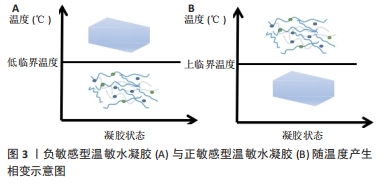
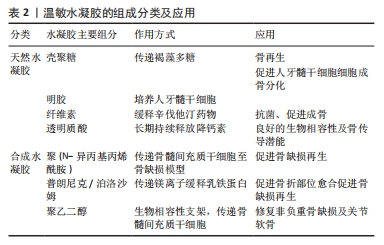
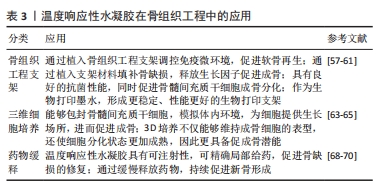
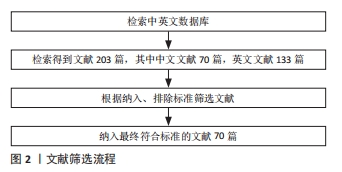
[1] KZHANG M, MATINLINNA JP, TSOI J, et al. Recent developments in biomaterials for long-bone segmental defect reconstruction: A narrative overview. J Orthop Translat. 2020;22:26-33.
[2] HO-SHUI-LING A, BOLANDER J, RUSTOM LE, et al. Bone regeneration strategies: Engineered scaffolds, bioactive molecules and stem cells current stage and future perspectives. Biomaterials. 2018;180:143-162.
[3] RODDY E, DEBAUN MR, DAOUD-GRAY A, et al. Treatment of critical-sized bone defects: clinical and tissue engineering perspectives. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2018;28(3):351-362.
[4] WUBNEH A, TSEKOURA EK, AYRANCI C, et al. Current state of fabrication technologies and materials for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2018;80:1-30.
[5] CUI ZK, KIM S, BALJON JJ, et al. Microporous methacrylated glycol chitosan-montmorillonite nanocomposite hydrogel for bone tissue engineering. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):3523.
[6] WU S, GAI T, CHEN J, et al. Smart responsive in situ hydrogel systems applied in bone tissue engineering. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;12:1389733.
[7] XIAN S, WEBBER MJ. Temperature-responsive supramolecular hydrogels. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(40):9197-9211.
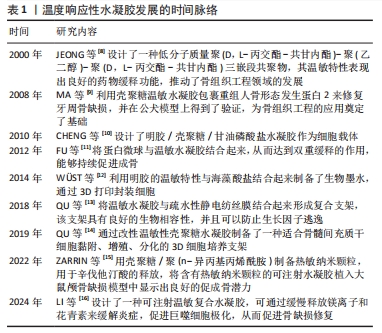
[8] JEONG B, BAE YH, KIM SW. Drug release from biodegradable injectable thermosensitive hydrogel of PEG-PLGA-PEG triblock copolymers. J Control Release. 2000;63(1-2):155-163.
[9] MA ZW, ZHANG YJ, WU ZF, et al. [A study on the effect of the chitosan thermosensitive hydrogel loading recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 on repairing periodontal defects]. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2008;26(1):23-26.
[10] CHENG YH, YANG SH, SU WY, et al. Thermosensitive chitosan-gelatin-glycerol phosphate hydrogels as a cell carrier for nucleus pulposus regeneration: an in vitro study. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(2):695-703.
[11] FU Y, DU L, WANG Q, et al. In vitro sustained release of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 microspheres embedded in thermosensitive hydrogels. Pharmazie. 2012;67(4):299-303.
[12] WUST S, GODLA ME, MULLER R, et al. Tunable hydrogel composite with two-step processing in combination with innovative hardware upgrade for cell-based three-dimensional bioprinting. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(2):630-640.
[13] QU Y, WANG B, CHU B, et al. Injectable and Thermosensitive Hydrogel and PDLLA Electrospun Nanofiber Membrane Composites for Guided Spinal Fusion. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(5):4462-4470.
