| [1] 贾焕英.膝关节软骨损伤磁共振扫描序列临床应用价值的研究[J].中国药物与临床,2017,17(6):826-827.[2] 林昊,张余,李国安.人工全膝关节研究新进展[J].医用生物力学, 2012,27(2):115-121.[3] 李春娥.膝关节有限元模型研究进展[J].科技经济导刊,2017, 1(9):158.[4] Tanska P, Mononen ME, Korhonen RK. A multi-scale finite element model for investigation of chondrocyte mechanics in normal and medial meniscectomy human knee joint during walking. J Biomech. 2015;48(8):1397-1406.[5] Naghibi BH, Janssen D, Van GS, et al. The influence of ligament modelling strategies on the predictive capability of finite element models of the human knee joint. J Biomech. 2017;65(5):1-11.[6] Kang KT, Koh YG, Son J, et al. Finite element analysis of the biomechanical effects of 3 posterolateral corner reconstruction techniques for the knee joint. Arthroscopy. 2017;33(8):1537-1550.[7] Woiczinski M, Steinbrück A, Weber P, et al. Development and validation of a weight-bearing finite element model for total knee replacement. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2016;19(10):1033.[8] Ali AA, Shalhoub SS, Cyr AJ, et al. Validation of predicted patellofemoral mechanics in a finite element model of the healthy and cruciate-deficient knee. J Biomech. 2016;49(2): 302-309.[9] Dong R, Liu Y, Zhang X, et al. The evaluation of the role of medial collateral ligament maintaining knee stability by a finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):64-71.[10] Rybicki EF, Simonen FA, Jr WE. On the mathematical analysis of stress in the human femur. J Biomech. 1972; 5(2): 203-215.[11] Wismans J, Veldpaus F, Janssen J, et al. A three-dimensional mathematical model of the knee-joint. J Biomech. 1980;13(8): 677-679.[12] Bendjaballah MZ, Shirazi A. Biomechanics of the human knee joint in compression: reconstruction, mesh generation and finite element analysis. Knee. 1995;2(2):69-79.[13] Jilani A, Shirazi-Adl A, Bendjaballah MZ. Biomechanics of human tibio-femoral joint in axial rotation. Knee. 1997;4(4): 203-213.[14] Caruntu DI, Hefzy MS. 3-D anatomically based dynamic modeling of the human knee to include tibio-femoral and patello-femoral joints. J Biomech Eng. 2004;126(1):44-53.[15] Zielinska B, Donahue TL. 3D finite element model of meniscectomy: changes in joint contact behavior. J Biomech Eng. 2006;128(1):115-123.[16] 姜华亮,华锦明,许新忠,等.正常人膝关节三维有限元模型的建立[J].苏州大学学报:医学版,2008,28(3):421-422.[17] Baldwin MA, Clary CW, Fitzpatrick CK, et al. Dynamic finite element knee simulation for evaluation of knee replacement mechanics. J Biomech. 2012;45(3):474-483.[18] 鲍春雨,郭宝川,孟庆华.人体膝关节有限元模型建立及其有效性验证[J].应用力学学报,2017,34(3):559-563.