中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (31): 4992-4997.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1984
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
硫化氢可对膝骨关节炎模型兔关节软骨发挥保护效应
李夏楠,田少奇,王远贺,刘江俊,丁 涛,褚国庆,孙 康
- (青岛大学附属医院关节外科,山东省青岛市 266500)
Hydrogen sulfide protects articular cartilage in rabbit models of knee osteoarthritis
Li Xianan, Tian Shaoqi, Wang Yuanhe, Liu Jiangjun, Ding Tao, Chu Guoqing, Sun Kang
- (Department of Joint Surgery, the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266500, Shandong Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
胱硫醚β合成酶:是一种细胞质中的同源四聚体,在维生素B6的催化下,胱硫醚β合成酶能使丝氨酸与同型半胱氨酸合成胱硫醚,其催化L-半胱氨酸生成内源性H2S。
胱硫醚γ裂解酶:是一种参与半胱氨酸合成的酶,催化胱硫醚脱氨水解成半胱氨酸、α酮丁酸及氨,是心血管中产生的一种重要的内源性H2S酶,主要存在于血管平滑肌、内皮细胞中。
基质金属蛋白酶:是酶活性依赖锌离子蛋白酶超家族,是关节软骨基质降解最主要的蛋白水解系统。
文题释义:
胱硫醚β合成酶:是一种细胞质中的同源四聚体,在维生素B6的催化下,胱硫醚β合成酶能使丝氨酸与同型半胱氨酸合成胱硫醚,其催化L-半胱氨酸生成内源性H2S。
胱硫醚γ裂解酶:是一种参与半胱氨酸合成的酶,催化胱硫醚脱氨水解成半胱氨酸、α酮丁酸及氨,是心血管中产生的一种重要的内源性H2S酶,主要存在于血管平滑肌、内皮细胞中。
基质金属蛋白酶:是酶活性依赖锌离子蛋白酶超家族,是关节软骨基质降解最主要的蛋白水解系统。
.jpg) 文题释义:
胱硫醚β合成酶:是一种细胞质中的同源四聚体,在维生素B6的催化下,胱硫醚β合成酶能使丝氨酸与同型半胱氨酸合成胱硫醚,其催化L-半胱氨酸生成内源性H2S。
胱硫醚γ裂解酶:是一种参与半胱氨酸合成的酶,催化胱硫醚脱氨水解成半胱氨酸、α酮丁酸及氨,是心血管中产生的一种重要的内源性H2S酶,主要存在于血管平滑肌、内皮细胞中。
基质金属蛋白酶:是酶活性依赖锌离子蛋白酶超家族,是关节软骨基质降解最主要的蛋白水解系统。
文题释义:
胱硫醚β合成酶:是一种细胞质中的同源四聚体,在维生素B6的催化下,胱硫醚β合成酶能使丝氨酸与同型半胱氨酸合成胱硫醚,其催化L-半胱氨酸生成内源性H2S。
胱硫醚γ裂解酶:是一种参与半胱氨酸合成的酶,催化胱硫醚脱氨水解成半胱氨酸、α酮丁酸及氨,是心血管中产生的一种重要的内源性H2S酶,主要存在于血管平滑肌、内皮细胞中。
