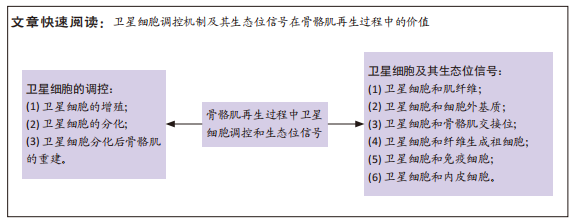
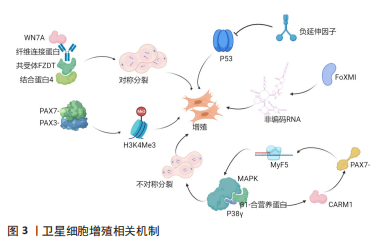
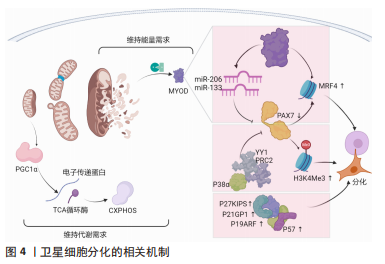
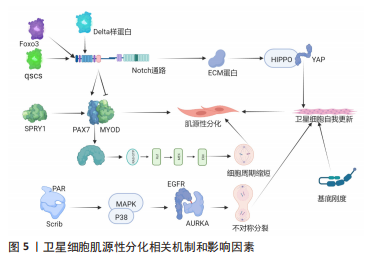
[1] FUCHS E, BLAU HM. Tissue Stem Cells: Architects of Their Niches. Cell Stem Cell. 2020;27(4):532-556.
[2] WEBSTER MT, MANOR U, LIPPINCOTT-SCHWARTZ J, et al. Intravital Imaging Reveals Ghost Fibers as Architectural Units Guiding Myogenic Progenitors during Regeneration. Cell Stem Cell. 2016;18(2):243-252.
[3] MOYLE LA, CHENG RY, LIU H, et al. Three-dimensional niche stiffness synergizes with Wnt7a to modulate the extent of satellite cell symmetric self-renewal divisions. Mol Biol Cell. 2020;31(16):1703-1713.
[4] CHANG NC, SINCENNES MC, CHEVALIER FP, et al. The Dystrophin Glycoprotein Complex Regulates the Epigenetic Activation of Muscle Stem Cell Commitment. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;22(5):755-768.e6.
[5] 王屿萌,廖苾芝,周达岸.大鼠骨骼肌挫伤修复过程中p38MAPK通路、炎症反应的作用[J].中国老年学杂志,2021,41(19):4340-4344.
[6] ROBINSON DCL, RITSO M, NELSON GM, et al. Negative elongation factor regulates muscle progenitor expansion for efficient myofiber repair and stem cell pool repopulation. Dev Cell. 2021;56(7):1014-1029.e7.
[7] CHEN Z, BU N, QIAO X, et al. Forkhead Box M1 Transcriptionally Regulates the Expression of Long Noncoding RNAs Snhg8 and Gm26917 to Promote Proliferation and Survival of Muscle Satellite Cells. Stem Cells. 2018;36(7):1097-1108.
[8] DIAO Y, GUO X, LI Y, et al. Pax3/7BP is a Pax7- and Pax3-binding protein that regulates the proliferation of muscle precursor cells by an epigenetic mechanism. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;11(2):231-241.
[9] MASSENET J, GARDNER E, CHAZAUD B, et al. Epigenetic regulation of satellite cell fate during skeletal muscle regeneration. Skelet Muscle. 2021; 11(1):4.
[10] PALA F, DI GIROLAMO D, MELLA S, et al. Distinct metabolic states govern skeletal muscle stem cell fates during prenatal and postnatal myogenesis. J Cell Sci. 2018; 131(14):jcs212977.
[11] RYALL JG, DELL’ORSO S, DERFOUL A, et al. The NAD(+)-dependent SIRT1 deacetylase translates a metabolic switch into regulatory epigenetics in skeletal muscle stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;16(2):171-183.
[12] SREENIVASAN K, RODRÍGUEZ-DELAROSA A, KIM J, et al. CHD4 ensures stem cell lineage fidelity during skeletal muscle regeneration. Stem Cell Reports. 2021;16(9):2089-2098.
