| [1] Williamson RV,Staheli LT.Partial physeal growth arrest: treatment by bridge resection and fat interposition.J Pediatr Orthop. 1990;10(6): 769-776.[2] Langenskiold A.The possibilities of eliminating premature partial closure of an epiphyseal plate caused by trauma or diseases.Acta Orthop Scand.1967;38:267279. [3] Martiana K,Low CK,Tan SK,et al.Comparison of various interpositional materials in the prevention of transphyseal bone bridge formation.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1996;(325):218-224.[4] Lee EH,Gao GX,Bose K.Management of partial growth arrest:physis, fat, or silastic.J Pediatr Orthop.1993;13(3): 368-372.[5] Cheon JE,Kim IO,Kim CJ,et al.Imaging findings after fat graft interposition in an injured growth plate: an experimental study in rabbits.Invest Radiol.2003;38(11):695-703.[6] Li EC,Xu RJ,Xue YL,et al.Treatment of growth plate injury with microencapsulated chondrocytes. Biotechnol Bioproc E. 2013;18: 655-662.[7] Ahn JI,Erdin RA,Smith R,et al.Chondrocyte injection in distraction epiphysiolysis (rabbit model).J Orthop Res. 2006; 24(3):355-365.[8] Lee EH,Gao GX,Bose K.Experimental studies on the prevention of growth arrest in immature rabbits. J Bone Joint Surg.1989;721-726.[9] Li W,Xu R,Huang J,et al.Treatment of rabbit growth plate injuries with oriented ECM scaffold and autologous BMSCs. Sci Rep.2017;7: 44140-44151.[10] 中华人民共和国科学技术部.关于善待实验动物的指导性意见. 2006-09-30.[11] Vaeanti CA,Langer R,Schloo B,et al. Synthetic Polymers seeded with chondroeytes provide a template for new ceartilage formation.Plast Reeonstr Surg. 1991;88(5): 753-759.[12] Hunziker EB.Articular cartilage repair: basic science and clinical progress: a review of the current status and prospects.Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2002;10(6):432-463.[13] He M,Callanan A.Comparison of methods for whole-organ decellulari- zation in tissue engineering of bioartificialorgans. Tissue Eng Part B Rev.2013;19(3):194-208.[14] Chung S,Ingle NP,Montero GA,et al.Bioresorbable elastomeric vascular tissue engineering scaffolds via melt spinning and electrospinning.Acta Biomater. 2010;6(6): 1958-1967.[15] Chen RN,Ho HO,Tsai YT,et al.Process development of an acellular dermal matrix (ADM) for biomedical applications. Biomaterials. 2004;25(13):2679-2686.[16] Rovak JM,Mungara AK,Aydin MA,et al.Effeets of vascular endothelial growth factor on nerve regeneration in aeellular nerve grafts.J Reconstr Microsurg.2004;20(1):53-58.[17] Borschel GH,Dennis RG,Kuzon WM Jr.Contraetile skeletal muscle etissue-engineered on an acellular scaffold.Plast Reeonstr Surg. 2004;113:595-602; discussion 603-604.[18] Cartmell JS,Dunn MG. Effect of chemical treatments on tendon cellularity and mechanieal properties. J Biomed Mater Res. 2000; 49(1):134-140.[19] Gilbert TW,Sellaro TL,Badylak SF.Decellularization of tissues and organs.Biomaterials.2006;27: 3675-3683.[20] Parmaksiz M,Elçin AE,Elçin YM.Decellularization of Bovine Small Intestinal Submucosa.Methods Mol Biol. 2017. doi:10.1007/7651_2017_33.[21] Nagasaka A,Hige S,Matsushima T,et al.Differential flotation centrifugation study of hepatitis C virus and response to interferon therapy.J Med Virol.1997;52(2):190-194. [22] Ye S,Su ZP,Zhang J,et al.Differential centrifugation in culture and differentiation of rat neural stem cells.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2008; 28(4):511-517.[23] 王玉,彭江,张莉,等.软骨细胞外基质/壳聚糖复合多孔支架和骨髓间充质干细胞构建组织工程软骨[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2010,18(20): 1715-1718.[24] Zhao YH,Yang Q,Xia Q,et al.In vitro cartilage production using an extracellular matrix-derived scaffold and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Chin Med J (Engl). 2013;126(16):3130-3137.[25] Yang Q,Peng J,Lu SB,et al.Evaluation of an extracellular matrix-derived acellular biphasic scaffold/cell construct in the repair of a large articular high-load-bearing osteochondral defect in a canine model.Chin Med J (Engl). 2011;124(23): 3930-3938.[26] Hunziker EB.Mechanism of longitudinal bone growth and its regulation by growth plate chondrocytes. Microsc Res Tech. 1994;28(6):505-519.[27] Abad V,Meyers JL,Weise M,et al.The role of the resting zone in growth plate chondrogenesis. Endocrinology. 2002;143(5): 1851-1857 |
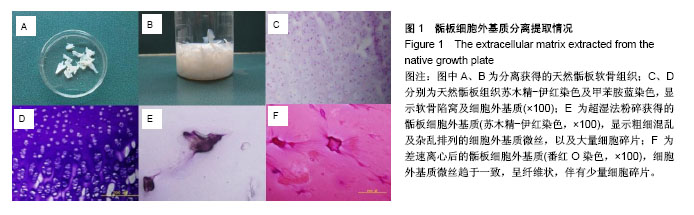
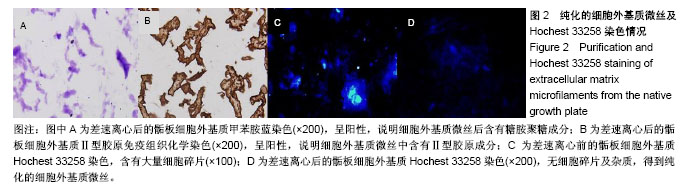
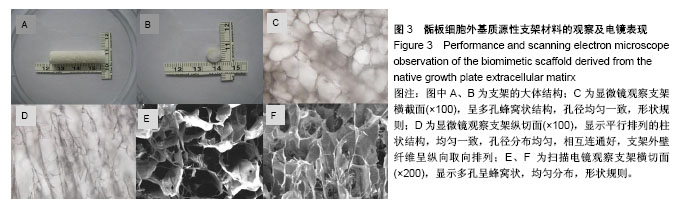
.jpg)
.jpg)