基质金属蛋白酶:是酶活性依赖锌离子蛋白酶超家族,是关节软骨基质降解最主要的蛋白水解系统。摘要
背景:H2S是重要的炎症调节因子,广泛存在于人体各组织器官中,在多个系统疾病中发挥着重要作用。
目的:通过研究兔膝骨关节炎模型中H2S对关节软骨退变的影响,探讨H2S对骨性关节炎的治疗作用。
方法:取32只新西兰大白兔随机分为空白对照组、骨性关节炎组、H2S干预组和抑制H2S生成组,每组8只。空白对照组不做处理,骨性关节炎组、H2S干预组和抑制H2S生成组以改良Hulth法建立骨性关节炎模型后,分别给予膝关节腔注射生理盐水、NaHS稀释液(60 μmol/L)、H2S合成酶抑制剂(氨基氧乙酸,37.5 mg/kg;炔丙基甘氨酸,60 mg/kg)各1 mL,1次/周,连续6周。实验方案于2018-03-01经青岛大学动物实验伦理委员会批准,批准号:AHQU-MAL2018032。
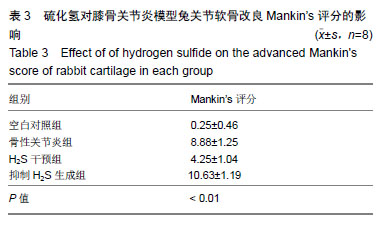
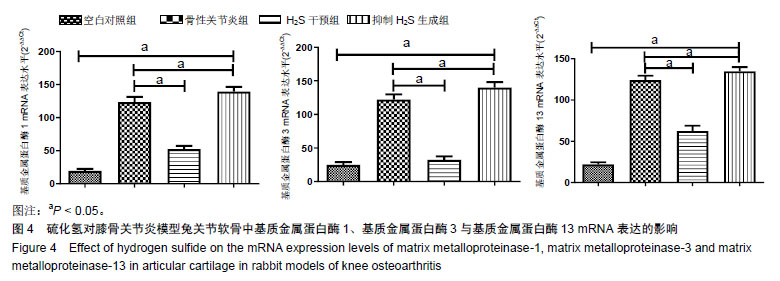
结果与结论:①病理变化:空白对照组关节软骨形态正常;骨性关节炎组关节软骨退变严重;H2S干预组关节软骨退变较轻;抑制H2S生成组关节软骨退变较骨性关节炎组更重;②Mankin’s评分:骨性关节炎组、H2S干预组和抑制H2S生成组评分较空白对照组均增加;H2S干预组较骨性关节炎组评分更低,抑制H2S生成组较骨性关节炎组评分高;③Ⅱ型胶原染色:与空白对照组比,骨性关节炎组Ⅱ型胶原阳性染色降低,分布不均;H2S干预组Ⅱ型胶原阳性染色较骨性关节炎组表达增多;抑制H2S生成组Ⅱ型胶原阳性染色降低且表浅层出现缺损;④与骨性关节炎组比较,H2S干预组关节软骨中基质金属蛋白酶1、基质金属蛋白酶3与基质金属蛋白酶13 mRNA表达水平降低;抑制H2S生成组上述mRNA表达水平增加。结果说明,H2S可以抑制关节软骨中基质金属蛋白酶1、基质金属蛋白酶3与基质金属蛋白酶13 mRNA的表达水平,减少关节软骨Ⅱ型胶原蛋白降解,对骨关节炎中的关节软骨有保护作用。
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
胱硫醚β合成酶:是一种细胞质中的同源四聚体,在维生素B6的催化下,胱硫醚β合成酶能使丝氨酸与同型半胱氨酸合成胱硫醚,其催化L-半胱氨酸生成内源性H2S。
胱硫醚γ裂解酶:是一种参与半胱氨酸合成的酶,催化胱硫醚脱氨水解成半胱氨酸、α酮丁酸及氨,是心血管中产生的一种重要的内源性H2S酶,主要存在于血管平滑肌、内皮细胞中。
基质金属蛋白酶:是酶活性依赖锌离子蛋白酶超家族,是关节软骨基质降解最主要的蛋白水解系统。
文题释义:
胱硫醚β合成酶:是一种细胞质中的同源四聚体,在维生素B6的催化下,胱硫醚β合成酶能使丝氨酸与同型半胱氨酸合成胱硫醚,其催化L-半胱氨酸生成内源性H2S。
胱硫醚γ裂解酶:是一种参与半胱氨酸合成的酶,催化胱硫醚脱氨水解成半胱氨酸、α酮丁酸及氨,是心血管中产生的一种重要的内源性H2S酶,主要存在于血管平滑肌、内皮细胞中。
基质金属蛋白酶:是酶活性依赖锌离子蛋白酶超家族,是关节软骨基质降解最主要的蛋白水解系统。