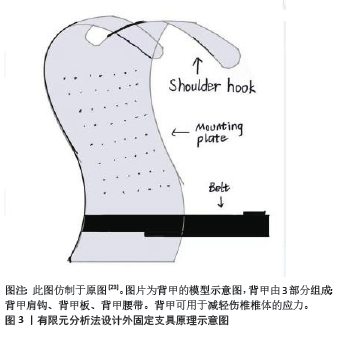
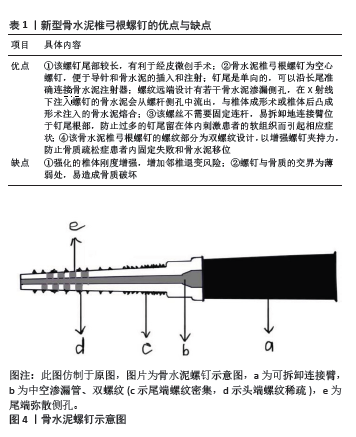
[1] ZHANG Q, CHON T, ZHANG Y, et al. Finite element analysis of the lumbar spine in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis subjected to different loads. Comput Biol Med. 2021;136:104745.
[2] WANG W, BARAN GR, BETZ RR, et al. The Use of Finite Element Models to Assist Understanding and Treatment For Scoliosis: A Review Paper. Spine Deform. 2014;2(1):10-27.
[3] NAOUM S, VASILIADIS AV, KOUTSERIMPAS C, et al. Finite Element Method for the Evaluation of the Human Spine: A Literature Overview. J Funct Biomater. 2021;12(3):43.
[4] CAI XY, SANG D, YUCHI CX, et al. Using finite element analysis to determine effects of the motion loading method on facet joint forces after cervical disc degeneration. Comput Biol Med. 2020;116:103519.
[5] BREKELMANS WA, POORT HW, SLOOFF TJ. A new method to analyse the mechanical behaviour of skeletal parts. Acta Orthop Scand. 1972; 43(5):301-317.
[6] BELYTSCHKO T, KULAK RF, SCHULTZ AB, et al. Finite element stress analysis of an intervertebral disc. J Biomech. 1974;7(3):277-285.
[7] MIZRAHI J, SILVA MJ, KEAVENY TM, et al. Finite-element stress analysis of the normal and osteoporotic lumbar vertebral body. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993;18(14):2088-2096.
[8] WEI W, ZHANG T, YANG J, et al. Material sensitivity of patient-specific finite element models in the brace treatment of scoliosis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1111449.
[9] WANG R, WU Z. Recent advancement in finite element analysis of spinal interbody cages: A review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1041973.
[10] SPIEGL UJA, SCHNAKE KJ, HARTMANN F, et al. Traumatic Fractures of the Thoracic Spine. Z Orthop Unfall. 2021;159(4):373-382.
[11] MURPHY J, MCLOUGHLIN E, DAVIES AM, et al. Is T9-11 the true thoracolumbar transition zone? J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2020;11(5): 891-895.
[12] WAN SHT, GULDENIZ O, YEUNG MHY, et al. Inter-screw index as a novel diagnostic indicator of tether breakage. Spine Deform. 2023;11(4): 887-895.
[13] SMITH CJ, ABDULAZEEZ MM, ELGAWADY M, et al. The Effect of Thoracolumbar Injury Classification in the Clinical Outcome of Operative and Non-Operative Treatments. Cureus. 2021;13(1): e12428.
[14] VACCARO AR, KIM DH, BRODKE DS, et al. Diagnosis and management of thoracolumbar spine fractures. Instr Course Lect. 2004;53: 359-373.
[15] LIU B, ZHU Y, LIU S, et al. National incidence of traumatic spinal fractures in China: Data from China National Fracture Study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(35):e12190.
[16] COSCIA MF, TRAMMELL TR, HAINES N. Thoracolumbar spinal fractures--concepts of treatment. Indiana Med. 1991;84(11): 92-796.
