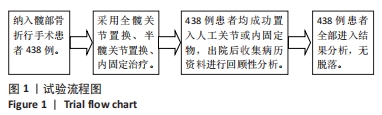
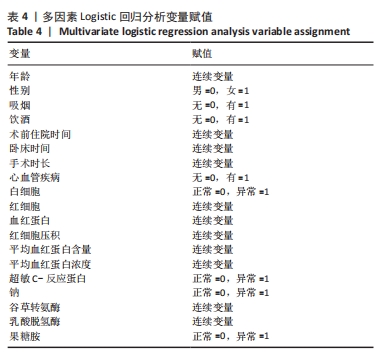
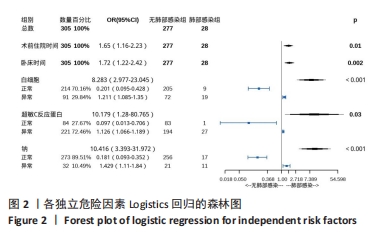
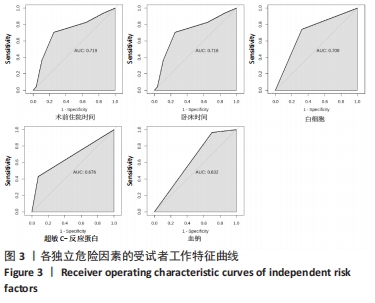
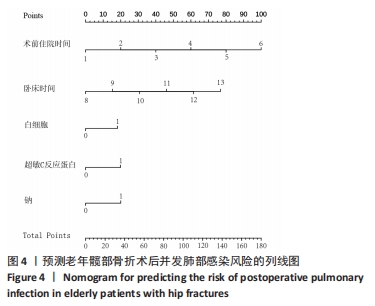
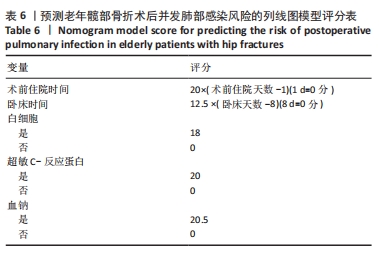
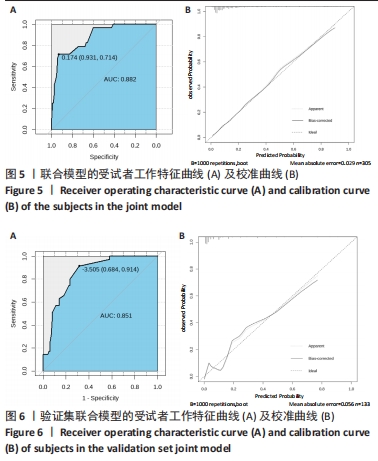
[1] SHIN KH, KIM JJ, SON SW, et al. Early Postoperative hypoalbuminaemia as a risk factor for postoperative pneumonia following hip fracture surgery. Clin Interv Aging. 2020;15:1907-1915.
[2] 张玉. 老年髋部骨折术后肺部感染风险模型的研究[D].合肥:安徽医科大学,2023.
[3] 张欣. 老年髋部骨折患者术后谵妄与肺炎风险预测中列线图的建立与验证[D].上海:中国人民解放军海军军医大学,2023.
[4] SUMAN VJ, ATKINSON EJ, O’FALLON WM, et al. A nomogram for predicting lifetime hip fracture risk from radius bone mineral density and age. Bone. 1993;14(6):843-846.
[5] FU M, ZHANG Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Characteristics of preoperative atrial fibrillation in geriatric patients with hip fracture and construction of a clinical prediction model: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Geriatr. 2023;23(1):310.
[6] JIANG J, XING F, LUO R, et al. Risk factors and prediction model of nomogram for preoperative calf muscle vein thrombosis in geriatric hip fracture patients. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023;10:1236451.
[7] HAN S, BAI Y, JIAO K, et al. Development and validation of a newly developed nomogram for predicting the risk of deep vein thrombosis after surgery for lower limb fractures in elderly patients. Front Surg. 2023;10:1095505.
[8] 雷英,刘艳丽,李阳,等.髋部骨折并发下肢深静脉血栓形成危险因素分析[J].中华创伤杂志,2019,35(9):817-822.
[9] 中华医学会呼吸病学分会感染学组.中国成人医院获得性肺炎与呼吸机相关性肺炎诊断和治疗指南(2018年版) [J].中华结核和呼吸杂志,2018,41(4):255-280.
[10] 周方伦,王利宏,单军标,等.合并肺栓塞髋部骨折患者手术与非手术治疗的疗效比较[J].中华创伤杂志,2019,35(10):907-912.
[11] 李金奇,崔北辰,王军强,等.老年髋部骨折患者术后2年内再发对侧髋部骨折的危险因素研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2021, 23(3):209-215.
[12] 韩超,李晓丹,孙翔,等.老年髋部骨折快速手术的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2023,37(12):1556-1561.