[19] 陈文栋,杨光.不同载荷条件下半月板动态仿真生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(11):1742-1747.[20] Manda K, Ryd L, Eriksson A. Finite element simulations of a focal knee resurfacing implant applied to localized cartilage defects in a sheep model. J Biomech. 2011;44(5):794-801.[21] 崔晓倩,王辅忠,张慧春.膝关节股骨远端软骨硬化前后力学性能分析[J].医用生物力学,2015,30(1):25-29.[22] Rao C, Fitzpatrick CK. A statistical finite element model of the knee accounting for shape and alignment variability. Medical Engineering&Physics. 2013,35(10):1450-1456.[23] 万超,郝智秀,温诗铸.前交叉韧带力学特性差异对膝关节有限元仿真结果的影响[J].医用生物力学,2012,27(4):375-380.[24] Donzelli PS, Spilker RL, Ateshian GA, et al. Contact analysis of biphasic transversely isotropic cartilage layers and correlations with tissue failure. J Biomech. 1999;32(10): 1037-1047.[25] Marouane H, Shiraziadl A, Hashemi J. Quantification of the role of tibial posterior slope in knee joint mechanics and ACL force in simulated gait. J Biomech. 2015;48(10):1899-905.[26] 吴辉群,严培培,耿兴云,等.基于Mimics软件虚拟人膝关节三维图像融合实验[J].中国组织工程研究,2011,15(48):8943-8946.[27] Song Y, Debski RE, Musahl V, et al. A three -dimensional finite element model of the human anterior cruciate ligament: a computational analysis with experimental validation. J Biomech. 2004;37(3):383- 390.[28] Peña AE, Calvo B, Martã¬Nez MA, et al. A three-dimensional finite element analysis of the combined behavior of ligaments and menisci in the healthy human knee joint. J Biomech. 2006;39(9):1686-1701.[29] Suggs J, Wang C, Li G. The effect of graft stiffness on knee joint biomechanics after ACL reconstruction-a 3D computational simulation. Clin Biomech. 2003;18(1):35-43.[30] Wascher DC, Markolf KL, Shapiro MS,et al. Direct in vitro measurement of forces in the cruciate ligaments. Part I: the effect of multiplane loading in the intact knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993;75(3):377-386.[31] Morkolf K. Stiffness and laxity of the knee-the contributions of the supporting structures. J Bone Joint Surg A. 1976;58(5): 583-594.[32] Naghibi H, Khoshgoftar M, Sprengers A, et al. A comparison between dynamic implicit and explicit finite element simulations of the native knee joint. Med Eng Phys. 2016; 10(38):1123-1130.[33] 王光达,张祚福,齐晓军,等.膝关节三维有限元模型的建立及生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2010,14(52):9702-9705. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
文题释义: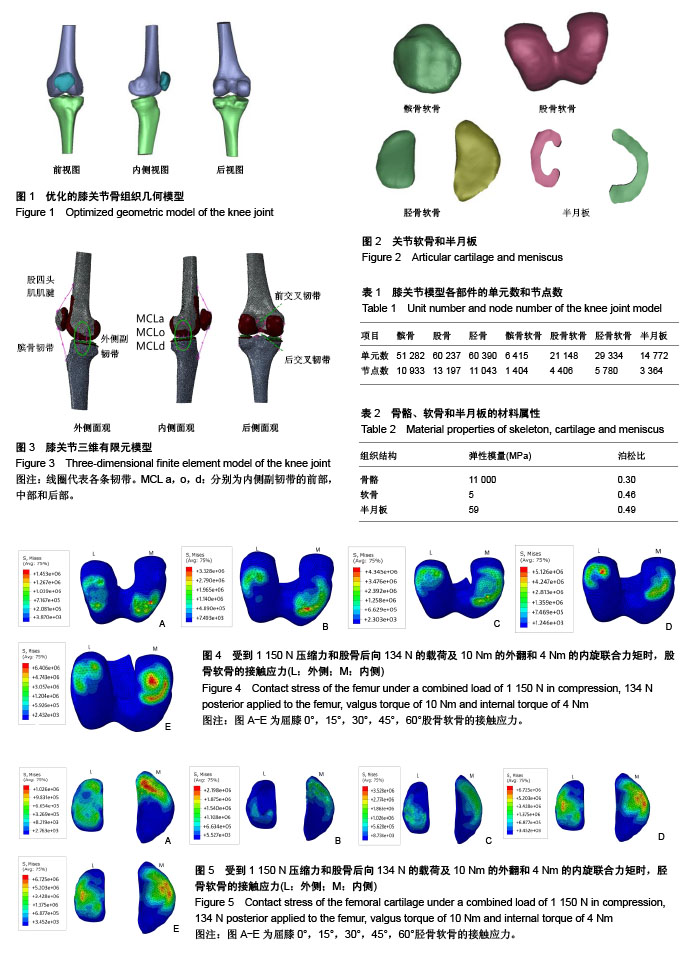
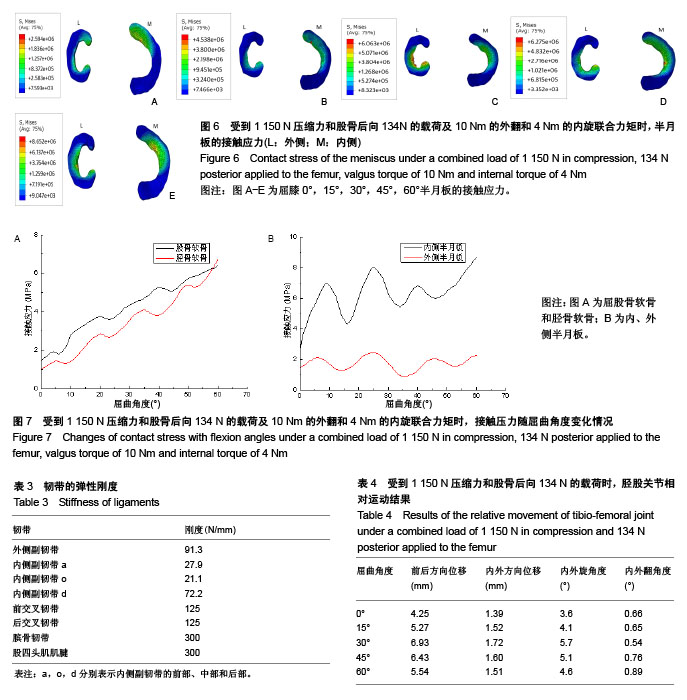
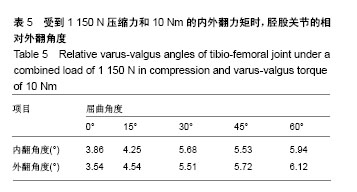
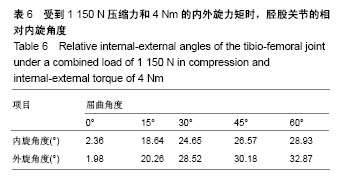
.jpg) 文题释义:
文题释义: