中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (10): 2178-2188.doi: 10.12307/2025.402
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
水凝胶:口腔颌面部组织缺损修复中的作用与问题
伍志鑫1,蒋雯雯2,詹健辉1,李杨书润1,任文燕1,王一宇1
- 1济宁医学院口腔医学院,山东省济宁市 272067;2济宁医学院临床医学院,山东省济宁市 272067
-
收稿日期:2024-02-29接受日期:2024-04-02出版日期:2025-04-08发布日期:2024-08-26 -
通讯作者:王一宇,副教授,济宁医学院口腔医学院,山东省济宁市 272067 -
作者简介:伍志鑫,男,2001年生,江西省景德镇市人,汉族,主要从事口腔医学研究。 -
基金资助:2023年度济宁医学院校级本科教学改革研究项目(yb202305),项目负责人,王一宇;济宁医学院大学生创新训练计划项目(cx2021131),项目负责人,任文燕
Hydrogels: role and problems in the repair of oral and maxillofacial defects
Wu Zhixin1, Jiang Wenwen2, Zhan Jianhui1, Li Yangshurun1, Ren Wenyan1, Wang Yiyu1
- 1School of Stomatology, Jining Medical University, Jining 272067, Shandong Province, China; 2School of Clinical Medicine, Jining Medical University, Jining 272067, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2024-02-29Accepted:2024-04-02Online:2025-04-08Published:2024-08-26 -
Contact:Wang Yiyu, Associate professor, School of Stomatology, Jining Medical University, Jining 272067, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Wu Zhixin, School of Stomatology, Jining Medical University, Jining 272067, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:2023 Annual School-level Undergraduate Teaching Reform Research Project of Jining Medical University, No. yb202305 (to WYY); College Students Innovation Training Program Project of Jining Medical University, No. cx2021131 (to RWY)
摘要:
文题释义:
口腔颌面部组织缺损:是一类由外伤、先天畸形、肿瘤切除等因素引起颌面部皮肤黏膜、牙齿、颌骨及牙周组织等组织或器官缺陷并导致功能障碍的常见疾病,对患者身心健康及生活质量产生严重影响。
水凝胶:是一种以水为分散介质的、极具亲水性的三维网状凝胶。由于交联网络结构的存在,使水凝胶具有较强的溶胀性和持水性,且不溶于水,能够模拟细胞外基质。此外,优异的生物相容性、机械可控性及刺激响应性使水凝胶在生物医学领域占据独特优势。
背景:水凝胶因优越的机械及生物性能在生物医学领域占据独特优势,已成为研究热点。目前水凝胶相关研究涉及组织工程和创口敷料等方面。
目的:综述水凝胶的优势性能与在口腔颌面部缺损修复领域中的应用研究进展,探讨水凝胶目前在应用推广中的局限以及在此领域所面临的挑战,为未来研究方向提供新思路。
方法:利用计算机检索PubMed、中国知网、万方数据库发表的相关文献,检索词为“水凝胶,口腔颌面部缺损,机械性能,组织工程,创口敷料”“hydrogel,oral and maxillofacial defects,mechanical properties,guided tissue regeneration,wound dressing”。通过阅读文题和摘要进行初步筛选,排除与文章主题不相关的文献,根据纳入标准和排除标准,最终纳入108篇文献进行结果分析。
结果与结论:①水凝胶具有良好的生物学活性、机械可控性及刺激响应等优势性能。②聚合物、金属和陶瓷联合制备的水凝胶复合物具有适当的机械性能、生物降解性以及可控的释放速率,契合颌面骨组织工程的需求。③纤维蛋白基水凝胶可填充穿过神经缺损区域的中空神经导管并促进轴突再生和生长从而恢复颌面神经功能。④控制纳米材料和水凝胶的相互作用可以改善肌纤维定向结构的形成以促进颌面肌组织再生。⑤多糖水凝胶,因具有控制药物递送和携带生物活性分子等作用,并且与其他材料联合应用可以产生与细胞外基质相匹配的最佳支架,因此逐渐成为修复不规则牙周缺损的首选。⑥磷酸钙或碳酸钙基水凝胶中填充不规则形状或精细的组织缺损并使牙体硬组织再矿化,自组装水凝胶制备简便且生物活性优良。⑦唾液腺来源的细胞外基质样凝胶有望参与许多唾液腺疾病的治疗。⑧水凝胶可作为伤口敷料结合生物黏合剂、脱细胞生物材料、抗微生物和抗氧化剂或干细胞等而被广泛用于治疗各种伤口。⑨纤维蛋白基水凝胶在口腔颌面部缺损修复中最具潜力,其具有优良的生物相容性、柔韧性和可塑性,可与细胞、细胞外基质蛋白和各种生长因子结合,能够促进间充质干细胞的成骨分化、轴突的再生与生长、血管生成、肌管分化、唾液腺组织再生和牙周组织再生,在口腔颌面部缺损组织的修复中具有广泛前景。然而其治疗效果取决于所携带物质的功能,复杂的制备工艺、安全性和长期疗效以及口腔颌面特殊的解剖结构是阻碍推广的难题,这也为未来的研究提供了方向。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7417-3065(王一宇);https://orcid.org/0009-0002-9426-1545(伍志鑫)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
伍志鑫, 蒋雯雯, 詹健辉, 李杨书润, 任文燕, 王一宇. 水凝胶:口腔颌面部组织缺损修复中的作用与问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(10): 2178-2188.
Wu Zhixin, Jiang Wenwen, Zhan Jianhui, Li Yangshurun, Ren Wenyan, Wang Yiyu. Hydrogels: role and problems in the repair of oral and maxillofacial defects[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 2178-2188.
2.1.1 生物学活性 诸多研究表明,细胞可以感知周围的基质并作出反应,而细胞外基质的理化性质又会持续影响细胞的生物学活性。组织中的细胞外基质大多数是由多糖和蛋白质等丝状物质构成的高度复杂、动态和水凝胶样网络。细胞外基质通过控制细胞生长和表型,为组织发育提供机械支持和生化信号。病变或损伤组织中的细胞外基质普遍缺失,从而因缺乏内源性细胞之间的沟通而阻碍组织修复[7]。通过设计由蛋白与细胞外基质成分组装而成的杂化水凝胶,如纤维增强水凝胶、双网络水凝胶或半互穿水凝胶等[8-10],可显著增强水凝胶的力学性能并模拟细胞外基质微环境[11]。KIM等[12]发现在细胞外基质水凝胶中生长的胃或肠道类器官的发育和功能与在基底膜基质中生长的类器官相当甚至优于基底膜基质。此外,胃肠道细胞外基质水凝胶通过提供模拟胃肠道组织的微环境,实现了类器官的长期传代和移植。LIU等[13]受天然细胞外基质的化学成分、纤维结构和生物功能的启发,开发了用于慢性伤口愈合的抗菌和组织环境响应型糖肽杂化水凝胶,该水凝胶可促进细胞增殖和巨噬细胞向M2表型极化,并对革兰阳性菌和革兰阴性菌均有较强的抗菌作用。SHAIK等[14]研究表明富含纤维蛋白的心脏细胞外基质水凝胶可以诱导人脐静脉内皮细胞形成强大的内皮细胞管,并促进人间充质干细胞球的出芽。
综上,具有良好生物相容性的水凝胶可作为载体支架承载细胞、细胞因子以及生物活性分子从而组装成杂化水凝胶,以调节细胞活性并改变生物学行为。基于水凝胶对细胞的作用机制复杂,在其设计上需要更多的关注,使其可以为细胞的培养提供更精准的微环境。
2.1.2 机械可控性 水凝胶的物理机械性质如硬度、孔隙率、黏弹性、降解性及表面地貌等,可以通过改变机械转导信号来调节动态整合素聚集、黏着斑复合体的积累和激活、细胞骨架重排、环境线索反应蛋白的激活、基因表达等,从而使细胞表现出不同的生物学特性和行为[15]。
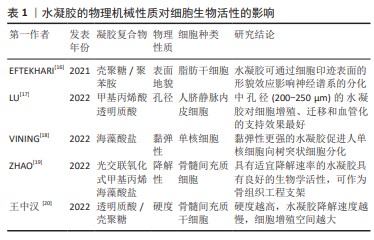
有研究构建了一系列具有硬度差异的水凝胶材料[16],对其诱导干细胞成骨分化和骨整合的合适硬度进行了筛选。结果证实硬度差异对细胞微环境中骨髓间充质干细胞的基因表达存在显著差异,细胞增殖效率和成骨分化趋势随微环境硬度呈依赖性增高。LU等[17]为研究水凝胶孔径对血管化的影响,采用明胶微球模板法制备不同孔径的甲基丙烯酸透明质酸水凝胶。GMS模板浸出后在水凝胶中形成均匀且高度互联的大孔,为诱导人脐静脉内皮细胞迁移和组织血管化提供了理想的物理微环境。体外实验表明,中大孔水凝胶(孔径200-250 μm,300-350 μm)促进了人脐静脉内皮细胞的增殖和迁移;体内实验表明,HAMA250水凝胶具有最佳的血管化行为,该孔径水凝胶中新生血管数量最多且 CD31表达最多,因此,内皮细胞迁移和组织血管化的最佳孔径为200-250 μm。VINING
等[18]研究水凝胶基质相对黏性或弹性性质对单核细胞行为的影响,发现弹性强的细胞外基质可引导单核细胞分化为树突状细胞,弹性软凝胶中细胞分化程度低于弹性硬凝胶。相比之下,在更黏的凝胶中,无论硬度如何,细胞仍然是未成熟的单核细胞,提示刚度和弹性均可刺激单核细胞分化。ZHAO等[19]研究发现,具有适宜降解速率的光交联、氧化和甲基丙烯酸海藻酸盐水凝胶具有良好的生物/组织相容性,其包覆的大鼠/兔间充质干细胞具有成骨分化的潜质,将兔间充质干细胞负载水凝胶植入胫骨缺骨区可发现新骨生成,可作为骨组织工程支架。EFTEKHARI等[16]利用细胞印迹技术证实壳聚糖和壳聚糖-聚苯胺衬底都能诱导大鼠脂肪干细胞从不规则的形状(在平坦的衬底上)转变为细长的和双极的神经元样大鼠肾上腺嗜铬细胞瘤细胞的形态;免疫染色分析显示,与平坦底物相比,壳聚糖和壳聚糖-聚苯胺均显著上调,大鼠脂肪干细胞中胶质纤维酸性蛋白和微管相关蛋白2 这两种神经前体细胞特异性基因的表达。表明细胞印迹表面的形貌效应在大鼠脂肪干细胞的神经启动中具有重要作用,见表1。综上,通过调整水凝胶的硬度、孔隙率、黏弹性、降解性、表面形貌等性能来影响细胞的分化、增殖和迁移,从而为口腔颌面部缺损修复的临床应用提供广阔前景。
2.1.3 刺激响应 水凝胶最突出的特性之一是能够响应外界刺激,包括温度、pH值、光、酶和电场等[21]。刺激响应型水凝胶因其优良性能,在生物医学领域具有广阔的应用前景。温度响应型水凝胶可随温度变化发生可逆的溶胶-凝胶转变,当处于溶胶状态时,可将药物或细胞混合到聚合物水溶液中,将溶液注入目标部位后,加热促使原位形成水凝胶库作为药物缓释系统,可减少给药次数并提高患者的舒适度和依从性[22-25]。pH值/电响应型水凝胶通常对氢离子或电荷产生响应,在pH值和电场的变化下,水凝胶会发生结构、膨胀状态和孔隙率的变化,进一步影响细胞活性[26]。光响应型水凝胶通过调节光线的照射,可以在凝胶中高精度地在时间和空间上创建刚度模式,且光解过程不会产生可溶的副产物。因此,与药物结合的光响应性水凝胶可达到缓释而避免过量或过少以影响治疗效果[27]。
近年来,为了满足不同条件下的多种需求,将无毒和生物相容性好的天然高分子材料如壳聚糖和透明质酸等,与其他高分子材料如明胶、纳米粒子结合,并负载典型药物、生物活性分子或纳米材料,随后,利用3D打印、静电纺丝和干细胞治疗等先进技术开发具有良好抗菌性、自愈性、可注射性和多刺激响应性的新型多功能水凝胶成为当前研究的热点[28]。
2.2 水凝胶在口腔颌面部缺损中的应用 近年来,随着水凝胶在生物医学领域的蓬勃发展,其应用于口腔颌面部缺损的修复日益增多。目前,生物水凝胶在口腔颌面部中的研究主要集中于组织工程与创口敷料两方面。
2.2.1 组织工程
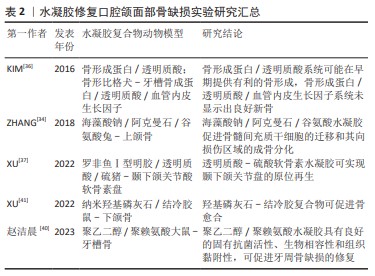
骨及软骨再生:口腔颌面部因肿瘤或创伤切除后往往会导致较大的颅颌骨缺损,从而引起细胞死亡及代谢功 能障碍,并阻碍骨组织的自我修复[29]。软骨组织在损伤后可以自我修复,但其自愈能力受限于损伤范围,较大的病变不能得到有效修复[30]。骨组织工程的目标系开发能够在不使用自体或异体移植的情况下修复骨缺损的骨移植替代物。这一目标目前面临2个主要挑战:第一,载体支架需要有适当的机械性能和生物可降解性;第二,它们应具有可控的释放速率。在所有类型的支架中,成分类似细胞外基质的水凝胶系统完美契合骨组织工程的需求[31]。水凝胶搭载生物材料已被广泛研究并用于骨组织构建,如与聚合物、金属和陶瓷联合制备的水凝胶复合物已被用于制造仿生骨支架。
海藻酸钠与硅酸盐生物材料(生物玻璃、硅酸盐生物陶瓷等)结合所制备的水凝胶可通过上调 CXCR4和ERK信号通路促进骨形成。海藻酸钠是一种具有生物相容性但缺乏成骨与血管生成能力的线性多糖,而硅酸盐生物材料已证实具有促进成骨分化和血管生成的作用[32-33]。ZHANG等[34]将海藻酸钠与硅酸盐生物材料结合制备出三元水凝胶体系——海藻酸钠/阿克曼石/谷氨酸复合材料以研究在体外和体内的成骨效果,结果表明,该水凝胶复合物可分别促进人骨髓间充质干细胞的迁移和其向损伤区域的成骨分化,从而促进骨形成,兔上颌窦底提升实验进一步验证了这一观点。
透明质酸作为一种基质成分,可与CD44,RHAMM或CD168等透明黏附蛋白的特殊蛋白结合,激活细胞参与增殖、分化、运动以及羟基磷灰石自身降解的信号系统[35]。基于透明质酸的支架和载体被塑造成刚性形式或胶体,透明质酸与其他材料结合后,可改变支架形态,提高矿化能力,使其更适合于骨再生。KIM等[36]使用透明质酸水凝胶搭载骨形态发生蛋白2和血管内皮生长因子,结果表明,这种只掺入骨形态发生蛋白2的支架递送系统可能在早期提供有利的骨形成,但同时搭载骨形态发生蛋白2和血管内皮生长因子却未显示出良好的新骨形成效果,这可能是高剂量的血管内皮生长因子会造成血管渗漏、抑制新骨形成,或可能是二者的联合使用虽可促进血管生成,但抑制成骨细胞的终末分化所致。XU等[37]构建了一种以天然聚合物为主要成分的仿生罗非鱼Ⅰ型/透明质酸-硫酸软骨素双网络水凝胶,不仅具有理想的抗压强度(11 MPa,高于张口时颞下颌关节盘的应力)和临床适应性(术中可塑形,手术时间3-5 min),而且具有明显逆转局部炎症微环境的能力,同时可促进颞下颌关节盘快速再生。
聚乙二醇/聚赖氨酸复合水凝胶可延长其在牙周袋内的存留时间,并形成永久非浸出性杀菌层起到长效杀灭牙周致病菌的作用,从而有利于牙槽骨缺损的修复。聚赖氨酸是一种具有内在抗菌活性的天然多肽,被广泛应用于药物递送和伤口愈合。由于聚赖氨酸富含的氨基带正电荷,容易通过诱导表面zeta电位与带负电荷的细菌细胞壁相互作用,最终抑制细菌生长[38]。聚乙二醇是一种重要的亲水聚合物,具有无毒、无免疫原性、良好的生物相容性和抗蛋白吸附等优点[39]。赵洁晨等[40]通过聚乙二醇-聚赖氨酸构建一种复合水凝胶,一方面,四臂聚乙二醇琥珀酰亚胺戊二酸酯末端活性酯能与牙周组织中的氨基反应,产生强黏附力使水凝胶固定于牙周袋内并延长存留时间;另一方面,聚赖氨酸中游离的赖氨酸残基中的氨基在水凝胶表面产生高密度阳离子表面,形成永久非浸出性杀菌层从而长效杀灭牙周致病菌,这可维持一个有益于牙周组织恢复的环境,从而有利于牙周骨缺损的修复。
结冷胶是一种线性多糖类水凝胶,因具有良好的稳定性及生物性能,现已广泛应用于组织工程领域。纳米羟基磷灰石具有良好的成骨性能,有学者以结冷胶为载体,负载纳米羟基磷灰石,制备了结冷胶/纳米羟基磷灰石水凝胶[41],并观察其修复大鼠下颌骨缺损的效果,结果显示该杂化水凝胶可注射入下颌骨缺损区域,术后4周缺损区可见大量新生骨及骨胶原组织,8周后骨缺损区形成支架样结构,新生骨组织及胶原、纤维组织生成较多,其有望作为一种新型生物材料用于口腔颌面部骨缺损的微创修复。
尽管各类水凝胶复合物在上述研究中显示出了一定的骨引导/骨诱导性,见表2,然而,骨与软骨组织再生仍面临挑战。例如,在宏观与微观上与原生微环境相似的水凝胶材料的构建、搭载生长因子或生物活性物质的生物支架的设计及不同类型细胞的准确放置,都是亟需解决的问题。通过结合不同的生物材料或利用材料功能化等制造技术制备水凝胶支架,可为再造复杂的天然骨和软骨结构提供新的可能性。
神经修复:口腔颌面部神经主要包括三叉神经与面神经。三叉神经损伤在口腔颌面部神经组织损伤中最为常见,患者可出现显著的功能缺损及生活质量下降[42]。面神经由于位置表浅且与腮腺紧密相连,很容易发生损伤。病变区域及其残端可发生华勒变性,包括轴突变性、脱髓鞘及吞噬作用。华勒变性过程中髓鞘的破坏会产生大量髓鞘碎片,严重阻碍神经再生和功能恢复[43]。轴突可以再生,但快速生长的结缔组织会阻碍再生过程,并可形成神经瘤。目前,通过利用生物材料构建了一种具有可注射性、生物降解性、生物相容性和神经再生能力的杂化水凝胶可实现神经修复。
纤维蛋白原是一种长度为45 nm的二聚体糖蛋白,由三对不同的链Aα,Bβ和γ链组成。在纤维蛋白原和凝血酶按所需比例混合后,在凝血酶的作用下裂解中央结构域区域的FPA和FPB,以暴露α链N端上的基序Gly-Pro-Arg和β链N端上的基序Gly-His-Arg-Pro。旋钮A与γ链C端的孔“a”互补,旋钮B与β链C端的孔“b”互补。通过这种方式,一个纤维蛋白原分子的中心区域可以结合其他相邻的纤维蛋白原分子末端结构域[44]。已有研究证实纤维蛋白基质可用于填充穿过神经缺损区域的中空神经导管,以促进轴突再生和生长[45]。MU等[46]将有利于轴突再生的纤维蛋白制备成类似于神经细胞外基质的纤维蛋白纳米水凝胶,并以其作为壳聚糖管底物用以修复兔颊支面神经缺损。结果表明,该水凝胶复合物具有良好的相容性,支持施万细胞的黏附和增殖;进一步的形态学、组织学和功能分析表明,纤维蛋白纳米纤维水凝胶预充的壳聚糖管可显著促进轴突再生、髓鞘再生和功能恢复,在面神经再生治疗中具有巨大的临床应用潜力。HU等[47]将一种温敏原位形成泊洛沙姆水凝胶作为载体递送碱性成纤维细胞生长因子治疗大鼠模型的面神经损伤,发现其可通过激活施万细胞中的PAK1信号通路促进自噬和抑制凋亡促进面神经修复,为未来临床研究提供了一种有前景的策略。以上研究表明,水凝胶可通过搭载神经细胞外基质样物质促进轴突再生和生长,从而实现神经组织再生。但目前相关报道仍较少,且长期有效性需进一步验证。有学者认为其关键难点在于:①再生神经是否能支配相关肌肉的咀嚼、面部表情和发音的频繁运动;②再生神经被颌骨、血管和唾液腺等重要解剖结构包围;③颅面区感觉恢复情况[48]。
血管再生:血管是由机械敏感的内皮细胞组成的管腔静息层,作为半通透的屏障介导血液和底层组织之间的小分子和蛋白质的交换。失去血管支持可导致组织微环境内缺乏足够的营养和氧交换,从而限制组织的生存、增殖和分化[49]。许多有前景的血管化策略需要复杂的细胞来源,或可导致生物因子从分泌部位迅速扩散并产生异位不良反应[50-51]。而水凝胶支架材料因具有可注射性、生物降解性且可控制药物缓释等性能,并可促进原位新生血管形成和基质沉积,已广泛应用于血管再生领域。
血管内皮生长因子在血管生成中起核心作用,参与新生血管形成过程的各个阶段,如细胞外基质的降解、内皮细胞的迁移和增殖、管腔形成、血管分支和修剪[52]。硅酸盐/海藻酸盐支架水凝胶可释放钙离子和硅酸离子,能有效刺激内皮细胞中血管内皮生长因子的mRNA表达。血管内皮生长因子信号由Notch信号通路调控,在动静脉分化、胚胎/出生后血管生成和动脉生成以及肿瘤血管生成中发挥重要作用[53]。LI等[54]利用创新的多面体寡聚硅氧烷纳米平台,通过点击化学高效地合成了有机-无机杂化纳米粒子,并通过气体微流控和离子交联技术成功地开发了一种封装有机-无机杂化纳米粒子的纳米水凝胶微球系统,可通过激活血管内皮生长因子信号通路,促进血红素加氧酶1表达,促进H型血管形成。GENG等[55]制备出一种由羧甲基壳聚糖和原儿茶醛组成的自修复水凝胶,并负载了超小的铜纳米颗粒,结果表明,该水凝胶具有抗菌性能,并依赖于铜纳米颗粒介导的铜转运蛋白质α链抗体激活,通过阻止血管内皮生长因子受体的自噬降解来刺激血管生成。
缺氧诱导因子1α是一种广泛表达的异二聚体转录因子,介导后生动物所有有核细胞对缺氧/缺血的适应性反应。细胞与缺氧或缺血环境的接触主要通过缺氧诱导因子1α介导的血管内皮生长因子诱导血管生成反应[56-57]。因此,通过稳定缺氧诱导因子1α可有利于血管生成。此外,外泌体或细胞外囊泡已成为携带药物到病变细胞的潜在治疗载体。在此基础上,WANG等[58]将缺氧诱导因子1α相互作用抑制剂负载于表皮干细胞来源的细胞外囊泡,制备具有良好生物相容性和良好机械性能的甲基丙烯酰明胶水凝胶,通过激活缺氧诱导因子1α信号通路对体外培养的人脐静脉内皮细胞功能发挥促进作用,且对伤口愈合和体内血管生成有治疗作用。YANG等[59]将人脂肪来源的干细胞/外泌体与聚氧丙烯聚氧乙烯共聚物水凝胶结合用于自体脂肪移植,人脂肪来源的干细胞/外泌体可以通过激活缺氧诱导因子1α/血管内皮生长因子信号通路来创造一个促进新生血管形成的再生微环境。
以水凝胶支架为基础的血管化策略已广泛应用于生物医学领域,但目前在口腔颌面部血管缺损修复的研究仍较少,仅局限于牙髓血管组织的再生。这可能是因为颌面部血管大多较表浅且生理活动频繁,受到空间稳定性的限制。此外,以水凝胶制备的创口敷料主要通过抑制细菌繁殖从而创造出利于血管组织修复的环境,但口腔颌面部的特点之一是血运丰富,抗感染能力强。这些可能是限制水凝胶在口腔颌面部血管缺损修复方面的原因。
肌肉组织再生:水凝胶应用于肌肉组织再生主要面临的挑战在于可注射支架在体内控制再生肌纤维的对齐,特别是在三维构型中。目前研究已证实控制纳米材料和水凝胶的相互作用可以改善定向结构的形成[60]。
