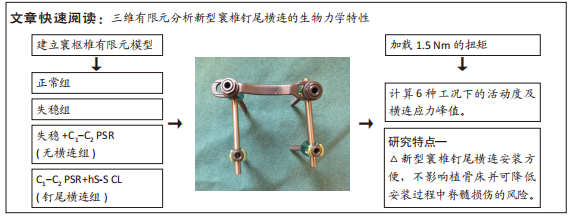
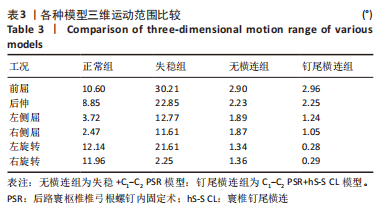
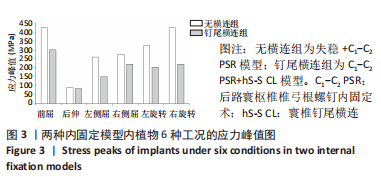
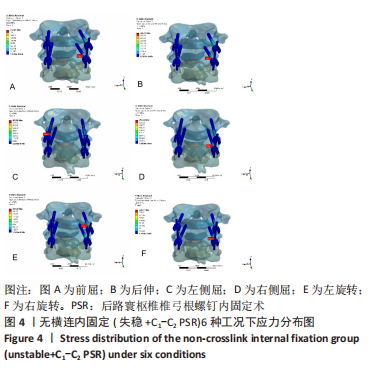
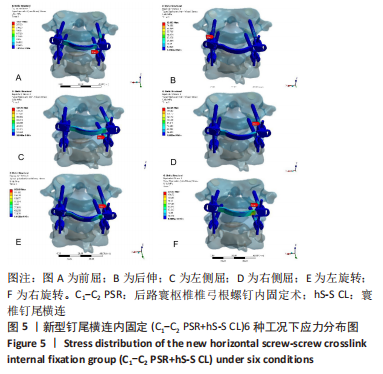
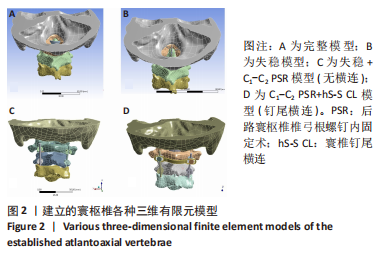
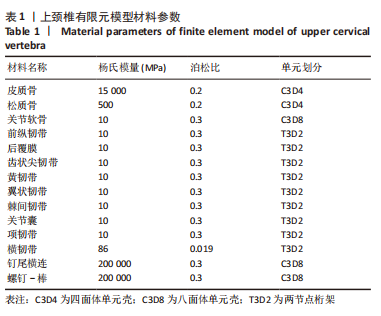
[1] ZHANG L, WANG H. Biomechanical Effects of Lateral Inclination C1 and C2 Pedicle Screws on Atlantoaxial Fixation. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(7): 2027-2033.
[2] TATTER C, FLETCHER-SANDERSJÖÖ A, PERSSON O, et al. Fluoroscopy-Assisted C1-C2 Posterior Fixation for Atlantoaxial Instability: A Single-Center Case Series of 78 Patients. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022;58(1):114.
[3] UNNI C, PETTAKKANDY V, P AJ, et al. Atlantoaxial Stabilization by Posterior C1 and C2 Screw-Rod Fixation for Various Pathologies: Case Series and Comprehensive Review of Literature. J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2021;12(2):228-235.
[4] DU JY, AICHMAIR A, KUEPER J, et al. Biomechanical analysis of screw constructs for atlantoaxial fixation in cadavers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2015;22(2):151-161.
[5] OUYANG B, ZOU X, LUO C, et al. Finite Element Analysis of Horizontal Screw-Screw Crosslink Used in C1-C2 Pedicle Screw-Rod Fixation. Med Sci Monit. 2021;27:e932026.
[6] MIZUNO T, SAKAKIBARA T, YOSHIKAWA T, et al. Biomechanical Stability of a Cross-Rod Connection with a Pedicle Screw System. Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 2018;24:26-30.
[7] CORNAZ F, WIDMER J, SNEDEKER JG, et al. Cross-links in posterior pedicle screw-rod instrumentation of the spine: a systematic review on mechanical, biomechanical, numerical and clinical studies. Eur Spine J. 2021;30(1):34-49.
[8] MIZUTANI J, INADA A, KATO K, et al. Advantages of an on-the-screwhead crosslink connector for atlantoaxial fixation using the Goel/Harms technique. J Clin Neurosci. 2018;50:183-189.
[9] 陈金水, 倪斌, 陈博,等.寰枢椎脱位三维非线性有限元模型的建立和分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2010,20(9):749-753.
[10] 马向阳,钟世镇,刘景发,等.寰椎椎弓根螺钉进钉点的解剖定位研究[J].骨与关节损伤杂志,2003,18(10):683-685.
