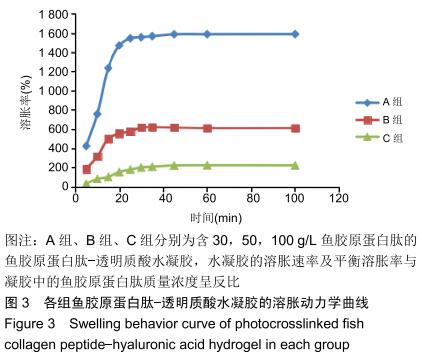
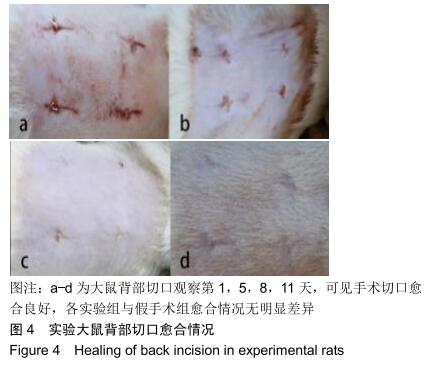
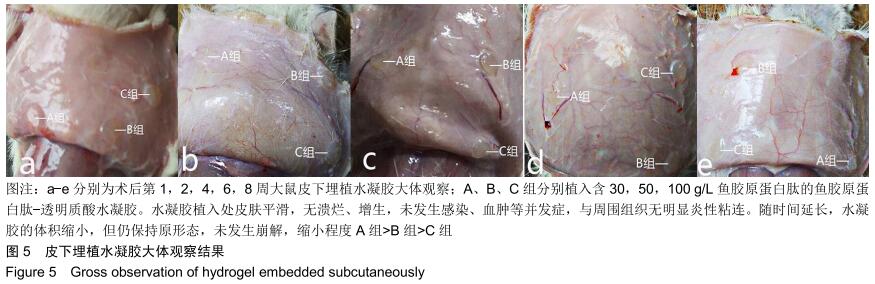
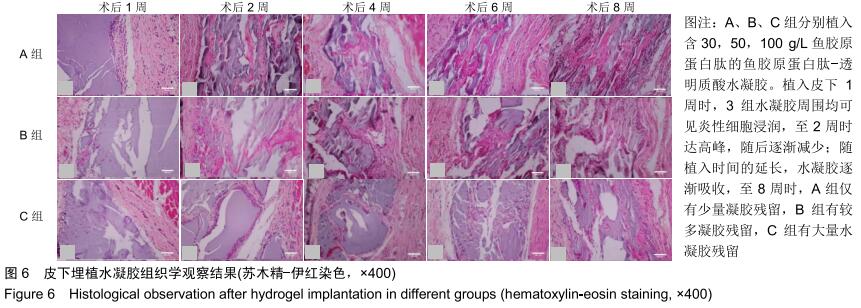
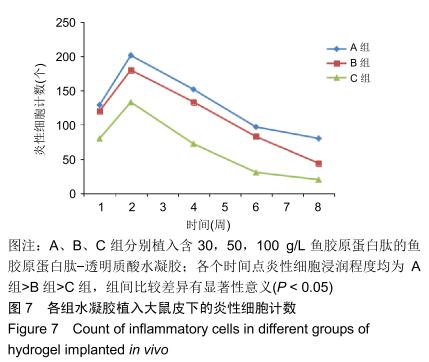
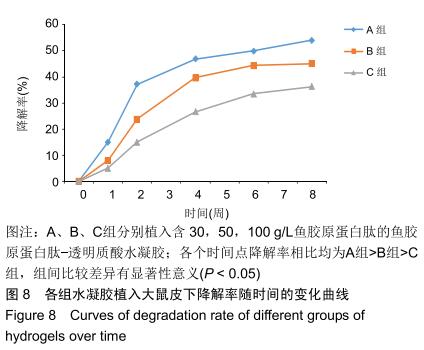
|
[1] 高春华,黄新友.组织工程与生物材料[J].上海生物医学工程, 2003,24(4):46-49.