[17] LI Y, FENG X, PAN J, et al. Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Versus Kyphoplasty for Thoracolumbar Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures in Patients with Distant Lumbosacral Pain. Pain Physician. 2021;24(3):E349-E356.
[18] TANASANSOMBOON T, KITTIPIBUL T, LIMTHONGKUL W, et al. Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture without Neurological Deficit: Review of Controversies and Current Evidence of Treatment. World Neurosurg. 2022;162:29-35.
[19] ROBLESGIL-MEDRANO A, TELLEZ-GARCIA E, BUENO-GUTIERREZ LC, et al. Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Anterior and Posterior Approaches. Spine Surg Relat Res. 2022;6(2):99-108.
[20] HAYOUN T, SIBONI R, OHL X, et al. Treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: comparison of the clinical and radiological outcomes of percutaneous versus open surgery. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2023;33(6):2393-2397.
[21] LIU G, TAN JH, KONG JC, et al. Thoracolumbar Injury Classification and Severity Score Is Predictive of Perioperative Adverse Events in Operatively Treated Thoracic and Lumbar Fractures. Asian Spine J. 2022;16(6):848-856.
[22] GAVIRA N, AMELOT A, COOK AR, et al. Thoracolumbar spinal fracture in children: Conservative or surgical treatment? Neurochirurgie. 2022;68(3):309-314.
[23] CHE M, WANG Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Finite Element Analysis of a New Type of Spinal Protection Device for the Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. Orthop Surg. 2022; 14(3):577-586.
[24] SPIEGL UJ, JOSTEN C, DEVITT BM, et al. Incomplete burst fractures of the thoracolumbar spine: a review of literature. Eur Spine J. 2017; 26(12):3187-3198.
[25] NEELEY OJ, KAFKA B, TECLE NE, et al. Percutaneous screw fixation versus open fusion for the treatment of traumatic thoracolumbar fractures: A retrospective case series of 185 Patients with a single-level spinal column injury. J Clin Neurosci. 2022;101:47-51.
[26] YAN J, LIAO Z, YU Y. Finite element analysis of dynamic changes in spinal mechanics of osteoporotic lumbar fracture. Eur J Med Res. 2022;27(1):142.
[27] HUANG S, ZHOU C, ZHANG X, et al. Biomechanical analysis of sandwich vertebrae in osteoporotic patients: finite element analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1259095.
[28] ZHANG L, LI J, YANG H, et al. Histological evaluation of bone biopsy results during PVP or PKP of vertebral compression fractures. Oncol Lett. 2013;5(1):135-138.
[29] WANG D, LI Y, YIN H, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of optimal distribution model of vertebroplasty. Ann Palliat Med. 2020;9(3):1062-1072.
[30] MURATORE M, ALLASIA S, VIGLIERCHIO P, et al. Surgical treatment of traumatic thoracolumbar fractures: a retrospective review of 101 cases. Musculoskelet Surg. 2021;105(1):49-59.
[31] ZHANG G, DU Y, JIANG G, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of different posterior fixation techniques for treating thoracolumbar burst fractures of osteoporosis old patients: a finite element analysis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1268557.
[32] VENMANS A, KLAZEN CA, LOHLE PN, et al. Natural history of pain in patients with conservatively treated osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: results from VERTOS II. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012;33(3):519-521.
[33] PAWAR A, BADHE V, GAWANDE M. Treatment of Osteoporotic Compression Fractures at Thoracolumbar Spine With Neurodeficit: Short-Segment Stabilization With Cement-Augmented Fenestrated Pedicle Screws and Vertebroplasty by Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Technique. Int J Spine Surg. 2022;16(3):465-471.
[34] XU H, FENG Q, MA X, et al. Biomechanical behaviour of a novel bone cement screw in the minimally invasive treatment of Kummell’s disease: a finite element study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023; 24(1):967.
[35] AHN Y, YOUN MS, HEO DH. Endoscopic transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a comprehensive review. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2019;16(5):373-380.
[36] SUN H, ZHU Y, HE QF, et al. Reinforcement strategy for lateral rafting plate fixation in posterolateral column fractures of the tibial plateau: The magic screw technique. Injury. 2017;48(12):2814-2826.
