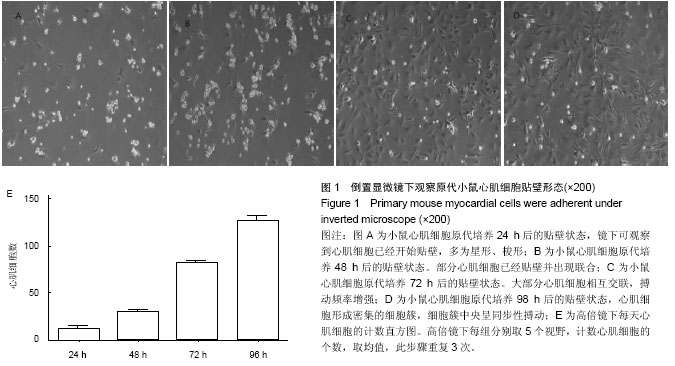
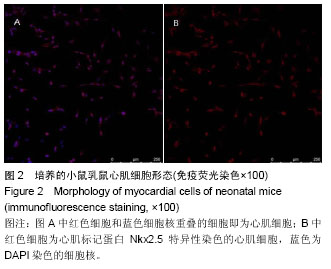
| [1] Slavici T, Avram C, Mnerie GV, et al. Economic efficiency of primary care for CVD prevention and treatment in Eastern European countries. BMC Health Serv Res. 2013;13:75-89.
[2] Bouillon K, Batty GD, Hamer M, et al. Cardiovascular disease risk scores in identifying future frailty: the Whitehall II prospective cohort study. Heart. 2013;99(10):737-742.
[3] Ward MJ, Kripalani S, Zhu Y, et al. Incidence of emergency department visits for st-elevation myocardial infarction in a recent six-year period in the united states. Am J Cardiol. 2015; 115(2):167-170.
[4] Vuylsteke ME, Thomis S, Guillaume G, et al. Epidemiological study on chronic venous disease in belgium and luxembourg: prevalence, risk factors, and symptomatology. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2015;49(4):432-439.
[5] Parameswaran S, Santhakumar R, Vidyasekar P, et al. Enrichment of cardiomyocytes in primary cultures of murine neonatal hearts. Cardiomyocytes. 2015;1299:17-25.
[6] Brand N, Lara-Pezzi E, Rosenthal N, et al. Analysis of cardiac myocyte biology in transgenic mice: a protocol for preparation of neonatal mouse cardiac myocyte cultures. Methods Mol Biol. 2010;633:113-124.
[7] Menasche P. Cell-based therapy for heart disease: a clinically oriented perspective. Mol Ther. 2009;17(5):758-766.
[8] Dutta AK, Sabirov RZ, Uramoto H, et al. Role of ATP-conductive anion channel in ATP release from neonatal rat cardiomyocytes in ischaemic or hypoxic conditions. J Physiol. 2004;559:799-812.
[9] Vandergriff AC, Hensley MT, Cheng K, et al. Isolation and cryopreservation of neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. J Vis Exp. 2015;9(98):e52726.
[10] Graham EL, Balla C, Franchino H, et al. Isolation, culture, and functional characterization of adult mouse cardiomyoctyes. J Vis Exp. 2013;24(79):e50289.
[11] Hein S, Kostin S, Schaper J, et al. Adult rat cardiac myocytes in culture: ‘Second-floor’ cells and coculture experiments. Exp Clin Cardiol. 2006;11(3):175-182.
[12] Zhou J, ZhangY, Wen X, et al. Telocytes accompanying cardiomyocyte in primary culture: two- and three-dimensional culture environment. J Cell Mol Med. 2010;14(11):2641-2645.
[13] Xu X, Colecraft HM. Primary Culture of Adult Rat Heart Myocytes. J Vis Exp. 2009;16(28):1308-1311.
[14] Dwyer J, Pluess M, Iskratsch T, et al. The Formin FHOD1 in Cardiomyocytes. Anat Rec. 2014;297(9):1560-1570.