[2] COSTA A, NARANJO JD, LONDONO R, et al. Biologic Scaffolds.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med.2017;7(9).pii: a025676. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a025676.
[3] 王馨,屈雷,窦忠英,等.组织工程生物支架材料[J].中国生物工程杂志,2003,23(10):15-18.
[4] BADYLAK SF, FREYTES DO, GILBERT TW. Reprint of: Extracellular matrix as a biological scaffold material: Structure and function.Acta Biomater.2015;23:S17-S26.
[5] 崔曼,张欣,马丽桃,等.新型三维复合仿生网络的构建及其组织相容性评价[J].天津医药, 2015,43(3):233-236.
[6] CHEUNG HK, HAN TT, MARECAK DM, et al. Composite hydrogel scaffolds incorporating decellularized adipose tissue for soft tissue engineering with adipose-derived stem cells. Biomaterials.2014;35(6):1914-1923.
[7] AHMED EM. Hydrogel: Preparation, characterization, and applications: A review.J Adv Res. 2015;6(2):105-121.
[8] ZHAO X, IRVINE SA, AGRAWAL A, et al. 3D patterned substrates for bioartificial blood vessels- The effect of hydrogels on aligned cells on a biomaterial surface.Acta Biomater.2015;26:159-168.
[9] DA SILVA DOMINGUES JF, ROEST S, WANG Y, et al. Macrophage phagocytic activity toward adhering staphylococci on cationic and patterned hydrogel coatings versus common biomaterials.Acta Biomater.2015;18:1-8.
[10] GOUJON LJ, SANTOSH H, BAHAREH S, et al. Tunable hydrogel thin films from reactive synthetic polymers as potential two-dimensional cell scaffolds.Langmuir. 2015; 31(20):5623.
[11] HOFFMAN AS. Hydrogels for biomedical applications. Ann N Y Acad Sci.2012;64(1):18-23.
[12] QIU Y, PARK K. Environment-sensitive hydrogels for drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2012;64(3):49-60.
[13] MALINEN MM, KANNINEN LK, CORLU A, et al. Differentiation of liver progenitor cell line to functional organotypic cultures in 3D nanofibrillar cellulose and hyaluronan-gelatin hydrogels. Biomaterials.2014;35(19): 5110-5121.
[14] PARHI R. Cross-Linked Hydrogel for Pharmaceutical Applications: A Review.Adv Pharm Bull. 2017;7(4):515-530.
[15] 李静静,郭璇,解军,等.琼脂糖/明胶/透明质酸/细胞外基质水凝胶的制备与性能表征[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(18): 2900-2908.
[16] NAAHIDI S, JAFARI M, LOGAN M, et al. Biocompatibility of hydrogel-based scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Biotechnol Adv.2017;35(5):530-544.
[17] SPANG MT, CHRISTMAN KL. Extracellular matrix hydrogel therapies: In vivo applications and development.Acta Biomater. 2018;68:1-14.
[18] SALDIN LT, CRAMER MC, VELANKAR SS, et al. Extracellular Matrix Hydrogels from Decellularized Tissues: Structure and Function.Acta Biomater.2016;49:1-15.
[19] XIE B, JIN L, LUO Z, et al. An injectable thermosensitive polymeric hydrogel for sustained release of Avastin® to treat posterior segment disease.Int J Pharm.2015;490(1): 375-383.
[20] PATI F, DATTA P, ADHIKARI B, et al. Collagen scaffolds derived from fresh water fish origin and their biocompatibility.J Biomed Mater Res A.2012;100A(4):1068-1079.
[21] NAGAI N, NAKAYAMA Y, ZHOU YM, et al. Development of salmon collagen vascular graft: mechanical and biological properties and preliminary implantation study.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2010;87B(2):432-439.
[22] YAMADA S, YAMAMOTO K, IKEDA T, et al. Potency of Fish Collagen as a Scaffold for Regenerative Medicine.Biomed Res Int.2014;2014(4976):302932.
[23] XU Y, WANG X. Application of 3D biomimetic models in drug delivery and regenerative medicine. Curr Pharm Des. 2015; 21(12):1618-1626.
