中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (29): 4311-4318.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.29.008
• 组织构建临床实践 clinical practice in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
有机磷中毒供肾移植的效果评价
董建辉,李海滨,孙煦勇,秦 科,廖吉祥,李美思,黄晓诞,黄 晨,黄 莹,曹 嵩,高 照,李壮江,聂 峰,杨建均
- 解放军第三〇三医院移植医学研究院,广西移植医学重点实验室,解放军广州军区器官移植中心,广西移植医学工程技术研究中心,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530021
Clinical effects of renal transplantation with kidneys from donors dying of organophosphate poisoning
Dong Jian-hui, Li Hai-bin, Sun Xu-yong, Qin Ke, Liao Ji-xiang, Li Mei-si, Huang Xiao-dan, Huang Chen, Huang Ying, Cao Song, Gao Zhao, Li Zhuang-jiang, Nie Feng, Yang Jian-jun
- Institute of Transplant Medicine, No. 303 Hospital of Chinese PLA; Guangxi Key Laboratory for Transplantation Medicine Guangxi, Department of Organ Transplantation in Guangzhou Military Region; Guangxi Transplantation Medicine Research Center of Engineering Technology, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
肾移植:通过外科手术的方法将器官捐献者的肾脏移植给患有肾脏病变并丧失肾脏功能的患者的一种器官移植手术。
有机磷中毒死亡者供肾移植:案例为有机磷中毒心脏死亡器官捐献供肾肾移植,国内尚未见有相关报道,通过各种干预手段对供体器官进行器官功能的维护,提高供肾质量,最终成功移植,并获得良好效果。利用此研究案例初步探索并总结供体综合维护经验,为此类供体捐献操作及临床应用提供一些早期的数据资料。
文题释义:
肾移植:通过外科手术的方法将器官捐献者的肾脏移植给患有肾脏病变并丧失肾脏功能的患者的一种器官移植手术。
有机磷中毒死亡者供肾移植:案例为有机磷中毒心脏死亡器官捐献供肾肾移植,国内尚未见有相关报道,通过各种干预手段对供体器官进行器官功能的维护,提高供肾质量,最终成功移植,并获得良好效果。利用此研究案例初步探索并总结供体综合维护经验,为此类供体捐献操作及临床应用提供一些早期的数据资料。
.jpg) 文题释义:
肾移植:通过外科手术的方法将器官捐献者的肾脏移植给患有肾脏病变并丧失肾脏功能的患者的一种器官移植手术。