[14] QU C, BAO Z, ZHANG X, et al. A thermosensitive RGD-modified hydroxybutyl chitosan hydrogel as a 3D scaffold for BMSCs culture on keloid treatment. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;125:78-86.
[15] ZARRIN NK, MOTTAGHITALAB F, REIS RL, et al. Thermosensitive chitosan/poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) nanoparticles embedded in aniline pentamer/silk fibroin/polyacrylamide as an electroactive injectable hydrogel for healing critical-sized calvarial bone defect in aging rat model. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;213:352-368.
[16] LI J, KE H, LEI X, et al. Controlled-release hydrogel loaded with magnesium-based nanoflowers synergize immunomodulation and cartilage regeneration in tendon-bone healing. Bioact Mater. 2024;36:62-82.
[17] SUN Z, SONG C, WANG C, et al. Hydrogel-Based Controlled Drug Delivery for Cancer Treatment: A Review. Mol Pharm. 2020;17(2):373-391.
[18] DEY M, OZBOLAT IT. 3D bioprinting of cells, tissues and organs. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):14023.
[19] YUAN B, ZHANG Y, WANG Q, et al. Thermosensitive vancomycin@PLGA-PEG-PLGA/HA hydrogel as an all-in-one treatment for osteomyelitis. Int J Pharm. 2022;627:122225.
[20] TAYLOR MJ, TOMLINS P, SAHOTA S. Thermoresponsive Gels. Gels. 2017; 3(1):4.
[21] ANDREAZZA R, MORALES A, PIENIZ S, et al. Gelatin-Based Hydrogels: Potential Biomaterials for Remediation. Polymers (Basel). 2023;15(4):1026.
[22] MOHANTO S, NARAYANA S, MERAI KP, et al. Advancements in gelatin-based hydrogel systems for biomedical applications: A state-of-the-art review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;253(Pt 5):127143.
[23] SAMIRANINEZHAD N, ASADI K, REZAZADEH H, et al. Using chitosan, hyaluronic acid, alginate, and gelatin-based smart biological hydrogels for drug delivery in oral mucosal lesions: A review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;252:126573.
[24] QIN Y, LI P, GUO Z. Cationic chitosan derivatives as potential antifungals: A review of structural optimization and applications. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;236:116002.
[25] ZHAO J, QIU P, WANG Y, et al. Chitosan-based hydrogel wound dressing: From mechanism to applications, a review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;244: 125250.
[26] GHOLAP AD, ROJEKAR S, KAPARE HS, et al. Chitosan scaffolds: Expanding horizons in biomedical applications. Carbohydr Polym. 2024;323:121394.
[27] DEHGHAN-BANIANI D, CHEN Y, WANG D, et al. Injectable in situ forming kartogenin-loaded chitosan hydrogel with tunable rheological properties for cartilage tissue engineering. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020;192:111059.
[28] ZHOU HY, JIANG LJ, CAO PP, et al. Glycerophosphate-based chitosan thermosensitive hydrogels and their biomedical applications. Carbohydr Polym. 2015;117:524-536.
[29] DENG A, KANG X, ZHANG J, et al. Enhanced gelation of chitosan/beta-sodium glycerophosphate thermosensitive hydrogel with sodium bicarbonate and biocompatibility evaluated. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;78:1147-1154.
[30] OHMES J, SAURE LM, SCHUTT F, et al. Injectable Thermosensitive Chitosan-Collagen Hydrogel as A Delivery System for Marine Polysaccharide Fucoidan. Mar Drugs. 2022;20(6):402.
[31] CAO H, WANG J, HAO Z, et al. Gelatin-based biomaterials and gelatin as an additive for chronic wound repair. Front Pharmacol. 2024;15:1398939.
[32] SAMIEI M, DALIR AE, AMIRYAGHOUBI N, et al. Injectable thermosensitive chitosan/gelatin hydrogel for dental pulp stem cells proliferation and differentiation. Bioimpacts. 2023;13(1):63-72.
