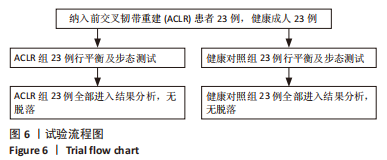
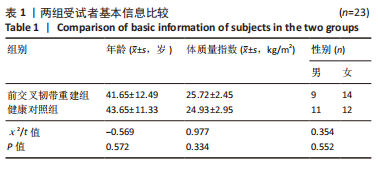
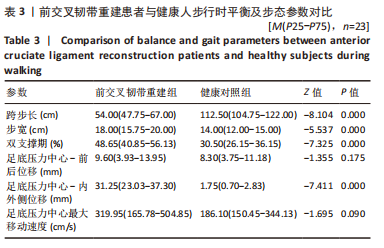
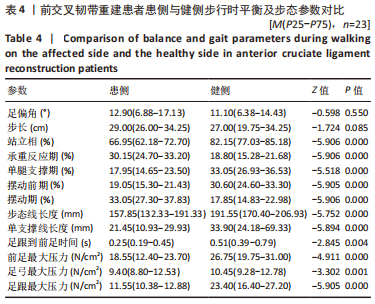
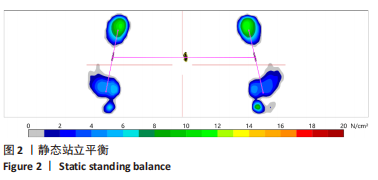
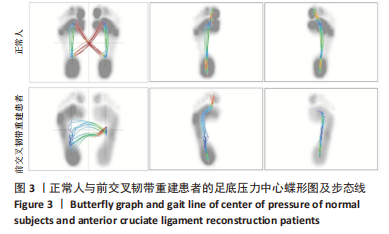
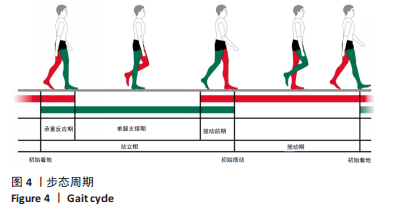
[1] 吴铭杰, 李亮, 张晓强, 等. 关节镜下双袢钛板悬吊重建膝关节前交叉韧带的稳定性[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(18):2878-2883.
[2] 高奉, 李方祥, 李国平. 前交叉韧带的机械感受器与本体感觉[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2012,31(6):541-547.
[3] 陈家, 魏世隽, 王洪. 关节镜下韧带重建术治疗前交叉韧带损伤的研究进展[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(16):1489-1494.
[4] FREEMAN MA, WYKE B. Articular contributions to limb muscle reflexes. The effects of partial neurectomy of the knee-joint on postural reflexes. Br J Surg. 1966; 53(1): 61-68.
[5] KENNEDY JC, ALEXANDER IJ, HAYES KC. Nerve supply of the human knee and its functional importance. Am J Sports Med. 1982;10(6):329-335.
[6] 张磊, 李义凯. 膝关节前交叉韧带本体感觉的研究进展[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2017,32(2):245-247.
[7] 王宇彤, 白伦浩, 温昱, 等. 前交叉韧带断裂后不同状态韧带残端内机械感受器的变化[J]. 中国综合临床,2018,34(1):34-37+97.
[8] MUSAHL V, KARLSSON J. Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear. N Engl J Med. 2019; 380(24):2341-2348.
[9] MONTALVO AM, SCHNEIDER DK, WEBSTER KE, et al. Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury Risk in Sport: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Injury Incidence by Sex and Sport Classification. J Athl Train. 2019;54(5):472-482.
[10] MONTALVO AM, SCHNEIDER DK, YUT L, et al. “What’s my risk of sustaining an ACL injury while playing sports?” A systematic review with meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2019;53(16):1003-1012.
[11] 周志鹏, 曲峰, 刘鹏, 等. 不同方向单腿跳跃落地及运动疲劳对非接触性前交叉韧带损伤风险的影响[J]. 中国体育科技,2017,53(1):111-117.
[12] GAO B, ZHENG NN. Alterations in three-dimensional joint kinematics of anterior cruciate ligament-deficient and -reconstructed knees during walking. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2010;25(3):222-229.
[13] RICHMOND JC. Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2018;26(4):165-167.
[14] HERZOG MM, MARSHALL SW, LUND JL, et al. Trends in Incidence of ACL Reconstruction and Concomitant Procedures Among Commercially Insured Individuals in the United States, 2002-2014. Sports Health. 2018;10(6):523-531.
[15] ROSSI R, COTTINO U, BRUZZONE M, et al. Total knee arthroplasty in the varus knee: tips and tricks. Int Orthop. 2019;43(1):151-158.
[16] LEE HM, CHENG CK, LIAU JJ. Correlation between proprioception, muscle strength, knee laxity, and dynamic standing balance in patients with chronic anterior cruciate ligament deficiency. Knee.2009;16(5):387-391.