有机磷中毒死亡者供肾移植:案例为有机磷中毒心脏死亡器官捐献供肾肾移植,国内尚未见有相关报道,通过各种干预手段对供体器官进行器官功能的维护,提高供肾质量,最终成功移植,并获得良好效果。利用此研究案例初步探索并总结供体综合维护经验,为此类供体捐献操作及临床应用提供一些早期的数据资料。
文题释义:
肾移植:通过外科手术的方法将器官捐献者的肾脏移植给患有肾脏病变并丧失肾脏功能的患者的一种器官移植手术。
有机磷中毒死亡者供肾移植:案例为有机磷中毒心脏死亡器官捐献供肾肾移植,国内尚未见有相关报道,通过各种干预手段对供体器官进行器官功能的维护,提高供肾质量,最终成功移植,并获得良好效果。利用此研究案例初步探索并总结供体综合维护经验,为此类供体捐献操作及临床应用提供一些早期的数据资料。摘要
背景:研究表明,心脏死亡器官捐献供肾受者的维持肌酐水平较高,心脏死亡器官捐献供肾其移植肾功能延迟恢复发生率也较高。
目的:分析有机磷中毒心脏死亡器官捐献供肾肾移植的临床效果。
方法:将有机磷中毒的2例捐献供者,给予相应维护,器官获取后,供肾使用脉冲式机器灌注,受者肾移植过程中、移植后给予免疫诱导、抗排斥、预防感染等治疗。收集供肾相关实验室检查以及零点穿刺病理资料,分析受者的肾移植后移植肾功能恢复情况、受者及移植物生存情况、并发症(移植肾功能延迟恢复与急性排斥反应)的发生率。
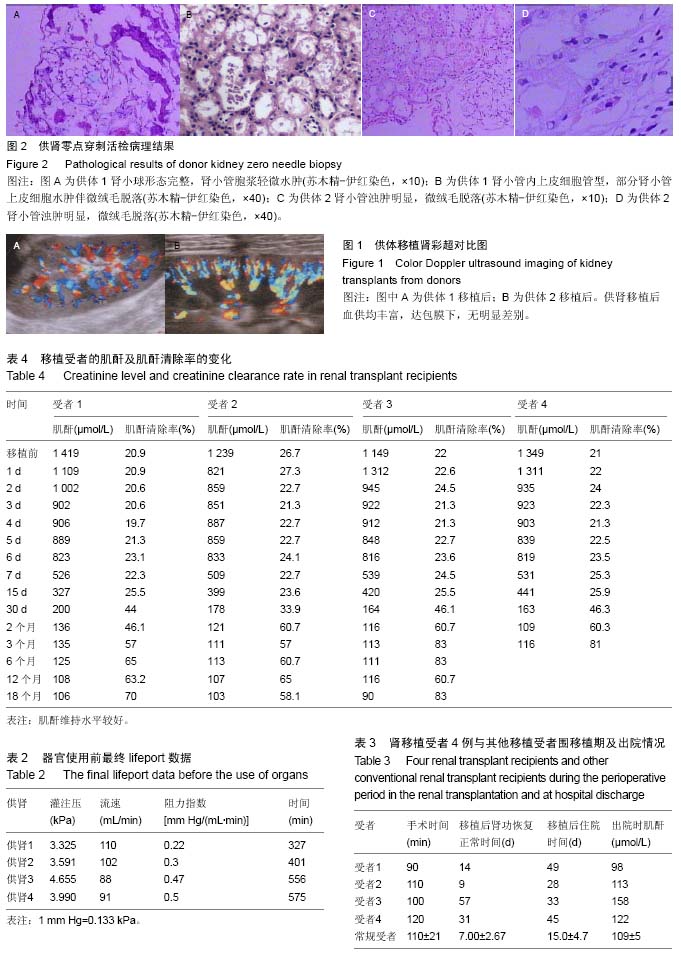
结果与结论:①4个供肾穿刺病理发现:所有供肾肾小球形态基本正常,肾小管均有不同程度的水肿、变性;②受者肾移植后急性排斥反应:4例发生率为0(0/4),移植肾功能延迟恢复发生率为75%(3/4),围手术期受者存活率及移植肾存活率均为100%(4/4);③所有受者出院时及出院后相关生物指标:肌酐、尿素氮均维持较低水平,移植肾功能良好,均未出现蛋白尿。有1例受者术后4个月因重症肺部感染带肾死亡;④结果提示:对于部分达到待捐状态的有机磷中毒供者,给予相关器官功能维护措施及使用机器灌注改善保存供肾方式,能有效改善器官捐献供肾的保存质量,移植后患者恢复良好。在目前器官来源严重匮乏情况下,重度有机磷中毒导致到达待捐献状态的患者在经系列器官功能维护后,一定条件下可以作为一种新的器官来源。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0003-0807-4007(董建辉)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
肾移植:通过外科手术的方法将器官捐献者的肾脏移植给患有肾脏病变并丧失肾脏功能的患者的一种器官移植手术。
有机磷中毒死亡者供肾移植:案例为有机磷中毒心脏死亡器官捐献供肾肾移植,国内尚未见有相关报道,通过各种干预手段对供体器官进行器官功能的维护,提高供肾质量,最终成功移植,并获得良好效果。利用此研究案例初步探索并总结供体综合维护经验,为此类供体捐献操作及临床应用提供一些早期的数据资料。
文题释义:
肾移植:通过外科手术的方法将器官捐献者的肾脏移植给患有肾脏病变并丧失肾脏功能的患者的一种器官移植手术。
有机磷中毒死亡者供肾移植:案例为有机磷中毒心脏死亡器官捐献供肾肾移植,国内尚未见有相关报道,通过各种干预手段对供体器官进行器官功能的维护,提高供肾质量,最终成功移植,并获得良好效果。利用此研究案例初步探索并总结供体综合维护经验,为此类供体捐献操作及临床应用提供一些早期的数据资料。