[33] ABDELHAMID HN, MATHEW AP. Cellulose-Based Nanomaterials Advance Biomedicine: A Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(10):5405.
[34] SUN Z, KUANG Y, AHMAD M, et al. Enhanced osmotic energy conversion through bacterial cellulose based double-network hydrogel with 3D interconnected nanochannels. Carbohydr Polym. 2023;305:120556.
[35] LI B, ZHANG L, WANG D, et al. Thermosensitive -hydrogel-coated titania nanotubes with controlled drug release and immunoregulatory characteristics for orthopedic applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;122:111878.
[36] ABATANGELO G, VINDIGNI V, AVRUSCIO G, et al. Hyaluronic Acid: Redefining Its Role. Cells. 2020;9(7):1743.
[37] YU P, XIE J, CHEN Y, et al. A thermo-sensitive injectable hydroxypropyl chitin hydrogel for sustained salmon calcitonin release with enhanced osteogenesis and hypocalcemic effects. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(2): 270-281.
[38] REN Z, WANG Y, MA S, et al. Effective Bone Regeneration Using Thermosensitive Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) Grafted Gelatin as Injectable Carrier for Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2015,7(34):19006-19015.
[39] RUSSO E, VILLA C. Poloxamer Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics. 2019;11(12):671.
[40] ABDELTAWAB H, SVIRSKIS D, SHARMA M. Formulation strategies to modulate drug release from poloxamer based in situ gelling systems. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2020;17(4):495-509.
[41] ABDELTAWAB H, SVIRSKIS D, BOYD BJ, et al. Injectable thermoresponsive gels offer sustained dual release of bupivacaine hydrochloride and ketorolac tromethamine for up to two weeks. Int J Pharm. 2021;604: 120748.
[42] PERUMAL G, RAMASAMY B, NANDKUMAR AM, et al. Influence of magnesium particles and Pluronic F127 on compressive strength and cytocompatibility of nanocomposite injectable and moldable beads for bone regeneration. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2018;88:453-462.
[43] PARK YE, CHANDRAMOULI K, WATSON M, et al. Sustained Delivery of Lactoferrin Using Poloxamer Gels for Local Bone Regeneration in a Rat Calvarial Defect Model. Materials (Basel). 2021;15(1):212.
[44] LIU J, ZHANG Y, LI Q, et al. Development of injectable thermosensitive polypeptide hydrogel as facile radioisotope and radiosensitizer hotspot for synergistic brachytherapy. Acta Biomater. 2020;114:133-145.
[45] PIAO L, XIANG P, ZHOU Y, et al. Thermo-sensitive PLGA-PEG-PLGA hydrogel for sustained release of EGF to inhibit cervical cancer recurrence. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2024;236:113795.
[46] NI P, DING Q, FAN M, et al. Injectable thermosensitive PEG-PCL-PEG hydrogel/acellular bone matrix composite for bone regeneration in cranial defects. Biomaterials. 2014;35(1):236-248.
[47] FU S, NI P, WANG B, et al. Injectable and thermo-sensitive PEG-PCL-PEG copolymer/collagen/n-HA hydrogel composite for guided bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2012;33(19):4801-4809.
[48] GUREL PG, ABAY AN, CUMBUL A, et al. Investigation of Vasculogenesis Inducing Biphasic Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021;7(4):1526-1538.
[49] WANG KH, LIU CH, TAN DH, et al. Block Sequence Effects on the Self-Assembly Behaviors of Polypeptide-Based Penta-Block Copolymer Hydrogels. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024;16(5):6674-6686.
[50] YU S, ZHANG D, HE C, et al. Injectable Thermosensitive Polypeptide-Based CDDP-Complexed Hydrogel for Improving Localized Antitumor Efficacy. Biomacromolecules. 2017;18(12):4341-4348.
[51] QUADIR MA, MORTON SW, DENG ZJ, et al. PEG-polypeptide block copolymers as pH-responsive endosome-solubilizing drug nanocarriers. Mol Pharm. 2014;11(7):2420-2430.
