| [1] Grassmayr MJ, Parker DA, Coolican MR, et al. Posterior cruciate ligament deficiency: biomechanical and biological consequences and the outcomes of conservative treatment. A systematic review.J Sci Med Sport. 2008;11(5): 433-443. [2] Wang CJ, Chan YS, Weng LH, et al. Comparison of autogenous and allogenous posterior cruciate ligament reconstructions of the knee. Injury. 2004;35(12):1279-1285.[3] Bosch U, Decker B, Möller HD,et al. Collagen fibril organization in the patellar tendon autograft after posterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. A quantitative evaluation in a sheep model. Am J Sports Med. 1995;23(2):196-202.[4] Ventura A, Terzaghi C, Legnani C,et al. Synthetic grafts for anterior cruciate ligament rupture: 19-year outcome study. Knee. 2010;17(2):108-113. [5] Takeyama N, Sakai H, Ohtake H, et al. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen on gene expressions of procollagen, matrix metalloproteinase and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase in injured medial collateral ligament and anterior cruciate ligament. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2007;15(4): 443-452.[6] Tang Z, Yang L, Xue R,et al. Differential expression of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in anterior cruciate ligament and medial collateral ligament fibroblasts after a mechanical injury: involvement of the p65 subunit of NF-kappaB.Wound Repair Regen. 2009;17(5): 709-716.[7] Cameron ML, Fu FH, Paessler HH, et al. Synovial fluid cytokine concentrations as possible prognostic indicators in the ACL-deficient knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 1994;2(1):38-44.[8] Schmidt CC, Georgescu HI, Kwoh CK,et al. Effect of growth factors on the proliferation of fibroblasts from the medial collateral and anterior cruciate ligaments. J Orthop Res. 1995; 13(2):184-190.[9] Zhang YJ, Jiang JH, Xie J, et al. Shengwu Huaxue yu Shengwu Wuli Jinzhan. 2011; 38(5):389-399.张艳君,蒋稼欢,谢静,等.赖氨酰氧化酶与人类疾病[J]. 生物化学与生物物理进展,2011, 38(5): 389-399.[10] Kim YM, Kim EC, Kim Y.The human lysyl oxidase-like 2 protein functions as an amine oxidase toward collagen and elastin. Mol Biol Rep. 2011;38(1):145-149.[11] Yu Q, Horak K, Larson DF. Role of T lymphocytes in hypertension-induced cardiac extracellular matrix remodeling. Hypertension. 2006;48(1):98-104.[12] Vater CA, Harris ED Jr, Siegel RC. Native cross-links in collagen fibrils induce resistance to human synovial collagenase. Biochem J. 1979;181(3):639-645.[13] Kagan HM, Li W. Lysyl oxidase: properties, specificity, and biological roles inside and outside of the cell. J Cell Biochem. 2003;88(4):660-672.[14] Xie J, Jiang J, Zhang Y,et al. Up-regulation expressions of lysyl oxidase family in Anterior Cruciate Ligament and Medial Collateral Ligament fibroblasts induced by Transforming Growth Factor-Beta 1. Int Orthop. 2012;36(1):207-213.[15] Mariani PP, Becker R, Rihn J, et al. Surgical treatment of posterior cruciate ligament and posterolateral corner injuries. An anatomical, biomechanical and clinical review. Knee. 2003; 10(4):311-324.[16] Peng J, Chi LX. Disan Junyi Daxue Xuebao. 2010;32(21): 2286-2289.彭锦,迟路湘.细胞间直接接触对骨髓间充质干细胞分化为血管内皮细胞的作用[J]. 第三军医大学学报,2010,32(21): 2286- 2289.[17] Xu XZ, Li ZQ, Wen ZH. Zhongguo Linchuang Shenjing Waike Zazhi. 2009;14(9):538-541.许锡镇,李志强,文志华. 缺氧条件下胶质瘤U251细胞培养上清液对血管内皮细胞形成管样结构的影响[J]. 中国临床神经外科杂志, 2009, 14(9): 538-541.[18] Lu XM, Chen L, Su N, et al. Zhongguo Guzhi Shusong Zazhi. 2008; 14(3): 159-163.鲁秀敏,陈林,苏楠,等.小鼠成骨细胞和破骨细胞共培养模型的建立[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2008,14(3): 159-163.[19] Zhang SY, Duan DB, Zhang L, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2012; 16(19): 3438-3441.张树鹰,段大波,张力,等. Transwell小室环境下兔成骨样细胞与骨髓基质干细胞的共培养及成骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2012, 16(19): 3438-3441.[20] Gill TJ, DeFrate LE, Wang C,et al. The biomechanical effect of posterior cruciate ligament reconstruction on knee joint function. Kinematic response to simulated muscle loads. Am J Sports Med. 2003;31(4):530-536.[21] Bosch U, Kasperczyk WJ. Healing of the patellar tendon autograft after posterior cruciate ligament reconstruction--a process of ligamentization? An experimental study in a sheep model. Am J Sports Med. 1992;20(5):558-566.[22] Pinnell SR, Martin GR.The cross-linking of collagen and elastin: enzymatic conversion of lysine in peptide linkage to alpha-aminoadipic-delta-semialdehyde (allysine) by an extract from bone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968;61(2):708-716.[23] Kim Y, Peyrol S, So CK, et al. Coexpression of the lysyl oxidase-like gene (LOXL) and the gene encoding type III procollagen in induced liver fibrosis. J Cell Biochem. 1999; 72(2):181-188.[24] Jourdan-Le Saux C, Tronecker H, Bogic L, et al. The LOXL2 gene encodes a new lysyl oxidase-like protein and is expressed at high levels in reproductive tissues. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(18):12939-12944.[25] Jourdan-Le Saux C, Tomsche A, Ujfalusi A,et al. Central nervous system, uterus, heart, and leukocyte expression of the LOXL3 gene, encoding a novel lysyl oxidase-like protein. Genomics. 2001;74(2):211-218.[26] Asuncion L, Fogelgren B, Fong KS, et al. A novel human lysyl oxidase-like gene (LOXL4) on chromosome 10q24 has an altered scavenger receptor cysteine rich domain. Matrix Biol. 2001;20(7):487-491.[27] Lucero HA, Kagan HM. Lysyl oxidase: an oxidative enzyme and effector of cell function. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006;63(19-20): 2304-2316.[28] Elbjeirami WM, Yonter EO, Starcher BC, et al. Enhancing mechanical properties of tissue-engineered constructs via lysyl oxidase crosslinking activity. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2003;66(3):513-521.[29] Mäki JM, Räsänen J, Tikkanen H, et al. Inactivation of the lysyl oxidase gene Lox leads to aortic aneurysms, cardiovascular dysfunction, and perinatal death in mice. Circulation. 2002;106(19):2503-2509.[30] Lau YK, Gobin AM, West JL. Overexpression of lysyl oxidase to increase matrix crosslinking and improve tissue strength in dermal wound healing. Ann Biomed Eng. 2006;34(8):1239- 1246.[31] Hou Y, Mao Z, Wei X, et al. The roles of TGF-beta1 gene transfer on collagen formation during Achilles tendon healing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;383(2):235-239.[32] Van Eijk F, Saris DB, Riesle J, et al. Tissue engineering of ligaments: a comparison of bone marrow stromal cells, anterior cruciate ligament, and skin fibroblasts as cell source. Tissue Eng. 2004;10(5-6):893-903.[33] Mariani PP, Becker R, Rihn J, et al. Surgical treatment of posterior cruciate ligament and posterolateral corner injuries. An anatomical, biomechanical and clinical review. Knee. 2003; 10(4):311-324.[34] Barlow Y, Willoughby J. Pathophysiology of soft tissue repair. Br Med Bull. 1992;48(3):698-711.[35] Zhou D, Lee HS, Villarreal F, et al. Differential MMP-2 activity of ligament cells under mechanical stretch injury: an in vitro study on human ACL and MCL fibroblasts. J Orthop Res. 2005; 23(4):949-957.[36] Wang YQ, Chen WQ, Qian YN, et al. Yiyong Shengwu Lixue. 2009; 24(3):165-168.王业全, 陈文琦, 钱宇娜, 等. 机械压应力作用下IL-1α与TNF-α对滑膜细胞MMP-2,-9活性的影响[J]. 医用生物力学, 2009, 24 (3):165-168.[37] Saunders KB, D'Amore PA. An in vitro model for cell-cell interactions. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1992;28A(7-8):521-528.[38] Proudfoot D, Fitzsimmons C, Torzewski J,et al. Inhibition of human arterial smooth muscle cell growth by human monocyte/macrophages: a co-culture study. Atherosclerosis. 1999;145(1):157-165.[39] Bellik L, Musilli C, Vinci MC, et al. Human mature endothelial cells modulate peripheral blood mononuclear cell differentiation toward an endothelial phenotype. Exp Cell Res. 2008;314(16):2965-2974. |
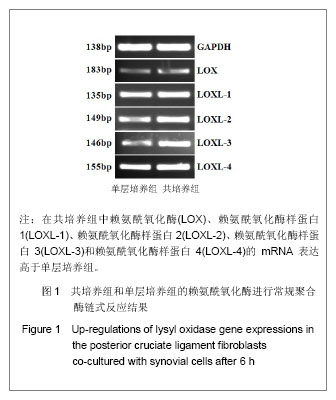
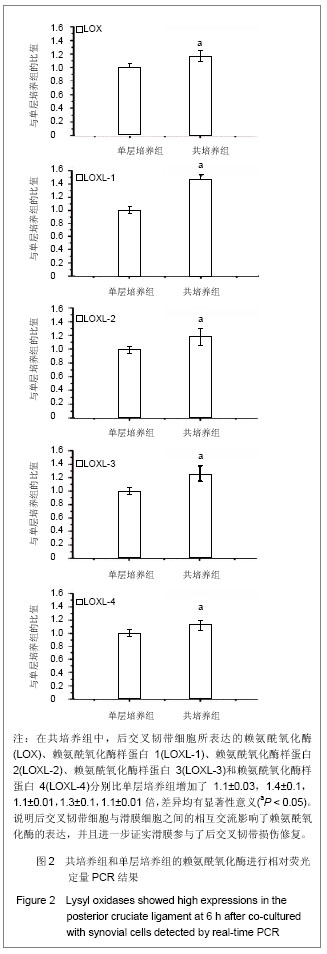
.jpg)
.jpg)