排列整齐的纳米纤维是三维纤维结构的基本骨架,类似于肌肉组织中的肌动蛋白肌球蛋白结构支架。由纳米纤维组成的多孔表面,这可能有助于向骨骼细胞输送营养物质和氧气。多核成肌细胞沿着纳米纤维支架在间隙中排列,形成一个与生理骨骼肌纤维形态相似的多纤维束,有利于肌肉再生[61]。WANG等[62]制备了可注射的磁控短纳米纤维/凝胶纳米纤维/水凝胶支架,证实其具有精确指导三维细胞排列和组织的能力。支架不仅能够诱导肌管形成,也可高度模拟不同解剖结构的各种骨骼肌组织和其他复杂的结构;该支架中磁控短纳米纤维的排列方向产生了组织良好的肌纤维(眼轮匝肌),对收缩力的改善和功能恢复具有良好的促进作用。KINOSHITA等[63]制备了基于丙烯酰基修饰的交联纳米可降解水凝胶支架,并通过细胞移植来修复舌肌,该水凝胶具有良好的孔隙率,小鼠成肌细胞与其黏附,可表现出正常的肌管分化;将其负载成肌细胞植入小鼠的舌缺损区,新生肌纤维显著增加。该生物材料在促进蛋白质和细胞介导的治疗和促进舌肌再生方面显示出巨大的潜力。
目前,在诸多颌面部肌肉再生领域中有关水凝胶的应用研究较少,但是其有着良好的应用前景。例如,在唇裂患者中,口轮匝肌存在缺陷,这种缺失的肌肉间隙即使在初次唇裂修复后仍持续存在。临床研究表明,唇部修复术后的远期效果较差,这可能是由于肌肉体积不足和瘢痕形成过多造成的。由于骨骼肌再生是肌肉生成和纤维生成的协调平衡[64],因此,有必要制定更有效的组织再生策略来提高治疗效果。而基于水凝胶的优异性能,在未来有望实现口轮匝肌及咀嚼肌等颌面部肌肉的再生。
牙周组织再生:近年来,多种新型水凝胶如纤维增强水凝胶、热敏壳聚糖水凝胶、高刚度转谷氨酰胺酶交联水凝胶等,均被证实具有促进牙周组织再生的作用[65]。尤其是注射的多糖水凝胶,因具有控制药物递送、携带生物活性分子等作用,并且与其他材料联合应用可以产生与细胞外基质相匹配的最佳支架,因此逐渐成为修复不规则牙周缺损的首选[66-67]。研究表明,水凝胶可作为屏障膜,使具有成骨潜能的细胞优先进入骨缺损区域,从而有足够的时间增殖并最终实现骨再生[68]。为设计出具有最佳机械强度、降解速率和独特治疗特性的水凝胶膜,目前可通过3种方法对其改性:①加入微米和/或纳米大小的无机粒子;②增加水凝胶聚合物的浓度或交联密度;③加入纳米或微纤维来增强其生物力学性能[69]。例如,有研究将制备壳聚糖/聚γ-谷氨酸/纳米羟基磷灰石水凝胶填充骨缺损区[70],并从血液中提取的富血小板纤维蛋白作为复合支架中间层,将静电纺丝法制备的聚己内酯/明胶纳米纤维作为最外层附着于软硬组织接头处,结果发现,该三层复合支架具有良好的形态、生物相容性、细胞屏障及体外成骨分化能力。
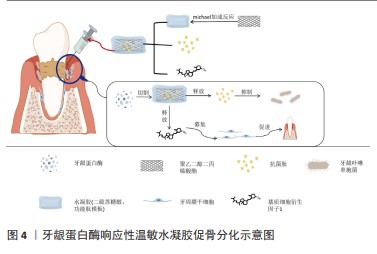
水凝胶一方面可作为支架材料引导组织再生,另一方面还可以通过控制药物递送进行载药抗菌。牙周炎是一种以微生物感染和牙槽骨吸收为特征的慢性感染性疾病,重建受损牙周组织的形态和功能是牙周再生治疗的理想目标[67]。牙龈卟啉单胞菌是牙周炎最重要的致病菌,其所分泌的牙龈蛋白酶会增加牙龈组织出血、水解宿主蛋白、激活炎症进展并导致牙周炎部位牙槽骨吸收[70]。LIU等[72]通过michael加成反应促进水凝胶支架与新型设计的功能肽模块交联,该功能肽模块具有锚定肽-短抗菌肽-锚定肽结构,并可被牙龈蛋白酶特异性切割。在牙龈蛋白酶的作用下,短抗菌肽从水凝胶载体中释放,从而强烈抑制牙龈卟啉单胞菌的生长;此外,该水凝胶可以进一步装载基质细胞衍生因子1,促进牙周膜干细胞的募集,并诱导成骨。因此,该水凝胶是治疗牙周炎的按需局部给药系统的一个很有前途的候选药物,见图4。水凝胶在牙槽骨再生领域中的研究已经取得了显著进展,但有关牙周膜-牙骨质结合的研究较少,牙周膜的修复仍是牙周组织工程研究的挑战。此外,目前关于水凝胶在牙周治疗的长期随访报道较少,需要进一步验证治疗方案的有效性。
核酸、碳水化合物和多肽等各种类型的自组装水凝胶因具有良好的生物相容性、可逆拆卸、机械耐用性、功能行为可定制、易于折叠形成二维/三维仿生矩阵等有价值的特性而受到极大关注。有学者将牙上皮干细胞系HAT-7细胞包裹并注射到自交联氧化海藻酸-羧甲基壳聚糖水凝胶中培养[77]。已有研究证实,HAT-7细胞具有pH调节和细胞内Ca2+信号传导的功能[78],结果显示,HAT-7细胞在体外保持了较高的活力,验证了水凝胶作为细胞递送载体和注射细胞治疗的适宜性;此外,HAT-7细胞能够保持形态并沉积矿物质,表明自交联水凝胶能够支持其存活及分化。
自组装水凝胶只需分子自组装过程即可制备,其与细胞质基质环境相似,是再生医学中良好的支架材料[79]。但关于自组装多肽水凝胶促进组织再生的具体机制研究较少,且存在许多问题:如具有三维结构的水凝胶机械化不稳定等,如何建立针对这种新型生物材料的全面监测体系也需要探索[80]。
唾液腺再生:口腔肿瘤切除术、头颈部放射治疗、药物治疗和一些自身免疫性疾病是导致唾液腺功能减退的常见原因[81]。唾液分泌的严重减少会导致口干,进一步发展会导致龋齿、口腔感染、吞咽障碍和味觉丧失等,甚至导致精神焦虑/抑郁[82],严重影响患者的生活质量。目前临床治疗口干症的方法包括刺激唾液分泌的药物和人工唾液替代物,但这些方法并不能提供长期的治疗效
果[83]。因此,一种既能改善患者口干症状,又能恢复唾液分泌功能的唾液腺组织重建再生疗法是非常必要的。
新鲜分离的唾液腺细胞可在层黏连蛋白1肽上生长并与纤维蛋白水凝胶化学连接。纤维蛋白水凝胶具有生物相容性和生物可降解性,并且能够支持细胞附着、活性和分化[84]。在体内伤口愈合小鼠模型中,层粘连蛋白1肽-纤维蛋白水凝胶可促进唾液腺再生,从而导致唾液分泌增加。有研究表明,纤维蛋白水凝胶支架可用于促进放射性唾液分泌功能低下患者的唾液腺功能[85]。水凝胶还为内源性唾液腺再生提供了促进再生的微环境,可作为一种强大的生物活性材料用于未来唾液腺疾病的治疗。WANG等[86]通过完全脱细胞、消化和凝胶化,成功制备了猪唾液腺来源的细胞外基质样水凝胶,该水凝胶既具有细胞外基质样的纳米纤维结构,又保留了来自天然唾液腺组织的功能性细胞外基质成分。研究表明,此水凝胶不仅支持细胞的活力和增殖,而且通过激活PI3K/AKT信号通路显著促进了3D培养的颌下腺间充质干细胞的迁移和募集;此外,该水凝胶还可以支持内源性唾液腺细胞的募集,从而形成功能性腺泡/导管样结构,而且还可以抑制唾液腺组织损伤部位的纤维生成从而抑制了瘢痕形成,在促进唾液腺再生方面显示出独特的优势。因此,猪唾液腺来源的细胞外基质样凝胶也有望参与许多其他唾液腺疾病的治疗。
2.2.2 创口敷料 理想的伤口敷料应具备以下标准:吸收渗出物的能力、允许气体交换、保持湿润的环境、屏蔽细菌、隔热及对宿主无害[87]。水凝胶因其良好的亲水性、生物相容性以及与细胞外基质相似的三维多孔结构,通过促进再上皮化达到更好的愈合效果。但传统水凝胶敷料因缺乏抗菌性、并且黏附性低、创面愈合延迟等缺点限制了其在创面治疗中的应用[88]。随着临床上对伤口修复要求的不断提高和基础研究的不断深入,人们对材料性能提出了越来越多的要求,增强单一/多重生物学功能的敷料开始出现,已成为最具竞争力的伤口敷料候选者。水凝胶可作为伤口敷料结合生物黏合剂、脱细胞生物材料、抗微生物和抗氧化剂(如银、抗生素药物和姜黄素)或干细胞等而被广泛用于治疗各种伤口。
聚合物水凝胶敷料因具有稳固黏着能力达到封闭创面的效果,并通过减少渗出、抑制创面组织炎症因子的分泌并诱导纤维细胞增殖,从而促进创面愈合。聚多巴胺是一种具有良好生物相容性的类黑色素聚合物,反应条件温和,易于制备。此外,它还具有高的近红外吸收、抗氧化、抗菌和黏接性能,聚多巴胺内在的抗氧化特性是通过清除炎症期后的活性氧来加速伤口愈合过程[89]。纳米银具有抗菌谱宽、耐药低等优点[90],银纳米颗粒沉积在还原氧化石墨烯上,得到的银/还原氧化石墨烯纳米复合材料比单独使用银显示出更好的抗菌活性[91]。在此基础上,HUANG等[92]采用N-异丙基丙烯酰胺和N,N’ 亚甲基双丙烯酰胺的化学交联制备出一种由聚多巴胺、银和氧化石墨烯组成的新型水凝胶,此类水凝胶具有有效的抗菌性能,对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌具有较高的抑制率;此外,对各种基底材料具有良好的黏附能力,应用于自固定创面比缝合创面更简便;更重要的是,它在近红外光照射下可产生强大的收缩力,发挥向心力,有助于加速创面愈合。实验表明,含有高浓度聚多巴胺的水凝胶经近红外照射后15 d内可完全修复创面缺损(1.0 cm×1.0 cm),创面愈合率可达100%。不过,有学者表示,这些含银等重金属离子很难被清除,从而在组织中积累[93]。
可注射水凝胶敷料联合干细胞被认为是修复深度严重烧伤创面的一种有前景的方法。干细胞的旁分泌机制在促进血管生成、胶原沉积、组织重塑和减少瘢痕形成等方面发挥着重要作用。然而,干细胞直接注射到创面区域,由于其滞留和存活的能力较低,严重限制了干细胞的功能。此外,复杂的创面微环境严重影响干细胞的行为,从而影响修复效果[97]。例如,WU等[98]设计并制备了一种由壳聚糖水凝胶和脂肪质干细胞来源的外泌体组成的复合创面敷料,以促进皮肤全层创面修复。随着壳聚糖水凝胶的降解,外泌体逐渐从敷料中释放出来。壳聚糖/外泌体在体外显示了增强的细胞迁移和血管生成特性;在大鼠皮肤创面模型中,壳聚糖/外泌体能促进正常的胶原沉积、血管生成和毛囊镶嵌再生。这些结果证明,含有脂肪质干细胞来源的外泌体的水凝胶敷料可以加速皮肤伤口愈合。
水凝胶可与导电材料结合作为敷料应用于伤口愈合等方面。导电生物材料具有与人体皮肤相似的导电性、良好的抗氧化和抗菌活性、电控药物传递和光热效应,在伤口愈合和皮肤组织工程中显示出巨大的潜力[99]。ZHAO等[100]以季铵化壳聚糖聚苯胺和苯甲醛基功能化聚乙二醇共聚癸二酸甘油为基础,研制了一系列可注射的导电自愈水凝胶,作为皮肤创伤愈合的抗菌、抗氧化和电活性敷料。这些水凝胶具有良好的自愈性、电活性、自由基清除能力、抗菌活性、黏附性、电导率、溶胀率和生物相容性。交联剂最佳浓度为1.5%的水凝胶表现出良好的体内血凝能力,并通过上调生长因子(包括血管内皮生长因子、表皮生长因子和转化生长因子β)的基因表达,进而促进肉芽组织厚度和胶原沉积。目前新型水凝胶敷料的发展,不仅满足损伤的基本闭合,而且具有止血、黏附及抗菌作用。不过,在受凝血功能、创口面积和病原体等因素影响下,水凝胶敷料的研究仍有待探索。
| [1] HO TC, CHANG CC, CHAN HP, et al. Hydrogels: properties and applications in biomedicine. Molecules. 2022;27(9):2902. [2] HUYNH V, IFRAIMOV N, WYLIE RG. Modulating the thermoresponse of polymer-protein conjugates with hydrogels for controlled release. Polymers (Basel). 2021;13(16):2772. [3] WANG X, MA Y, LU F, et al. The diversified hydrogels for biomedical applications and their imperative roles in tissue regeneration. Biomater Sci. 2023;11(8):2639-2660. [4] TONSOMBOON K, BUTCHER AL, OYEN ML. Strong and tough nanofibrous hydrogel composites based on biomimetic principles. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;72:220-227. [5] ZOU Z, LI H, XU G, et al. Current knowledge and future perspectives of exosomes as nanocarriers in diagnosis and treatment of diseases. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18:4751-4778. [6] JU Y, HU Y, YANG P, et al. Extracellular vesicle-loaded hydrogels for tissue repair and regeneration. Mater Today Bio. 2022;18:100522. [7] FREEDMAN BR, KUTTLER A, BECKMANN N, et al. Enhanced tendon healing by a tough hydrogel with an adhesive side and high drug-loading capacity. Nat Biomed Eng. 2022;6(10):1167-1179. [8] ZHU C, HUANG C, ZHANG W, et al. Biodegradable-glass-fiber reinforced hydrogel composite with enhanced mechanical performance and cell proliferation for potential cartilage repair. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(15):8717. [9] NONOYAMA T, GONG JP. Tough Double Network Hydrogel and Its Biomedical Applications. Annu Rev Chem Biomol Eng. 2021;12:393-410. [10] RINOLDI C, LANZI M, FIORELLI R, et al. Three-dimensional printable conductive semi-interpenetrating polymer network hydrogel for neural tissue applications. Biomacromolecules. 2021;22(7):3084-3098. [11] FERCANA GR, YERNENI S, BILLAUD M, et al. Perivascular extracellular matrix hydrogels mimic native matrix microarchitecture and promote angiogenesis via basic fibroblast growth factor. Biomaterials. 2017; 123:142-154. [12] KIM S, MIN S, CHOI YS, et al. Tissue extracellular matrix hydrogels as alternatives to Matrigel fo r culturing gastrointestinal organoids. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):1692. [13] LIU W, GAO R, YANG C, et al. ECM-mimetic immunomodulatory hydrogel for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus-infected chronic skin wound healing. Sci Adv. 2022;8(27):eabn7006. [14] SHAIK R, XU J, WANG Y, et al. Fibrin-enriched cardiac extracellular matrix hydrogel promotes in vitro angiogenesis. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023;9(2):877-888. [15] CAO H, DUAN L, ZHANG Y, et al. Current hydrogel advances in physicochemical and biological response-driven biomedical application diversity. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):426. [16] EFTEKHARI BS, ESKANDARI M, JANMEY PA, et al. Conductive chitosan/polyaniline hydrogel with cell-imprinted topography as a potential substrate for neural priming of adipose derived stem cells. RSC Adv. 2021;11(26):15795-15807. [17] LU D, ZENG Z, GENG Z, et al. Macroporous methacrylated hyaluronic acid hydrogel with different pore sizes forin vitroandin vivoevaluation of vascular ization. Biomed Mater. 2022. doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/ac494b. [18] VINING KH, MARNETH AE, ADU-BERCHIE K, et al. Mechanical checkpoint regulates monocyte differentiation in fibrotic niches. Nat Mater. 2022;21(8):939-950. [19] ZHAO D, WANG X, CHENG B, et al. Degradation-kinetics-controllable and tissue-regeneration-matchable photocross-linked alg inate hydrogels for bone repair. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(19):21886-21905. [20] 王中汉.基于多糖水凝胶构建的硬度差异细胞微环境调控骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化及骨整合的实验研究[D].长春:吉林大学, 2022. [21] CHANG S, WANG S, LIU Z, et al. Advances of stimulus-responsive hydrogels for bone defects repair in tissue engineering. Gels. 2022; 8(6):389. [22] MARTWONG E, TRAN Y. Lower critical solution temperature phase transition of poly (PEGMA) hydrogel thin films. Langmuir. 2021;37(28): 8585-8593. [23] SHI J, YU L, DING J. PEG-based thermosensitive and biodegradable hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2021;128:42-59. [24] LAVANYA K, CHANDRAN SV, BALAGANGADHARAN K, et al. Temperature- and pH-responsive chitosan-based injectable hydrogels for bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020; 111:110862. [25] DEEN GR, LOH XJ. Stimuli-responsive cationic hydrogels in drug delivery applications. Gels. 2018;4(1):13. [26] BORDBAR-KHIABANI A, GASIK M. Smart hydrogels for advanced drug delivery systems. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(7):3665. [27] PARK KY, ODDE DJ, DISTEFANO MD. Photoresponsive hydrogels for studying mechanotransduction of cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2600: 133-153. [28] YUAN N, SHAO K, HUANG S, et al. Chitosan, alg inate, hyaluronic acid and other novel multifunctional hydrogel dressings for wound healing: a review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;240:124321. [29] YU H, FENG M, MAO G, et al. Implementation of photosensitive, injectable, interpenetrating, and kartogenin-modified GELMA/PEDGA biomimetic scaffolds to restore cartilage integrity in a full-thickness osteochondral defect model. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2022;8(10): 4474-4485. [30] LI Y, LI L, LI Y, et al. Enhancing cartilage repair with optimized supramolecular hydrogel-based scaffold and pulsed electromagnetic field. Bioact Mater. 2022;22:312-324. [31] NABAVI MH, SALEHI M, EHTERAMI A, et al. A collagen-based hydrogel containing tacrolimus for bone tissue engineering. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2020;10(1):108-121. [32] JAYACHANDRAN V, MURUGAN SS, DALAVI PA, et al. Alg inate-based composite microspheres: preparations and applications for bone tissue engineering. Curr Pharm Des. 2022;28(13):1067-1081. [33] FERREIRA SA, YOUNG G, JONES JR, et al. Bioglass/carbonate apatite/collagen composite scaffold dissolution products promote human osteoblast differentiation. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021; 118:111393. [34] ZHANG X, ZHU Y, CAO L, et al. Alg inate-aker injectable composite hydrogels promoted irregular bone regeneration through stem cell recruitment and osteogenic differentiation. J Mater Chem B. 2018; 6(13):1951-1964. [35] ZHAI P, PENG X, LI B, et al. The application of hyaluronic acid in bone regeneration. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;151:1224-1239. [36] KIM SK, CHO TH, HAN JJ, et al. Comparative study of BMP-2 alone and combined with VEGF carried by hydrogel for maxillary alveolar bone regeneration. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016;13(2):171-181. [37] XU X, SUI B, LIU X, et al. A bioinspired and high-strengthed hydrogel for regeneration of perforated temporomandibular joint disc: construction and pleiotropic immunomodulatory effects. Bioact Mater. 2022;25: 701-715. [38] YANG R, XUE W, LIAO H, et al. Injectable poly lysine and dextran hydrogels with robust antibacterial and ROS-scavenging activity for wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;223(Pt A):950-960. [39] SUN S, CUI Y, YUAN B, et al. Drug delivery systems based on polyethylene glycol hydrogels for enha nced bone regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1117647. [40] 赵洁晨,任乐,魏玉,等.一种固有抗菌的黏附性可注射水凝胶用于牙周炎骨缺损治疗的初步研究[J].口腔医学,2023,43(11):989-995. [41] XU LJ, YUAN H, YE Q, et al. Repair of mandibular defects with hydrogel loaded with nano-hydroxyapatite in rats. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2022;31(5):449-453. [42] KALEEM A, AMAILUK P, HATOUM H, et al. The trigeminal nerve injury. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2020;32(4):675-687. [43] GORDON T. Peripheral nerve regeneration and muscle reinnervation. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(22):8652. [44] YU Z, LI H, XIA P, et al. Application of fibrin-based hydrogels for nerve protection and regeneration after spinal cord injury. J Biol Eng. 2020; 14:22. [45] PARK CH, WOO KM. Fibrin-based biomaterial applications in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018; 1064:253-261. [46] MU X, SUN X, YANG S, et al. Chitosan tubes prefilled with aligned fibrin nanofiber hydrogel enhance facial nerve regeneration in rabbits. ACS Omega. 2021;6(40):26293-26301. [47] HU B, ZHANG H, XU M, et al. Delivery of basic fibroblast growth factor through an in situ forming smart hydrogel activates autophagy in schwann cells and improves facial nerves generation via the PAK-1 signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:778680. [48] ZHANG Q, NGUYEN P, BURRELL JC, et al. Harnessing 3D collagen hydrogel-directed conversion of human GMSCs into SCP-like cells to generate functionalized nerve conduits. NPJ Regen Med. 2021;6(1):59. [49] WANG Y, KESHAVARZ M, BARHOUSE P, et al. Strategies for regenerative vascular tissue engineering. Adv Biol (Weinh). 2023;7(5): e2200050. [50] SARKAR B, NGUYEN PK, GAO W, et al. Angiogenic self-assembling peptide scaffolds for functional tis sue regeneration. Biomacromolecules. 2018;19(9):3597-3611. [51] GIANNI-BARRERA R, DI MAGGIO N, MELLY L, et al. Therapeutic vascular ization in regenerative medicine. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2020;9(4): 433-444. [52] DASHNYAM K, BUITRAGO JO, BOLD T, et al. Angiogenesis-promoted bone repair with silicate-shelled hydrogel fiber scaffolds. Biomater Sci. 2019;7(12):5221-5231. [53] CAO L, ARANY PR, WANG YS, et al. Promoting angiogenesis via manipulation of VEGF responsiveness wi th notch signaling. Biomaterials. 2009;30(25):4085-4093. [54] LI J, WEI G, LIU G, et al. Regulating type h vessel formation and bone metabolism via bone-targeting oral micro/nano-hydrogel microspheres to prevent bone loss. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(15):e22073 81. [55] GENG X, LIU K, WANG J, et al. Preparation of ultra-small copper nanoparticles-loaded self-healing hydrogels with antibacterial, inflammation-suppressing and angiogenesis-enhancing properties for promoting diabetic wound healing. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18: 3339-3358. [56] HAN Y, GONG T, ZHANG C, et al. HIF-1α stabilization enhances angio-/vascu logenic properties of SHED. J Dent Res. 2020;99(7):804-812. [57] REY S, SEMENZA GL. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1-dependent mechanisms of vascular ization and vascular remodelling. Cardiovasc Res. 2010;86(2):236-242. [58] WANG Y, CAO Z, WEI Q, et al. VH298-loaded extracellular vesicles released from gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel facilitate diabetic wound healing by HIF-1α-mediated enhancement of angiogenesis. Acta Bi omater. 2022;147:342-355. [59] YANG F, LI Z, CAI Z, et al. Pluronic F-127 hydrogel loaded with human adipose-derived stem cell-d erived exosomes improve fat graft survival via HIF-1α-mediated enhancement of angiogenesis. Int J Nan omedicine. 2023;18:6781-6796. [60] PARDO A, GÓMEZ-FLORIT M, BARBOSA S, et al. Magnetic nanocomposite hydrogels for tissue engineering: design concepts and remote actuation strategies to control cell fate. ACS Nano. 2021; 15(1):175-209. [61] JANG Y, KIM SM, KIM E, et al. Biomimetic cell-actuated artificial muscle with nanofibrous bundles. Microsyst Nanoeng. 2021;7:70. [62] WANG L, LI T, WANG Z, et al. Injectable remote magnetic nanofiber/hydrogel multiscale scaffold for functional anisotropic skeletal muscle regeneration. Biomaterials. 2022;285:121537. [63] KINOSHITA N, SASAKI Y, MARUKAWA E, et al. Crosslinked nanogel-based porous hydrogel as a functional scaffold for tongue muscle regeneration. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2020;31(10):1254-1271. [64] LI JG, CHENG X, HUANG YX, et al. Wnt7a promotes muscle regeneration in branchiomeric orbicularis or is muscle. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2021; 14(6):693-704. [65] WANG W, WANG A, HU G, et al. Potential of an aligned porous hydrogel scaffold combined with periodontal ligament stem cells or gingival mesenchymal stem cells to promote tissue regeneration in rat periodontal defects. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023;9(4):1961-1975. [66] ALKHURSANI SA, GHOBASHY MM, AL-GAHTANY SA, et al. Application of nano-inspired scaffolds-based biopolymer hydrogel for bone and periodontal tissue regeneration. Polymers (Basel). 2022;14(18):3791. [67] LI M, LV J, YANG Y, et al. Advances of hydrogel therapy in periodontal regeneration-a materials perspective review. Gels. 2022;8(10):624. [68] WANG Y, YANG Z, CHEN X, et al. Silk fibroin hydrogel membranes prepared by a sequential cross-linking strategy for guided bone regeneration. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2023;147:106133. [69] DUBEY N, FERREIRA JA, DAGHRERY A, et al. Highly tunable bioactive fiber-reinforced hydrogel for guided bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2020;113:164-176. [70] ZHANG L, DONG Y, LIU Y, et al. Multifunctional hydrogel/platelet-rich fibrin/nanofibers scaffolds with cell barrier and osteogenesis for guided tissue regeneration/guided bone regeneration applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;253(Pt 4):126960. [71] XU W, ZHOU W, WANG H, et al. Roles of Porphyromonas g ingivalis and its virulence factors in periodontitis. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2020;120:45-84. [72] LIU S, WANG YN, MA B, et al. Gingipain-responsive thermosensitive hydrogel loaded with SDF-1 facili tates in situ periodontal tissue regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(31):36880-36893. [73] MOHABATPOUR F, CHEN X, PAPAGERAKIS S, et al. Novel trends, challenges and new perspectives for enamel repair and regeneration to treat dental defects. Biomater Sci. 2022;10(12):3062-3087. [74] ZHANG Z, BI F, GUO W. Research advances on hydrogel-based materials for tissue regeneration and remineralization in tooth. Gels. 2023;9(3):245. [75] ZHANG S, ZHAO Y, DING S, et al. Facile synthesis of in situ formable Alg inate composite hydrogels with Ca2+-induced healing ability. Tissue Eng Part A. 2021;27(19-20):1225-1238. [76] LIU Z, LU J, CHEN X, et al. A novel amelogenesis-inspired hydrogel composite for the remineralization of enamel non-cavitated lesions. J Mater Chem B. 2022;10(48):10150-10161. [77] MOHABATPOUR F, YAZDANPANAH Z, PAPAGERAKIS S, et al. Self-crosslinkable oxidized alg inate-carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogels as an injectable cell carrier for in vitro dental enamel regeneration. J Funct Biomater. 2022;13(2):71. [78] FÖLDES A, SANG-NGOEN T, KÁDÁR K, et al. Three-dimensional culture of ameloblast-originated hat-7 cells for functional modeling of defective tooth enamel formation. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:682654. [79] NAJAFI H, JAFARI M, FARAHAVAR G, et al. Recent advances in design and applications of biomimetic self-assembled peptide hydrogels for hard tissue regeneration. Biodes Manuf. 