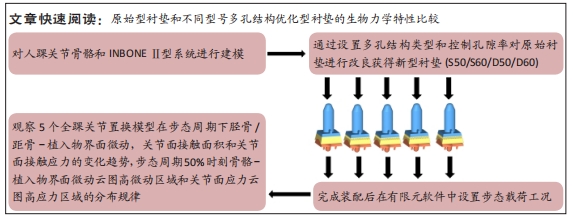
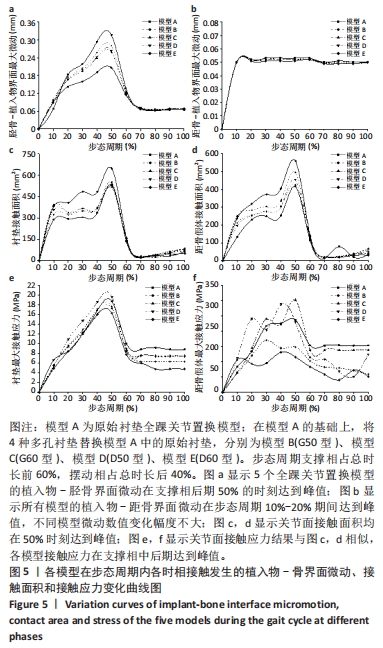
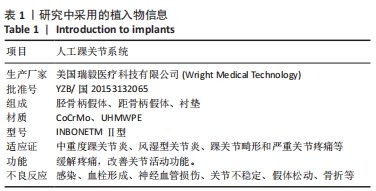
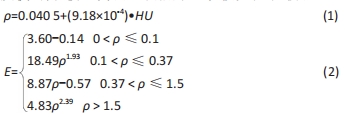[1] DELEU PA, BESSE JL, NAAIM A, et al. Change in gait biomechanics after total ankle replacement and ankle arthrodesis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2020;73:213-225.
[2] NAJEFI AA, GHANI Y, GOLDBERG AJ. Bone Cysts and Osteolysis in Ankle Replacement. Foot Ankle Int. 2021;42(1):55-61.
[3] PFAHL K, RÖSER A, EDER J, et al. Outcomes of Salvage Procedures for Failed Total Ankle Arthroplasty. Foot Ankle Int. 2023;44(4):262-269.
[4] SOPHER RS, AMIS AA, CALDER JD, et al. Total ankle replacement design and positioning affect implant-bone micromotion and bone strains. Med Eng Phys. 2017;42:80-90.
[5] MUJUKIAN A, HO NC, DAY MJ, et al. A Systematic Review of Unsystematic Total Ankle Replacement Wear Evaluations. JBJS Rev. 2020;8(3):0091.
[6] JEYASEELAN L, SI-HYEONG PARK S, AL-RUMAIH H, et al. Outcomes Following Total Ankle Arthroplasty: A Review of the Registry Data and Current Literature. Orthop Clin North Am. 2019;50(4):539-548.
[7] HENRICSON A, CARLSSON Å. Survival Analysis of the Single- and Double-Coated STAR Ankle up to 20 Years: Long-Term Follow-up of 324 Cases From the Swedish Ankle Registry. Foot Ankle Int. 2015; 36(10):1156-1160.
[8] KOH DTS, CHEN JY, TAN SM, et al. Mid-Term Functional and Radiological Outcomes of Total Ankle Replacement in an Asian Cohort. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2022;61(2):363-368.
[9] MUKHERJEE K, GUPTA S. Combined Bone Ingrowth and Remodeling Around Uncemented Acetabular Component: A Multiscale Mechanobiology-Based Finite Element Analysis. J Biomech Eng. 2017; 139(9). doi: 10.1115/1.4037223.
[10] FAN W, FU X, LI Z, et al. Porous Ultrahigh Molecular Weight Polyethylene/Functionalized Activated Nanocarbon Composites with Improved Biocompatibility. Materials (Basel, Switzerland). 2021; 14(20):6065.
[11] MAKSIMKIN AV, SENATOV FS, ANISIMOVA NY, et al. Multilayer porous UHMWPE scaffolds for bone defects replacement. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol App. 2017;73:366-372.
[12] 刘志强, 宫赫, 高甲子, 等. 基于三周期极小曲面的新型梯度支架设计及其力学、渗透、组织分化特性研究[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2021,38(5):960-968.
[13] ZHANG Z, LI H, FOGEL GR, et al. Biomechanical Analysis of Porous Additive Manufactured Cages for Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Finite Element Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2018;111:581-591.
[14] YU G, LI Z, LI S, et al. The select of internal architecture for porous Ti alloy scaffold: A compromise between mechanical properties and permeability. Mater Des. 2020;192:108754.
[15] DAVOODI E, MONTAZERIAN H, MIRHAKIMI AS, et al. Additively manufactured metallic biomaterials. Bioactive Materials. 2022;15: 214-249.
[16] GUO X, ZHOU J, TIAN Y, et al. Biomechanical effect of different plate-to-disc distance on surgical and adjacent segment in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion - a finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):340.
[17] 刘庆波, 苏知杨, 王恒峰, 等. 三周期极小化曲面单元结构骨小梁假体的生物力学性能[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(15):2297-2301.
[18] TUNCER M, HANSEN UN, AMIS AA. Prediction of structural failure of tibial bone models under physiological loads: effect of CT density-modulus relationships. Med Eng Phys. 2014;36(8):991-997.
[19] MONDAL S, GHOSH R. Bone remodelling around the tibia due to total ankle replacement: effects of implant material and implant-bone interfacial conditions. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2019;22(16):1247-1257.
[20] YU J, ZHAO D, CHEN WM, et al. Finite element stress analysis of the bearing component and bone resected surfaces for total ankle replacement with different implant material combinations. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s12891-021-04982-3
[21] ZHANG Y, CHEN Z, ZHAO D, et al. Articular geometry can affect joint kinematics, contact mechanics, and implant-bone micromotion in total ankle arthroplasty. J Orthop Res. 2023;41(2):407-417.
[22] ZHANG Q, CHEN Z, ZHANG J, et al. Insert conformity variation affects kinematics and wear performance of total knee replacements. Clinical biomechanics (Bristol, Avon). 2019;65:19-25.
[23] ISO, ISO 22622-2019, Implants for surgery - Wear of total ankle-joint prostheses - Loading and displacement parameters for wear-testing machines with load or displacement control corresponding environmental conditions for test, International Organization Environmental Standardization, London, UK, 2019.
[24] JAMJOOM BA, SIDDIQUI BM, SALEM H, et al. Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes of Revision Total Ankle Arthroplasty Using the INBONE II Prosthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2022;104(17):1554-1562.
[25] NAUDE JJ, SARAGAS NP, FERRAO PNF. CT Scan Assessment and Functional Outcome of Periprosthetic Bone Grafting After Total Ankle Arthroplasty at Medium-term Follow-up. Foot Ankle Int. 2022; 43(5):609-619.
[26] KOTNIS R, PASAPULA C, ANWAR F, et al. The management of failed ankle replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88(8):1039-1047.
[27] WILLEGGER M, TRNKA H, SCHUH RJCRFA. The Hintegra ankle arthroplasty: intermediate term results of 16 consecutive ankles and a review on the current literature. Clin Res Foot Ankle. 2013;2:124.
[28] SAKODA H, OSAKA Y, UETSUKI K, et al. Evaluating the durability of UHMWPE biomaterials used for articulating surfaces of joint arthroplasty using delamination tests. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2019;107(1):65-72.
[29] 李银标. UHMWPE人工关节材料增材制造进展[J]. 塑料,2022, 51(1):127-130.
[30] CURRIER BH, HECHT PJ, NUNLEY JA, et al. Analysis of Failed Ankle Arthroplasty Components. Foot Ankle Int. 2019;40(2):131-138.
[31] POURZAL R, KNOWLTON CB, HALL DJ, et al. How Does Wear Rate Compare in Well-functioning Total Hip and Knee Replacements? A Postmortem Polyethylene Liner Study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016; 474(8):1867-1875.
[32] LEE GW, SEO HY, JUNG DM, et al. Comparison of Preoperative Bone Density in Patients With and Without Periprosthetic Osteolysis Following Total Ankle Arthroplasty. Foot Ankle Int. 2021;42(5):575-581.
[33] SCHWABE MT, HANNON CP. The Evolution, Current Indications and Outcomes of Cementless Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Clin Med. 2022; 11(22):6608.
[34] ANIJS T, WOLFSON D, MERCER A, et al. Experimental measurements of femoral primary stability in two cementless posterior-stabilized knee replacement implants. Med Eng Phys. 2022;99:103734.
[35] MCGREGOR M, PATEL S, MCLACHLIN S, et al. Architectural bone parameters and the relationship to titanium lattice design for powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. Additive Manufacturing. 2021;47: 102273.
[36] HOU CJ, LIU YT, XU W, et al. Additive manufacturing of functionally graded porous titanium scaffolds for dental applications. Biomater Adv. 2022;139:213018.
[37] YANG L, YAN C, FAN H, et al. Investigation on the orientation dependence of elastic response in Gyroid cellular structures. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2019;90:73-85.
[38] MA S, TANG Q, FENG Q, et al. Mechanical behaviours and mass transport properties of bone-mimicking scaffolds consisted of gyroid structures manufactured using selective laser melting. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2019;93:158-169.
[39] ZHANG Y, CHEN Z, ZHAO H, et al. Comparison of joint load, motions and contact stress and bone-implant interface micromotion of three implant designs for total ankle arthroplasty. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022;223:106976. |