[37] REN P, CHENG X, LU C, et al. Finite Element Analysis of a Novel Anterior Locking Plate for Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture. Biomed Res Int. 2021; 2021:2949419.
[38] LANGRANA NA, HARTEN RR, LIN DC, et al. Acute thoracolumbar burst fractures: a new view of loading mechanisms. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(5):498-508.
[39] ZENG ZL, ZHU R, LI SZ, et al. Formative mechanism of intracanal fracture fragments in thoracolumbar burst fractures: a finite element study. Chin Med J (Engl). 2013;126(15):2852-2858.
[40] LEE KH, YUE WM, YEO W, et al. Clinical and radiological outcomes of open versus minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(11):2265-2270.
[41] HUANG C, ZHANG C, SU F, et al. Finite element analysis of minimally invasive nail placement and traditional nail placement in the treatment of lumbar 1 vertebral compression fracture. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023;102(26):e34145.
[42] ALTAY M, OZKURT B, AKTEKIN CN, et al. Treatment of unstable thoracolumbar junction burst fractures with short- or long-segment posterior fixation in magerl type a fractures. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(8): 1145-1155.
[43] LIMTHONGKUL W, WANNARATSIRI N, SUKJAMSRI C, et al. Biomechanical Comparison Between Posterior Long-Segment Fixation, Short-Segment Fixation, and Short-Segment Fixation With Intermediate Screws for the Treatment of Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture: A Finite Element Analysis. Int J Spine Surg. 2023;17(3):442-448.
[44] MITTAL S, IFTHEKAR S, AHUJA K, et al. Outcomes of Thoracolumbar Fracture-Dislocation Managed by Short-Segment and Long-Segment Posterior Fixation: A Single-Center Retrospective Study. Int J Spine Surg. 2021;15(1):55-61.
[45] SONG Y, PANG X, ZHU F. Finite element analysis of the indirect reduction of posterior pedicle screw fixation for a thoracolumbar burst fracture. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(41):e30965.
[46] WANG H, ZHANG Y, XIANG Q, et al. Epidemiology of traumatic spinal fractures: experience from medical university-affiliated hospitals in Chongqing, China, 2001-2010. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012;17(5):459-468.
[47] YE C, LUO Z, YU X, et al. Comparing the efficacy of short-segment pedicle screw instrumentation with and without intermediate screws for treating unstable thoracolumbar fractures. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(34):e7893.
[48] LIU H, WANG H, LIU J, et al. Biomechanical comparison of posterior intermediate screw fixation techniques with hybrid monoaxial and polyaxial pedicle screws in the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fracture: a finite element study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):122.
[49] PRAY C, FEROZ NI, NIGIL HAROON N. Bone Mineral Density and Fracture Risk in Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Meta-Analysis. Calcif Tissue Int. 2017;101(2):182-192.
[50] WESTERVELD LA, VERLAAN JJ, ONER FC. Spinal fractures in patients with ankylosing spinal disorders: a systematic review of the literature on treatment, neurological status and complications. Eur Spine J. 2009;18(2):145-156.
[51] ZHANG T, WANG Y, ZHANG P, et al. Different fixation pattern for thoracolumbar fracture of ankylosing spondylitis: A finite element analysis. PLoS One. 2021;16(4):e0250009.
[52] FOURNEY DR, FRANGOU EM, RYKEN TC, et al. Spinal instability neoplastic score: an analysis of reliability and validity from the spine oncology study group. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(22):3072-3077.
[53] COSTA MC, ELTES P, LAZARY A, et al. Biomechanical assessment of vertebrae with lytic metastases with subject-specific finite element models. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2019;98:268-290.
[54] RICHTERMAN A, RICHARD-GREENBLATT M, WHITAKER K. Back Pain, Fever, and Cough in a 46-Year-Old Man. JAMA. 2021;326(20): 2070-2071.
[55] 李翔, 司建炜. 脊柱结核病灶清除术中单节段短椎弓根钉固定的三维有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2019,23(28):4552-4557. |