| [1] 梁家仪,李长东,张为远,等.Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号通路的激活/抑制对小鼠在位子宫内膜及子宫内膜异位症模型的影响[J].中华医学杂志,2012,92(19):1352-1356.[2] 丛青.小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向子宫内膜腺上皮分化的蛋白质组学研究[D].上海:复旦大学,2012.[3] 刘君,赵志梅,夏天,等.子宫内膜异位症干细胞与Wnt/β- catenin信号通路[J].国际妇产科学杂志, 2015,42(4): 409-412.[4] Moggio A, Pittatore G, Cassoni P, et al. Sorafenib inhibits growth, migration, and angiogenic potential of ectopic endometrial mesenchymal stem cells derived from patients with endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 2012; 98(6):1521-1530.e2.[5] 周琦,李霞,陶玲,等.Wnt/β-catenin 信号通路4个基因在子宫内膜异位症中的表达及意义[J].新疆医科大学学报, 2014,37(12):1585-1590.[6] 谢伟,刘义,廉红梅,等.雌激素对子宫内膜异位症在位内膜间质细胞β-catenin mRNA的影响[J].生殖与避孕, 2008, 28(1):7-11.[7] 海娜,刘义,吕立群,等.基因转染DKK1对17β-雌二醇促进子宫内膜异位症患者在位子宫内膜间质细胞VEGF和MMP-9表达的影响[J].华中科技大学学报:医学版, 2010, 39(6):738-743.[8] Valentijn AJ, Palial K, Al-Lamee H, et al. SSEA-1 isolates human endometrial basal glandular epithelial cells: phenotypic and functional characterization and implications in the pathogenesis of endometriosis. Hum Reprod. 2013;28(10):2695-2708.[9] Alexander M, Cope N, Renninson J, et al. Relationship between endometriosis, endometrioid adenocarcinoma, gliomatosis peritonei, and carcinoid tumor in a patient with recurrent ovarian teratoma. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2011;30(2):151-157.[10] Kao AP, Wang KH, Long CY, et al. Interleukin-1β induces cyclooxygenase-2 expression and promotes the invasive ability of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from ovarian endometrioma. Fertil Steril. 2011;96(3):678-684.e1.[11] 满奕村,刘义,谢伟,等.阻断Wnt/β-catenin信号通路对17β-雌二醇作用后子宫内膜异位症患者在位子宫内膜间质细胞活化的影响[J].华中科技大学学报:医学版,2009, 38(4):421-424,429.[12] Prianishnikov VA. On the concept of stem cell and a model of functional-morphological structure of the endometrium. Contraception. 1978;18(3):213-223.[13] Gargett CE, Schwab KE, Zillwood RM,et al. Isolation and culture of epithelial progenitors and mesenchymal stem cells from human endometrium.Biol Reprod. 2009;80(6):1136-1145.[14] 黄冬花,陈美红,张晓玲,等.β-catenin在卵巢子宫内膜异位症间质细胞的表达及临床意义[J].中国妇幼保健,2014, 29(16):2495-2497.[15] Osuga Y, Koga K, Tsutsumi O, et al. Stem cell factor (SCF) concentrations in peritoneal fluid of women with or without endometriosis. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2000;44(4):231-235.[16] León M, Vaccaro H, Alcázar JL, et al. Extended transvaginal sonography in deep infiltrating endometriosis: use of bowel preparation and an acoustic window with intravaginal gel: preliminary results. J Ultrasound Med. 2014;33(2):315-321.[17] 于岚.雌激素介导ERα调控子宫内膜间质细胞β-catenin表达的分子机制及在子宫内膜异位症形成和发展中的意义[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2011. [18] Hwang JH, Oh JJ, Wang T, et al. Identification of biomarkers for endometriosis in eutopic endometrial cells from patients with endometriosis using a proteomics approach. Mol Med Rep. 2013;8(1):183-188.[19] 杜正娟.低氧介导下HIF-1对ß-catenin表达的影响及在子宫内膜异位症发病机制中的作用[D]. 武汉:华中科技大学,2013. [20] 刘儒彪.