.
[51] ZHAO H, JIANG C, ZHAO M, et al. Comparisons of accelerated continuous and intermittent theta burst stimulation for treatment-resistant depression and suicidal ideation. Biol Psychiatry. 2024;96(1):26-33.
[52] SANNA A, FOLLESA P, PULIGHEDDU M, et al. Cerebellar continuous theta burst stimulation reduces levodopa-induced dyskinesias and decreases serum BDNF levels. Neurosci Lett. 2020;716(3):134653.
[53] LI H, CUI L, LI J, et al. Comparative efficacy and acceptability of neuromodulation procedures in the treatment of treatment-resistant depression: a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Affect Disord. 2021;287(10):115-124.
[54] BAKER TE, ROBLES D. Theta burst stimulation of the hyperdirect pathway boosts inhibitory control and reduces craving and smoking in nicotine-dependent adults. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2023;8(11):1072-1074.
[55] SU H, CHEN T, JIANG H, et al. Intermittent theta burst transcranial magnetic stimulation for methamphetamine addiction: a randomized clinical trial. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2020;31(2):158-161.
[56] BOZZAY ML, BRIGIDO S, VAN TWM, et al. Intermittent theta burst stimulation in veterans with mild alcohol use disorder. J Affect Disord. 2021;293(16):314-319.
[57] HUANG D, CHAI D, HUANG P, et al. Continuous theta burst stimulation for the treatment of delirium after non-cardiac surgery. J Clin Anesth. 2023;90(7):111217.
[58] BOUCHER PO, OZDEMIR RA, MOMI D, et al. Sham-derived effects and the minimal reliability of theta burst stimulation. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):21170.
[59] TANG Z, LIU T, LIU Y, et al. Different doses of intermittent theta burst stimulation for upper limb motor dysfunction after stroke: a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Front Neurosci. 2023;17:1259872.
[60] STRAFELLA R, MOMI D, ZOMORRODI R, et al. Identifying neurophysiological markers of intermittent theta burst stimulation in treatment-resistant depression using transcranial magnetic stimulation-electroencephalography. Biol Psychiatry. 2023;94(6):454-465.
[61] CAULFIELD KA, BROWN JC. The problem and potential of TMS’ infinite parameter space: a targeted review and road map forward. Front Psychiatry. 2022;13:867091.
[62] EIBL T, SCHREY M, LIEBERT A, et al. Influence of clinical and tumor-specific factors on the resting motor threshold in navigated transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neurophysiol Clin. 2023;53(6):102920.
[63] CAI G, XU J, DING Q, et al. Electroencephalography oscillations can predict the cortical response following theta burst stimulation. Brain Res Bull. 2024;208(3):110902.
[64] STRUCKMANN W, BODEN R, GINGNELL M, et al. Modulation of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex functional connectivity after intermittent theta-burst stimulation in depression: combining findings from fNIRS and fMRI. Neuroimage Clin. 2022;34(2): 103028.
[65] WANG J, ZHANG J, YU H, et al. Editorial: human machine interface-based neuromodulation solutions for neurorehabilitation. Front Neurosci. 2022; 16:987455.
[66] WANG H, ZHENG H, WU H, et al. Behavior-dependent corticocortical contributions to imagined grasping: a BCI-triggered TMS study. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2022;31:519-529.
[67] WEN Y, HAO X, CHEN X, et al. Theta-burst stimulation combined with virtual-reality reconsolidation intervention for methamphetamine use disorder: study protocol for a randomized-controlled trial. Front Psychiatry. 2022;13:903242.