[17] MELNYK M, FAIST M, GOTHNER M, et al. Changes in stretch reflex excitability are related to “giving way” symptoms in patients with anterior cruciate ligament rupture. J Neurophysiol. 2007;97(1):474-480.
[18] 李玉周, 王婧怡, 胡英琪. 前交叉韧带重建术后短期足底压力分布及平衡特征研究[J]. 体育科学,2020,40(5):52-59.
[19] 马钊, 周谋望, 谷莉, 等. 前交叉韧带重建术后患者平衡功能的研究[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2010,25(7):625-627+631.
[20] GOKALP O, AKKAYA S, AKKAYA N, et al. Preoperative and postoperative serial assessments of postural balance and fall risk in patients with arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2016;29(2):343-350.
[21] WILLIAMS GN, SNYDER-MACKLER L, BARRANCE PJ, et al. Quadriceps femoris muscle morphology and function after ACL injury: a differential response in copers versus non-copers. J Biomech. 2005;38(4):685-693.
[22] PALMIERI-SMITH RM, MCLEAN SG, ASHTON-MILLER JA, et al. Association of quadriceps and hamstrings cocontraction patterns with knee joint loading. J Athl Train. 2009;44(3):256-263.
[23] GRANACHER U, GOLLHOFER A, HORTOBÁGYI T, et al. The importance of trunk muscle strength for balance, functional performance, and fall prevention in seniors: a systematic review. Sports Med. 2013;43(7):627-641.
[24] FERNANDES TL, FELIX EC, BESSA F, et al. Evaluation of static and dynamic balance in athletes with anterior cruciate ligament injury - A controlled study. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2016;71(8):425-429.
[25] KAPRELI E, ATHANASOPOULOS S, GLIATIS J, et al. Anterior cruciate ligament deficiency causes brain plasticity: a functional MRI study. Am J Sports Med. 2009; 37(12):2419-2426.
[26] THOMAS AC, WOJTYS EM, BRANDON C, et al. Muscle atrophy contributes to quadriceps weakness after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Sci Med Sport. 2016;19(1):7-11.
[27] TOURVILLE TW, VOIGT TB, CHOQUETTE RH, et al. Skeletal muscle cellular contractile dysfunction after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction contributes to quadriceps weakness at 6-month follow-up. J Orthop Res. 2022;40(3):727-737.
[28] ALFAYYADH A, NEAL K, WILLIAMS JR, et al. Limb and sex-related differences in knee muscle co-contraction exist 3 months after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2022;66:102693.
[29] HOWELLS BE, CLARK RA, ARDERN CL, et al. The assessment of postural control and the influence of a secondary task in people with anterior cruciate ligament reconstructed knees using a Nintendo Wii Balance Board. Br J Sports Med. 2013; 47(14):914-919.
[30] YU PA, FAN CH, KUO LT, et al. Differences in gait and muscle strength of patients with acute and chronic anterior cruciate ligament injury. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2020;80:105161.
[31] POZZI F, DI STASI S, ZENI JA JR, et al. Single-limb drop landing biomechanics in active individuals with and without a history of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: A total support analysis. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2017;43: 28-33.
[32] THOMA LM, GRINDEM H, LOGERSTEDT D, et al. Coper Classification Early After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Rupture Changes With Progressive Neuromuscular and Strength Training and Is Associated With 2-Year Success: The Delaware-Oslo ACL Cohort Study. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47(4):807-814.
[33] SHIMIZU T, SAMAAN MA, TANAKA MS, et al. Abnormal Biomechanics at 6 Months Are Associated With Cartilage Degeneration at 3 Years After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. Arthroscopy. 2019;35(2):511-520.
[34] WEBSTER KE, HEWETT TE. Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury and Knee Osteoarthritis: An Umbrella Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin J Sport Med. 2022;32(2):145-152.
[35] CHEN T, WANG S, LI Y, et al. Radiographic Osteoarthritis Prevalence Over Ten Years After Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. Int J Sports Med. 2019; 40(11):683-695.
[36] MANICKAM A, GARDINER MD. Gait assessment in general practice. Aust J Gen Pract. 2021;50(11):801-806.
[37] 马启寿,廖燕锬,李中元,等. FES辅助跑步机训练提高脑卒中下肢偏瘫患者步行能力的研究[J]. 按摩与康复医学,2022,13(14):22-25,28.
[38] 董元丽,高华,杨瑞贞, 等. 脑血管储备功能与老年人步态及平衡功能的相关性[J]. 中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2021,23(11):1125-1128.
[39] 章雨威,张秋霞,袁金凤. 不同速度下功能性踝关节不稳者与常人步态参数的比较研究. 中国康复医学杂志,2015,30(11):1151-1154.
[40] LYLE MA, JENSEN JC, HUNNICUTT JL, et al. Identification of strength and spatiotemporal gait parameters associated with knee loading during gait in persons after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Athl Train. 2021. doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-0186.21.
|