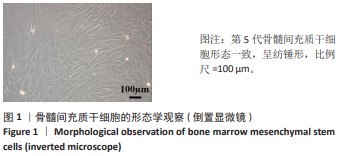
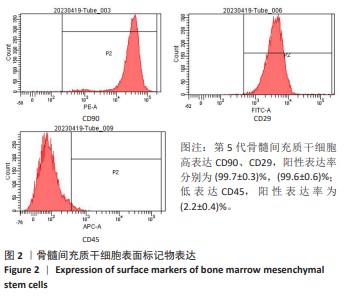
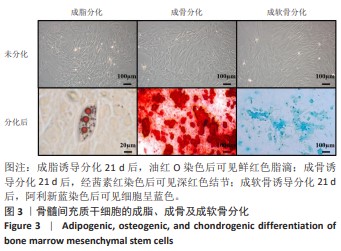
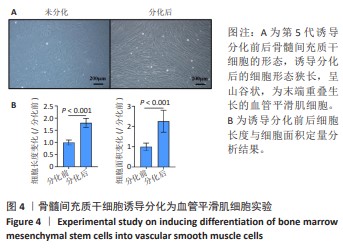
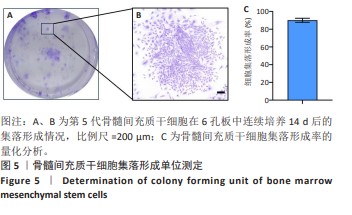
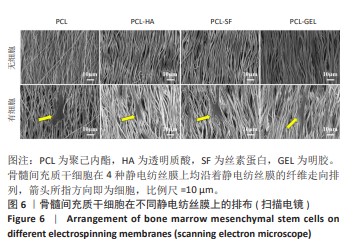
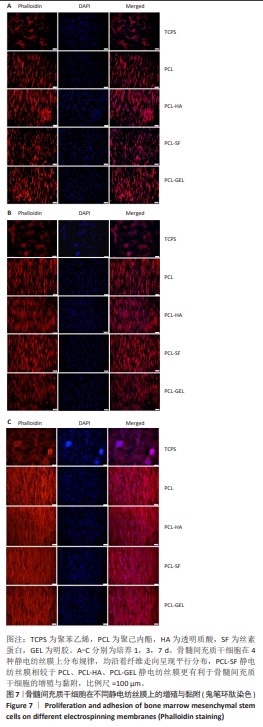
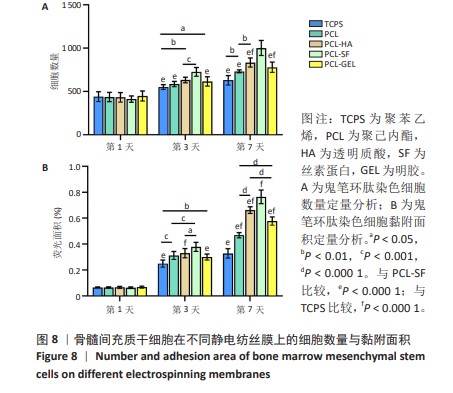
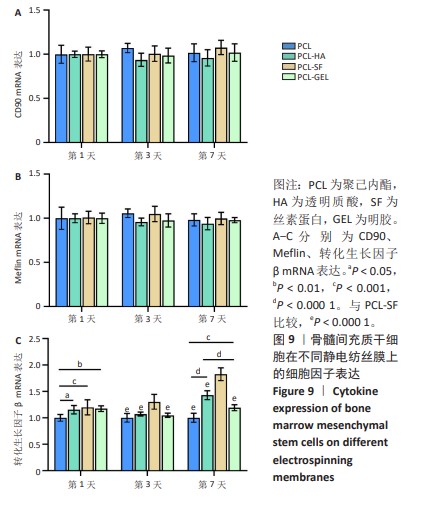
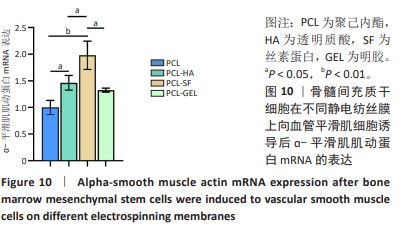
[1] MALLIS P, KOSTAKIS A, STAVROPOULOS-GIOKAS C, et al. Future perspectives in small-diameter vascular graft engineering. Bioengineering. 2020;7(4):160.
[2] GONG W, LEI D, LI S, et al. Hybrid small-diameter vascular grafts: Anti-expansion effect of electrospun poly ε-caprolactone on heparin-coated decellularized matrices. Biomaterials. 2016;76:359-370.