靶向siRNA阻断Wnt/β-catenin信号通路对子宫内膜异位症患者在位内膜间质细胞VEGF和MMP-9表达的影响[D]. 武汉:华中科技大学,2010. [21] 郑婷婷.靶向siRNA阻断Wnt/β-catenin信号通路对子宫内膜异位症裸鼠模型异位子宫内膜VEGF和MMP-9表达及血管生成的影响[D]. 武汉:华中科技大学,2010. [22] 王罡.siRNA阻断wnt/b-catenin信号通路对子宫内膜异位症患者在位内膜间质细胞侵袭能力的影响[D]. 武汉:华中科技大学,2010. [23] Uzan C, Cortez A, Dufournet C, et al. Endometrium from women with and without endometriosis, and peritoneal, ovarian and bowel endometriosis, show different c-kit protein expression. J Reprod Immunol. 2005;65(1):55-63.[24] Götte M, Wolf M, Staebler A, et al. Increased expression of the adult stem cell marker Musashi-1 in endometriosis and endometrial carcinoma.J Pathol. 2008;215(3):317-329.[25] Abbas S, Ihle P, Köster I, et al. Prevalence and incidence of diagnosed endometriosis and risk of endometriosis in patients with endometriosis-related symptoms: findings from a statutory health insurance-based cohort in Germany. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2012;160(1):79-83. [26] 朱利利,熊正文,李永申. Wnt 信号转导通路与女性常见肿瘤的关系[J].解放军医药杂志,2013,25(6):94-96.[27] Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, Kandoth C, Schultz N, et al. Integrated genomic characterization of endometrial carcinoma. Nature. 2013;497(7447):67-73.[28] 谢伟.17β-雌二醇对子宫内膜异位症患者在位子宫内膜间质细胞β-catenin mRNA和蛋白表达的影响[D]. 武汉:华中科技大学,2008.[29] 郭久柏,张琦.β-连环素与E-钙粘素在子宫异位内膜、子宫内膜癌和正常子宫内膜中的表达对比研究[J].中国医学创新,2010,7(19):10-12. [30] Ali-Fehmi R, Khalifeh I, Bandyopadhyay S, et al. Patterns of loss of heterozygosity at 10q23.3 and microsatellite instability in endometriosis, atypical endometriosis, and ovarian carcinoma arising in association with endometriosis. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2006;25(3):223-229. [31] 李长东.Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的激活/抑制对小鼠在位子宫内膜及子宫内膜异位症模型的影响[C]//中华医学会第六次全国妇科内镜及微创技术学术会议论文集, 2013: 271-272.[32] 王立宏.E-cadherin及β-catenin在子宫内膜异位症患者在位内膜、异位内膜上皮表达的研究[D].北京:中国人民解放军军医进修学院,2002.[33] Sakr S, Naqvi H, Komm B, et al. Endometriosis impairs bone marrow-derived stem cell recruitment to the uterus whereas bazedoxifene treatment leads to endometriosis regression and improved uterine stem cell engraftment. Endocrinology. 2014;155(4):1489-1497.[34] Adammek M, Greve B, Kässens N, et al. MicroRNA miR-145 inhibits proliferation, invasiveness, and stem cell phenotype of an in vitro endometriosis model by targeting multiple cytoskeletal elements and pluripotency factors. Fertil Steril. 2013;99(5):1346-1355.e5.[35] Hsu CY, Hsieh TH, Tsai CF, et al. miRNA-199a-5p regulates VEGFA in endometrial mesenchymal stem cells and contributes to the pathogenesis of endometriosis. J Pathol. 2014;232(3):330-343.[36] 石亚楠,黄河玲,郭瑞峰,等.Galectin-3和β-catenin在子宫内膜异位症中的表达及二者的相关性[J].天津医药, 2015,43(8):876-878,879. [37] 郑婷婷,刘义,于岚,等.靶向siRNA阻断Wnt/β-catenin信号通路对子宫内膜异位症裸鼠模型异位子宫内膜VEGF和MMP-9表达的影响[J].华中科技大学学报:医学版, 2011,40(1):22-27. [38] 谢伟,刘义,廉红梅,等.17β-雌二醇对子宫内膜异位症患者在位子宫内膜间质细胞β-catenin mRNA和蛋白表达的影响[J].生殖医学杂志,2008,17(3):169-174. |
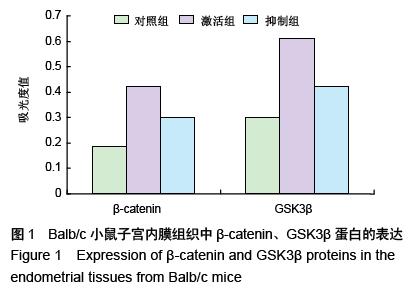
.jpg)
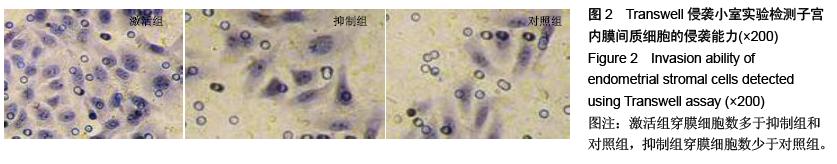
.jpg)
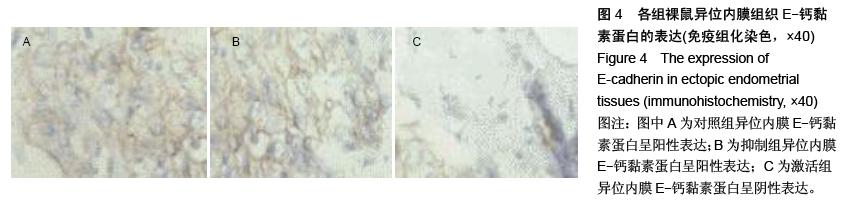
.jpg)
.jpg)