[11] 马向阳, 尹庆水, 吴增晖,等.枢椎椎弓根螺钉进钉点的解剖定位研究[J].中华外科杂志,2006,44(8):562-564.
[12] CAI XH, LIU ZC, YANG Y, et al. Evaluation of biomechanical properties of anterior atlantoaxial transarticular locking plate system using three-dimensional finite element analysis. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(12):2686-2694.
[13] ZHANG BC, LIU HB, CAI XH, et al. Biomechanical comparison of a novel transoral atlantoaxial anchored cage with established fixation technique - a finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:261.
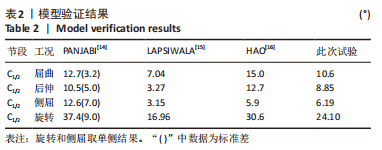
[14] PANJABI MM, DVORÁK J, CRISCO J, et al. Instability in injury of the alar ligament. A biomechanical model. Orthopade. 1991;20(2):112-120.
[15] LAPSIWALA SB, ANDERSON PA, OZA A, et al. Biomechanical Comparison of Four C1 to C2 Rigid Fixative Techniques: Anterior Transarticular, Posterior Transarticular, C1 to C2 Pedicle, and C1 to C2 Intralaminar Screws. Neurosurgery. 2006;58(3):516-521; discussion 516-522.
[16] HAO Z, JING B. Nonlinear Finite Element Analysis of C0-C1-C2 Complex under Physiologic Loads. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2005;2005:6165-6167.
[17] YUAN B, ZHOU S, CHEN X, et al. Gallie technique versus atlantoaxial screw-rod constructs in the treatment of atlantoaxial sagittal instability: a retrospective study of 49 patients. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):105.
[18] CAVALCANTI KUßMAUL A, KÜHLEIN T, GREINER A, et al. Improving stability of atlantoaxial fusion: a biomechanical study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2022 Dec 22. doi: 10.1007/s00590-022-03465-y.
[19] GU Y, HE S, WANG Y, et al. Biomechanical analysis of atlantoaxial intraarticular fusion cages with posterior pedicle screws fixation using finite element method. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2022;98:105735.
[20] ERBULUT DU, MUMTAZ M, ZAFARPARANDEH I, et al. Biomechanical Study on Three Screw-Based Atlantoaxial Fixation Techniques: A Finite Element Study. Asian Spine J. 2022;16(6):831-838.
[21] CHEN Q, CHEN J, CHEN F, et al. Biomechanics of the effect of subaxial cervical spine degeneration on atlantoaxial complex in idiopathic retro-odontoid pseudotumor development. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020;106314. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.106314.
[22] ZANG Q, LI J, LIU Y, et al. Atlantoaxial Non-Fusion Using Biomimetic Artificial Atlanto-Odontoid Joint: Technical Innovation and Initial Biomechanical Study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2022;47(11):825-832.
[23] PROGIN A, VOUMARD B, FRIKER B, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of two dorsal and two ventral stabilization techniques for atlantoaxial joint instability in toy-breed dogs. Am J Vet Res. 2021;82(10):802-810.
[24] LI T, MA C, DU YQ, et al. The Role of Transverse Connectors in C1-C2 fixation for Atlantoaxial Instability: Is It Necessary? A Biomechanical Study - ScienceDirect. World Neurosurg. 2020;140:e212-e218.
[25] SHI L, SHEN K, DENG R, et al. Novel unilateral C1 double screw and ipsilateral C2 pedicle screw placement combined with contralateral laminar screw–rod fixation for atlantoaxial instability. Eur Spine J. 2019;28(2):362-369.
[26] NI B, ZHAO W, GUO Q, et al. Comparison of Outcomes Between C1-C2 Screw-Hook Fixation and C1-C2 Screw-Rod Fixation for Treating Reducible Atlantoaxial Dislocation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017;42(20): 1587-1593.
[27] 陈金水,林松庆,徐皓,等.两种寰枢椎后路内固定系统的三维有限元分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(13):1217-1222.
[28] 潘宝顺,唐焕章,陈金水,等.一种新型后路寰枢椎固定系统的设计及有限元分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2020,30(4)353-359.
[29] 邹小宝,马向阳,杨浩志,等.新型后路寰枢椎板间融合器生物力学特征的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(28):4529-4534.
[30] 姚文君,李才,许刚,等.重度骨质疏松条件下后路枢椎三种内固定方式的有限元分析[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2022,40(2):198-203.
[31] LIM TH, KIM JG, FUJIWARA A, et al.Biomechanical evaluation of diagonal fixation in pedicle screw instrumentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(22):2498-2503.
[32] 陶文明,彭昊,廉凯.胸腰椎椎弓根钉内固定术后螺钉断裂的原因分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(4):397-399. |