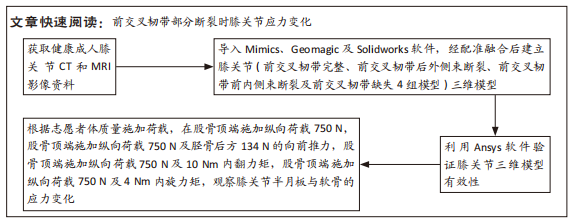
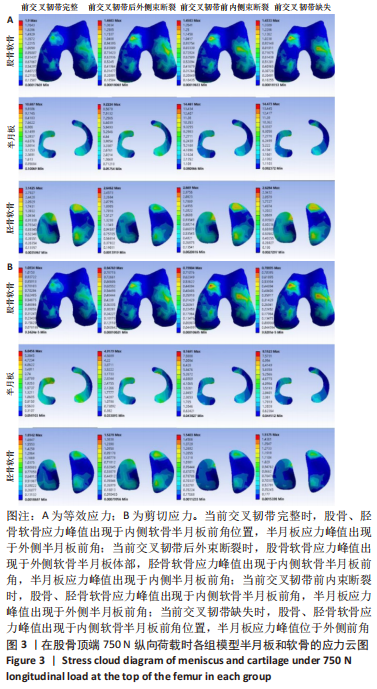
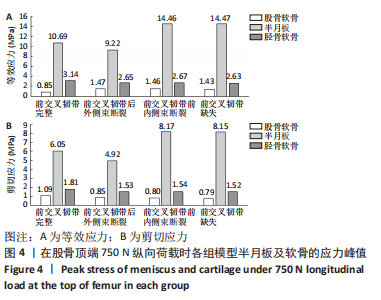
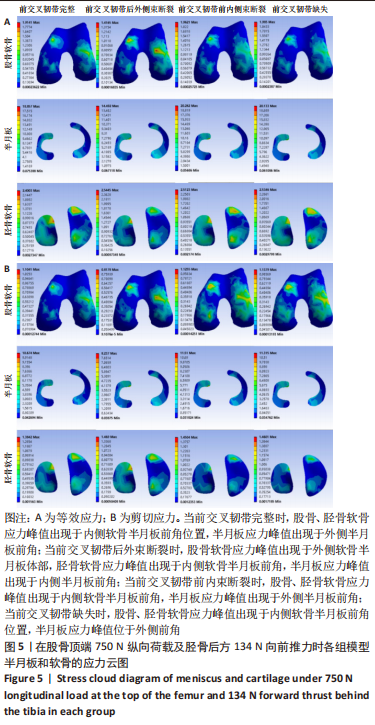
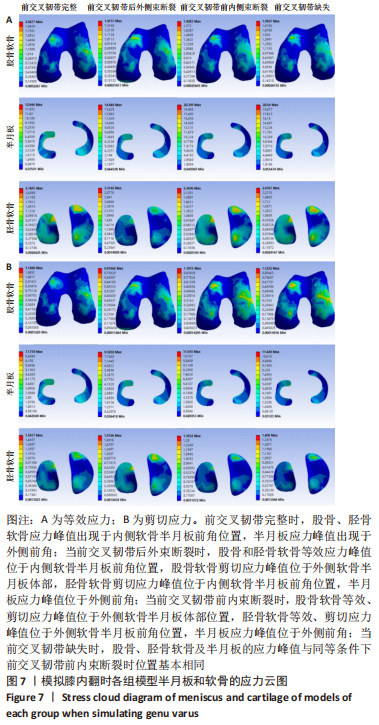
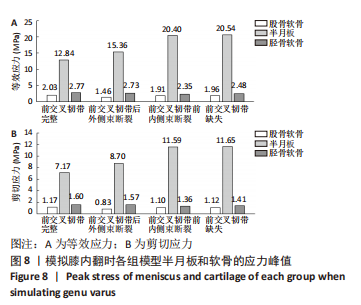
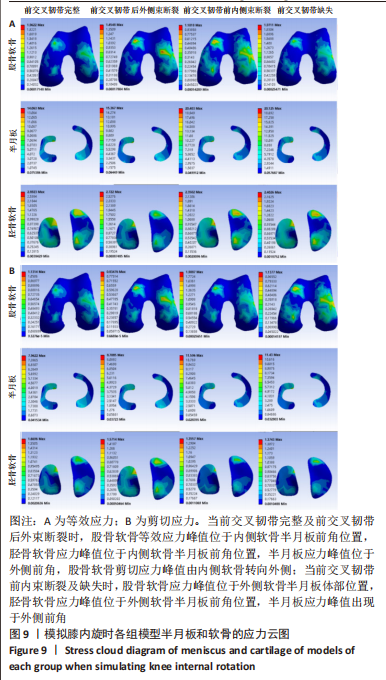
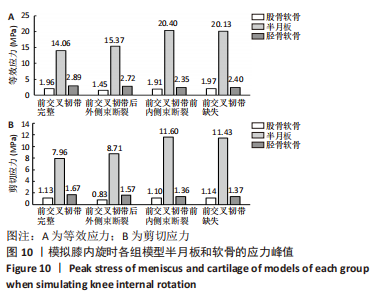
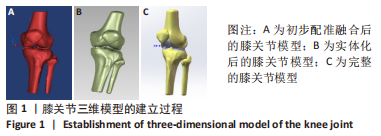
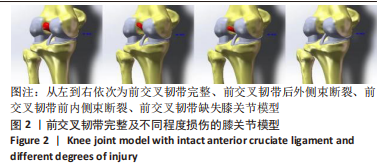
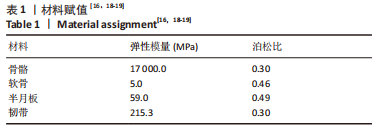
[1] ABRUSCATO K, BROWNING K, DELEANDRO D, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of the lever sign in detecting anterior cruciate ligamet tears:a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2019;14(1):2-13.
[2] PERKINS CA, WILLIMON SC. Pediatric anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction.Orthop Clin North Am. 2020;51(1):55-63.
[3] UĞUR L. Comparison of reaction forces on the anterior cruciate and anterolateral ligaments during internal rotation and anterior drawer forces at different flexion angles of the knee joint. Int J Med Robot. 2017;13(4):e1815.
[4] 张家豪,任爽,邵嘉艺,等.前交叉韧带生物力学止点重建的解剖学与有限元分析[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2019,51(3):586-590.
