| [1] Bansal D, Miyake K, Vogel SS, et al. Defective membrane repair in dysferlin-deficient muscular dystrophy. Nature. 2003; 423(6936):168-172.[2] Cardenas AM, Gonzalez-Jamett AM, Cea LA, et al. Dysferlin function in skeletal muscle: possible pathological mechanisms and therapeutical targets in dysferlinopathies. Exp Neurol. 2016;283(Pt A):246-254.[3] Chiu YH, Hornsey MA, Klinge L, et al. Attenuated muscle regeneration is a key factor in dysferlin-deficient muscular dystrophy. Hum Mol Genet. 2009;18(11):1976-1989.[4] Gallardo E, de Luna N, Diaz-Manera J, et al. Comparison of dysferlin expression in human skeletal muscle with that in monocytes for the diagnosis of dysferlin myopathy. PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e29061.[5] Woudt L, Di Capua GA, Krahn M, et al. Toward an objective measure of functional disability in dysferlinopathy. Muscle Nerve. 2016;53(1):49-57.[6] Yin X, Wang Q, Chen T, et al. CD4+ cells, macrophages, MHC-I and C5b-9 involve the pathogenesis of dysferlinopathy. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(3):3069-3075. [7] Codding SJ, Marty N, Abdullah N, et al. Dysferlin Binds SNAREs (Soluble N-Ethylmaleimide-sensitive Factor (NSF) Attachment Protein Receptors) and Stimulates Membrane Fusion in a Calcium-sensitive Manner. J Biol Chem. 2016; 291(28):14575-14584.[8] Murphy RM, Lamb GD. Endogenous calpain-3 activation is primarily governed by small increases in resting cytoplasmic [Ca2+] and is not dependent on stretch. J Biol Chem. 2009; 284(12):7811-7819.[9] 徐玉明,曹建民,李俊平,等.大鼠运动性肌损伤特征micro RNA表达及其膜损伤调控靶点的预测[J].生理学报,2017,69(3): 276-284.[10] Tidball JG. Mechanisms of muscle injury, repair, and regeneration. Compr Physiol. 2011;1(4):2029-2062.[11] Sorimachi H, Imajoh-Ohmi S, Emori Y, et al. Molecular cloning of a novel mammalian calcium-dependent protease distinct from both m- and mu-types. Specific expression of the mRNA in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1989;264(33):20106-20111. [12] 徐玉明,李俊平,王瑞元.低氧训练诱导大鼠腓肠肌抗肌营养不良蛋白和代谢酶变化及延长高速力竭运动时间[J].生理学报, 2012, 64(1):455-462.[13] 崔玉鹏,杨则宜.血清CK活性变化与运动导致的骨骼肌损伤[J].中国运动医学杂志,2004,23(3):343-347.[14] 高志强,陈广卿,王国庆,等.