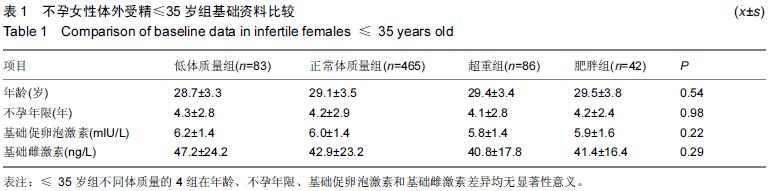
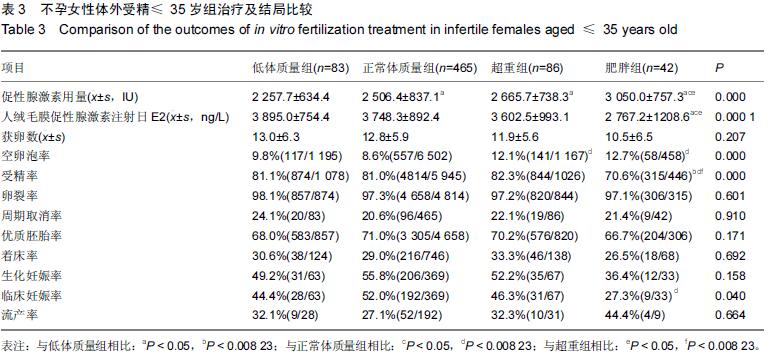
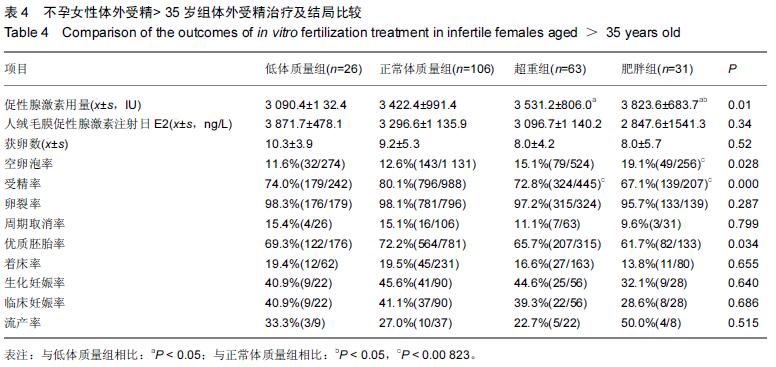
| [1] 乐杰.妇产科学[M].7版,北京:人民卫生出版社,2008:351. [2] 宋荣, 蔡霞.肥胖与育龄期女性生殖功能研究进展[J].中国优生与遗传杂志,2011,19(2):9-11. [3] Maheshwari A, Stofberg L, Bhattacharya S. Effect of overweight and obesity on assisted reproductive technology a systematic review. Hum Reprod Update. 2007;13:433-444. [4] Metwally M, Ong KJ, Ledger WL, et al. Does high body mass index increase the risk of miscarriage after sponta- neous and assisted conception? A meta-analysis of the evidence. Fertil Steril. 2008; 90:714-726. [5] Veleva Z, Tiitinen A, Vilska S, et al. High and low BMI increase the risk of miscarriage after IVF/ICSI and FET. Hum Reprod. 2008;23: 878-884. [6] Parker K, Wong B, Link B, et al. Does body mass index (BMI) affect IVF outcomes?. Fertil Steril. 2011; 96(3): S124. [7] Matalliotakis I, Cakmak H, Sakkas D, et al. Impact of body mass index on IVF and ICSI outcome: a retrospective study. Reprod Biomed.2008; Online 16: 778-783. [8] 庄广伦.现代辅助生育技术[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2005:112-113. [9] Marie N, Tom F, Margaret R, et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. The Lancet. 2014; 384(9945):766-781. [10] Villareal D, Apovian C, Kushner R, et al. Obesity in older adults: technical re-view and position statement of the American Society for Nutrition and NAASO, The Obesity Society. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005; 82 (5): 923-934. [11] 兰永连,王树玉.肥胖与生殖[J].中国优生与遗传杂志,2013, 21(7):5-6+10. [12] Zeynep Özcan D, Berna D. Impact of obesity on infertility in women. J Turk Ger Gynecol. 2015; 16:111-117. [13] Van der Steeg JW, Steures P, Eijkemans MJ, et al. Predictive value of pregnancy history in subfertile couples: results from a nationwide cohort study in the Netherlands. Fertil Steril.2008; 90:521-527. [14] Brewer C, Balen A.The adverse effects of obesity on conception and implantation. Reproduction.2011; 140: 347–364. [15] Zhang D, Zhu Y, Gao H, et al. Overweight and obesity negatively affect the outcomes of ovarian stimulation and in vitro fertilization: a cohort study of 2628 Chinese women. Gynecol endocrinol.2010; 26(5):325-332. [16] 沈蕾,丁之德. 肥胖对生殖影响的研究进展[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志,2013,32(5):400-404. [17] Bellver J, Pellicer A, García-Velasco, et al. Obesity reduces uterine receptivity: clinical experience from 9,587 first cycles of ovum donation with normal weight donors. Fertil Steril. 2013; 100(4):1050-1058. [18] Zeng X, Pang H, Li X, et al. Impact of obesity on endometrial blood flow in women without polycystic ovarian syndrome during intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2013; 11(1):57. [19] Kim A, Han JE, Yoon TK, et al. Relationship between endometrial and subendometrial blood flow measured by three-dimensional power Doppler ultrasound and pregnancy after intrauterine insemination. Fertil Steril. 2010; 94(2):747-752. [20] Bellver J, Ayllon Y, Ferrando M, et al. Female obesity impairs in vitro fertilization outcome without affecting embryo quality. Fertil Steril.2010; 93:447-454. [21] Sathya A, Balasubramanyam S, Gupta S, et al. Effect of body mass index on in vitro fertilization outcomes inwomen. J Hum Reprod Sci.2010; 3:135-138. [22] 李星,杨菁,尹太郎,等.体外受精-胚胎移植者体质量指数对妊娠结局的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(8):3289-3291. [23] 陈巧莉,叶虹,邓华丽,等.体质量指数对年轻女性体外受精-胚胎移植助孕及其妊娠结局的影响[J].实用妇产科杂志, 2013,29(10):791-793. [24] 卓胜楠,张印峰,张帅,等.不孕症女性体质量指数对IVF/ICSI治疗结局的影响[J]. 生殖与避孕,2013,33(8):534-539. [25] 陈巧莉,叶虹,裴莉,等.多囊卵巢综合症患者IVF-ET前达英- 35预处理不同时间临床效果分析[J]. 生殖与避孕, 2010, 30(10):710-712. [26] 杨星,梁晓燕.肥胖与自然生育力[J]. 实用妇产科杂志,2011, 27(5):326-328. [27] Xuan J, Gongxian W, Sisun L, et al. Survey of the situation of infertile women seeking in vitro fertilization treatment in China. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013: 179098. |
.jpg)

.jpg)