[24] FERNÁNDEZ-GARCÍA L, MARÍ-BUYÉ N, BARIOS JA, et al. Safety and tolerability of silk fibroin hydrogels implanted into the mouse brain.Acta Biomater.2016;45:262-275.
[25] GUZIEWICZ N, BEST A, PEREZ-RAMIREZ B, et al. Lyophilized silk fibroin hydrogels for the sustained local delivery of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. Biomaterials. 2011;32(10):2642-2650.
[26] KOGAN G, ŠOLTÉS L, STERN R, et al. Hyaluronic acid: a natural biopolymer with a broad range of biomedical and industrial applications.Biotechnol Lett.2007;29(1):17-25.
[27] HSIEH MF, SHEU CL, YANG HW. Micro-Lithographic Fabrication of Collagen and Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Scaffolds. Adv Mater Res.2013;647:170-175.
[28] 曹璐娟.透明质酸超分子凝胶及纳米凝胶的制备及生物医学应用研究[D].无锡:江南大学,2014.
[29] VALMIKINATHAN CM, MUKHATYAR VJ, JAIN A, et al. Photocrosslinkable chitosan based hydrogels for neural tissue engineering.Soft Matter.2012;8(6):1964-1976.
[30] CHIEN HW, CHENG PH, CHEN SY, et al. Low-fouling and functional poly(carboxybetaine) coating via a photo-crosslinking process.Biomater Sci.2017;5(3):523-531.
[31] CREDI C, DE MC, MOLENA E, et al. Direct photo-patterning of hyaluronic acid baits onto a fouling-release perfluoropolyether surface for selective cancer cell capture and immobilization. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2016;62: 414-422.
[32] KIM S, LEE S, LEE J, et al. Tissue adhesive, rapid forming, and sprayable ECM hydrogel via recombinant tyrosinase crosslinking.Biomaterials.2018;178:401-412.
[33] GHUMAN H, GERWIG M, NICHOLLS FJ, et al. Long-term retention of ECM hydrogel after implantation into a sub-acute stroke cavity reduces lesion volume.Acta Biomater. 2017;63: 50-63.
[34] AHEARNE M. Development of an ECM hydrogel for corneal tissue engineering.Acta Ophthalmol.2014;92(s253).DOI: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.2014.1726.x.
[35] LIU C. Development of an ECM-mimetic, Electrospun Hydrogel Scaffold for Soft Tissue Repair Application. Dissertations & Theses-Gradworks,2014.
[36] HIROAKI S, SHUNJI Y, EIJI K, et al. In vivo biological responses and bioresorption of tilapia scale collagen as a potential biomaterial.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2009;20(10): 1353-1368.
[37] 魏志君,施春英,程连强,等.鱼胶原蛋白肽-透明质酸水凝胶制备及其生物相容性[J].青岛大学医学院学报,2017,53(5):600-603.
[38] BRIGHAM MD, ALEXANDER B, EDWARD L, et al. Mechanically robust and bioadhesive collagen and photocrosslinkable hyaluronic acid semi-interpenetrating networks.Tissue Eng Part A.2009;15(7):1645.
[39] RINAUDO M. Chitin and chitosan: Properties and applications. Cheminform.2007;31(7):603-632.
[40] 刘捷,王芳,马盈盈,等.热处理对聚乙烯醇/胶原水解物复合膜性能的影响[J].中国皮革, 2010,39(15):13-15.
[41] 周慧通,方大为,王波,等.冷冻干燥法制备CS/AMPS/PEGDA光交联多孔水凝胶及其性能[J].材料科学与工程学报, 2015,33(3): 432-437.
[42] 赵江,蒋国强,孙佳丽,等.释药用壳聚糖温敏凝胶体内外形态与溶蚀降解研究[J].高校化学工程学报, 2010,24(3):456-461.
[43] KAMATH KR, PARK K. Biodegradable hydrogels in drug delivery.Adv Drug Deliv Rev.1993;11(1):59-84.
[44] JIN S, BIAN F, LIU M, et al. Swelling mechanism of porous P(VP-co-MAA)/PNIPAM semi-IPN hydrogels with various pore sizes prepared by a freeze treatment.Polym Int. 2010; 58(2):142-148.
[45] KIM SW, YOU HB, OKANO T. Hydrogels: Swelling, Drug Loading, and Release.Pharm Res.1992;9(3):283-290.
[46] LIM YH, KIM D, LEE DS. Drug releasing characteristics of thermo- and pH-sensitive interpenetrating polymer networks based on poly (N-isopropylacrylamide).J Appl Polym Sci. 1997; 64(13):2647-2655.
[47] 杨兵,侯萍,张会,等.光聚合型pH敏感水凝胶的制备及药物缓释性能[J].高分子材料科学与工程, 2019,35(4):19-25.
[48] ABUREESH MA, OLADIPO AA, GAZI M. Facile synthesis of glucose-sensitive chitosan-poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogel: Drug release optimization and swelling properties.Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;90:75-80.
[49] 胡杨,蒋远干,但卫华,等.胃蛋白酶提取猪皮胶原的研究[J].中国皮革,2010,39(23):11-16.
[50] ZHANG W, WANG X, MA J, et al. Preparation of chitosan/pumpkin polysaccharide hydrogel for potential application in drug delivery and tissue engineering.J Porous Mater. 2017;24(2):497-506.
[51] 宋福来,刘万顺,韩宝芹.壳聚糖即型水凝胶的理化性质、止血功能和生物相容性研究[J].功能材料, 2014,45(9):9065-9069.
[52] 郭清奎,吕志前,张袆,等.新型可完全降解材料聚外消旋乳酸-三亚甲基碳酸酯聚合物体内降解行为和组织相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(34):6368-6374.
[53] HUANG KF, HSU WC, HSIAO JK, et al. Collagen-glycosaminoglycan matrix implantation promotes angiogenesis following surgical brain trauma.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014(3):672409.
[54] LIM SM, SONG DK, OH SH, et al. In vitro and in vivo degradation behavior of acetylated chitosan porous beads.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2012;19(4):453-466.
[55] 符锋,秦喆,李晓红,等.胶原/壳聚糖复合支架植入大鼠不同部位降解速率的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(6):864-870.
[56] GORHAM SD, LIGHT ND, DIAMOND AM, et al. Effect of chemical modifications on the susceptibility of collagen to proteolysis. II. Dehydrothermal crosslinking.Int J Biol Macromol.1992;14(3):129-138.
[57] HUTMACHER DW. Scaffolds in tissue engineering bone and cartilage.Biomaterials. 2000;21(24):2529-2543.
[58] LUO J, MENG Y, ZHENG L, et al. Fabrication and characterization of Chinese giant salamander skin composite collagen sponge as a high-strength rapid hemostatic material. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2019;30(4):247-262.
[59] 杨中民.明胶—透明质酸/纳米生物玻璃复合材料的制备及性能研究[D].湘潭:湖南科技大学,2013.
[60] WEI Y, CHANG YH, LIU CJ, et al. Integrated Oxidized-Hyaluronic Acid/Collagen Hydrogel with beta-TCP Using Proanthocyanidins as a Crosslinker for Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics. 2018;10(2):37.
[61] 吴炜,毛天球,封兴华,等.胶原-透明质酸支架的制备及其与软骨细胞复合培养的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2007, 21(4):401-405.
[62] 陈琳,吕洋,管利东,等.生物支架材料胶原膜交联前后的特性分析[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2008,22(2):183-187.
[63] SHAHBAN S, BROWN R, CHEEMA U, et al. Enhancing the mechanical properties of collagen by photo-chemical cross-linking. Int J Surg.2012;10(8):S54.
[64] 杜国辉.交联透明质酸的制备、性质及治疗骨关节炎的疗效研究[D].济南:山东大学,2010.
[65] 顾华,何黎.透明质酸在表皮重建中生物学意义的实验研究[C].中华医学会第16次全国皮肤性病学术年会,中国广东广州,2010.
|