2021;4(4):735-756. [80] LI S, YU Q, LI H, et al. Self-assembled peptide hydrogels in regenerative medicine. Gels. 2023;9(8):653. [81] OGLE OE. Salivary gland diseases. Dent Clin North Am. 2020;64(1): 87-104. [82] ITONAGA T, TOKUUYE K, MIKAMI R, et al. Mathematical evaluation of post-radiotherapy salivary gland function using salivary gland scintigraphy. Br J Radiol. 2022;95(1130):20210718. [83] KLINOVSKAYA AS, GURGENADZE AP, BAZIKYAN EA, et al. Sialendoscopy in diagnosis and treatment of salivary gland disorders. Stomatolog iia (Mosk). 2020;99(3):83-86. [84] DOS SANTOS HT, NAM K, BROWN CT, et al. Trimers conjugated to fibrin hydrogels promote salivary gland function. J Dent Res. 2021; 100(3):268-275. [85] NAM K, DOS SANTOS HT, MASLOW F, et al. Lamin in-1 peptides conjugated to fibrin hydrogels promote salivary gland regeneration in irradiated mouse submandibular glands. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:729180. [86] WANG T, HUANG Q, RAO Z, et al. Injectable decellular ized extracellular matrix hydrogel promotes salivary gland regeneration via endogenous stem cell recruitment and suppression of fibrogenesis. Acta Biomater. 2023;169:256-272. [87] YAO Y, ZHANG A, YUAN C, et al. Recent trends on burn wound care: hydrogel dressings and scaffolds. Biomater Sci. 2021;9(13):4523-4540. [88] BRUMBERG V, ASTRELINA T, MALIVANOVA T, et al. Modern wound dressings: hydrogel dressings. Biomedicines. 2021;9(9):1235. [89] YAZDI MK, ZARE M, KHODADADI A, et al. Polydopamine biomaterials for skin regeneration. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2022;8(6):2196-2219. [90] YUAN Y, DING L, CHEN Y, et al. Nano-silver functionalized polysaccharides as a platform for wound dressings: a review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;194:644-653. [91] NICHOLS F, CHEN S. Graphene oxide quantum dot-based functional nanomaterials for effective antimicrobial applications. Chem Rec. 2020;20(12):1505-1515. [92] HUANG H, HE D, LIAO X, et al. An excellent antibacterial and high self-adhesive hydrogel can promote wound fully healing driven by its shrinkage under NIR. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;129: 112395. [93] XU L, YE Q, XIE J, et al. An injectable gellan gum-based hydrogel that inhibits Staphylococcus aureus for infected bone defect repair. J Mater Chem B. 2022;10(2):282-292. [94] KUMARI A, RAINA N, WAHI A, et al. Wound-healing effects of curcumin and its nanoformulations: a comprehensive review. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(11):2288. [95] YOON SJ, HYUN H, LEE DW, et al. Visible light-cured glycol chitosan hydrogel containing a beta-cyclodextrin-curcumin inclusion complex improves wound healing in vivo. Molecules. 2017;22(9):1513. [96] FATHI P, SIKORSKI M, CHRISTODOULIDES K, et al. Zeolite-loaded alg inate-chitosan hydrogel beads as a topical hemostat. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2018;106(5):1662-1671. [97] YU Q, SUN H, YUE Z, et al. Zwitter ionic polysaccharide-based hydrogel dressing as a stem cell carrier to accelerate burn wound healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(7):e2202309. [98] WU D, TAO S, ZHU L, et al. Chitosan hydrogel dressing loaded with adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promotes skin full-thickness wound repair. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024;7(2):1125-1134. [99] YU R, ZHANG H, GUO B. Conductive biomaterials as bioactive wound dressing for wound healing and skin tissue engineering. Nanomicro Lett. 2021;14(1):1. [100] ZHAO X, WU H, GUO B, et al. Antibacterial anti-oxidant electroactive injectable hydrogel as self-healing wound dressing with hemostasis and adhesiveness for cutaneous wound healing. Biomaterials. 2017;122:34-47. [101] WENG Y, CAO Y, SILVA CA, et al. Tissue-engineered composites of bone and cartilage for mandible condy lar reconstruction. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2001;59(2):185-190. [102] DOBIE K, SMITH G, SLOAN AJ, et al. Effects of alg inate hydrogels and TGF-beta 1 on human dental pulp repair in vitro. Connect Tissue Res. 2002;43(2-3):387-390. [103] CHEN F, WU Z, WANG Q, et al. Preparation and biological characteristics of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2-loaded dextran-co-gelatin hydrogel microspheres, in vitro and in vivo studies. Pharmacology. 2005;75(3):133-144. [104] CAO Y, MEI ML, LI QL, et al. Agarose hydrogel biomimetic mineralization model for the regeneration of enamel prismlike tissue. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6(1):410-420. [105] MIYAJIMA H, MATSUMOTO T, SAKAI T, et al. Hydrogel-based biomimetic environment for in vitro modulation of branching morphogenesis. Biomaterials. 2011;32(28):6754-6763. [106] VARONI E, TSCHON M, PALAZZO B, et al. Agarose gel as biomaterial or scaffold for implantation surgery: characterization, histological and histomorphometric study on soft tissue response. Connect Tissue Res. 2012;53(6):548-554. [107] MATSUMINE H, SASAKI R, TABATA Y, et al. Facial nerve regeneration using basic fibroblast growth factor-impregnated gelatin microspheres in a rat model. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2016;10(10):E559-E567. [108] SALZLECHNER C, HAGHIGHI T, et al. Adhesive hydrogels for maxillofacial tissue regeneration using minimally invasive procedures. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020;9(4):e1901134. |