[15] Saini H, Navaei A, Van Putten A, et al. 3D Cardiac microtissues encapsulated with the co-culture of cardiomyocytes and cardiac fibroblasts. Adv Healthc Mater. 2015.
[16] Wilsbacher LD, Coughlin SR. Analysis of cardiomyocyte development using immunofluorescence in embryonic mouse heart. J Vis Exp. 2015;26(97):52644.
[17] Chen A, Yang L, Gui X, et al. Protective role of Klotho on cardiomyocytes upon hypoxia/reoxygenation via downregulation of Akt and FOXO1 phosphorylation. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11(3):2013-2019.
[18] Sirabella D, Cimetta E, Vunjak-Novakovic G. et al. Recent advances in engineering human cardiac tissue from pluripotent stem cells. Exp Biol Med. 2015;240(8):1008-1018.
[19] Boudreau-Béland J, Duverger JE, Petitjean E, et al. Spatiotemporal stability of neonatal rat cardiomyocyte monolayers spontaneous activity is dependent on the culture substrate. PLoS One. 2015;10(6):e0127977.
[20] Tyukavin AI, Belostotskaya GB, Golovanova TA, et al. Stimulation of proliferation and differentiation of rat resident myocardial cells with apoptotic bodies of cardiomyocytes. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2015;159(1):138-141.
[21] O'Meara CC, Wamstad JA, Gladstone RA, et al. "Transcriptional reversion of cardiac myocyte fate during mammalian cardiac regeneration. Circ Res. 2015;116(5): 804-815.
[22] Sreejit P, Kumar S, Verma R, et al. An improved protocol for primary culture of cardiomyocyte from neonatal mice. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2008;44(3-4):45-50.
[23] Polinger IS. Separation of cell types in embryonic heart cell cultures. Exp Cell Res. 1970;63(1):78-82.
[24] Simpson P, Savion S. Differentiation of rat myocytes in single cell cultures with and without proliferating nonmyocardial cells. Cross-striations, ultrastructure, and chronotropic response to isoproterenol. Circ Res. 1982;50(1):101-116.
[25] Uchida T, Nagayama M, Taira T, et al. Optimal temperature range for low-temperature preservation of dissociated neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Cryobiology. 2011;63(3): 279-284.
[26] Golden H, Gollapudi D, Gerilechaogetu F, et al. Isolation of cardiac myocytes and fibroblasts from neonatal rat pups. Cardiovasc Dev. 2012;205-214.
[27] McCain ML, Agarwal A, Nesmith HW, et al. Micromolded gelatin hydrogels for extended culture of engineered cardiac tissues. Biomaterials. 2014;35(21):5462-5471.
[28] Annabi N, Selimovi? Š, Cox JPA, et al. Hydrogel-coated microfluidic channels for cardiomyocyte culture. Lab Chip. 2013;13(18):3569-3577.
[29] Mei JC, Wu AY, Wu PC, et al. Three-dimensional extracellular matrix scaffolds by microfluidic fabrication for long-term spontaneously contracted cardiomyocyte culture. Tissue Eng Part A. 2014;20(21-22):2931-2941.
[30] Birla R, Dow D, Huang YC, et al. Methodology for the formation of functional, cell-based cardiac pressure generation constructs in vitro. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2008;44(8-9):340-350.
[31] Chiu YW, Chen WP, Su CC, et al. The arrhythmogenic effect of self-assembling nanopeptide hydrogel scaffolds on neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes. Nanomedicine. 2014; 10(5):1065-1073.
[32] 陶静,马依彤,李晓梅,等.原代乳鼠心肌细胞培养方法的改进[J].中华心血管病杂志,2014,42(1):53-56.
[33] 包馨慧,李晓梅,杨毅宁,等.原代乳鼠心肌细胞分离培养的改进[J].新疆医科大学学报,2015,38(5):564-570. |