大鼠运动性骨骼肌损伤后血清肌酸激酶、乳酸脱氢酶以及波形蛋白的变化[J].中国老年学杂志, 2016, 36(15):3634-3637.[15] Aoki M, Liu J, Richard I, et al. Genomic organization of the dysferlin gene and novel mutations in Miyoshi myopathy. Neurology. 2001;57(2):271-278.[16] 周小亭.Dysferlin肌病一家系DYSF基因突变研究[D].南宁:广西医科大学,2016.[17] 纪颖清.一次性离心运动后低氧暴露对p94和dysferlin的影响[D].北京:北京体育大学,2016.[18] Lukyanenko V, Muriel JM, Bloch RJ. Coupling of excitation to Ca2+ release is modulated by dysferlin. J Physiol. 2017;595(15):5191-5207.[19] Glover L, Brown RH, Jr. Dysferlin in membrane trafficking and patch repair. Traffic. 2007;8(7):785-794.[20] Bansal D, Campbell KP. Dysferlin and the plasma membrane repair in muscular dystrophy. Trends Cell Biol. 2004;14(4): 206-213.[21] Millay DP, Goonasekera SA, Sargent MA, et al. Calcium influx is sufficient to induce muscular dystrophy through a TRPC-dependent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(45):19023-19028.[22] Roche JA, Tulapurkar ME, Mueller AL, et al. Myofiber damage precedes macrophage infiltration after in vivo injury in dysferlin-deficient A/J mouse skeletal muscle. Am J Pathol. 2015;185(6):1686-1698. [23] Roche JA, Ru LW, Bloch RJ. Distinct effects of contraction-induced injury in vivo on four different murine models of dysferlinopathy. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012: 134031. [24] Biondi O, Villemeur M, Marchand A, et al. Dual effects of exercise in dysferlinopathy. Am J Pathol. 2013;182(6): 2298-2309. [25] Redpath GM, Sophocleous RA, Turnbull L, et al. Ferlins Show Tissue-Specific Expression and Segregate as Plasma Membrane/Late Endosomal or Trans-Golgi/Recycling Ferlins. Traffic. 2016;17(3):245-266.[26] 吴迎,伊木清,曾凡星.MG53基因敲除对小鼠延迟性肌肉酸痛期骨骼肌损伤的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志,2017,32(6):636-642.[27] 伊木清,M JJ.MG53-肌细胞损伤的“分子绷带”[J].中国运动医学杂志,2012,31(12):1117-1121.[28] 张岩,吴鸿昆,吕凤祥等.MG53-是人类疾病的“双刃剑”[J].生理学报,2016,68(4):505-516.[29] 田源,唐成林,黄思琴,等.按摩对大鼠骨骼肌急性钝挫伤后膜修复蛋白dysferlin和annexin A1表达的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志, 2016,31(8):841-846.[30] Demonbreun AR, Mcnally EM. Plasma Membrane Repair in Health and Disease. Curr Top Membr. 