[13] 刘泽民,吕欣,刘晋元,等.髋部骨折2342例流行病学分布特点的单中心分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(32):5085-5091.
[14] SHEEHAN KJ, WILLIAMSON L, ALEXANDER J, et al. Prognostic factors of functional outcome after hip fracture surgery: a systematic review. Age Ageing. 2018;47(5):661-670.
[15] CHANG W, LV H, FENG C, et al. Preventable risk factors of mortality after hip fracture surgery: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2018;52:320-328.
[16] 岳睿,李晓玉,杨明辉,等.老年髋部骨折患者围手术期输血和危险因素[J].首都医科大学学报,2021,42(4):629-634.
[17] 应璞,诸磊,许岳,等.老年股骨粗隆间骨折术后1年内死亡分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2022,30(4):294-298.
[18] TIAN Y, ZHU Y, ZHANG K, et al. Incidence and risk factors for postoperative pneumonia following surgically treated hip fracture in geriatric patients: a retrospective cohort study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;24;17(1):179.
[19] 罗颢文,涂江龙,刘建模,等.特征选择技术在江西地区缺血性脑卒中合并肺部感染风险预测模型中的应用[J].现代预防医学,2020, 47(22):4038-4041+4052.
[20] 姜源涛,姜源波.老年髋部骨折患者围手术期肺部感染危险因素分析[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2013,23(21):5185-5187.
[21] HE P, FAN SY, GUAN JQ, et al. Mediation analysis for the relationship between dyslipidemia and coronary artery disease via hypersensitive C-reactive protein in a case-control study. Coron Artery Dis. 2020; 31(7):613-619.
[22] LIU Y, HUANG X, LIU Y, et al. Application value of hypersensitive C-reactive protein, lactic acid and myoglobin in the combined detection of myocarditis. Exp Ther Med. 2019;17(6):4471-4476.
[23] 白植琴,钱彩华,陆华东,等.重症肺部感染患者血清感染学指标和免疫学指标对预后的预测价值[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2022, 32(20):3052-3056.
[24] LO RH, KALANTAR-ZADEH K, YOU AS, et al. Dysnatremia and risk of bloodstream infection in dialysis patients. Clin Kidney J. 2022;15(12): 2322-2330.
[25] CASTELLO LM, GAVELLI F, BALDRIGHI M, et al. Hypernatremia and moderate-to-severe hyponatremia are independent predictors of mortality in septic patients at emergency department presentation: A sub-group analysis of the need-speed trial. Eur J Intern Med. 2021; 83:21-27.
[26] LEUNG AA, MCALISTER FA, FINLAYSON SR, et al. Preoperative hypernatremia predicts increased perioperative morbidity and mortality. Am J Med. 2013;126(10):877-86.
[27] 吕璟,蒋泽磊,陈薛连,等.高血压脑出血患者肺部感染的危险因素及TLR4/NF-κB通路水平[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2023,33(20): 3057-3060.
[28] 李婷,裴永菊,王文慧,等.基于Logistic回归模型分析影响高血压脑出血患者术后肺部感染的危险因素[J].实用中西医结合临床, 2023,23(11):56-59.
[29] 任一欣,吴娜,房美,等.老年高血压合并冠心病患者PCI术后合并肺部感染的危险因素[J].中国老年学杂志,2023,43(6):1290-1292.
[30] SINGH JA, HOUSTON TK, PONCE BA, et al. Smoking as a risk factor for short-term outcomes following primary total hip and total knee replacement in veterans. Arthritis Care Res. 2011;63(10): 1365-1374.
[31] 刘星星,贺清明.老年髋部骨折病人肺部感染危险因素的Meta分析[J].护理研究,2021,35(2):195-205.
[32] 白静,巴楠,张小娟,等.胃癌根治术后肺部感染病原菌及危险因素[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2020,30(21): 3316-3320.
[33] XIAO H, ZHOU H, LIU K, et al. Development and validation of a prognostic nomogram for predicting post-operative pulmonary infection in gastric cancer patients following radical gastrectomy. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):14587.
[34] BOHL DD, SERSHON RA, SALTZMAN BM, et al. Incidence, risk factors, and clinical implications of pneumonia after surgery for geriatric hip fracture. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(5):1552-1556.
[35] 张玉,孙炜,孙维超,等.入院红细胞体积分布宽度与老年髋部骨折术后肺部感染的关系及其预测价值[J].天津医药,2022,50(6): 608-612.
[36] 尹鹏滨,吕厚辰,张里程,等.髋部骨折患者住院期间新发肺部感染的危险因素分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2015,17(9):745-750.
[37] 张丽琴,杨雅瑾,刘庆军,等.老年髋部骨折患者术后肺部感染的危险因素分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2022,37(4):395-397.
[38] 孙春生,郑欣,郭开今,等.入院时低基础代谢率与老年髋部骨折患者死亡率的关系[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(16):2467-2471.
[39] 李莉,陈念,柯柳,等.老年髋部骨折围术期肺部感染危险因素分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(35):5736-5740. |