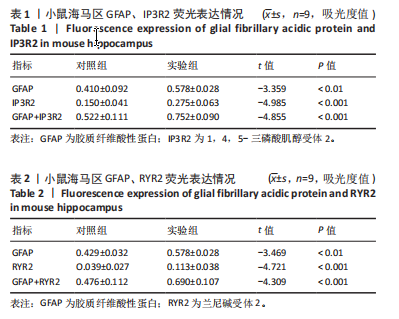
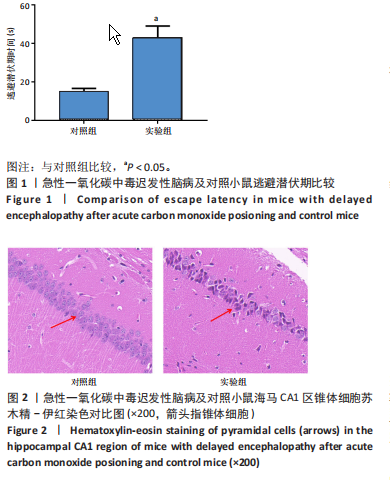
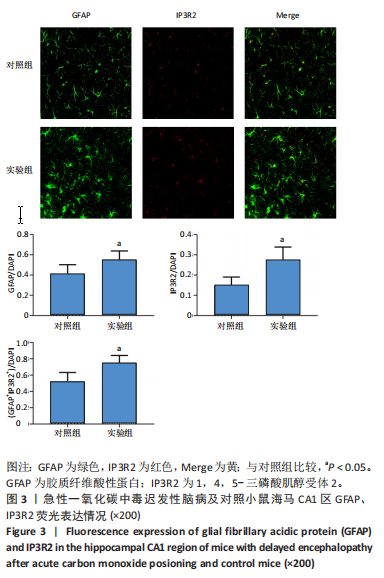
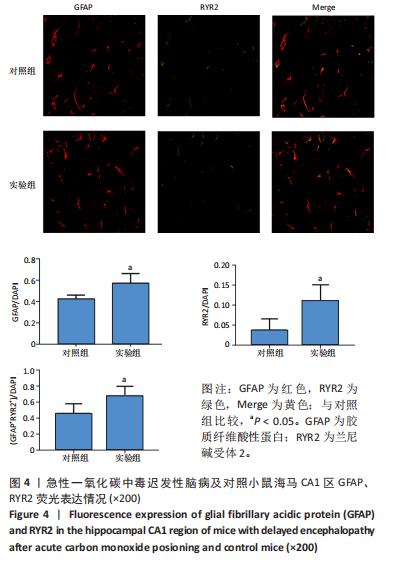
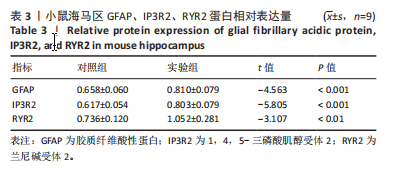
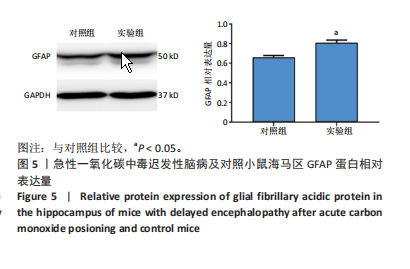
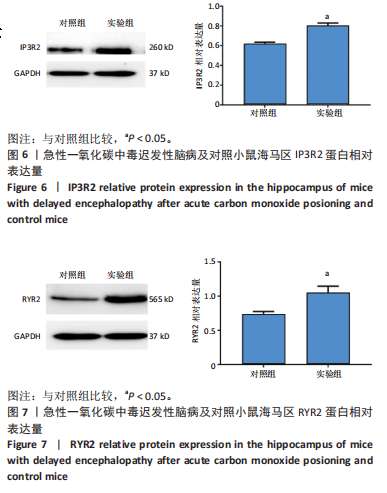
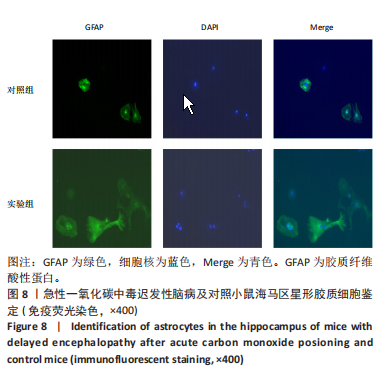
[1] MATTIUZZI C, LIPPI G. Worldwide epidemiology of carbon monoxide poisoning. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2020;39(4):387-392.
[2] ROSE JJ, WANG L, XU Q, et al. Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: Pathogenesis, Management, and Future Directions of Therapy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;195(5):596-606.
[3] YANAGIHA K, ISHII K, TAMAOKA A. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor treatment alleviated cognitive impairment caused by delayed encephalopathy due to carbon monoxide poisoning: two case reports and a review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(8):e6125.
[4] BANO D, ANKARCRONA M. Beyond the critical point: An overview of excitotoxicity, calcium overload and the downstream consequences. Neurosci Lett. 2018;663:79-85.
[5] ZHAO N, LIANG P, ZHUO X, et al. After treatment with methylene blue is effective against delayed encephalopathy after acute carbon monoxide poisoning. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018;122(5):470-480.
[6] ZHANG W, YU J, GUO M, et al. Dexmedtomidine attenuats glutamate-induced cytotoxicity by inhibiting the mitochondrial mediated apptotic pathway. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:922139.
[7] BI MJ, SUN XN, ZOU Y, et al. N-butylphthalide improves cognitive function in rats after carbon monoxide poisoning. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:64.
[8] ESCARTIN C, GALEA E, LAKATOS A, et al. Reactive astrocyte nomenclature, definitions, and future directions. Nat Neurosci. 2021;24(3):312-325.
[9] LIM D, RONCO V, GROLLA AA, et al. Glial calcium signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2014;167:45-65.
[10] EGOROVA PA, BEZPROZVANNY IB. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors and neurodegenerative disorders. FEBS J. 2018;285(19):3547-3565.
[11] MURALI S, ZHANG M, NURSE CA. Evidence that 5-HT stimulates intracellular Ca2+ signalling and activates pannexin-1 currents in type II cells of the rat carotid body. J Physiol. 2017;595(13):4261-4277.
[12] ZHANG T, GUO T, MISHRA S, et al. Phospholamban ablation rescues sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) handling but exacerbates cardiac dysfunction in CaMKIIdelta(C) transgenic mice. Circ Res. 2010;106(2):354-362.
[13] DEMYDENKO K, EKHTERAEI-TOUSI S, RODERICK HL. Inositol 1, 4, 5-trisphosphate receptors in cardiomyocyte physiology and disease. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2022;377(1864):20210319.
[14] ROSA N, IVANOVA H, WAGNER LE 2ND, et al. Bcl-xL acts as an inhibitor of IP3R channels, thereby antagonizing Ca2+-driven apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2022;29(4):788-805.
[15] HAMADA K, MIKOSHIBA K. IP3 Receptor Plasticity Underlying Diverse Functions. Annu Rev Physiol. 2020;82:151-176.
[16] SMITH HA, TAYLOR CW. Dissociation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate from IP3 receptors contributes to termination of Ca2+ puffs. J Biol Chem. 2023; 299(2):102871.
[17] KOFUJI P, ARAQUE A. G-Protein-Coupled Receptors in Astrocyte-Neuron Communication. Neuroscience. 2021;456:71-84.
[18] OKUBO Y, KANEMARU K, SUZUKI J, et al. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor type 2-independent Ca2+ release from the endoplasmic reticulum in astrocytes. Glia. 2019;67(1):113-124.
[19] REICHENBACH N, DELEKATE A, BREITHAUSEN B, et al. P2Y1 receptor blockade normalizes network dysfunction and cognition in an Alzheimer’s disease model. J Exp Med. 2018;215(6):1649-1663.
[20] ADASME T, HAEGER P, PAULA-LIMA AC, et al. Involvement of ryanodine receptors in neurotrophin-induced hippocampal synaptic plasticity and spatial memory formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(7):3029-3034.
[21] MORE JY, BRUNA BA, LOBOS PE, et al. Calcium Release Mediated by Redox-Sensitive RyR2 Channels Has a Central Role in Hippocampal Structural Plasticity and Spatial Memory. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018;29(12):1125-1146.
[22] DATTA D, LESLIE SN, WANG M, et al. Age-related calcium dysregulation linked with tau pathology and impaired cognition in non-human primates. Alzheimers Dement. 2021;17(6):920-932.
[23] LACAMPAGNE A, LIU X, REIKEN S, et al. Post-translational remodeling of ryanodine receptor induces calcium leak leading to Alzheimer’s disease-like pathologies and cognitive deficits. Acta Neuropathol. 2017;134(5):749-767.
[24] 牛翻燕,项文平,薛慧,等.星形胶质细胞及其炎症因子在CO中毒所致迟发性脑损伤中的作用[J].脑与神经疾病杂志,2022,30(11):665-670.
[25] 王雅明,项文平,牛翻燕,等.P2Y1受体介导星形胶质细胞的激活在急性一氧化碳中毒迟发性脑病中的作用[J].中风与神经疾病杂志,2023, 40(2):103-108.
[26] OCHI S, ABE M, LI C, et al. The nicotinic cholinergic system is affected in rats with delayed carbon monoxide encephalopathy. Neurosci Lett. 2014;569:33-37.
[27] LANANNA BV, MCKEE CA, KING MW, et al. Chi3l1/YKL-40 is controlled by the astrocyte circadian clock and regulates neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. Sci Transl Med. 2020;12(574):eaax3519.
[28] XUE M, YONG VW. Neuroinflammation in intracerebral haemorrhage: immunotherapies with potential for translation. Lancet Neurol. 2020; 19(12):1023-1032.
[29] KUSHNIR A, WAJSBERG B, MARKS AR. Ryanodine receptor dysfunction in human disorders. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2018;1865(11 Pt B): 1687-1697.
[30] LI R, DANG S, YAO M, et al.Osthole alleviates neuropathic pain in mice by inhibiting the P2Y1-receptor-dependent JNK signaling pathway. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(9):7945-7962.
[31] BADIA-SOTERAS A, HEISTEK TS, KATER MSJ, et al. Retraction of Astrocyte Leaflets From the Synapse Enhances Fear Memory. Biol Psychiatry. 2023;94(3):226-238.
[32] KOL A, GOSHEN I. The memory orchestra: the role of astrocytes and oligodendrocytes in parallel to neurons. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2021;67:131-137.
[33] LYON KA, ALLEN NJ. From Synapses to Circuits, Astrocytes Regulate Behavior. Front Neural Circuits. 2022;15:786293.
[34] KATER MSJ, BADIA-SOTERAS A, VAN WEERING JRT, et al. Electron microscopy analysis of astrocyte-synapse interactions shows altered dynamics in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023;17:1085690.
[35] PADMASHRI R, SURESH A, BOSKA MD, et al. Motor-Skill Learning Is Dependent on Astrocytic Activity. Neural Plast. 2015;2015:938023.
[36] PINTO-DUARTE A, ROBERTS AJ, OUYANG K, et al. Impairments in remote memory caused by the lack of Type 2 IP3 receptors. Glia. 2019;67(10):1976-1989.
[37] GOENAGA J, ARAQUE A, KOFUJI P, et al. Calcium signaling in astrocytes and gliotransmitter release. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2023;15:1138577.
[38] NAVARRETE M, PEREA G, FERNANDEZ DE SEVILLA D, et al. Astrocytes mediate in vivo cholinergic-induced synaptic plasticity. PLoS Biol. 2012;10(2):e1001259.
[39] BERTAN F, WISCHHOF L, SOSULINA L, et al. Loss of Ryanodine Receptor 2 impairs neuronal activity-dependent remodeling of dendritic spines and triggers compensatory neuronal hyperexcitability. Cell Death Differ. 2020;27(12):3354-3373.
[40] YAO J, SUN B, INSTITORIS A, et al. Limiting RyR2 Open Time Prevents Alzheimer’s Disease-Related Neuronal Hyperactivity and Memory Loss but Not β-Amyloid Accumulation. Cell Rep. 2020;32(12):108169.
[41] Dridi H, Liu Y, Reiken S, et al. Heart failure-induced cognitive dysfunction is mediated by intracellular Ca2+ leak through ryanodine receptor type 2. Nat Neurosci. 2023;26(8):1365-1378.
[42] Huffels CFM, Osborn LM, Cappaert NLM, et al. Calcium signaling in individual APP/PS1 mouse dentate gyrus astrocytes increases ex vivo with Aβ pathology and age without affecting astrocyte network activity. J Neurosci Res. 2022;100(6):1281-1295.
[43] SHAH D, GSELL W, WAHIS J, et al. Astrocyte calcium dysfunction causes early network hyperactivity in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Rep. 2022;40(8):111280.
[44] BAKKER A, KRAUSS GL, ALBERT MS, et al. Reduction of hippocampal hyperactivity improves cognition in amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Neuron. 2012;74(3):467-474.
[45] INSTITORIS A, MURPHY-ROYAL C, TARANTINI S, et al. Whole brain irradiation in mice causes long-term impairment in astrocytic calcium signaling but preserves astrocyte-astrocyte coupling. Geroscience. 2021;43(1):197-212. |