[52] JIN GW, REJINOLD NS, CHOY JH. Polyphosphazene-Based Biomaterials for Biomedical Applications. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(24):15993.
[53] SEO BB, KOH JT, SONG SC. Tuning physical properties and BMP-2 release rates of injectable hydrogel systems for an optimal bone regeneration effect. Biomaterials. 2017;122:91-104.
[54] ZHANG W, WANG N, YANG M, et al. Periosteum and development of the tissue-engineered periosteum for guided bone regeneration. J Orthop Translat. 2022;33:41-54.
[55] JURCZAK P, LACH S. Hydrogels as Scaffolds in Bone-Related Tissue Engineering and Regeneration. Macromol Biosci. 2023;23(11):e2300152.
[56] SAUNDERS L, MA PX. Self-Healing Supramolecular Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering Applications. Macromol Biosci. 2019;19(1):e1800313.
[57] JI X, SHAO H, LI X, et al. Injectable immunomodulation-based porous chitosan microspheres/HPCH hydrogel composites as a controlled drug delivery system for osteochondral regeneration. Biomaterials. 2022;285: 121530.
[58] TAN Z, LUO Y, YANG L. Basic fibroblast growth factor/chitosan derivatives/collagen composite thermosensitive hydrogel promotes perio-dontal tissue regeneration in rats. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2023;41(1):21-28.
[59] MAKVANDI P, ALI GW, DELLA SF, et al. Hyaluronic acid/corn silk extract based injectable nanocomposite: A biomimetic antibacterial scaffold for bone tissue regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;107:110195.
[60] DUTTA SD, BIN J, GANGULY K, et al. Electromagnetic field-assisted cell-laden 3D printed poloxamer-407 hydrogel for enhanced osteogenesis. RSC Adv. 2021;11(33):20342-20354.
[61] MIAO G, LIANG L, LI W, et al. 3D Bioprinting of a Bioactive Composite Scaffold for Cell Delivery in Periodontal Tissue Regeneration. Biomolecules. 2023;13(7):1062.
[62] LANGHANS SA. Three-Dimensional in Vitro Cell Culture Models in Drug Discovery and Drug Repositioning. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:6.
[63] JI X, YUAN X, MA L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-loaded thermosensitive hydroxypropyl chitin hydrogel combined with a three-dimensional-printed poly(epsilon-caprolactone) /nano-hydroxyapatite scaffold to repair bone defects via osteogenesis, angiogenesis and immunomodulation. Theranostics. 2020;10(2):725-740.
[64] RETHORE G, BOYER C, KOUADIO K, et al. Silanization of Chitosan and Hydrogel Preparation for Skeletal Tissue Engineering. Polymers (Basel). 2020;12(12):2823.
[65] O’DONNELL BT, AL-GHADBAN S, IVES CJ, et al. Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells Retain Their Adipocyte Differentiation Potential in Three-Dimensional Hydrogels and Bioreactors (dagger). Biomolecules. 2020; 10(7):1070.
[66] DIMATTEO R, DARLING NJ, SEGURA T. In situ forming injectable hydrogels for drug delivery and wound repair. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018;127:167-184.
[67] ZHU J, TANG X, JIA Y, et al. Applications and delivery mechanisms of hyaluronic acid used for topical/transdermal delivery - A review. Int J Pharm. 2020;578:119127.
[68] AKAY AS, ARISAN V, CEVHER E, et al. Oxytocin-loaded sustained-release hydrogel graft provides accelerated bone formation: An experimental rat study. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(8):1676-1687.
[69] PONTREMOLI C, BOFFITO M, LAURANO R, et al. Mesoporous Bioactive Glasses Incorporated into an Injectable Thermosensitive Hydrogel for Sustained Co-Release of Sr(2+) Ions and N-Acetylcysteine. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(9):1890.
[70] FANG X, LEI L, JIANG T, et al. Injectable thermosensitive alginate/beta-tricalcium phosphate/aspirin hydrogels for bone augmentation. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2018;106(5):1739-1751. |