[5] ISMAIL SA, BUTTON K, SIMIC M, et al. Three-dimensional kinematic and kinetic gait deviations in individuals with chronic anterior cruciate ligament deficient knee: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2016;35:68-80.
[6] 时会娟,丁立,任爽,等.前交叉韧带重建术后步行过程中的生物力学特征[J].科技导报,2020,38(6):25-33.
[7] AKALıN Y, AVCı Ö, İNCE Sİ, et al. Comparison of cases with anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction accompanied by simultaneous medial meniscus bucket handle tear repair and isolated medial meniscus bucket handle tear repair. J Knee Surg. 2022;35(11):1242-1248.
[8] ZSIDAI B, NARUP E, SENORSKI EH, et al. The knee injury and osteoarthritis outcome score: shortcomings in evaluating knee function in persons undergoing ACL reconstruction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022; 30(11):3594-3598.
[9] JONES MH, SPINDLER KP. Risk factors for radiographic joint space narrowing and patient reported outcomes of post-traumatic osteoarthritis after ACL reconstruction: Data from the MOON cohort. J Orthop Res. 2017;35(7): 1366-1374.
[10] 黄竞敏,胡文晋,李冬超,等.陈旧性前交叉韧带损伤伴发内侧半月板撕裂与胫骨平台后倾角相关性研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2017,37(18): 1156-1162.
[11] 颜冰,王和鸣.膝半月板载荷的压敏片测量[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2010,18(2):1-2.
