中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (30): 4873-4878.doi: 10.12307/2022.768
• 干细胞基础实验 basic experiments of stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
川楝子醇提物通过线粒体途径诱导白血病CEM细胞的凋亡
吴慧婷,朱大诚,徐笑明,常 娜
- 江西中医药大学,江西省南昌市 330004
Ethanol extract of toosendan induces apoptosis of leukemia CEM cells through mitochondrial pathway
Wu Huiting, Zhu Dacheng, Xu Xiaoming, Chang Na
- Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330004, Jiangxi Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
细胞凋亡的线粒体途径:细胞凋亡主要包括3种途径,其中线粒体途径为最重要的途径之一,当细胞受到如癌基因激活、缺氧等刺激时,可导致线粒体膜电位下降,有序折叠的嵴变得宽大,线粒体通透性转换孔开放诱导线粒体膜通透性增加,进而促进相关凋亡因子的释放,最终导致细胞死亡。
川楝子醇提物:川楝子为楝科植物的干燥成熟果实,经体积分数为80%乙醇提取,乙酸乙酯分离可得到主要药用成分川楝素,其具有神经递质抑制、驱虫及抗癌等作用,能有效抑制肿瘤细胞增殖及促进细胞凋亡,是一个极具潜力的候选抗癌药物。
CME细胞:是一种来源于人急性T淋巴细胞白血病患者外周血中的白血病细胞株,在体外悬浮生长,呈圆球状。
背景:苦寒中药川楝子具有小毒,对生长环境要求不高,在实体瘤中能显著抑制肿瘤细胞的增殖,但在血液肿瘤中报道较少,基于前期研究结果,并结合中医“以毒攻毒”理论探讨其主要成分川楝素抗急性淋巴细胞白血病的作用机制。
目的:探究川楝子醇提物抑制白血病CEM细胞增殖的作用机制。
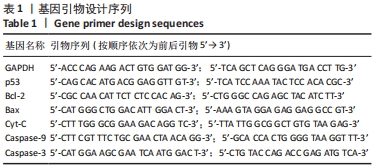
方法:人急性T淋巴细胞白血病CEM细胞培养至对数生长期,经5种浓度梯度川楝子醇提物作用24,48,72 h后,通过MTT实验求得各组细胞抑制率。考虑到受渗透压影响并保证后续实验的开展,筛选出川楝子醇提物低、中、高质量浓度(16,80,400 mg/L),作用大鼠外周血淋巴细胞24,48,72 h,采用MTT实验和吉姆萨-瑞氏染色探究其毒性作用,通过Hoechst 33258染色观察CEM细胞凋亡小体,RT-qPCR实验检测川楝子醇提物作用CEM细胞24,48 h后p53、Bcl-2、Bax、Cyt-C、Caspase-9和Caspase-3 基因转录情况,Western blot实验检测川楝子醇提物作用CEM细胞24,48 h后p53、Bcl-2、Bax蛋白的表达。
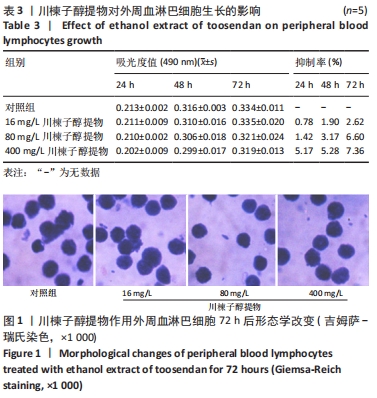
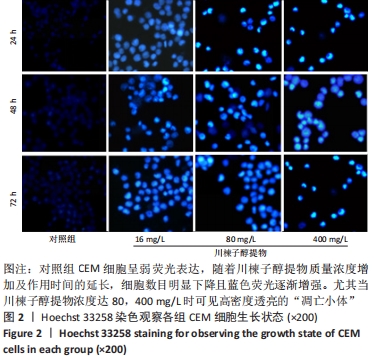
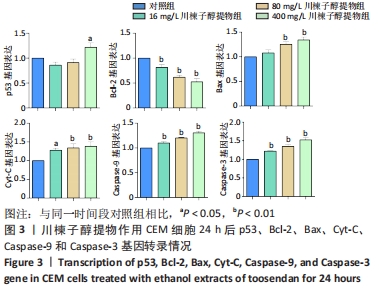
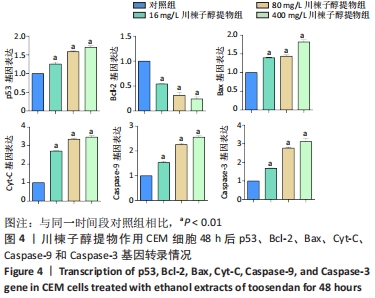
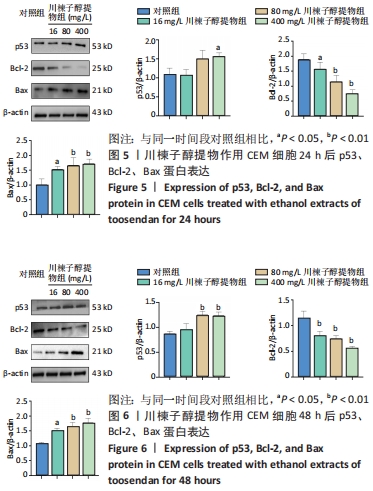
结果与结论:①16,80,400 mg/L川楝子醇提物对正常淋巴细胞无明显抑制作用;②16,80,400 mg/L川楝子醇提物作用CEM细胞经Hoechst 33258染色能看到蓝色亮光的凋亡小体;③与对照组比较,80,400 mg/L川楝子醇提物作用CEM细胞后能提高p53、Bax、Cyt-C、Caspase-9和Caspase-3基因转录水平(P < 0.05或P < 0.01),降低Bcl-2基因转录水平(P < 0.05或P < 0.01),尤其以48 h较为突出;④给药24 h后,相较于对照组,16,80,400 mg/L川楝子醇提物组Bcl-2蛋白表达下调,Bax蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05或P < 0.01),400 mg/L川楝子醇提物组p53蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05),给药48 h后,相较于对照组,80,400 mg/L川楝子醇提物组p53蛋白表达明显上调(P < 0.01),Bcl-2蛋白表达下调(P < 0.05或P < 0.01),Bax蛋白表达则显著升高(P < 0.05或P < 0.01);⑤结果表明,川楝子醇提物能显著抑制白血病CEM细胞的增殖,在一定范围内呈现浓度和时间依赖性,其机制可能是通过诱导线粒体介导的细胞凋亡途径来实现的。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1232-2061 (吴慧婷)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: