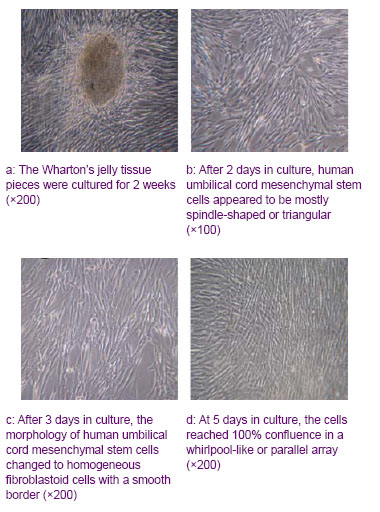
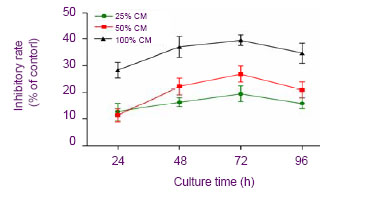
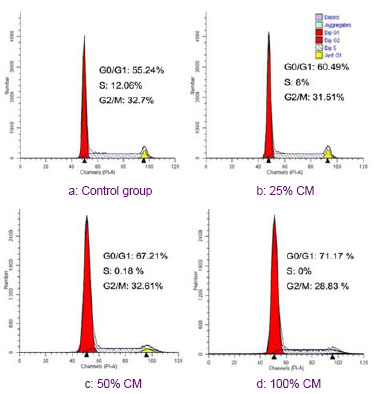
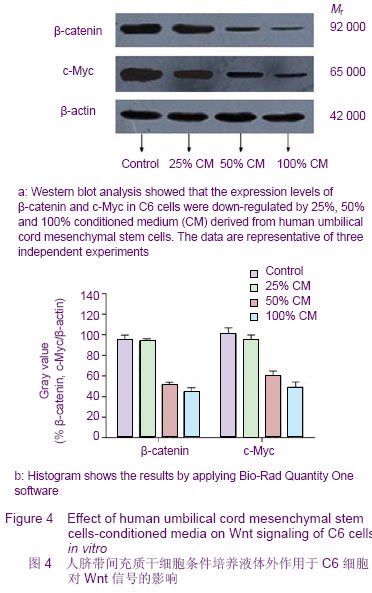
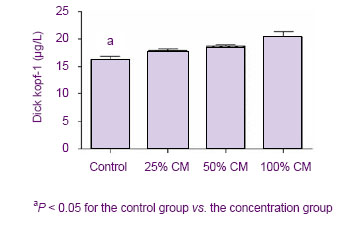
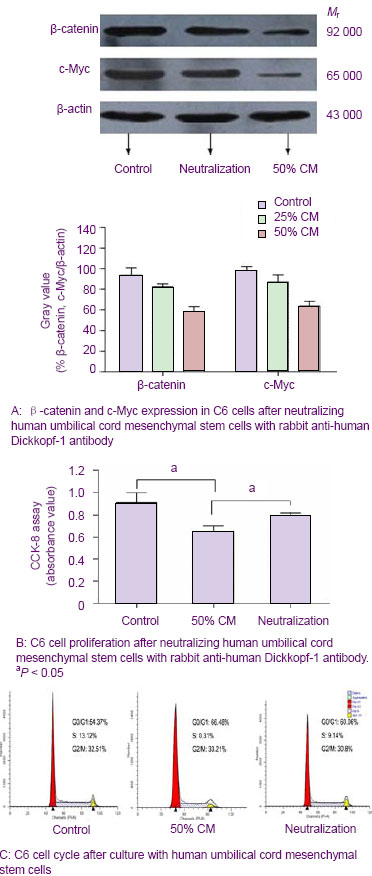
| [1] Donato V, Papaleo A, Castrichino A, et al. Prognostic implication of clinical and pathologic features in patients with glioblastoma multiforme treated with concomitant radiation plus temozolomide. Tumori. 2007;93(3):248-256.[2] Kang SG, Kim JH, Nam DH,et al. Clinical and radiological prognostic factors of anaplastic oligodendroglioma treated by combined therapy. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2005; 45(5): 232-238. [3] Scheda A, Finjap JK, Tuettenberg J, et al. Ef?cacy of different regimens of adjuvant radiochemotherapy for treatment of glioblastoma. Tumori.2007; 93(1):31-36.[4] Fagioli F, Berger M, Braeh del Preyer A, et al.Regression of metastatic oateosmcoma following non-myeloab]ative stem cell transplantation.Haenmtologiea. 2003; 88(5):16.[5] Omuro Y, Matsumote G, Sasaki T, et al.Regression of nunresectable pancreatic tumor following nonmyeloablative allogeneic peripheral-blood stem-cell transplantation.Bone Marrow Transplant.2003; 31(10):943-945.[6] Kim S K, Cargioll TG, Machluf Mt, et al.PEX-Producing human neural stem cells inhibit tumor growth in a mouse g1ioma model.Clin Cancer Res. 2005; 11(16):5965-5970.[7] Khakoo AY, Pati S, Anderson SA, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells exert potent antitumorigenic effects in a model of Kaposi’s sarcoma.J Exp Med.2006; 203(5):1235-1247.[8] Jiao HL, Guan FX, Yang B,et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibit C6 glioma via downregulation of cyclin D1. Neurology India.2011; 59(2): 241-247.[9] Yang F, Zeng Q, Yu G,et al.Wnt/beta-catenin signaling inhibits death receptor-mediated apoptosis and promotes invasive growth of HNSCC. Cell Signal.2006; 18(2):679-687.[10] Baek SH, Kioussi C, Briata P. Regulated subset of G1 growth-control genes in response to derepression by the Wnt pathway. Proc Natl Acad USA.2003;100(6): 3245-3250.[11] Brott BK, Sokol SY. Regulation of Wnt/LRP signaling by distinct domains of Dickkopf proteins. Mol Cell Biol.2002; 22(17):6100-6110.[12] Chen G, Shukeir N, Potti A, et al. Up-regulation of Wnt-1 and beta-catenin production in patients with advanced metastatic prostate carcinoma: potential pathogenetic and prognosticimplications. Cancer. 2004; 101(6):1345-1356.[13] Byun T, Karimi M, Marsh JL, et al. Expression of secreted Wnt antagonists in gastrointestinal tissues: potential role in stem cell homeostasis. J Clin Pathol. 2005; 58(5):515-519.[14] Mao B, Wu W, Li Y, et al. LDL-receptor-related protein 6 is a receptor for Dickkopf proteins. Nature.2001; 411(6835): 321-325.