2016;77:67-96. [31] Hitchcock JK, Katz AA, Schafer G. Dynamic reciprocity: the role of annexin A2 in tissue integrity. J Cell Commun Signal. 2014;8(2):125-133. [32] Gabel M, Delavoie F, Demais V, et al. Annexin A2-dependent actin bundling promotes secretory granule docking to the plasma membrane and exocytosis. J Cell Biol. 2015;210(5): 785-800. [33] Defour A, Medikayala S, Van Der Meulen JH, et al. Annexin A2 links poor myofiber repair with inflammation and adipogenic replacement of the injured muscle. Hum Mol Genet. 2017;26(11):1979-1991. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
运动性肌损伤:运动性骨骼肌损伤(exercise-indused muscle damage,EIMD)是指进行大强度、长时间或不习惯运动后所产生的骨骼肌超微结构损伤,通常的表现为延迟性肌肉酸痛,即肌肉酸痛并不发生在运动期间或运动后即刻,而是在运动后的24 h逐渐加剧。
Dysferlin:Dysferlin是一种与肌肉修复有关的Ⅱ型跨膜蛋白,主要存在肌纤维膜和肌纤维囊泡中,其由DYSF基因编码,又被称为与dystrophy有关的fer-1-like蛋白,在骨骼肌细胞膜修复过程中起关键作用。
文题释义:
运动性肌损伤:运动性骨骼肌损伤(exercise-indused muscle damage,EIMD)是指进行大强度、长时间或不习惯运动后所产生的骨骼肌超微结构损伤,通常的表现为延迟性肌肉酸痛,即肌肉酸痛并不发生在运动期间或运动后即刻,而是在运动后的24 h逐渐加剧。
Dysferlin:Dysferlin是一种与肌肉修复有关的Ⅱ型跨膜蛋白,主要存在肌纤维膜和肌纤维囊泡中,其由DYSF基因编码,又被称为与dystrophy有关的fer-1-like蛋白,在骨骼肌细胞膜修复过程中起关键作用。.jpg) 文题释义:
运动性肌损伤:运动性骨骼肌损伤(exercise-indused muscle damage,EIMD)是指进行大强度、长时间或不习惯运动后所产生的骨骼肌超微结构损伤,通常的表现为延迟性肌肉酸痛,即肌肉酸痛并不发生在运动期间或运动后即刻,而是在运动后的24 h逐渐加剧。
Dysferlin:Dysferlin是一种与肌肉修复有关的Ⅱ型跨膜蛋白,主要存在肌纤维膜和肌纤维囊泡中,其由DYSF基因编码,又被称为与dystrophy有关的fer-1-like蛋白,在骨骼肌细胞膜修复过程中起关键作用。
文题释义:
运动性肌损伤:运动性骨骼肌损伤(exercise-indused muscle damage,EIMD)是指进行大强度、长时间或不习惯运动后所产生的骨骼肌超微结构损伤,通常的表现为延迟性肌肉酸痛,即肌肉酸痛并不发生在运动期间或运动后即刻,而是在运动后的24 h逐渐加剧。
Dysferlin:Dysferlin是一种与肌肉修复有关的Ⅱ型跨膜蛋白,主要存在肌纤维膜和肌纤维囊泡中,其由DYSF基因编码,又被称为与dystrophy有关的fer-1-like蛋白,在骨骼肌细胞膜修复过程中起关键作用。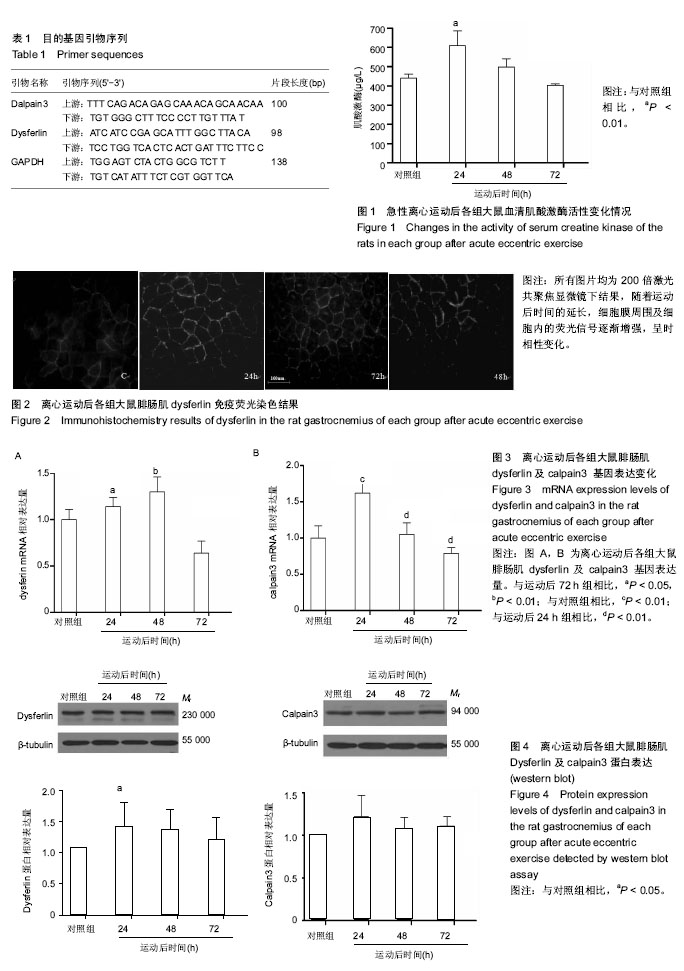
.jpg) 文题释义:
运动性肌损伤:运动性骨骼肌损伤(exercise-indused muscle damage,EIMD)是指进行大强度、长时间或不习惯运动后所产生的骨骼肌超微结构损伤,通常的表现为延迟性肌肉酸痛,即肌肉酸痛并不发生在运动期间或运动后即刻,而是在运动后的24 h逐渐加剧。
Dysferlin:Dysferlin是一种与肌肉修复有关的Ⅱ型跨膜蛋白,主要存在肌纤维膜和肌纤维囊泡中,其由DYSF基因编码,又被称为与dystrophy有关的fer-1-like蛋白,在骨骼肌细胞膜修复过程中起关键作用。
文题释义:
运动性肌损伤:运动性骨骼肌损伤(exercise-indused muscle damage,EIMD)是指进行大强度、长时间或不习惯运动后所产生的骨骼肌超微结构损伤,通常的表现为延迟性肌肉酸痛,即肌肉酸痛并不发生在运动期间或运动后即刻,而是在运动后的24 h逐渐加剧。
Dysferlin:Dysferlin是一种与肌肉修复有关的Ⅱ型跨膜蛋白,主要存在肌纤维膜和肌纤维囊泡中,其由DYSF基因编码,又被称为与dystrophy有关的fer-1-like蛋白,在骨骼肌细胞膜修复过程中起关键作用。