[12] 陈凯宁,农明善,叶青,等.前交叉韧带缺失对膝半月板各部分应力影响的有限元研究[J].中国运动医学杂志,2017,36(7):594-598.
[13] YAO J, SNIBBE J, MALONEY M, et al. Stresses and strains in the medial meniscus of an ACL deficient knee under anterior loading: a finite element analysis with image-based experimental validation. J Biomech Eng. 2006; 128(1):135-141.
[14] NG AW, GRIFFITH JF, HUNG EH, et al. MRI diagnosis of ACL bundle tears: value of oblique axial imaging. Skeletal Radiol. 2013;42(2):209-217.
[15] 周天平,徐一宏,徐卫东.前交叉韧带损伤处理相关国际指南解读及其临床应用[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2021,15(6):718-724.
[16] 王俊然,杜玮瑾,王长江,等.有限元分析不同屈曲状态下胫-股关节的生物力学变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(31):4975-4981.
[17] 王健全,敖英芳,刘平,等.前交叉韧带股骨止点临床解剖学研究[J].中国运动医学杂志,2007,26(3): 266-270.
[18] 张晓辉,王俊,廖八根.前交叉韧带重建联合内侧半月板部分切除术后不同屈膝状态下胫股关节生物力学变化的有限元分析[J].中国医药导报,2021,18(27):30-34.
[19] REN S, SHI H, LIU Z, et al. Finite element analysis and experimental validation of the anterior cruciate ligament and implications for the injury mechanism. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022;9(10):590.
[20] PEÑA E, CALVO B, MARTÍNEZ MA, et al. A three-dimensional finite element analysis of the combined behavior of ligaments and menisci in the healthy human knee joint. J Biomech. 2006;39(9):1686-1701.
[21] NI Q, WANG X, GUO Q, et al. High-grade pivot-shift phenomenon after anterior cruciate ligament injury is associated with asymmetry of lateral and medial compartment anterior tibial translation and lateral meniscus posterior horn tears. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022;30(11): 3700-3707.
[22] DHILLON MS, RANGASAMY K, RAJNISH RK, et al. Paediatric anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries: current concepts review. Indian J Orthop. 2022;56(6):952-962.
[23] 陈彦飞,鲁超,赵勇,等.基于CT影像动态膝关节有限元模型的构建及仿真力学分析[J].中国骨伤,2020,33(5):479-484.
[24] 陈文栋,李彦林,许鹏,等.基于MRI建立膝关节前交叉韧带三维数字化模型[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(52):9725-9728.
[25] 吴冰,陆伟,田毅,等.基于MRI快速建立前交叉韧带三维数字化模型初步报道[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2014,32(5):571-579.
[26] 张吉超,董跃福,牟志芳,等.骨关节炎患者在不同步态角度下膝关节内部生物力学变化的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(9): 1357-1361.
[27] UNAL OK, DAGTAS MZ, DEMIR C, et al. The ffects of roximal ibular steotomy on the nee and nkle oints: a inite lement nalysis. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2021;88(4):313-320.
[28] 李冰言,张吉超,张震,等.基于有限元分析的重度膝骨关节炎膝关节生物力学研究[J].医学研究生学报,2021,34(10): 1052-1056.
[29] 吴铮,任静,万建杉,等.步态周期下半月板损伤对膝关节生物力学性能的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(21):3299-3303.
[30] ZHANG KJ, LI L, YANG LF, et al. Effect of degenerative and radial tears of the meniscus and resultant meniscectomy on the knee joint: a finite element analysis. J Orthop Transl. 2019;18:20-31.
[31] XIE F, YANG L, GUO L, et al. A Study on Construction Three-Dimensional Nonlinear Finite Element Model and Stress Distribution Analysis of Anterior Cruciate Ligament. J Biomech Eng. 2009;131(12):121007.
[32] 谢峰.ACL功能缺失对膝半月板、关节软骨影响的临床和有限元仿真研究[D].重庆:第三军医大学,2010.
|