[15] Karahuseyinoglu S, Cinar O, Kilic E, et al. Biology of stem cells in human umbilical cord stroma: in situ and in vitro surveys. Stem Cells.2007; 25(2) :319-331.[16] Livraghi T, Meloni F, Frosi A, et al. Treatment with stem cell differentiation stage factors of intermediate-advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Res. 2005;15(7/8):399-408.[17] Lu YR, Yuan Y, Wang XJ,et al. The growth inhibitory effect of mesenchymal stem cells on tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Biol Ther. 2008; 7(2):245-251.[18] Qiao L, Xu ZL, Zhao TJ,et al. Dkk-1 secreted by mesenchymal stem cells inhibits growth of breast cancer cells via depression of Wnt signaling. Cancer Lett. 2008; 269(1): 67-77.[19] Moon RT, Kohn AD, De Ferrari GV,et al. Wnt and β-catenin signalling: diseases and therapies.Nat Rev Genet. 2004; 5(9): 691-701.[20] Fodde R, Brabletz T. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in cancer stemness and malignant behavior. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007; 19(2):150-158.[21] Glennie S, Soeiro I, Dyson PJ,et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induce division arrest anergy of activated T cells. Blood. 2005; 105(7): 2821-2827. [22] Corcione A, Benvenuto F, Ferretti E, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate B-cell functions. Blood. 2006; 107(1): 367-372.[23] Sotiropoulou PA, Perez SA, Gritzapis AD,et al. Interactions between human mesenchymal stem cells and natural killer cells. Stem Cells.2006; 24(1): 74-85.[24] Zhu Y, Sun Z, Han Q, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells inhibit cancer cell proliferation by secreting DKK-1. Leukemia. 2009; 23(5):925-933.[25] Meisel R, Zibert A, Laryea M,et al. Human bone marrow stromal cells inhibit allogeneic T-cell responses by indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase-mediated tryptophan degradation. Blood.2004; 103(12): 4619-4621.[26] Qiao L, Xu ZL, Zhao TJ, et al. Suppression of tumorigenesis by human mesenchymal stem cells in a hepatoma model. Cell Res. 2008;18(12): 500-507. [27] Ramasamy R, Lam EF, Soeiro I, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit proliferation and apoptosis of tumor cells: impact on in vivo tumor growth. Leukemia.2007; 21(2):304–310.[28] Zhu W, Xu W, Jiang R, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow favor tumor cell growth in vivo. Exp Mol Pathol.2006; 80(3): 267-274.[29] Ma Y, Hao XM, Zhang S,et al. The in vitro and in vivo effects of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on the growth of breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat.2011; 80(1): 267-274.[30] Studeny M, Marini FC, Dembinski JL.Mesenchymal stem cells: potential precursors for tumor stroma and targeted-delivery vehicles for anticancer agents, J. Natl. Cancer Inst.2004; 96 (21):1593–1603. |