[3] CAO X, MAHARJAN S, ASHFAQ R, et al. Bioprinting of Small-Diameter Blood Vessels. Engineering. 2021;7:832-844.
[4] YOGI A, RUKHLOVA M, CHARLEBOIS C, et al. Differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells into vascular smooth muscle cells for tissue engineering applications. Biomedicines. 2021;9(7):797.
[5] KHARBIKAR BN, MOHINDRA P, DESAI TA. Biomaterials to enhance stem cell transplantation. Cell Stem Cell. 2022;29(5):692-721.
[6] LEAL BBJ, WAKABAYASHI N, OYAMA K, et al. Vascular Tissue Engineering: Polymers and Methodologies for Small Caliber Vascular Grafts. Front Cardiovas. Med. 2021;7:592361.
[7] CHANG S, SONG S, LEE J, et al. Phenotypic modulation of primary vascular smooth muscle cells by short-term culture on micropatterned substrate. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e88089.
[8] DING DC, SHYU WC, LIN SZ. Mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Transplant. 2011;20(1):5-14.
[9] SHOJAEI F, RAHMATI S, BANITALEBI DEHKORDI M. A review on different methods to increase the efficiency of mesenchymal stem cell-based wound therapy. Wound Repair Regen. 2019;27(6):661-671.
[10] ZHANG X, BENDECK MP, SIMMONS CA, et al. Deriving vascular smooth muscle cells from mesenchymal stromal cells: Evolving differentiation strategies and current understanding of their mechanisms. Biomaterials. 2017;145:9-22.
[11] BAKER N, BOYETTE LB, TUAN RS. Characterization of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in aging. Bone. 2015;70:37-47.
[12] HAYAT U, RAZA A, BILAL M, et al. Biodegradable polymeric conduits: Platform materials for guided nerve regeneration and vascular tissue engineering. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2022;67:103014.
[13] KUNDU B, RAJKHOWA R, KUNDU SC, et al. Silk fibroin biomaterials for tissue regenerations. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65(4):457-470.
[14] PRAKASH NJ, MANE PP, GEORGE SM, et al. Silk Fibroin As an Immobilization Matrix for Sensing Applications. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021;7(6):2015-2042.
[15] MAZUREK Ł, SZUDZIK M, RYBKA M, et al. Silk Fibroin Biomaterials and Their Beneficial Role in Skin Wound Healing. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(12):1852.
[16] CHEN K, LI Y, LI Y, et al. Silk Fibroin Combined with Electrospinning as a Promising Strategy for Tissue Regeneration. Macromol Biosci. 2023; 23(2):e2200380.
[17] YANG C, LI S, HUANG X, et al. Silk Fibroin Hydrogels Could Be Therapeutic Biomaterials for Neurological Diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:2076680.
[18] MARINHO A, NUNES C, REIS S. Hyaluronic acid: A key ingredient in the therapy of inflammation. Biomolecules. 2021;11(10):1518.
[19] GRAÇA MFP, MIGUEL SP, CABRAL CSD, et al. Hyaluronic acid-Based wound dressings: A review. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;241:116364.
[20] ROSSATTO A, TROCADO DOS SANTOS J, ZIMMER FERREIRA ARLINDO M, et al. Hyaluronic acid production and purification techniques: a review. Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2023;53(1):1-11.
[21] PEREIRA H, SOUSA DA, CUNHA A, et al. Hyaluronic Acid. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1059:137-153.
[22] AHMADY A, ABU SAMAH NH. A review: Gelatine as a bioadhesive material for medical and pharmaceutical applications. Int J Pharm. 2021;608:121037.
[23] DE VALENCE S, TILLE JC, MUGNAI D, et al. Long term performance of polycaprolactone vascular grafts in a rat abdominal aorta replacement model. Biomaterials. 2012;33(1):38-47.
[24] HOSSEINZADEH S, ZAREI-BEHJANI Z, BOHLOULI M, et al. Fabrication and optimization of bioactive cylindrical scaffold prepared by electrospinning for vascular tissue engineering. Iran Polym J. 2022; 31(2):127-141.
[25] VALENCE SD, TILLE JC, CHAABANE C, et al. Plasma treatment for improving cell biocompatibility of a biodegradable polymer scaffold for vascular graft applications. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2013;85(1):78-86.
[26] HUANG L, GUO S, JIANG Y, et al. A preliminary study on polycaprolactone and gelatin-based bilayered tubular scaffolds with hierarchical pore size constructed from nano and microfibers for vascular tissue engineering. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2021;32(14): 1791-1809.
[27] ASHAMMAKHI N, GHAVAMINEJAD A, TUTAR R, et al. Highlights on Advancing Frontiers in Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2022; 28(3):633-664.
[28] YOUSEFI-AHMADIPOUR A, ASADI F, PIRSADEGHI A, et al. Current Status of Stem Cell Therapy and Nanofibrous Scaffolds in Cardiovascular Tissue Engineering. Regen Eng Transl Med. 2021:0123456789.
[29] WEEKES A, BARTNIKOWSKI N, PINTO N, et al. Biofabrication of small diameter tissue-engineered vascular grafts. Acta Biomater. 2022;138: 92-111.
[30] MIRANDA-NIEVES D, ASHOUR A, CHAIKOF EL. Bioinspired Vascular Grafts. Organ Tissue Eng. 2021:3-22.
[31] LI N, RICKEL AP, SANYOUR HJ, et al. Vessel graft fabricated by the on-site differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells towards vascular cells on vascular extracellular matrix scaffold under mechanical stimulation in a rotary bioreactor. J Mater Chem B. 2019;7(16):2703-2713.
[32] PURWANINGRUM M, JAMILAH NS, PURBANTORO SD, et al. Comparative characteristic study from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Vet Sci. 2021;22(6):e74.
[33] GREENWALD SE, BERRY CL. Improving vascular grafts: the importance of mechanical and haemodynamic properties. J Pathol. 2000;190(3): 292-299.
[34] HICKEY RJ, PELLING AE. Cellulose biomaterials for tissue engineering. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019;7:45.
[35] XING Y, GU Y, GUO L, et al. Gelatin coating promotes in situ endothelialization of electrospun polycaprolactone vascular grafts. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2021;32(9):1161-1181.
[36] GHOLIPOURMALEKABADI M, SAPRU S, SAMADIKUCHAKSARAEI A, et al. Silk fibroin for skin injury repair: Where do things stand? Adv Drug Deli Rev. 2020;153:28-53.
[37] CORTES H, CABALLERO-FLORÁN IH, MENDOZA-MUÑOZ N, et al. Hyaluronic acid in wound dressings. Cell Mol Biol. 2020;66(4):191-198.
[38] O’CONNOR RA, CAHILL PA, MCGUINNESS GB. Effect of electrospinning parameters on the mechanical and morphological characteristics of small diameter PCL tissue engineered blood vessel scaffolds having distinct micro and nano fibre populations – A DOE approach. Polym Test. 2021;96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2021.107119
[39] YANG S, ZHENG X, QIAN M, et al. Nitrate-Functionalized poly(ε-Caprolactone) Small-Diameter Vascular Grafts Enhance Vascular Regeneration via Sustained Release of Nitric Oxide. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:770121.
[40] ZHAO L, LI X, YANG L, et al. Evaluation of remodeling and regeneration of electrospun PCL/fibrin vascular grafts in vivo. Mater Sci Eng C. 2021; 118:111441 .
[41] LU X, ZOU H, LIAO X, et al. Construction of PCL-collagen@PCL@PCL-gelatin three-layer small diameter artificial vascular grafts by electrospinning. Biomed Mater. 2022;18(1):10.1088/1748-605X/aca269
[42] TANG D, CHEN S, HOU D, et al. Regulation of macrophage polarization and promotion of endothelialization by NO generating and PEG-YIGSR modified vascular graft. Mater Sci Eng C. 2018;84:1-11.
[43] FOMBY P, CHERLIN AJ, HADJIZADEH A, et al. Stem cells and cell therapies in lung biology and diseases: Conference report. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2010;12(3):181-204.
[44] FAYON A, MENU P, EL OMAR R. Cellularized small-caliber tissue-engineered vascular grafts: looking for the ultimate gold standard. NPJ Regen Med. 2021;6(1):46.
[45] WEI Y, WANG F, GUO Z, et al. Tissue-engineered vascular grafts and regeneration mechanisms. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2022;165:40-53.
[46] CRUPI A, COSTA A, TARNOK A, et al. Inflammation in tissue engineering: The Janus between engraftment and rejection. Eur J Immunol. 2015; 45(12):3222-3236.
[47] SHI J, YANG Y, CHENG A, et al. Metabolism of vascular smooth muscle cells in vascular diseases. Am J Physiol Hear Circ Physiol. 2020;319(3): H613-H631. |