| [1]Melo AC, Andrighetto AR, Hirt SD, et al. Risk factors associated with the failure of miniscrews - A ten-year cross sectional study. Braz Oral Res. 2016;30(1):e124. [2]峥嵘,陈岩,包雪梅,等.不锈钢和钛合金微种植体稳定性的生物力学实验研究[J].内蒙古医科大学学报,2016,38(3):195-199.[3]Brown RN, Sexton BE, Gabriel Chu TM, et al. Comparison of stainless steel and titanium alloy orthodontic miniscrew implants: a mechanical and histologic analysis. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2014;145(4):496-504. [4]雷菲菲,梁芮,张晓洁,等.两种微螺钉种植体支抗在上颌后牙根间区的稳定性研究[J].口腔医学研究,2016,32(5):531-533.[5]Nienkemper M, Santel N, Hönscheid R, et al. Orthodontic mini-implant stability at different insertion depths : Sensitivity of three stability measurement methods. J Orofac Orthop. 2016;77(4):296-303.[6]Sivamurthy G, Sundari S. Stress distribution patterns at mini-implant site during retraction and intrusion--a three-dimensional finite element study. Prog Orthod. 2016;17:4.[7]Shen S, Sun Y, Zhang C, et al. Bivariate optimization of orthodontic mini-implant thread height and pitch. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2015;10(1):109-116. [8]颜丹,张锡忠,王增全,等.螺距对支抗微种植体—骨界面影响的三维有限元分析[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2015,42(5):557-561.[9]Seifi M, Matini NS. Evaluation of primary stability of innovated orthodontic miniscrew system (STS): An ex-vivo study. J Clin Exp Dent. 2016;8(3):e255-259.[10]Cha JY, Hwang CJ, Kwon SH, et al. Strain of bone-implant interface and insertion torque regarding different miniscrew thread designs using an artificial bone model. Eur J Orthod. 2015;37(3):268-274. [11]Knutson KJ, Berzins DW. Corrosion of orthodontic temporary anchorage devices. Eur J Orthod. 2013;35(4):500-506. [12]Tabuchi M, Ikeda T, Nakagawa K, et al. Ultraviolet photofunctionalization increases removal torque values and horizontal stability of orthodontic miniscrews. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2015;148(2):274-282. [13]Yanaguizawa MS, Suzuki SS, Martinez EF, et al. Effects of Low-Level Laser Therapy in Orthodontic Patients on Immediate Inflammatory Response After Mini-Implants Insertion: A Preliminary Report. Photomed Laser Surg. 2017; 35(1):57-63. [14]Garcez AS, Suzuki SS, Martinez EF, et al. Effects of low-intensity laser therapy over mini-implants success rate in pigs. Lasers Med Sci. 2015;30(2):727-732.[15]郭泽鸿,周磊,容明灯,等.纯钛种植体激光-微弧氧化表面处理对早期骨结合的影响[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2014,24(3):208-213.[16]周宏志,刘琳,陈小冬,等.荧光标记法对“脑回形”微弧氧化表面种植体早期骨结合的评价[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志, 2016,17(5): 271-276.[17]Ganzorig K, Kuroda S, Maeda Y, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound enhances bone formation around miniscrew implants. Arch Oral Biol. 2015;60(6):902-910. [18]Miura K, Motoyoshi M, Inaba M, et al. A preliminary study of the effects of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound exposure on the stability of orthodontic miniscrews in growing rats. Eur J Orthod. 2014;36(4):419-424.[19]Jang I, Shim SC, Choi DS, et al. Effect of TiO2 nanotubes arrays on osseointegration of orthodontic miniscrew. Biomed Microdevices. 2015;17(4):76. [20]Oh EJ, Nguyen TD, Lee SY, et al. Enhanced compatibility and initial stability of Ti6Al4V alloy orthodontic miniscrews subjected to anodization, cyclic precalcification, and heat treatment. Korean J Orthod. 2014;44(5):246-253.[21]丁元圣,赵玥,郭睿,等.含氟羟基磷灰石涂层对正畸微种植体骨结合及周围炎的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2016,32(5): 624-626.[22]武秀萍,Hee Moonkyung,李冰,等.微种植体表面酸蚀喷砂处理对周围骨组织NGF表达的影响[J].山西医科大学学报,2015, 46(3):231-233,283.[23]Marquezan M, de Freitas AO, Nojima LI. Miniscrew covering: an alternative to prevent traumatic lesions. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2012;141(2):242-244. [24]沙焱,吕超贤,韩建民,等.助攻式、自攻式微种植体支抗植入法在微种植体矫治错牙合畸形中的应用[J].山东医药, 2015,55(11): 75-76.[25]Tepedino M, Masedu F, Chimenti C. Comparative evaluation of insertion torque and mechanical stability for self-tapping and self-drilling orthodontic miniscrews - an in vitro study. Head Face Med. 2017;13(1):10.[26]邹毅军.探讨用两种不同方法植入微种植体支抗的稳定性[J].当代医药论丛,2014(1):135-136.[27]Iijima M, Muguruma T, Kawaguchi M, et al. In vivo degradation of orthodontic miniscrew implants: surface analysis of as-received and retrieved specimens. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2015;26(2):71. [28]Sharifi M, Ghassemi A, Bayani S. Effect of insertion method and postinsertion time interval prior to force application on the removal torque of orthodontic miniscrews. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2015;30(1):35-40. [29]Poorsattar Bejeh Mir A, Ravadgar M, Poorsattar Bejeh Mir M. Optimized orthodontic palatal miniscrew implant insertion angulation: a finite element analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2015;30(1):e1-9.[30]董晶,张哲湛,周国良.Ⅱ类骨质中正畸微种植体锥度及植入角度对支抗稳定性影响的三维有限元分析[J].华西口腔医学杂志, 2014,32(1):13-17.[31]于海璐,蔡兴伟,马龙,等.不同植入角度及载荷方向对微种植体稳定性影响的三维有限元分析[J].解放军医学院学报, 2016,37(3): 261-265,270.[32]Lee J, Kim JY, Choi YJ, et al. Effects of placement angle and direction of orthopedic force application on the stability of orthodontic miniscrews. Angle Orthod. 2013;83(4):667-673.[33]Perillo L, Jamilian A, Shafieyoon A, et al. Finite element analysis of miniscrew placement in mandibular alveolar bone with varied angulations. Eur J Orthod. 2015;37(1):56-59. [34]Araghbidikashani M, Golshah A, Nikkerdar N, et al. In-vitro impact of insertion angle on primary stability of miniscrews. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2016;150(3):436-443. [35]Migliorati M, Drago S, Schiavetti I, et al. Orthodontic miniscrews: an experimental campaign on primary stability and bone properties. Eur J Orthod. 2015;37(5):531-538. [36]Veli I, Uysal T, Baysal A, et al. Buccal cortical bone thickness at miniscrew placement sites in patients with different vertical skeletal patterns. J Orofac Orthop. 2014;75(6):417-429.[37]曹小青,张莉,刘龙坤.正畸用微种植钉种植成功的多因素分析[J].口腔医学研究,2016,32(1):79-82.[38]莫嘉骥,姒蜜思,周仲豪,等.Straumann种植体早期稳定性相关因素的研究[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2012,10(5):381-385.[39]邹双双,雷勇华,张亚梅,等.微种植体植入初期稳定性:错颌上颌后牙区颊侧骨皮质厚度分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(12):1837-1841.[40]Shan LH, Guo N, Zhou GJ, et al. Finite Element Analysis of Bone Stress for Miniscrew Implant Proximal to Root Under Occlusal Force and Implant Loading. J Craniofac Surg. 2015;26(7):2072-2076.[41]Garg KK, Gupta M. Assessment of stability of orthodontic mini-implants under orthodontic loading: A computed tomography study. Indian J Dent Res. 2015;26(3):237-243.[42]Bae MJ, Kim JY, Park JT, et al. Accuracy of miniscrew surgical guides assessed from cone-beam computed tomography and digital models. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2013;143(6): 893-901.[43]Qiu LL, Li S, Bai YX. Preliminary safety and stability assessment of orthodontic miniscrew implantation guided by surgical template based on cone-beam CT images. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016;51(6):336-340.[44]Motoyoshi M, Sanuki-Suzuki R, Uchida Y, et al. Maxillary sinus perforation by orthodontic anchor screws. J Oral Sci. 2015;57(2):95-100. [45]李文艳,彭嘉琪,林巍,等.微种植体颌骨植入区的CBCT测量分析[J].口腔医学,2015,35(1):29-33.[46]Brunski JB. Biomechanical factors affecting the bone-dental implant interface. Clin Mater. 1992;10(3):153-201.[47]Bayani S, Masoomi F, Aghaabbasi S, et al. Evaluation of the Effect of Platelet-Released Growth Factor and Immediate Orthodontic Loading on the Removal Torque of Miniscrews. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2016;31(2):471-477.[48]Migliorati M, Drago S, Gallo F, et al. Immediate versus delayed loading: comparison of primary stability loss after miniscrew placement in orthodontic patients-a single-centre blinded randomized clinical trial. Eur J Orthod. 2016;38(6): 652-659. [49]Catharino PC, Dominguez GC, Pinto Ddos S Jr, et al. Histologic, histomorphometric, and radiographic monitoring of bone healing around in-office-sterilized orthodontic mini-implants with or without immediate load: study in rabbit tibiae. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2014;29(2):321-330.[50]范莉,缪喆,唐国华.正畸微种植体稳定性的临床共振频率分析[J].上海口腔医学,2014,23(5):614-618.[51]李金平,时超,周冠军,等.微种植体植入扭矩及载荷时机对稳定性的影响[J].河北医药,2015,37(24):3740-3742.[52]吴也可,赵立星.持续或间断应力加载下正畸微种植体稳定性的组织形态学和生物力学分析[J].口腔医学研究, 2016,32(4): 326-330. |
.jpg)
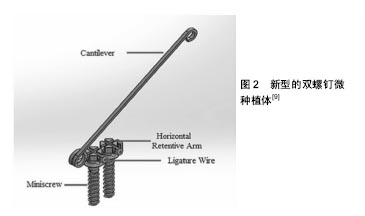
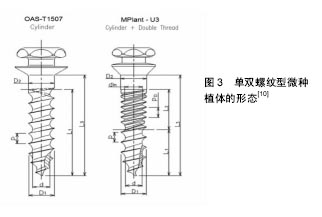
.jpg)
.jpg)