[13] SREENIVASAN K, IANNI A, KÜNNE C, et al. Attenuated Epigenetic Suppression of Muscle Stem Cell Necroptosis Is Required for Efficient Regeneration of Dystrophic Muscles. Cell Rep. 2020;31(7):107652.
[14] CHEN X, YUAN J, XUE G, et al. Translational control by DHX36 binding to 5’UTR G-quadruplex is essential for muscle stem-cell regenerative functions. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):5043.
[15] TAYLOR MV, HUGHES SM. Mef2 and the skeletal muscle differentiation program. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017;72:33-44.
[16] WOSCZYNA MN, PEREZ CARBAJAL EE, WAGNER MW, et al. Targeting microRNA-mediated gene repression limits adipogenic conversion of skeletal muscle mesenchymal stromal cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2021;28(7):1323-1334.e8.
[17] 徐齐宇,王锋,张全兵,等.生肌调节因子在肌肉发育、发生和再生中的作用[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2021,43(6):571-576.
[18] HORI S, HIRAMUKI Y, NISHIMURA D, et al. PDH-mediated metabolic flow is critical for skeletal muscle stem cell differentiation and myotube formation during regeneration in mice. FASEB J. 2019;33(7):8094-8109.
[19] HOFFMANN C, HÖCKELE S, KAPPLER L, et al. The effect of differentiation and TGFβ on mitochondrial respiration and mitochondrial enzyme abundance in cultured primary human skeletal muscle cells. Sci Rep. 2018; 8(1):737.
[20] LAUTAOJA JH, PEKKALA S, PASTERNACK A, et al. Differentiation of Murine C2C12 Myoblasts Strongly Reduces the Effects of Myostatin on Intracellular Signaling. Biomolecules. 2020;10(5):695.
[21] YUCEL N, WANG YX, MAI T, et al. Glucose Metabolism Drives Histone Acetylation Landscape Transitions that Dictate Muscle Stem Cell Function. Cell Rep. 2019;27(13):3939-3955.e6.
[22] SHINTAKU J, PETERSON JM, TALBERT EE, et al. MyoD Regulates Skeletal Muscle Oxidative Metabolism Cooperatively with Alternative NF-κB. Cell Rep. 2016;17(2):514-526.
[23] MILLAY DP, O’ROURKE JR, SUTHERLAND LB, et al. Myomaker is a membrane activator of myoblast fusion and muscle formation. Nature. 2013;499(7458):301-305.
[24] ZHANG Q, VASHISHT AA, O’ROURKE J, et al. The microprotein Minion controls cell fusion and muscle formation. Nat Commun. 2017;8:15664.
[25] QUINN ME, GOH Q, KUROSAKA M, et al. Myomerger induces fusion of non-fusogenic cells and is required for skeletal muscle development. Nat Commun. 2017;8:15665.
[26] TOMIDA T, ADACHI-AKAHANE S. Roles of p38 MAPK signaling in the skeletal muscle formation, regeneration, and pathology. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2020;155(4):241-247.
[27] 贺舟,常青,唐成林,等.大鼠骨骼肌急性损伤后早期运动训练和按摩对肌卫星细胞增殖相关因子的影响[J].中国康复理论与实践,2020, 26(1):49-54.
[28] HU X, LI J, FU M, et al. The JAK/STAT signaling pathway: from bench to clinic. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):402.
[29] MANDL M, WAGNER SA, HATZMANN FM, et al. Sprouty1 Prevents Cellular Senescence Maintaining Proliferation and Differentiation Capacity of Human Adipose Stem/Progenitor Cells. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2020; 75(12):2308-2319.
[30] GARCÍA-PRAT L, PERDIGUERO E, ALONSO-MARTÍN S, et al. FoxO maintains a genuine muscle stem-cell quiescent state until geriatric age. Nat Cell Biol. 2020; 22(11):1307-1318.
[31] ZHOU B, LIN W, LONG Y, et al. Notch signaling pathway: architecture, disease, and therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):95.
[32] TROY A, CADWALLADER AB, FEDOROV Y, et al. Coordination of satellite cell activation and self-renewal by Par-complex-dependent asymmetric activation of p38α/β MAPK. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;11(4):541-553.
[33] GUREVICH DB, NGUYEN PD, SIEGEL AL, et al. Asymmetric division of clonal muscle stem cells coordinates muscle regeneration in vivo. Science. 2016;353(6295):aad9969.
[34] COSGROVE BD, GILBERT PM, PORPIGLIA E, et al. Rejuvenation of the muscle stem cell population restores strength to injured aged muscles. Nat Med. 2014; 20(3):255-264.
[35] CHOI IY, LIM HT, CHE YH, et al. Inhibition of the Combinatorial Signaling of Transforming Growth Factor-Beta and NOTCH Promotes Myotube Formation of Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Skeletal Muscle Progenitor Cells. Cells. 2021;10(7):1649.
[36] 赵莉娟,张宏,张国辉,等.Hippo信号通路在骨骼肌损伤修复中作用的研究进展[J].山东医药,2020,60(1):109-112.
[37] EVANO B, KHALILIAN S, LE CARROU G, et al. Dynamics of Asymmetric and Symmetric Divisions of Muscle Stem Cells In Vivo and on Artificial Niches. Cell Rep. 2020;30(10):3195-3206.e7.
[38] 陈炜,陈雨诗,刘禹熙,等.自噬对再生中肌肉干细胞的作用[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2022,44(3):484-491.
[39] LI EW, MCKEE-MUIR OC, GILBERT PM. Cellular Biomechanics in Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2018;126:125-176.
[40] SAMPATH SC, SAMPATH SC, HO ATV, et al. Induction of muscle stem cell quiescence by the secreted niche factor Oncostatin M. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1531.
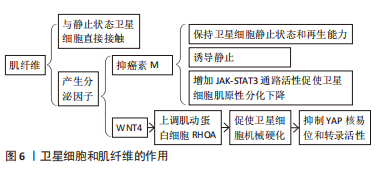
[41] ELIAZER S, MUNCIE JM, CHRISTENSEN J, et al. Wnt4 from the Niche Controls the Mechano-Properties and Quiescent State of Muscle Stem Cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2019;25(5):654-665.e4.
[42] BRIGHTWELL CR, LATHAM CM, THOMAS NT, et al. A glitch in the matrix: the pivotal role for extracellular matrix remodeling during muscle hypertrophy. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022;323(3):C763-C771.
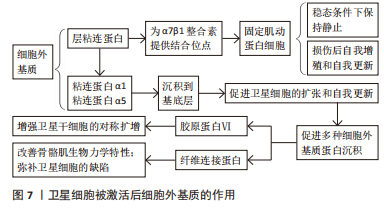
[43] ROZO M, LI L, FAN CM. Targeting β1-integrin signaling enhances regeneration in aged and dystrophic muscle in mice. Nat Med. 2016;22(8):889-896.
[44] 李伦宇,靳松林,黄增浩,等.肌卫星细胞自我更新及其信号调控的应用热点及问题[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(2):304-310.
[45] TIERNEY MT, GROMOVA A, SESILLO FB, et al. Autonomous Extracellular Matrix Remodeling Controls a Progressive Adaptation in Muscle Stem Cell Regenerative Capacity during Development. Cell Rep. 2016;14(8):1940-1952.
[46] TAKENAKA-NINAGAWA N, KIM J, ZHAO M, et al. Collagen-VI supplementation by cell transplantation improves muscle regeneration in Ullrich congenital muscular dystrophy model mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):446.
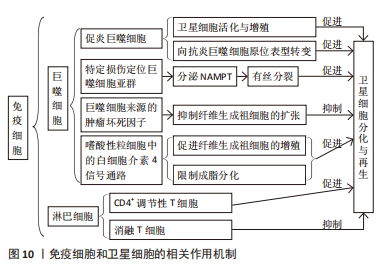
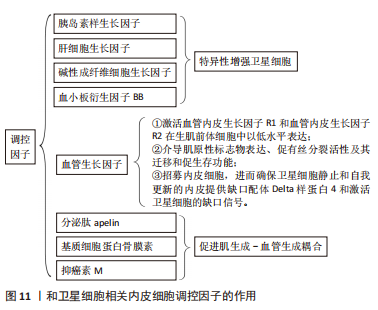
[47] RATNAYAKE D, NGUYEN PD, ROSSELLO FJ, et al. Macrophages provide a transient muscle stem cell niche via NAMPT secretion. Nature. 2021; 591(7849):281-287.
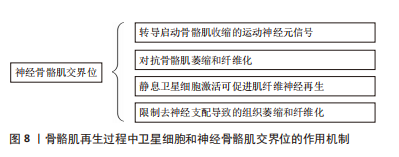
[48] LIU W, CHAKKALAKAL JV. The Composition, Development, and Regeneration of Neuromuscular Junctions. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2018;126:99-124.
[49] MADARO L, PASSAFARO M, SALA D, et al. Denervation-activated STAT3-IL-6 signalling in fibro-adipogenic progenitors promotes myofibres atrophy and fibrosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20(8):917-927.
[50] LIU L, YUE X, SUN Z, et al. Reduction of senescent fibro-adipogenic progenitors in progeria-aged muscle by senolytics rescues the function of muscle stem cells. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022;13(6):3137-3148.
[51] BRITTO FA, GNIMASSOU O, DE GROOTE E, et al. Acute environmental hypoxia potentiates satellite cell-dependent myogenesis in response to resistance exercise through the inflammation pathway in human. FASEB J. 2020;34(1):1885-1900.
[52] ARCHACKA K, GRABOWSKA I, MIERZEJEWSKI B, et al. Hypoxia preconditioned bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal/stem cells enhance myoblast fusion and skeletal muscle regeneration. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):448.dPMC8351116.
[53] SHANG M, CAPPELLESSO F, AMORIM R, et al. Macrophage-derived glutamine boosts satellite cells and muscle regeneration. Nature. 2020; 587(7835):626-631.
[54] CHEN A, TANG S, HE J, et al. Small extracellular vesicles from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells: a potential promoter of fat graft survival. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):263.
[55] KOPINKE D, ROBERSON EC, REITER JF. Ciliary Hedgehog Signaling Restricts Injury-Induced Adipogenesis. Cell. 2017;170(2):340-351.e12.
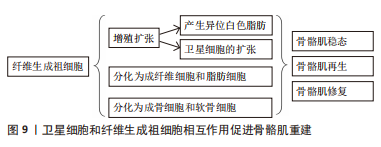
[56] MALECOVA B, GATTO S, ETXANIZ U, et al. Dynamics of cellular states of fibro-adipogenic progenitors during myogenesis and muscular dystrophy. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):3670.
[57] LEMOS DR, BABAEIJANDAGHI F, LOW M, et al. Nilotinib reduces muscle fibrosis in chronic muscle injury by promoting TNF-mediated apoptosis of fibro/adipogenic progenitors. Nat Med. 2015;21(7):786-794.
[58] DE OLIVEIRA RC, WILSON SE. Fibrocytes, Wound Healing, and Corneal Fibrosis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020;61(2):28.
[59] 王伦平,陈蕊,严金川,等.巨噬细胞在不同组织再生中的研究进展[J].中国病理生理杂志,2021,37(3):565-570.
[60] 张子涵,杨欢,黄庆生,等.细胞因子介导的骨骼肌系统与免疫系统间调控网络[J].医用生物力学,2022,37(2):374-378.
[61] 程建红,洪莉,洪莎莎,等.巨噬细胞在骨骼肌损伤再生中的研究进展[J].医学综述,2021,27(16):3125-3129.
[62] HEREDIA JE, MUKUNDAN L, CHEN FM, et al. Type 2 innate signals stimulate fibro/adipogenic progenitors to facilitate muscle regeneration. Cell. 2013; 153(2):376-388.
[63] BAHT GS, BAREJA A, LEE DE, et al. Meteorin-like facilitates skeletal muscle repair through a Stat3/IGF-1 mechanism. Nat Metab. 2020;2(3):278-289.
[64] BURZYN D, KUSWANTO W, KOLODIN D, et al. A special population of regulatory T cells potentiates muscle repair. Cell. 2013;155(6):1282-1295.
[65] 彭勇,孙飙,戴剑松.调节性T细胞影响骨骼肌损伤再生能力机制的研究进展[J].生命的化学,2020,40(11):2053-2061.
[66] KOIKE H, MANABE I, OISHI Y. Mechanisms of cooperative cell-cell interactions in skeletal muscle regeneration. Inflamm Regen. 2022;42(1):48.
|