| [1] | 赖鹏宇, 梁 冉, 沈 山. 组织工程技术修复颞下颌关节:问题与挑战[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | 赵增波, 李晨曦, 窦晨雷, 马 娜, 周冠军. 壳聚糖/甘油磷酸钠/海藻酸钠/益母草碱水凝胶的抗炎与促成骨作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(4): 678-685. |
| [3] | 董美林, 都海宇, 刘 源. 负载槲皮素的羧甲基壳聚糖水凝胶促进糖尿病大鼠创面愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(4): 692-699. |
| [4] | 张 博, 张 振, 江 东. 单宁酸改性互穿网络水凝胶促进断裂跟腱术后的组织重塑[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(4): 721-729. |
| [5] | 刘浩洋, 谢 强, 沈梦然, 任岩松, 马金辉, 王佰亮, 岳德波, 王卫国. 可降解锌基合金在骨缺损修复重建中的应用及研究热点和不足[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(4): 839-845. |
| [6] | 张 煜, 徐睿安, 方 蕾, 历龙飞, 刘姝妍, 丁凌雪, 王悦熹, 郭子琰, 田 丰, 薛佳佳. 梯度人工骨修复支架调控骨骼系统组织的修复与再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(4): 846-855. |
| [7] | 王自林, 牟秋菊, 刘宏杰, 申玉雪, 祝丽丽. 载富血小板血浆水凝胶对L929细胞氧化损伤的保护作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(4): 771-779. |
| [8] | 赵红霞, 孙政伟, 韩 阳, 吴学超, 韩 静. 富血小板纤维蛋白复合甲基丙烯酰化明胶水凝胶的促成骨性能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(4): 809-817. |
| [9] | 肖 放, 黄 雷, 王 琳. 磁性纳米材料与磁场效应加速骨损伤修复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(4): 827-838. |
| [10] | 俞 磊, 张 巍, 秦 毅, 葛高然, 柏家祥, 耿德春. 贻贝启发接枝骨形态发生蛋白2成骨活性肽的介孔生物玻璃修复股骨髁缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(22): 4629-4638. |
| [11] | 李永航, 李文铭, 严才平, 王星宽, 向 超, 张 袁, 蒋 科, 陈 路. 抗纤维化与促“H”型血管核壳结构生物支架修复临界骨缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(16): 3420-3431. |
| [12] | 王仁智, 陈远汾, 李金玮. 3D打印中空管道双交联水凝胶组织工程支架[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(16): 3432-3439. |
| [13] | 冯淑琦, 张诗咏, 姚珂奕, 唐渝菲, 王 锴, 周雪梅, 向 琳 . 光响应纳米材料在骨组织再生中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(16): 3469-3475. |
| [14] | 何 蕊, 李重一, 王瑞瑶, 曾 丹, 范代娣. MXene基水凝胶在创面修复领域的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(16): 3486-3493. |
| [15] | 陈明伟, 余雯莉, 夏苏杭, 陈 宾, 陈文忠, 李锋侦, 周 宇, 司文腾. 携载microRNA-140外泌体/海藻酸钠/胶原水凝胶修复关节软骨损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(16): 3326-3334. |
随着组织工程的兴起,水凝胶在组织修复和再生中的应用日益广泛。在生物医学领域中应用的水凝胶可根据其来源分为天然水凝胶和人工合成水凝胶[1]。天然水凝胶包括胶原、明胶、透明质酸和壳聚糖等,具有良好的生物相容性和生物降解性,但机械性能较差,且受到外源宿主内潜在的免疫原性的限制[2]。人工合成的水凝胶如聚乙(烯)二醇衍生物、聚己内酯和聚乙烯醇等,具有成分稳定、结构可控和免疫原性低等特点[3],且可承受较强的机械载荷[4],因此成为研究热点。基于其优良的性能,研究人员尝试通过物理或共价交联天然或合成聚合物,调节亲疏水比或添加功能物质以增加、修饰和扩展新衍生水凝胶的特性和应用[5]。水凝胶可作为提供再生模板或基质的载体支架,一方面细胞可在其上黏附和增殖,并协调其反应,从而在损伤后再生受损组织;另一方面,其搭载的药物、细胞因子及干细胞等的额外刺激可促进组织再生[6],这些特性为水凝胶在口腔颌面部组织缺损修复中的应用奠定基础。
水凝胶已被报道可广泛应用于创口敷料和组织工程等方面,但鲜见有关水凝胶在口腔颌面部缺损修复应用的综述。并且,目前有关口腔颌面部缺损修复应用的综述多局限于仅针对颌面骨缺损修复或某一种类水凝胶在口腔颌面部缺损修复中的应用,复合水凝胶在口腔颌面部各组织中的应用描述欠详细,且对水凝胶所具有的独特性能缺乏分析。文章就水凝胶的优势性能与其在口腔颌面部缺损修复领域中的应用展开研究,揭示了其在骨、神经、血管、肌肉、唾液腺、牙体及牙周组织受损时促进组织再生的机制及潜能,探讨水凝胶目前在应用推广中的局限以及在此领域所面临的挑战,进一步推动各类水凝胶在颌面部组织再生领域中的应用。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2024年2月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 2010年1月至2024年2月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 中国知网、万方和PubMed数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“水凝胶,口腔颌面部缺损,机械性能,创口敷料,组织工程”;英文检索词为“hydrogel,oral and maxillofacial defects,mechanical properties,wound dressing,guided tissue regeneration”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 综述、研究原著及著作。
1.1.6 手工检索策略 无。
1.1.7 检索策略 以PubMed数据库为例,检索策略见图2。
1.1.8 检索文献量 共检索到868篇相关文献,其中中文文献101篇,英文文献767篇。万方及中国知网数据库检索到101篇,PubMed数据库检索到767篇。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①有关水凝胶类材料的机械性能、生物性能及刺激响应性的文献;②有关水凝胶类材料在口腔颌面部缺损中应用的文献;③同一领域中论点、论据可靠的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①重复性研究且与研究目的无相关性的文献;②资料无法提取的部分文献;③较为陈旧的文献。
1.3 文献质量评估及数据的提取 共检索到868篇相关文献,通过阅读文章后排除研究目标与该综述不相关、重复发表的文献760篇,实际纳入108篇,中文2篇,英文106篇。中国知网数据库2篇,PubMed数据库106篇,见图3。
3.3 综述的创新性 虽然水凝胶凭借优异的生物相容性、机械可控性及独特的刺激响应性已广泛应用于生物医学相关的不同领域,但有关水凝胶在口腔颌面部缺损修复应用的综述较少。文章从概述水凝胶区别于其他生物支架的优势性能出发,阐述水凝胶在口腔颌面部骨及软骨、神经、牙髓组织、肌肉组织、牙周组织、牙体硬组织、唾液腺组织缺损修复以及创口敷料等方面的应用并探讨其相关机制、应用前景及局限性,为其在口腔颌面外科领域提出了可能的发展方向。
3.4 综述的重要意义 基于水凝胶优良的生物学活性、机械可控性、刺激响应性等特性,近年来已成为各生物医学领域的研究热点。同时,水凝胶作为载体支架可契合口腔颌面部缺损修复的需求,改善目前传统手术治疗存在的并发症与不良预后。文章较为全面地回顾既往在口腔颌面部缺损修复中有关水凝胶应用的研究,总结水凝胶的优势性能可根据不同应用部位选择不同种类的水凝胶以达到最佳治疗效果,并分析尚存在的挑战与未来的前景,为水凝胶在口腔科学的深度研究提供新思路与新的理论指导。
3.5 课题组专家的意见与建议 水凝胶的材料特性非常适合细胞培养、组织工程、再生医学、药物递送和生物传感等领域。部分水凝胶的响应特性可使其经历材料变化,使其更具有应用前景。目前尚存几大关键问题亟待解决:①组织再生过程所需的空间稳定性是否会影响口腔颌面行使日常功能,如咀嚼、吞咽和言语等;②水凝胶复合物的安全性和长期疗效尚待验证;③水凝胶复合物制备工艺的最简化与最佳疗效的权衡;④水凝胶的临床转化不足。这些为未来研究提供思路,随着材料学的发展,期待能够开发出更加优良的水凝胶材料以满足临床需要。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||